Abstract
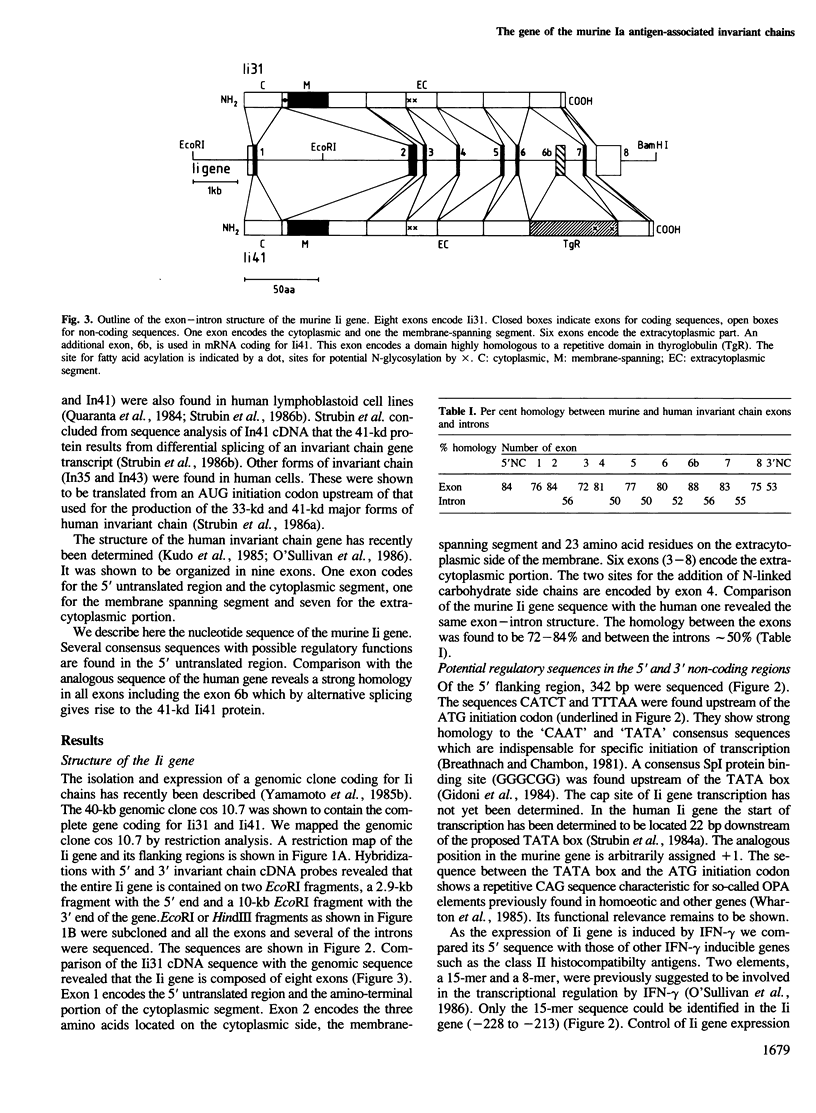
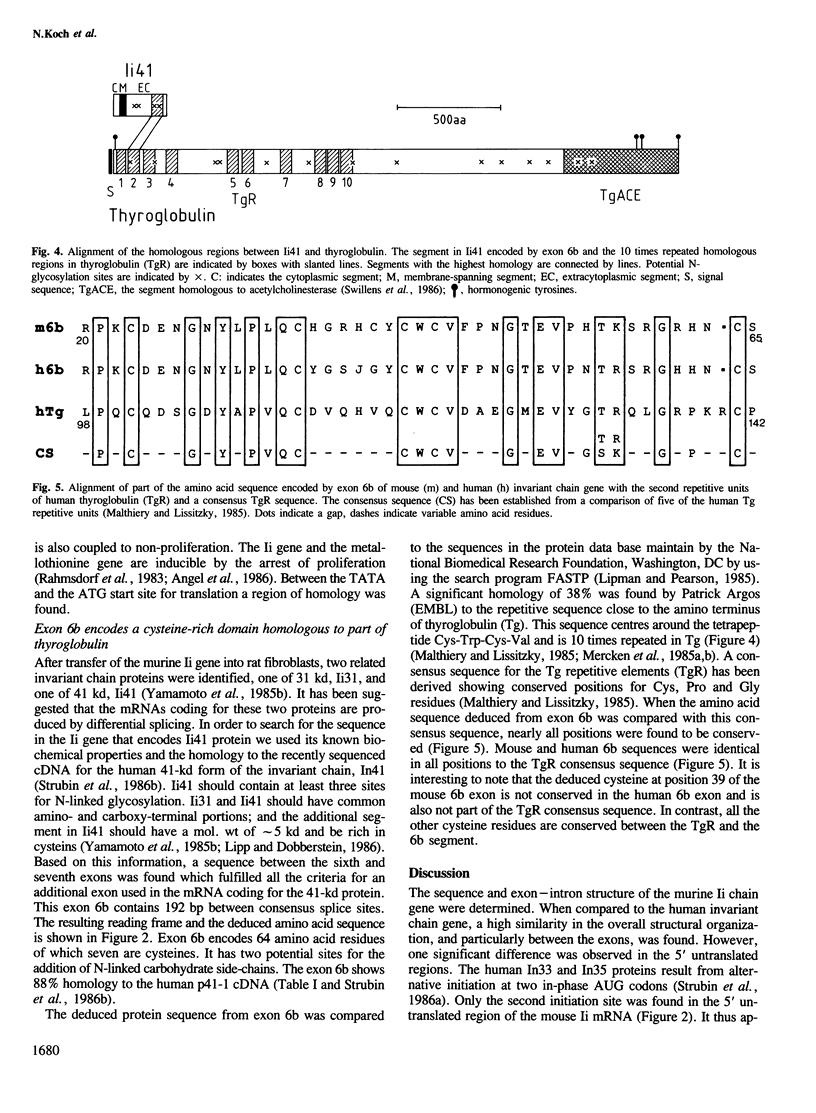
The gene for murine Ia-associated invariant (Ii) chains (Ii31 and Ii41) was characterized by sequence analysis. The gene extends over approximately 9 kb and is organized in nine exons. Exon 1 encodes the 5' untranslated region and the cytoplasmic segment, exon 2 the membrane spanning segment and adjacent amino acids and exons 3-8 the extracytoplasmic portion of Ii31. Putative promoter sequences were found upstream of the start of the coding sequence. Between exons 6 and 7 an additional, alternatively spliced exon 6b has been identified. This exon is spliced into the mRNA coding for the Ii-related Ii41 protein. Exon 6b encodes a cysteine-rich domain of 64 amino acids. It shows a remarkably high homology to the repetitive elements in thyroglobulin, a precursor for thyroid hormone. Based on this homology, it is suggested that this domain (TgR) in Tg and in Ii41 may play a role either in hormone formation or as a carrier in the transport of molecules (thyroid hormone or processed antigen respectively) between intracellular compartments.
Full text
PDF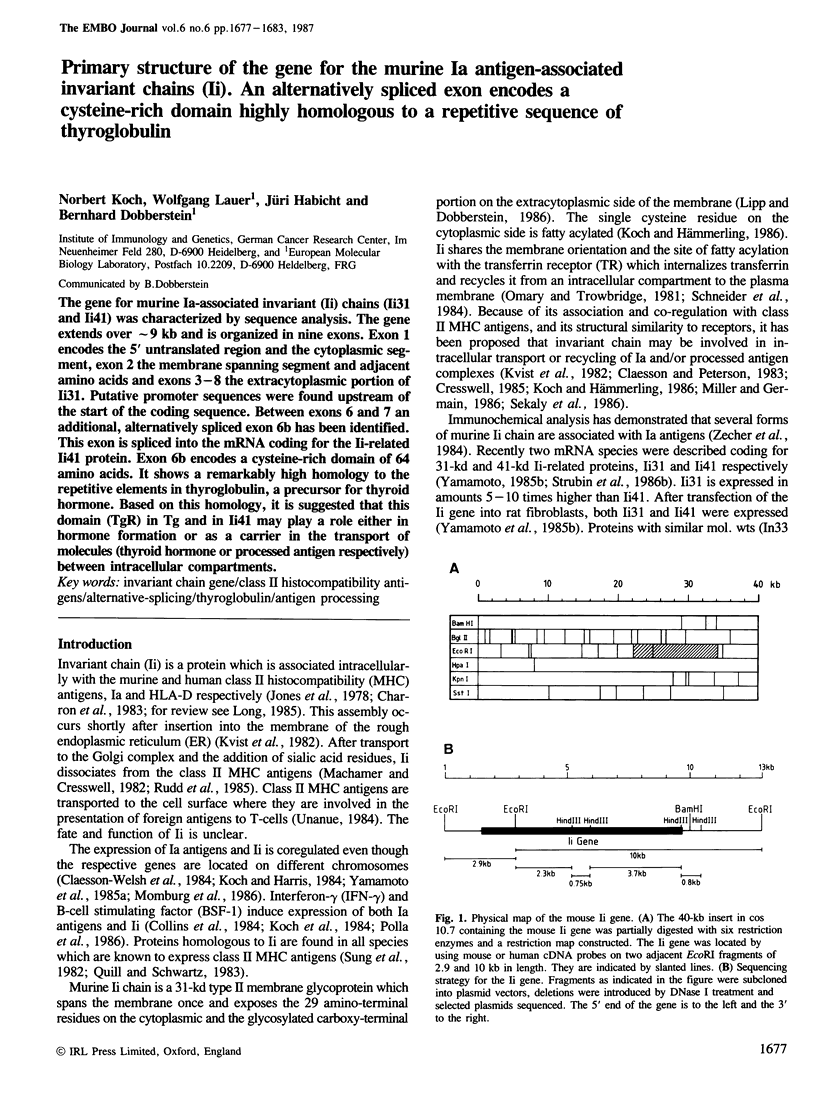




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Pöting A., Mallick U., Rahmsdorf H. J., Schorpp M., Herrlich P. Induction of metallothionein and other mRNA species by carcinogens and tumor promoters in primary human skin fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1760–1766. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron D. J., Aellen-Schulz M. F., St Geme J., 3rd, Erlich H. A., McDevitt H. O. Biochemical characterization of an invariant polypeptide associated with Ia antigens in human and mouse. Mol Immunol. 1983 Jan;20(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson-Welsh L., Barker P. E., Larhammar D., Rask L., Ruddle F. H., Peterson P. A. The gene encoding the human class II antigen-associated gamma chain is located on chromosome 5. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(1):89–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00373450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson L., Larhammar D., Rask L., Peterson P. A. cDNA clone for the human invariant gamma chain of class II histocompatibility antigens and its implications for the protein structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7395–7399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claesson L., Peterson P. A. Association of human gamma chain with class II transplantation antigens during intracellular transport. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 21;22(13):3206–3213. doi: 10.1021/bi00282a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins T., Korman A. J., Wake C. T., Boss J. M., Kappes D. J., Fiers W., Ault K. A., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Strominger J. L., Pober J. S. Immune interferon activates multiple class II major histocompatibility complex genes and the associated invariant chain gene in human endothelial cells and dermal fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cresswell P. Intracellular class II HLA antigens are accessible to transferrin-neuraminidase conjugates internalized by receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8188–8192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzog V. Pathways of endocytosis in thyroid follicle cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;91:107–139. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61315-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., Hewgill D., McDevitt H. O. Detection of a common polypeptide chain in I--A and I--E sub-region immunoprecipitates. Mol Immunol. 1979 Jan;16(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(79)90027-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch N., Harris A. W. Differential expression of the invariant chain in mouse tumor cells: relationship to B lymphoid development. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):12–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch N., Hämmerling G. J. The HLA-D-associated invariant chain binds palmitic acid at the cysteine adjacent to the membrane segment. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3434–3440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch N., Wong G. H., Schrader J. W. Ia antigens and associated invariant chain are induced simultaneously in lines of T-dependent mast cells by recombinant interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1361–1369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., Glaros D., Khoury G., Jay G. Alternative RNA splicing in expression of the H-2K gene. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):602–604. doi: 10.1038/306602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudo J., Chao L. Y., Narni F., Saunders G. F. Structure of the human gene encoding the invariant gamma-chain of class II histocompatibility antigens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8827–8841. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Lehrach H., Goody R. S. A new method of DNA sequencing using deoxynucleoside alpha-thiotriphosphates. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):173–177. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J. O., Holland E. C., Drickamer K. Characterization of the gene encoding the major rat liver asialoglycoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12523–12527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B. Signal recognition particle-dependent membrane insertion of mouse invariant chain: a membrane-spanning protein with a cytoplasmically exposed amino terminus. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2169–2175. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O. In search of a function for the invariant chain associated with Ia antigens. Surv Immunol Res. 1985;4(1):27–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02918583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Cresswell P. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the invariant chain associated with HLA-DR antigens. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2564–2569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machamer C. E., Cresswell P. Monensin prevents terminal glycosylation of the N- and O-linked oligosaccharides of the HLA-DR-associated invariant chain and inhibits its dissociation from the alpha-beta chain complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1287–1291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malthiéry Y., Lissitzky S. Sequence of the 5'-end quarter of the human-thyroglobulin messenger ribonucleic acid and of its deduced amino-acid sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):53–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08717.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Simons M. J., De Martynoff G., Swillens S., Vassart G. Presence of hormonogenic and repetitive domains in the first 930 amino acids of bovine thyroglobulin as deduced from the cDNA sequence. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 15;147(1):59–64. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08718.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Simons M. J., Swillens S., Massaer M., Vassart G. Primary structure of bovine thyroglobulin deduced from the sequence of its 8,431-base complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):647–651. doi: 10.1038/316647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Germain R. N. Efficient cell surface expression of class II MHC molecules in the absence of associated invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1478–1489. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Momburg F., Koch N., Möller P., Moldenhauer G., Butcher G. W., Hämmerling G. J. Differential expression of Ia and Ia-associated invariant chain in mouse tissues after in vivo treatment with IFN-gamma. J Immunol. 1986 Feb 1;136(3):940–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musti A. M., Avvedimento E. V., Polistina C., Ursini V. M., Obici S., Nitsch L., Cocozza S., Di Lauro R. The complete structure of the rat thyroglobulin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):323–327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Uehara H., Ewenstein B. M., Kindt T. J., Coligan J. E. Primary structural: analysis of the transplantation antigens of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:1025–1052. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell J., Quaranta V. Chloroquine affects biosynthesis of Ia molecules by inhibiting dissociation of invariant (gamma) chains from alpha-beta dimers in B cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Oct 1;162(4):1371–1376. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan D. M., Larhammar D., Wilson M. C., Peterson P. A., Quaranta V. Structure of the human Ia-associated invariant (gamma)-chain gene: identification of 5' sequences shared with major histocompatibility complex class II genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4484–4488. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Biosynthesis of the human transferrin receptor in cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):12888–12892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polla B. S., Poljak A., Geier S. G., Nathenson S. G., Ohara J., Paul W. E., Glimcher L. H. Three distinct signals can induce class II gene expression in a murine pre-B-cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4878–4882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quaranta V., Majdic O., Stingl G., Liszka K., Honigsmann H., Knapp W. A human Ia cytoplasmic determinant located on multiple forms of invariant chain (gamma, gamma 2, gamma 3). J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1900–1905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quill H., Schwartz B. D. Invariant proteins associated with guinea-pig Ia antigens. Mol Immunol. 1983 Dec;20(12):1333–1345. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90164-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Murialdo H., Delius H., Chai J. H., Poustka A., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. Analysis of cosmids using linearization by phage lambda terminase. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Koch N., Mallick U., Herrlich P. Regulation of MHC class II invariant chain expression: induction of synthesis in human and murine plasmocytoma cells by arresting replication. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):811–816. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01507.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rall L. B., Scott J., Bell G. I., Crawford R. J., Penschow J. D., Niall H. D., Coghlan J. P. Mouse prepro-epidermal growth factor synthesis by the kidney and other tissues. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):228–231. doi: 10.1038/313228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Bodmer J. G., Bodmer W. F., Crumpton M. J. HLA-D region antigen-associated invariant polypeptides as revealed by two-dimensional gel analysis. Glycosylation and structural inter-relationships. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1927–1936. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Rogers J. H., Hüppi K., Brack C., Traunecker A., Maki R., Wall R., Tonegawa S. Domains and the hinge region of an immunoglobulin heavy chain are encoded in separate DNA segments. Nature. 1979 Feb 22;277(5698):627–633. doi: 10.1038/277627a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Owen M. J., Banville D., Williams J. G. Primary structure of human transferrin receptor deduced from the mRNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):675–678. doi: 10.1038/311675b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekaly R. P., Tonnelle C., Strubin M., Mach B., Long E. O. Cell surface expression of class II histocompatibility antigens occurs in the absence of the invariant chain. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1490–1504. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. A., Lauer W., Dembić Z., Mayer W. E., Lipp J., Koch N., Hämmerling G., Klein J., Dobberstein B. Structure of the murine Ia-associated invariant (Ii) chain as deduced from a cDNA clone. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):873–877. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01899.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Berte C., Mach B. Alternative splicing and alternative initiation of translation explain the four forms of the Ia antigen-associated invariant chain. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3483–3488. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04673.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Long E. O., Mach B. Two forms of the Ia antigen-associated invariant chain result from alternative initiations at two in-phase AUGs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):619–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90626-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung E., Duncan W. R., Streilein J. W., Jones P. P. Detection of two distinct class II alpha:beta:Ii complexes in the Syrian hamster. Immunogenetics. 1982;16(5):425–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00372101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Ludgate M., Mercken L., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Analysis of sequence and structure homologies between thyroglobulin and acetylcholinesterase: possible functional and clinical significance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Transy C., Lalanne J. L., Kourilsky P. Alternative splicing in the 5' moiety of the H-2Kd gene transcript. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2383–2386. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunnacliffe A., Sims J. E., Rabbitts T. H. T3 delta pre-mRNA is transcribed from a non-TATA promoter and is alternatively spliced in human T cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1245–1252. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04353.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R. Antigen-presenting function of the macrophage. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:395–428. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.002143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Herle A. J., Vassart G., Dumont J. E. Control of thyroglobulin synthesis and secretion. (First of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1979 Aug 2;301(5):239–249. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197908023010504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassart G., Bacolla A., Brocas H., Christophe D., de Martynoff G., Leriche A., Mercken L., Parma J., Pohl V., Targovnik H. Structure, expression and regulation of the thyroglobulin gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 May;40(2-3):89–97. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Yedvobnick B., Finnerty V. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. opa: a novel family of transcribed repeats shared by the Notch locus and other developmentally regulated loci in D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90308-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Floyd-Smith G., Francke U., Koch N., Lauer W., Dobberstein B., Schäfer R., Hämmerling G. J. The gene encoding the Ia-associated invariant chain is located on chromosome 18 in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1985;21(1):83–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00372244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Koch N., Steinmetz M., Hämmerling G. J. One gene encodes two distinct Ia-associated invariant chains. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3461–3467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zecher R., Ballhausen W., Reske K., Linder D., Schlüter M., Stirm S. The invariant chains of mouse class II antigens: biochemical properties and molecular relationship. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):511–517. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140606. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehetner G., Lehrach H. A computer program package for restriction map analysis and manipulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):335–349. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



