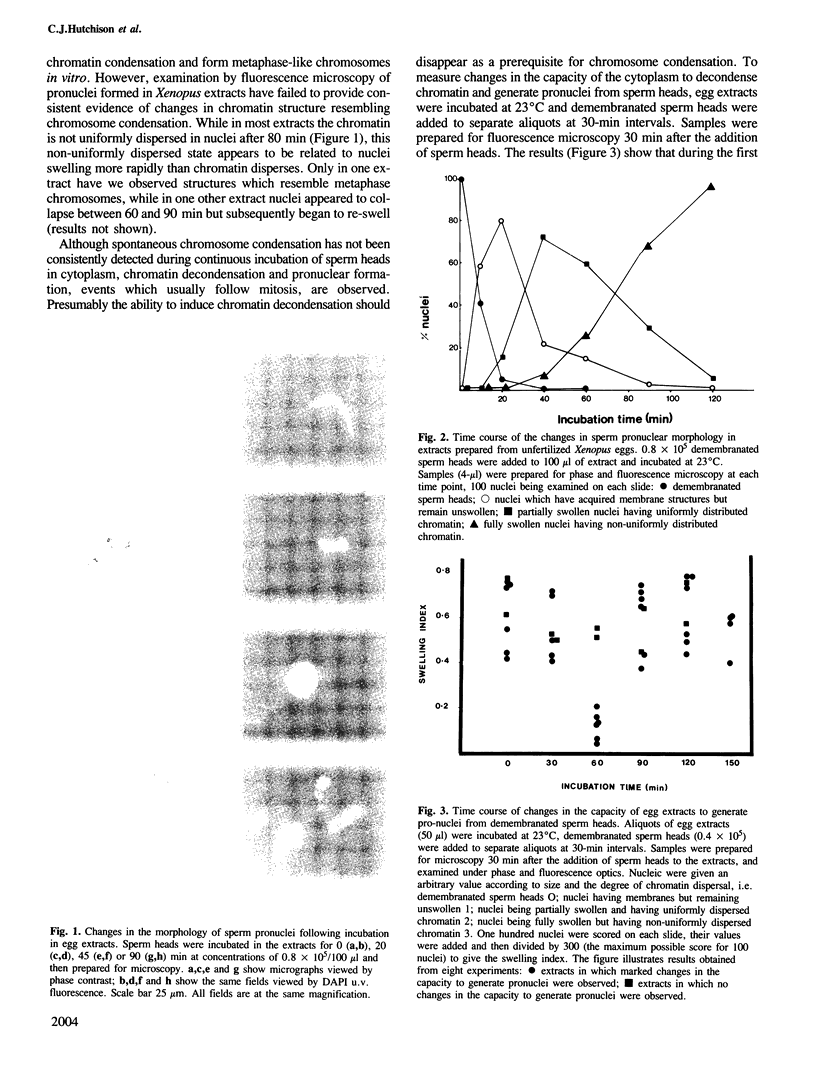
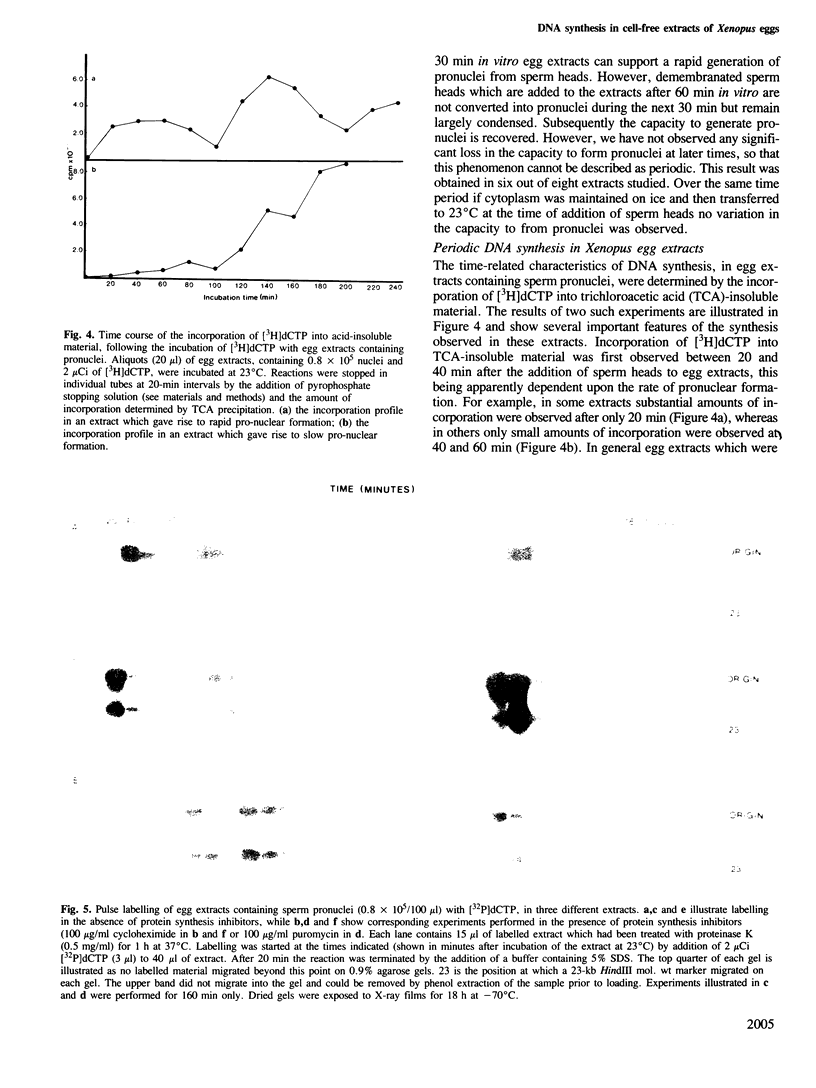
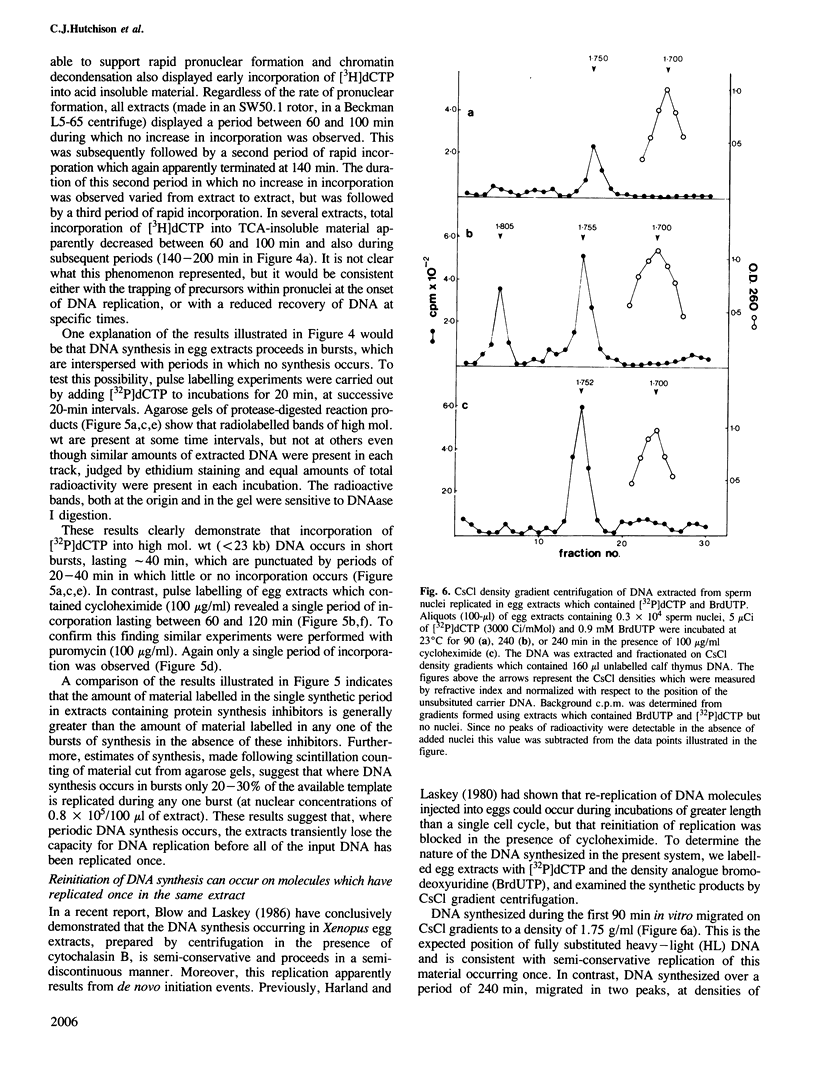
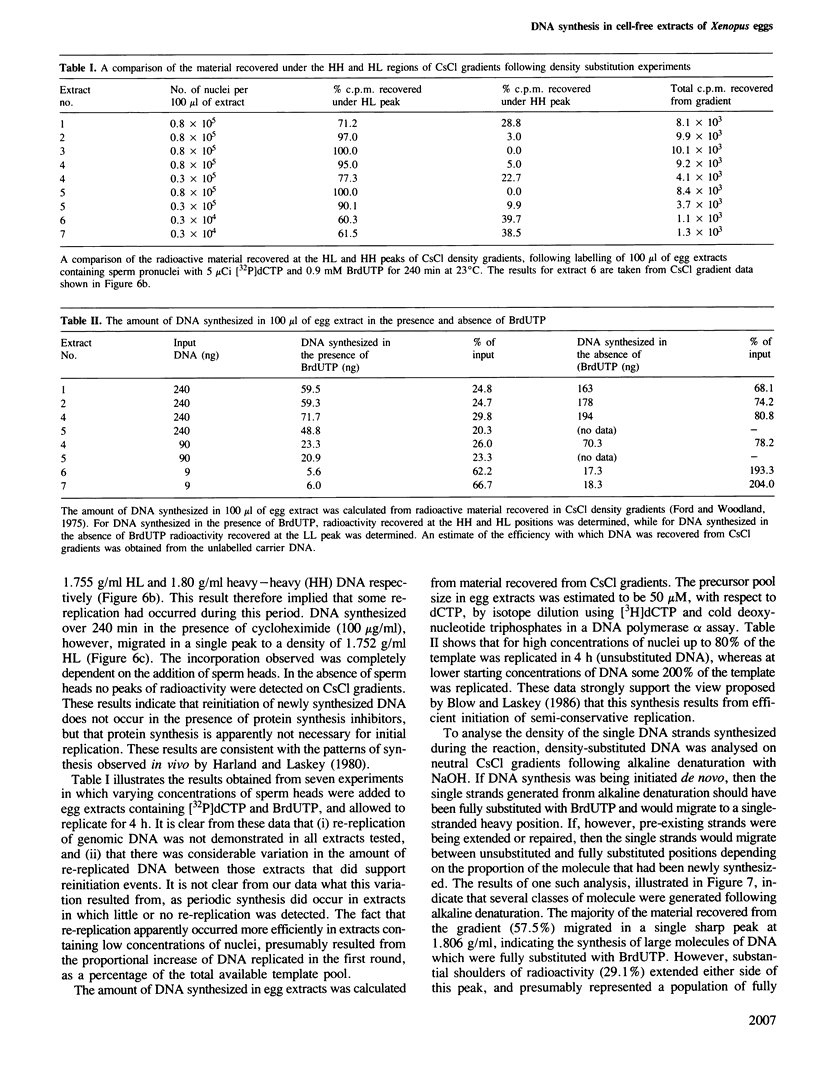
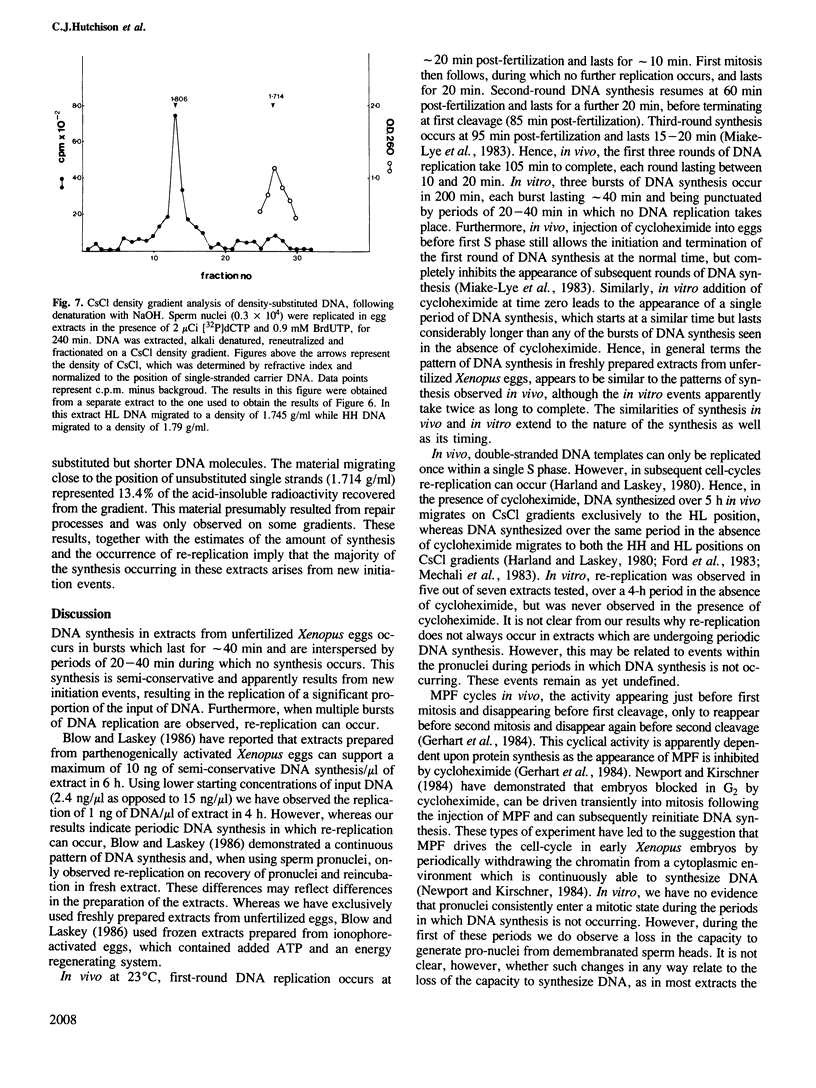
Abstract
Cell-free extracts prepared from unfertilized eggs of Xenopus laevis support DNA synthesis on sperm pronuclei. Continuous labelling studies using [3H]dCTP and pulse labelling studies using [32P]dCTP demonstrate that synthesis occurs in short bursts of 40 min, which are punctuated by periods of 20-40 min during which no synthesis occurs. Density substitution experiments using bromodeoxyuridine demonstrate that this synthesis involves the initiation of replication and reveals that re-initiation events can occur following multiple bursts of replication. The periodic properties of these extracts are sensitive to protein synthesis inhibitors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blow J. J., Laskey R. A. Initiation of DNA replication in nuclei and purified DNA by a cell-free extract of Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):577–587. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90622-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenberg H. J., Huberman J. A. Eukaryotic chromosome replication. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:245–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.001333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C. Maturation promoting factor and cell cycle regulation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):271–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C., Woodland H. R. DNA synthesis in ocytes and eggs of Xenopus laevis injected with DNA. Dev Biol. 1975 Mar;43(1):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90140-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Injected nuclei in frog oocytes: fate, enlargement, and chromatin dispersal. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Dec;36(3):523–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R. M., Laskey R. A. Regulated replication of DNA microinjected into eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):761–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Gurdon J. B. Induction of polyoma DNA synthesis by injection into frog-egg cytoplasm. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Sep 3;37(3):467–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Maller J. L. Induction of nuclear envelope breakdown, chromosome condensation, and spindle formation in cell-free extracts. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):518–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Formation in vitro of sperm pronuclei and mitotic chromosomes induced by amphibian ooplasmic components. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):719–721. doi: 10.1126/science.6601299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Kirschner M. W. Induction of early mitotic events in a cell-free system. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90071-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Newport J., Kirschner M. Maturation-promoting factor induces nuclear envelope breakdown in cycloheximide-arrested embryos of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):81–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Kearsey S. Lack of specific sequence requirement for DNA replication in Xenopus eggs compared with high sequence specificity in yeast. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):55–64. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90526-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méchali M., Méchali F., Laskey R. A. Tumor promoter TPA increases initiation of replication on DNA injected into xenopus eggs. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the cell cycle during early Xenopus development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nurse P., Bissett Y. Gene required in G1 for commitment to cell cycle and in G2 for control of mitosis in fission yeast. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):558–560. doi: 10.1038/292558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C., Brill D., Bownes M., Ford C. Drosophila nuclei replicate in Xenopus eggs. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1980 Feb;55:183–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodland H. R., Pestell R. Q. Determination of the nucleoside triphosphate contents of eggs and oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(3):597–605. doi: 10.1042/bj1270597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler M. K., Marini N. J., Stowers D. J., Benbow R. M. Stockpiling of DNA polymerases during oogenesis and embryogenesis in the frog, Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):974–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]