Abstract
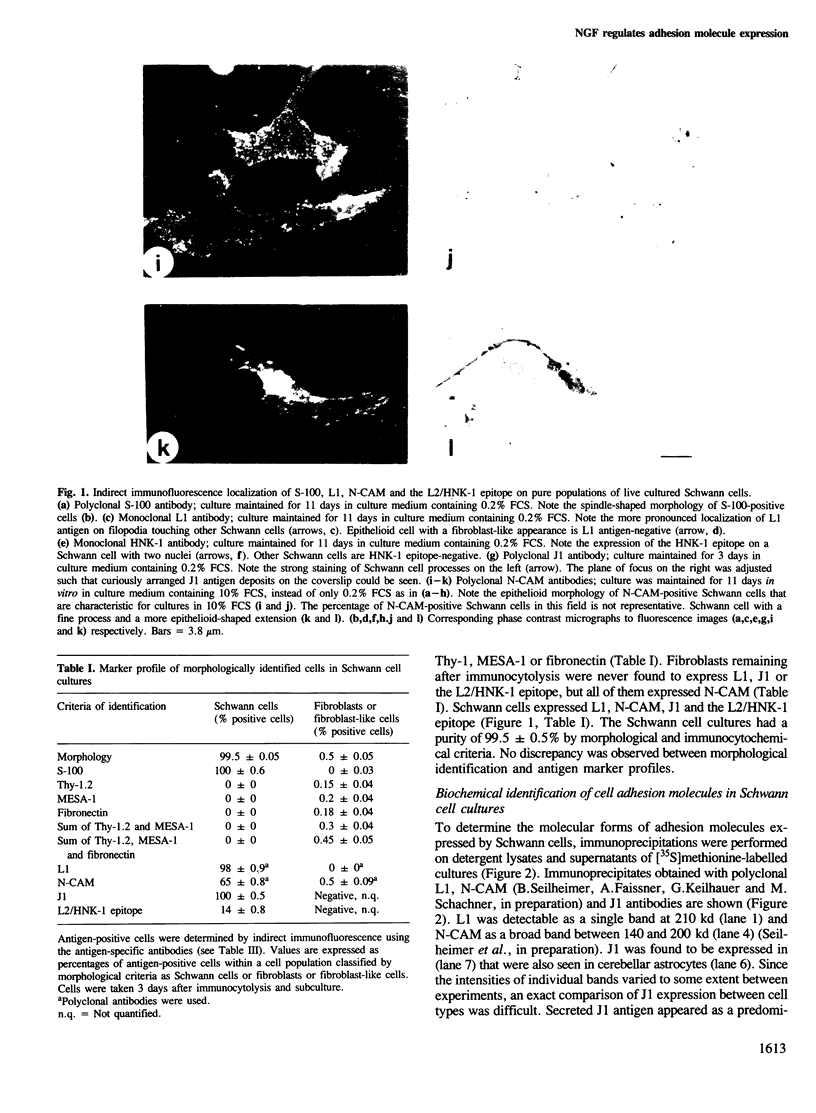
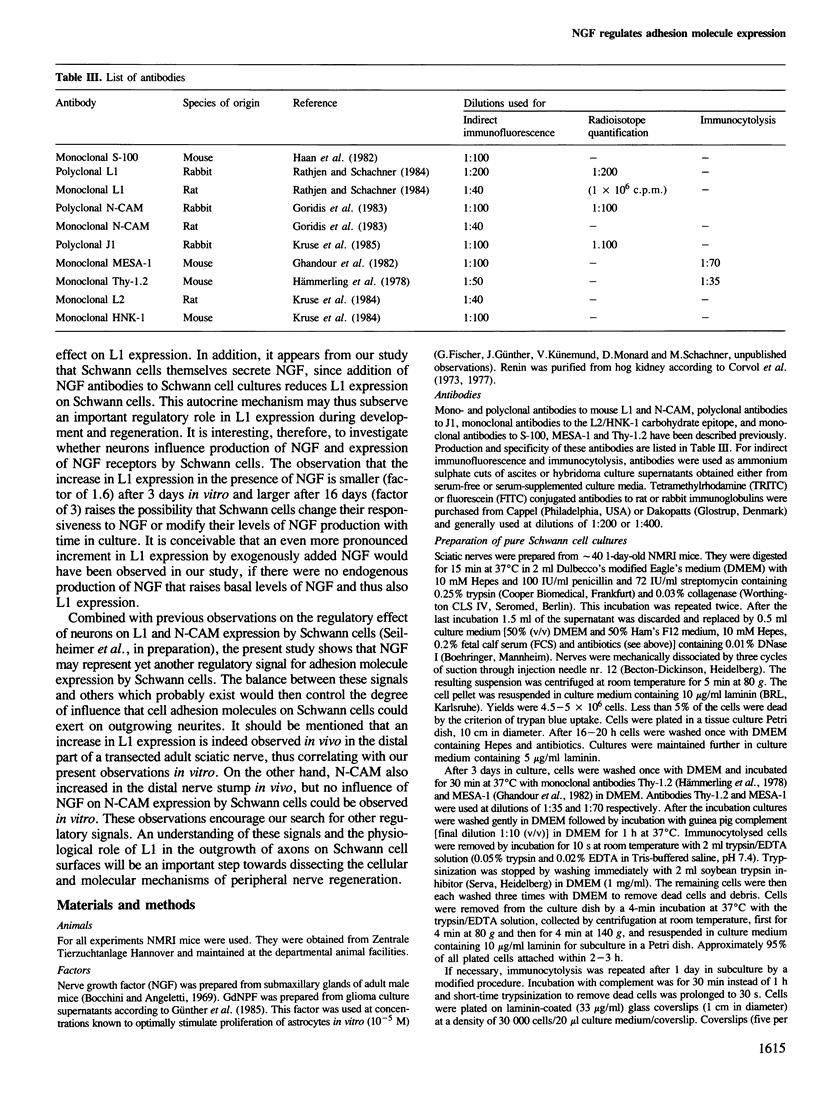
Schwann cells from early postnatal mouse sciatic nerve were obtained as a homogenous population and shown by indirect immunofluorescence to express the neural cell adhesion molecules L1, N-CAM and J1 and their common carbohydrate epitope L2/HNK-1. L1 and N-CAM are synthesized in molecular forms that are slightly different from those expressed by small cerebellar neurons or astrocytes. As in astrocytes, the J1 antigen is expressed by Schwann cells in multiple forms generally ranging from 160 to 230 kd in the reduced state. J1 is secreted by Schwann cells in a 230-kd mol. wt form. Expression of L1 by Schwann cells can be regulated by nerve growth factor (NGF). L1 expression on the cell surface is increased 1.6-fold in the presence of NGF after 3 days of maintenance in vitro and 3-fold after 16 days. NGF does not change expression of N-CAM. The glia-derived neurite-promoting factor (GdNPF) increases L1 expression by a factor of 1.9 and decreases N-CAM expression by a factor of 0.4 after 3 days in vitro. J1 expression on Schwann cell surfaces remains unchanged in the presence of NGF or GdNPF. Antibodies to NGF abolish the influence of NGF on L1 expression. Addition of NGF antibodies to the Schwann cell cultures without exogenously added NGF decreases L1 expression, indicating that Schwann cells secrete NGF that may influence L1 expression by an autocrine mechanism. Our experiments show for the first time that cell adhesion molecule expression on a non-neuronal cell, the Schwann cell, can be directly regulated by the neurotrophic factor NGF. These observations indicate a considerable degree of 'plasticity' of peripheral glia in regulating cell adhesion molecule expression.
Full text
PDF
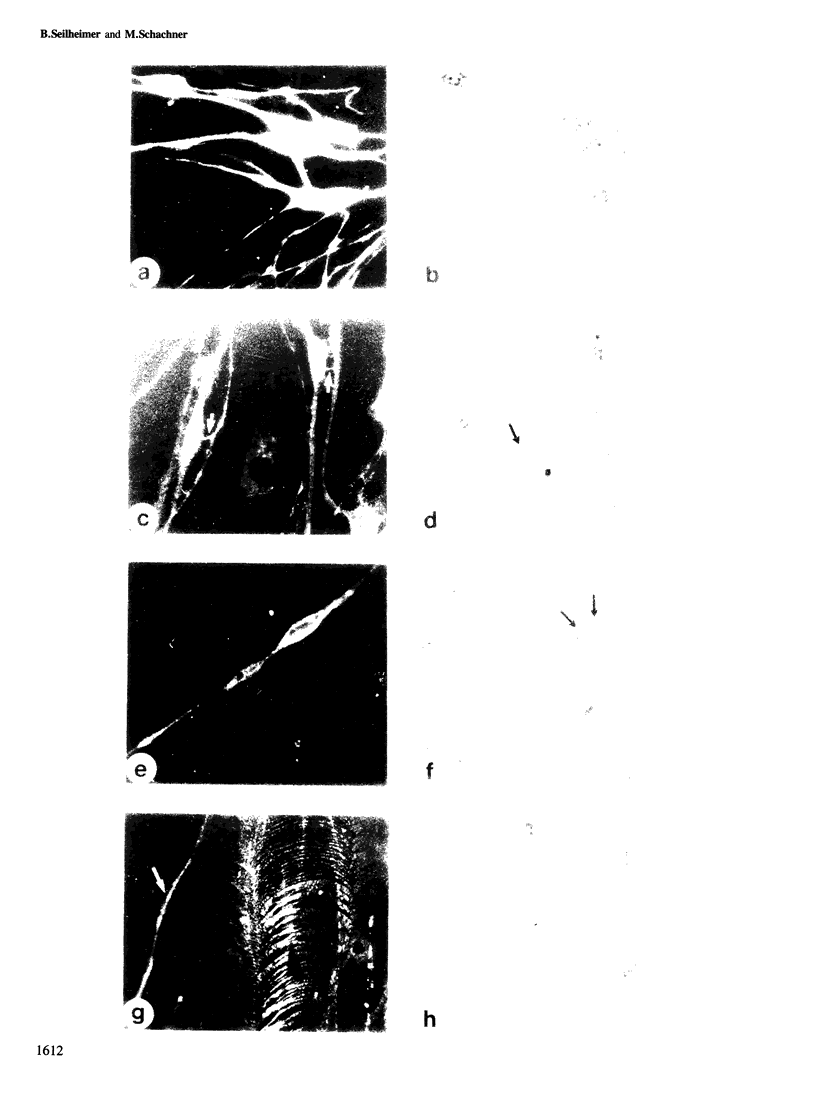


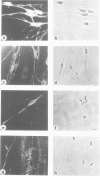
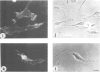
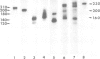
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bocchini V., Angeletti P. U. The nerve growth factor: purification as a 30,000-molecular-weight protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Oct;64(2):787–794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.2.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bock E., Richter-Landsberg C., Faissner A., Schachner M. Demonstration of immunochemical identity between the nerve growth factor-inducible large external (NILE) glycoprotein and the cell adhesion molecule L1. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2765–2768. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockes J. P., Fields K. L., Raff M. C. Studies on cultured rat Schwann cells. I. Establishment of purified populations from cultures of peripheral nerve. Brain Res. 1979 Apr 6;165(1):105–118. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetto S., Fambrough D. M. Synthesis, insertion into the plasma membrane, and turnover of alpha-bungarotoxin receptors in chick sympathetic neurons. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):555–569. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvol P., Devaux C., Ito T., Sicard P., Ducloux J., Menard J. Large scale purification of hog renin. Physicochemical characterization. Circ Res. 1977 Nov;41(5):616–622. doi: 10.1161/01.res.41.5.616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvol P., Devaux C., Menard J. Pepstatin, an inhibitor for renin purification by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80790-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faissner A., Teplow D. B., Kübler D., Keilhauer G., Kinzel V., Schachner M. Biosynthesis and membrane topography of the neural cell adhesion molecule L1. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3105–3113. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04052.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G., Schachner M. In vitro reaggregation of dissociated mouse cerebellar cells. I. Demonstration of different aggregation mechanisms. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Jun;139(2):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90253-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghandour S., Langley K., Gombos G., Hirn M., Hirsch M. R., Goridis C. A surface marker for murine vascular endothelial cells defined by monoclonal antibody. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Feb;30(2):165–170. doi: 10.1177/30.2.7061819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Deagostini-Bazin H., Hirn M., Hirsch M. R., Rougon G., Sadoul R., Langley O. K., Gombos G., Finne J. Neural surface antigens during nervous system development. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):527–537. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guenther J., Nick H., Monard D. A glia-derived neurite-promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1963–1966. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03878.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper G. P., Barde Y. A., Edgar D., Ganten D., Hefti F., Heumann R., Naujoks K. W., Rohrer H., Turner J. E., Thoenen H. Biological and immunological properties of the nerve growth factor from bovine seminal plasma: comparison with the properties of mouse nerve growth factor. Neuroscience. 1983;8(2):375–387. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., Lemke H., Hämmerling U., Höhmann C., Wallich R., Rajewsky K. Monoclonal antibodies against murine cell surface antigens: anti-H-2, anti-Ia and anti-T cell antibodies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:100–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keilhauer G., Faissner A., Schachner M. Differential inhibition of neurone-neurone, neurone-astrocyte and astrocyte-astrocyte adhesion by L1, L2 and N-CAM antibodies. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):728–730. doi: 10.1038/316728a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsching S., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor in sympathetic ganglia and corresponding target organs of the rat: correlation with density of sympathetic innervation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3513–3516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Keilhauer G., Faissner A., Timpl R., Schachner M. The J1 glycoprotein--a novel nervous system cell adhesion molecule of the L2/HNK-1 family. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):146–148. doi: 10.1038/316146a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse J., Mailhammer R., Wernecke H., Faissner A., Sommer I., Goridis C., Schachner M. Neural cell adhesion molecules and myelin-associated glycoprotein share a common carbohydrate moiety recognized by monoclonal antibodies L2 and HNK-1. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):153–155. doi: 10.1038/311153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee V. M., Greene L., Shelanski M. L. Identification of neural and adrenal medullary surface membrane glycoproteins recognized by antisera to cultured rat sympathetic neurons and PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Neuroscience. 1981;6(12):2773–2786. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90119-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Schachner M. Epidermal growth factor stimulates DNA-synthesis of astrocytes in primary cerebellar cultures. Cell Tissue Res. 1981;220(2):393–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00210517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillien L. E., Claude P. Nerve growth factor is a mitogen for cultured chromaffin cells. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):632–634. doi: 10.1038/317632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martini R., Schachner M. Immunoelectron microscopic localization of neural cell adhesion molecules (L1, N-CAM, and MAG) and their shared carbohydrate epitope and myelin basic protein in developing sciatic nerve. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2439–2448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire J. C., Greene L. A., Furano A. V. NGF stimulates incorporation of fucose or glucosamine into an external glycoprotein in cultured rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):357–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monard D., Solomon F., Rentsch M., Gysin R. Glia-induced morphological differentiation in neuroblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1894–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieke J., Schachner M. Expression of the neural cell adhesion molecules L1 and N-CAM and their common carbohydrate epitope L2/HNK-1 during development and after transection of the mouse sciatic nerve. Differentiation. 1985;30(2):141–151. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen F. G., Schachner M. Immunocytological and biochemical characterization of a new neuronal cell surface component (L1 antigen) which is involved in cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer H., Sommer I. Simultaneous expression of neuronal and glial properties by chick ciliary ganglion cells during development. J Neurosci. 1983 Aug;3(8):1683–1693. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-08-01683.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rush R. A. Immunohistochemical localization of endogenous nerve growth factor. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):364–367. doi: 10.1038/312364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. W., Catterall W. A. Biosynthesis and processing of the alpha subunit of the voltage-sensitive sodium channel in rat brain neurons. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):437–444. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90664-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Rossie S., Catterall W. A. A large intracellular pool of inactive Na channel alpha subunits in developing rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4847–4851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnitzer J., Schachner M. Characterization of isolated mouse cerebellar cell populations in vitro. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Dec;1(4):457–470. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun M. M., Fambrough D. M. The (Na+ + K+)-ATPase of chick sensory neurons. Studies on biosynthesis and intracellular transport. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1009–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Clark H. B., Johnson E. M., Jr Induction of nerve growth factor receptor in Schwann cells after axotomy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4094–4098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]