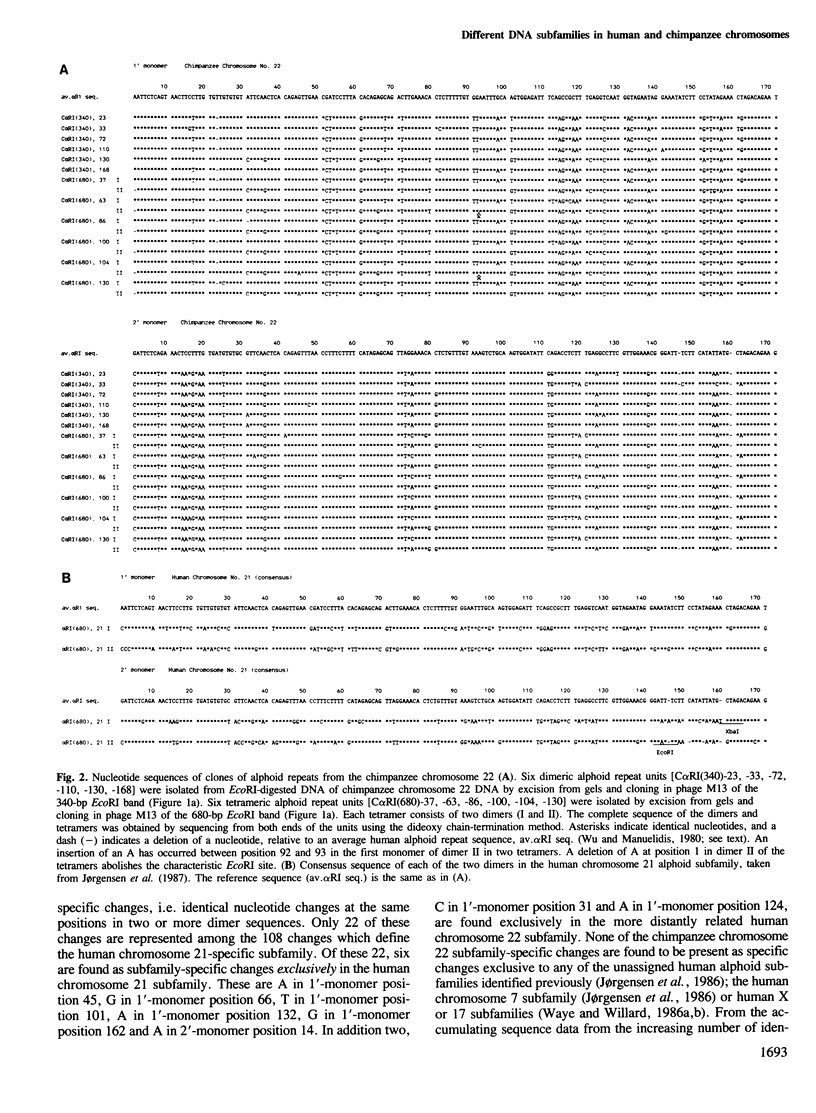
Abstract
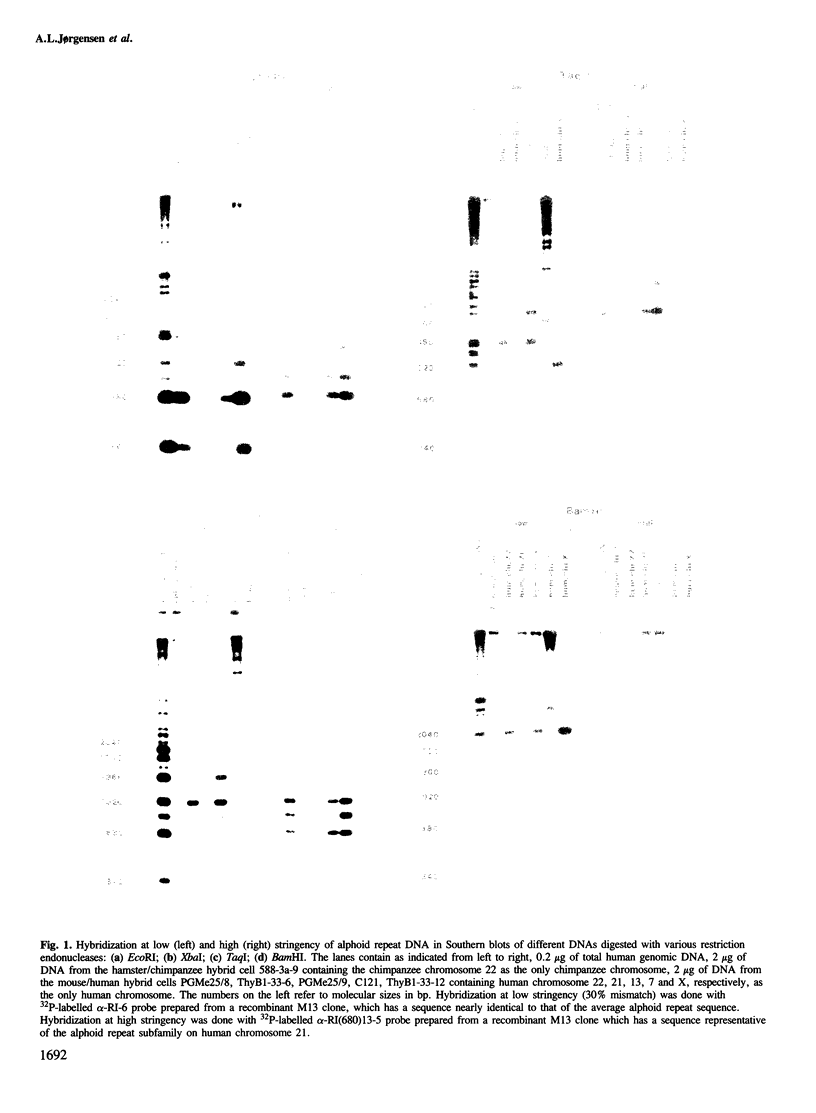
The alphoid repeat DNA on chimpanzee chromosome 22 was compared with alphoid repeat DNA on its human homologue, chromosome 21. Hybridization of different alphoid probes under various conditions of stringency show that the alphoid repeats of chimpanzee chromosome 22 are not closely related to those of human chromosome 21. Sequence analysis of cloned dimer and tetramer EcoRI fragments from chimpanzee chromosome 22 confirm the low overall level of homology, but reveal the presence of several nucleotide changes which are exclusive to the chromosome 21 subfamily of human alphoid DNA. Southern blot analysis of alphoid repeat DNA on the chimpanzee X chromosome suggests this subfamily has been strongly conserved during and since the separation of chimpanzee and man although the two subfamilies can be distinguished on the basis of Taq I restriction fragments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Britten R. J. Rates of DNA sequence evolution differ between taxonomic groups. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1393–1398. doi: 10.1126/science.3082006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devilee P., Slagboom P., Cornelisse C. J., Pearson P. L. Sequence heterogeneity within the human alphoid repetitive DNA family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2059–2073. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dover G. Molecular drive: a cohesive mode of species evolution. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):111–117. doi: 10.1038/299111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Chromosome-specific subfamilies within human alphoid repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen A. L., Bostock C. J., Bak A. L. Homologous subfamilies of human alphoid repetitive DNA on different nucleolus organizing chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1075–1079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop B. F., Goodman M., Xu P., Chan K., Slightom J. L. Primate eta-globin DNA sequences and man's place among the great apes. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):234–238. doi: 10.1038/319234a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Bostock C., Robertson M., Christie S., Mitchen J. L., Dahlberg J. E. U1 small nuclear RNA genes are located on human chromosome 1 and are expressed in mouse-human hybrid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2211–2220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shmookler Reis R. J., Srivastava A., Beranek D. T., Goldstein S. Human alphoid family of tandemly repeated DNA. Sequence of cloned tetrameric fragments and analysis of familial divergence. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):31–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan T., Webb D., Dover G. A. Transition stages of molecular drive in multiple-copy DNA families in Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1701–1708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: nucleotide sequence analysis of the 2.0 kilobasepair repeat from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 25;13(8):2731–2743. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.8.2731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Molecular analysis of a deletion polymorphism in alpha satellite of human chromosome 17: evidence for homologous unequal crossing-over and subsequent fixation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 11;14(17):6915–6927. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.17.6915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye J. S., Willard H. F. Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3156–3165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe J., Darling S. M., Erickson R. P., Craig I. W., Buckle V. J., Rigby P. W., Willard H. F., Goodfellow P. N. Isolation and characterization of an alphoid centromeric repeat family from the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1985 Apr 20;182(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90234-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. C., Manuelidis L. Sequence definition and organization of a human repeated DNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):363–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]