Abstract
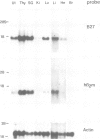
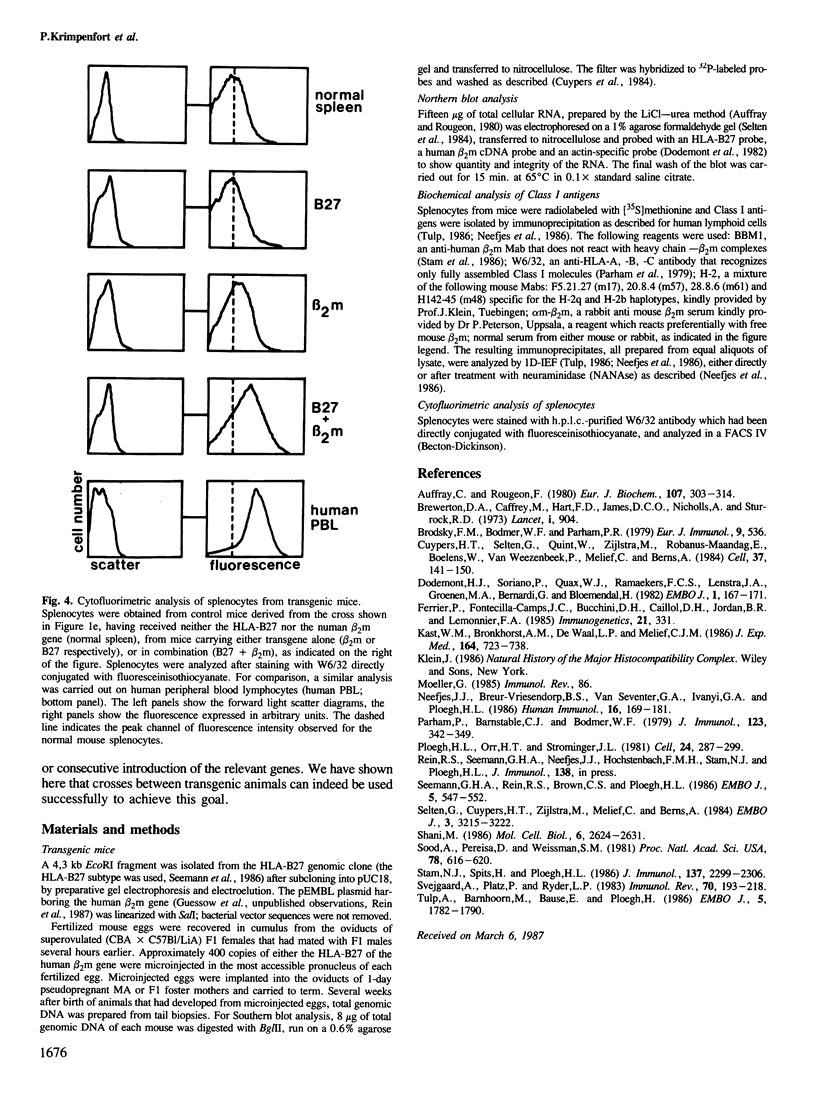
In man a number of diseases are associated with certain alleles of MHC antigens. The most pronounced example is ankylosing spondylitis, which is strongly associated with HLA-B27. As a first step towards a model system to study the basis of this association, transgenic mice were generated that showed cell surface expression of the HLA-B27 antigen biochemically indistinguishable from HLA-B27 antigen expressed on human cells. This result was obtained by crossing two independently derived strains of mice, one of which is transgenic for the HLA-B27 heavy chain gene, and the other carrying and expressing the human beta 2m gene. Examination of HLA-B27 and human beta 2m mRNA in various tissues shows the two genes to be expressed in a coordinate fashion. The mRNA levels follow those of endogenous H-2 Class I genes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewerton D. A., Hart F. D., Nicholls A., Caffrey M., James D. C., Sturrock R. D. Ankylosing spondylitis and HL-A 27. Lancet. 1973 Apr 28;1(7809):904–907. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodsky F. M., Bodmer W. F., Parham P. Characterization of a monoclonal anti-beta 2-microglobulin antibody and its use in the genetic and biochemical analysis of major histocompatibility antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jul;9(7):536–545. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodemont H. J., Soriano P., Quax W. J., Ramaekers F., Lenstra J. A., Groenen M. A., Bernardi G., Bloemendal H. The genes coding for the cytoskeletal proteins actin and vimentin in warm-blooded vertebrates. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01142.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrier P., Fontecilla-Camps J. C., Bucchini D., Caillol D. H., Jordan B. R., Lemonnier F. A. Altered structure of HLA class I heavy chains associated with mouse beta-2 microglobulin. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(4):321–331. doi: 10.1007/BF00430798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Bronkhorst A. M., de Waal L. P., Melief C. J. Cooperation between cytotoxic and helper T lymphocytes in protection against lethal Sendai virus infection. Protection by T cells is MHC-restricted and MHC-regulated; a model for MHC-disease associations. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):723–738. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefjes J. J., Breur-Vriesendorp B. S., van Seventer G. A., Iványi P., Ploegh H. L. An improved biochemical method for the analysis of HLA-class I antigens. Definition of new HLA-class I subtypes. Hum Immunol. 1986 Jun;16(2):169–181. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(86)90046-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F. Use of a monoclonal antibody (W6/32) in structural studies of HLA-A,B,C, antigens. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemann G. H., Rein R. S., Brown C. S., Ploegh H. L. Gene conversion-like mechanisms may generate polymorphism in human class I genes. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression of a chimeric actin-globin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2624–2631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svejgaard A., Platz P., Ryder L. P. HLA and disease 1982--a survey. Immunol Rev. 1983;70:193–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb00715.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulp A., Barnhoorn M., Bause E., Ploegh H. Inhibition of N-linked oligosaccharide trimming mannosidases blocks human B cell development. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1783–1790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]