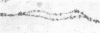Abstract
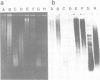
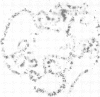
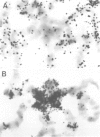
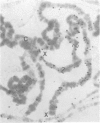
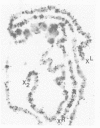
In situ hybridization of (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n to the polytene chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster reveals a clearly non-random distribution of chromosomal sites for this sequence. Sites are distributed over most euchromatic regions but the density of sites along the X chromosome is significantly higher than the density over the autosomes. All autosomes show approximately equal levels of hybridization except chromosome 4 which has no detectable stretches of (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n. Another striking feature is the lack of hybridization of the beta-heterochromatin of the chromocenter. The specific sites are conserved between different strains of D. melanogaster. The same overall chromosomal pattern of hybridization is seen for the other Drosophila species studied, including D. simulans, a sibling species with a much lower content of middle repetitive DNA, and D. virilis, a distantly related species. The evolutionary conservation of the distribution of (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n suggests that these sequences are of functional importance. The distribution patterns seen for D. pseudoobscura and D. miranda raise interesting speculations about function. In these species a chromosome equivalent to an autosomal arm of D. melanogaster has been translocated onto the X chromosome and acquired dosage compensation. In each species the new arm of the X also has a higher density of (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n similar to that seen on other X chromosomes. In addition to correlations with dosage compensation, the depletion of (dC-dA)n.(dG-dT)n in beta-heterochromatin and chromosome 4 may also be related to the fact that these regions do not normally undergo meiotic recombination.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham I., Lucchesi J. C. Dosage compensation of genes on the left and right arms of the X chromosome of Drosophila pseudoobscura and Drosophila willistoni. Genetics. 1974 Dec;78(4):1119–1126. doi: 10.1093/genetics/78.4.1119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Chandrasekaran R., Birdsall D. L., Leslie A. G., Ratliff R. L. Left-handed DNA helices. Nature. 1980 Feb 21;283(5749):743–745. doi: 10.1038/283743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belote J. M., Lucchesi J. C. Control of X chromosome transcription by the maleless gene in Drosophila. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):573–575. doi: 10.1038/285573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M., Wilson A. C. Molecular evolution in Drosophila and the higher Diptera II. A time scale for fly evolution. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(1):1–13. doi: 10.1007/BF02100622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock H. W., Roberts D. B. Location of the LSP-1 Genes in Drosophila Species by IN SITU Hybridization. Genetics. 1983 Jan;103(1):75–92. doi: 10.1093/genetics/103.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter A. T. Electron microscopy of meiosis in Drosophila melanogaster females. I. Structure, arrangement, and temporal change of the synaptonemal complex in wild-type. Chromosoma. 1975;51(2):157–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00319833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia W., Savakis C., Karp R., Pelham H., Ashburner M. Mutation of the Adh gene of Drosophila melanogaster containing an internal tandem duplication. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):679–688. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90388-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chino M, Kikkawa H. Mutants and Crossing over in the Dot-like Chromosome of DROSOPHILA VIRILIS. Genetics. 1933 Mar;18(2):111–116. doi: 10.1093/genetics/18.2.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B., Long E. O., DiNocera P. P., Pardue M. L. Ribosomal insertion-like elements in Drosophila melanogaster are interspersed with mobile sequences. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowsett A. P., Young M. W. Differing levels of dispersed repetitive DNA among closely related species of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4570–4574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gall J. G., Cohen E. H., Polan M. L. Reptitive DNA sequences in drosophila. Chromosoma. 1971;33(3):319–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00284948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. The ubiquitous potential Z-forming sequence of eucaryotes, (dT-dG)n . (dC-dA)n, is not detectable in the genomes of eubacteria, archaebacteria, or mitochondria. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):3010–3013. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Huang S. Y., Garrard W. T. Chromatin structure of the potential Z-forming sequence (dT-dG)n X (dC-dA)n. Evidence for an "alternating-B" conformation. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 25;183(2):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90218-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. A novel repeated element with Z-DNA-forming potential is widely found in evolutionarily diverse eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6465–6469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haniford D. B., Pulleyblank D. E. Facile transition of poly[d(TG) x d(CA)] into a left-handed helix in physiological conditions. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):632–634. doi: 10.1038/302632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiec E. B., Holloman W. K. Homologous pairing of DNA molecules by Ustilago rec1 protein is promoted by sequences of Z-DNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90264-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Separable cis-acting control elements for expression of the white gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3489–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifschytz E., Lindsley D. L. The role of X-chromosome inactivation during spermatogenesis (Drosophila-allocycly-chromosome evolution-male sterility-dosage compensation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):182–186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macknight R H. The Sex-Determining Mechanism of Drosophila Miranda. Genetics. 1939 Mar;24(2):180–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/24.2.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee A. S., Chatterjee S. N. Chromosomal basis of dosage compensation in Drosophila VIII. Faster replication and hyperactivity of both arms of the X-chromosome in males of Drosophila pseudoobscura and their possible significance. Chromosoma. 1975 Nov 24;53(2):91–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00333038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. The sequence (dC-dA)n X (dG-dT)n forms left-handed Z-DNA in negatively supercoiled plasmids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1821–1825. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardue M. L., Dawid I. B. Chromosomal locations of two DNA segments that flank ribosomal insertion-like sequences in Drosophila: flanking sequences are mobile elements. Chromosoma. 1981;83(1):29–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00286014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimpinelli S., Sullivan W., Prout M., Sandler L. On biological functions mapping to the heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Apr;109(4):701–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.4.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Steller H., Bozzetti M. P. Multiple upstream regulatory elements control the expression of the Drosophila white gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Lucchesi J. C. The role of sexuality in dosage compensation in Drosophila. Genetics. 1969 Mar;61(3):607–618. doi: 10.1093/genetics/61.3.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinemann M. Multiple sex chromosomes in Drosophila miranda: a system to study the degeneration of a chromosome. Chromosoma. 1982;86(1):59–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00330730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel E., Pelling C., Arnheim N. Incomplete dosage compensation in an evolving Drosophila sex chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):931–935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treco D., Arnheim N. The evolutionarily conserved repetitive sequence d(TG.AC)n promotes reciprocal exchange and generates unusual recombinant tetrads during yeast meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3934–3947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. W., Schwartz H. E. Nomadic gene families in Drosophila. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):629–640. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]