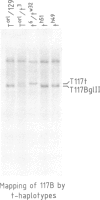
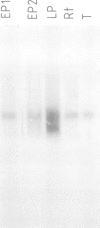
Abstract
We have used an approach based on the observation of CpG-rich regions near the 5' end of many genes to screen a panel of cosmids derived from the t-complex and tested candidate sequences for evidence of transcription in a number of different mouse tissues. One gene so identified is expressed specifically in testicular germ cells and maps to a subregion of the t-complex also containing loci involved in transmission ratio distortion and male sterility. The transcript is first detected during the pachytene stage of the first meiotic division, but is expressed in highest levels in the later haploid spermatogenic stages. Sequence analysis verified the existence of a CpG-rich element on the 5' end of the gene and predicts a unique protein species with no significant homologies to those previously determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bird A. P. CpG-rich islands and the function of DNA methylation. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):209–213. doi: 10.1038/321209a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. R., Bird A. P. Long-range restriction site mapping of mammalian genomic DNA. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):477–481. doi: 10.1038/322477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandley A. C., Hotta Y., Stern H. Biochemical analysis of meiosis in the male mouse. I. Separation of DNA labelling of specific spermatogenic stages. Chromosoma. 1977 Jul 8;62(3):243–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00286046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudley K., Potter J., Lyon M. F., Willison K. R. Analysis of male sterile mutations in the mouse using haploid stage expressed cDNA probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 25;12(10):4281–4293. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.10.4281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Martin G. R., Lyon M. F., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Silver L. M. Molecular probes define different regions of the mouse t complex. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B. G., Barlow D. P., Lehrach H. A large inverted duplication allows homologous recombination between chromosomes heterozygous for the proximal t complex inversion. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):813–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90078-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B., Bućan M., Mains P. E., Frischauf A. M., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S., Merlino G. T., Pastan I. Promoter region of the human Harvey ras proto-oncogene: similarity to the EGF receptor proto-oncogene promoter. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1378–1381. doi: 10.1126/science.2999983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kettaneh N. P., Hartl D. L. Histone transition during spermiogenesis is absent in segregation distorter males of Drosophila melanogaster. Science. 1976 Sep 10;193(4257):1020–1021. doi: 10.1126/science.821147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Hammerberg C. The control of differentiation by the T complex. Immunol Rev. 1977 Jan;33:70–104. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00363.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Lehrach H., Goody R. S. A new method of DNA sequencing using deoxynucleoside alpha-thiotriphosphates. DNA. 1986 Apr;5(2):173–177. doi: 10.1089/dna.1986.5.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Evans E. P., Jarvis S. E., Sayers I. t-Haplotypes of the mouse may involve a change in intercalary DNA. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):38–42. doi: 10.1038/279038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F. Male sterility of the mouse t-complex is due to homozygosity of the distorter genes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):357–363. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90770-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rackwitz H. R., Zehetner G., Murialdo H., Delius H., Chai J. H., Poustka A., Frischauf A., Lehrach H. Analysis of cosmids using linearization by phage lambda terminase. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert B., Barton P., Minty A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Bonhomme F., Catalan J., Chazottes D., Guénet J. L., Buckingham M. Investigation of genetic linkage between myosin and actin genes using an interspecific mouse back-cross. Nature. 1985 Mar 14;314(6007):181–183. doi: 10.1038/314181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röhme D., Fox H., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Edström J. E., Mains P., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Molecular clones of the mouse t complex derived from microdissected metaphase chromosomes. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):783–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shedlovsky A., Guenet J. L., Johnson L. L., Dove W. F. Induction of recessive lethal mutations in the T/t-H-2 region of the mouse genome by a point mutagen. Genet Res. 1986 Apr;47(2):135–142. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300022977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M. Genetic organization of the mouse t complex. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):239–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90406-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver L. M. Mouse t haplotypes. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:179–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Washburn L. L., Eicher E. M. Sex reversal in XY mice caused by dominant mutation on chromosome 17. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):338–340. doi: 10.1038/303338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willison K. R., Dudley K., Potter J. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a haploid expressed gene encoding t complex polypeptide 1. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):727–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90839-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Engelmyer E., Duggal R. N., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Mutter G. L., Ponzetto C., Viviano C., Zakeri Z. F. Isolation of a mouse cDNA coding for a developmentally regulated, testis-specific transcript containing homeo box homology. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1229–1235. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04351.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehetner G., Lehrach H. A computer program package for restriction map analysis and manipulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):335–349. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]