Abstract
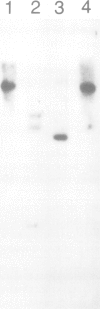
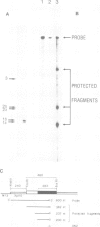
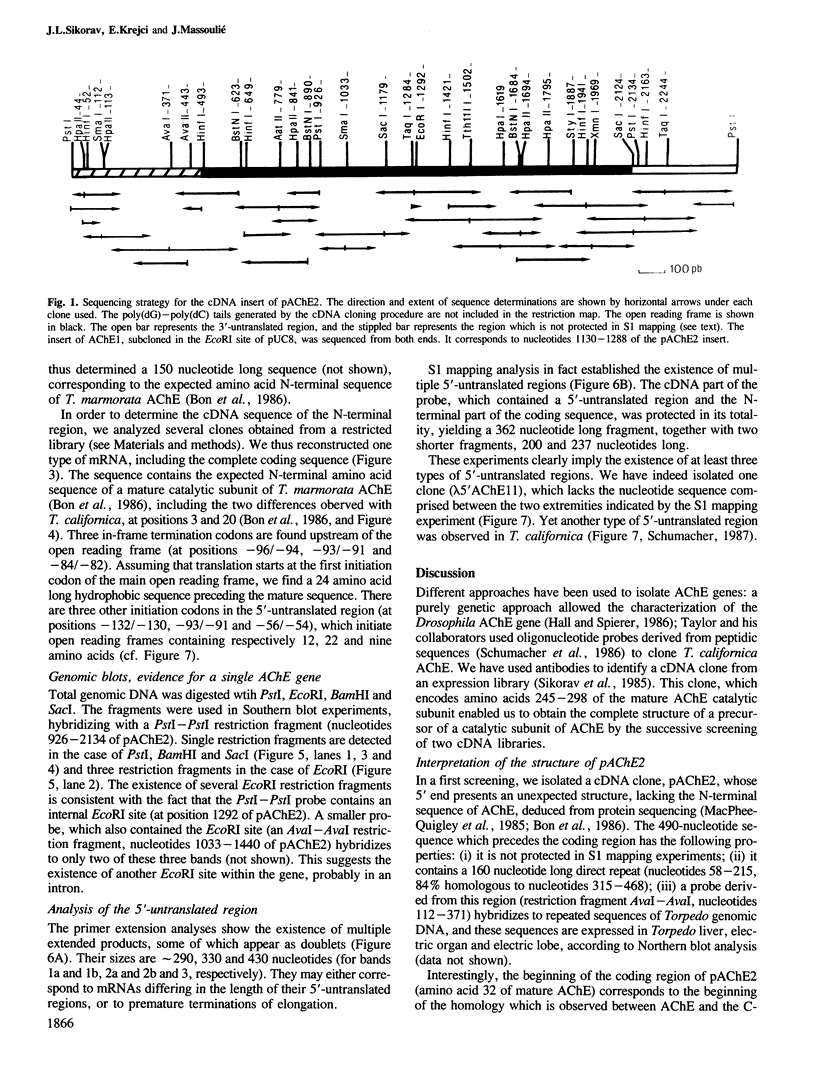
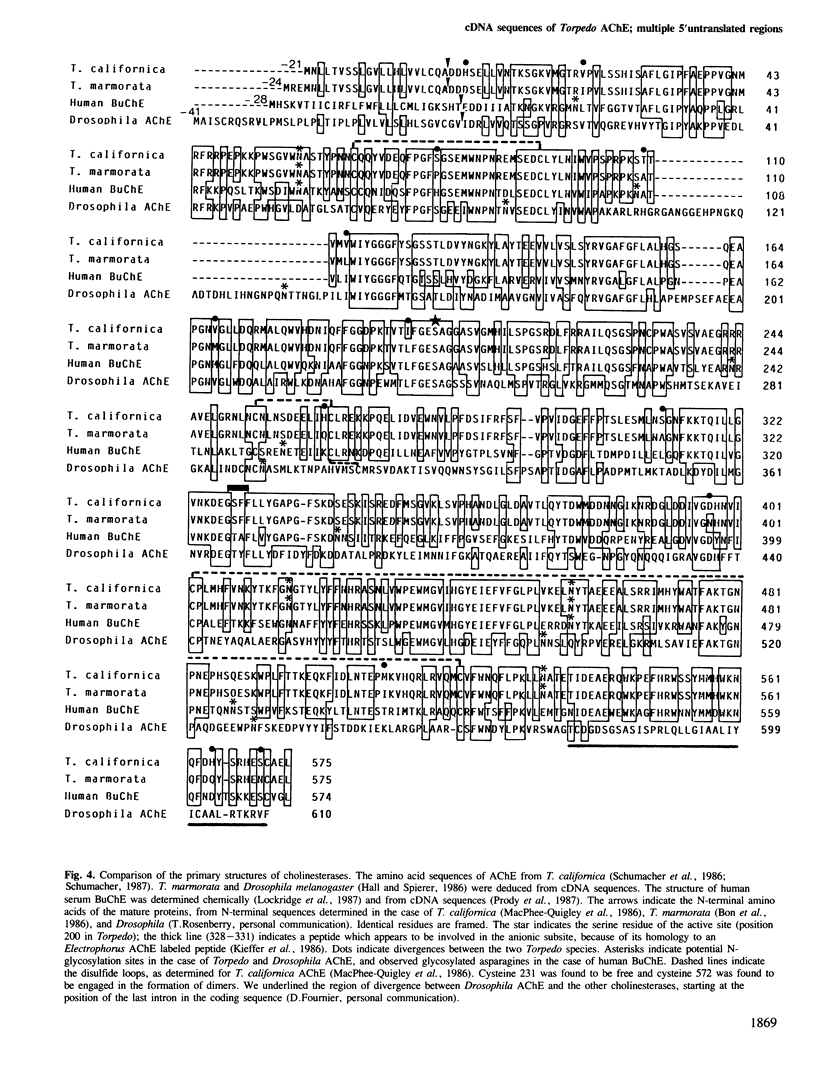
cDNA clones coding for a catalytic subunit of acetylcholinesterase were isolated from cDNA libraries constructed from Torpedo marmorata electric organ. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned cDNAs codes for a 599-amino acid precursor containing a 24-amino acid signal peptide. This primary structure has been compared with the sequences of Torpedo californica and Drosophila melanogasta acetylcholinesterases, and with that of human butyrylcholinesterase. Genomic blot experiments carried out with cDNA restriction fragments used as hybridization probes are in agreement with the existence of a single gene coding for the different catalytic subunits of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase. Unexpectedly, we observed multiple 5'-untranslated regions, which may contain several initiation codons.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Nageotte R., Chambraud B., Rougeon F. Mouse immunoglobulin genes: a bacterial plasmid containing the entire coding sequence for a pre-gamma 2a heavy chain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Mar 25;8(6):1231–1241. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avvedimento V. E., Musti A. M., Obici S., Cocozza S., Di Lauro R. Structural organization of the 3' half of the rat thyroglobulin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 25;12(8):3461–3472. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.8.3461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bon S., Chang J. Y., Strosberg A. D. Identical N-terminal peptide sequences of asymmetric forms and of low-salt-soluble and detergent-soluble amphiphilic dimers of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase. Comparison with bovine acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):206–212. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81112-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Citri Y., Colot H. V., Jacquier A. C., Yu Q., Hall J. C., Baltimore D., Rosbash M. A family of unusually spliced biologically active transcripts encoded by a Drosophila clock gene. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):42–47. doi: 10.1038/326042a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doctor B. P., Camp S., Gentry M. K., Taylor S. S., Taylor P. Antigenic and structural differences in the catalytic subunits of the molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5767–5771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5' leader. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarsfeld A., Devillers-Thiéry A., Giraudat J., Changeux J. P. A single gene codes for the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit in Torpedo marmorata: structural and developmental implications. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):35–41. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo T., Fukuda K., Mikami A., Maeda A., Takahashi H., Mishina M., Haga T., Haga K., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Cloning, sequencing and expression of complementary DNA encoding the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):411–416. doi: 10.1038/323411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockridge O., Bartels C. F., Vaughan T. A., Wong C. K., Norton S. E., Johnson L. L. Complete amino acid sequence of human serum cholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):549–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor P., Taylor S. Primary structures of the catalytic subunits from two molecular forms of acetylcholinesterase. A comparison of NH2-terminal and active center sequences. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12185–12189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacPhee-Quigley K., Vedvick T. S., Taylor P., Taylor S. S. Profile of the disulfide bonds in acetylcholinesterase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13565–13570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massoulié J., Bon S. The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1982;5:57–106. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.05.030182.000421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercken L., Simons M. J., Swillens S., Massaer M., Vassart G. Primary structure of bovine thyroglobulin deduced from the sequence of its 8,431-base complementary DNA. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):647–651. doi: 10.1038/316647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. P., Hinnebusch A. G. Multiple upstream AUG codons mediate translational control of GCN4. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Multiple mRNAs for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase determined by multiple transcription initiation sites and intron splicing sites in the 5'-untranslated region. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10369–10377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1975;43:103–218. doi: 10.1002/9780470122884.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher M., Camp S., Maulet Y., Newton M., MacPhee-Quigley K., Taylor S. S., Friedmann T., Taylor P. Primary structure of Torpedo californica acetylcholinesterase deduced from its cDNA sequence. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):407–409. doi: 10.1038/319407a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Grassi J., Bon S. Synthesis in vitro of precursors of the catalytic subunits of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo marmorata and Electrophorus electricus. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):519–524. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Vallette F., Grassi J., Massoulié J. Isolation of a cDNA clone for a catalytic subunit of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase. FEBS Lett. 1985 Dec 2;193(2):159–163. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swillens S., Ludgate M., Mercken L., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Analysis of sequence and structure homologies between thyroglobulin and acetylcholinesterase: possible functional and clinical significance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 May 29;137(1):142–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant J. P., Massoulié J., Bon S. Polymorphism of pseudocholinesterase in Torpedo marmorata tissues: comparative study of the catalytic and molecular properties of this enzyme with acetylcholinesterase. J Neurochem. 1985 Feb;44(2):580–592. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb05452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]