Abstract
The E3/19K protein of human adenovirus type 2 binds to HLA class I antigens and blocks their terminal glycosylation and cell surface expression. The nature of this interaction is non-covalent and involves neither disulfide bridges between the two molecules nor their carbohydrates. The murine H-2 Kd antigen associates with the E3/19K protein in a similar fashion to human HLA antigens whereas the allelic product H-2 Kk does not. Hybrid genes between the Kd and Kk alleles were constructed and their products were expressed in embryonic kidney cells together with the E3/19K protein. This allowed us to identify the alpha 1 and alpha 2 domains as the essential structures of the histocompatibility antigens for binding the viral protein. Interestingly, these domains are also crucial for T cell recognition. The implications for the evolution of adenoviruses and their ability to cause persistent infections are discussed.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed C. M., Chanda R. S., Stow N. D., Zain B. S. The nucleotide sequence of mRNA for the Mr 19 000 glycoprotein from early gene block III of adenovirus 2. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen H., Wraith D., Pala P., Askonas B., Flavell R. A. Domain interactions of H-2 class I antigens alter cytotoxic T-cell recognition sites. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):279–281. doi: 10.1038/309279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson M., Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Archibald A. L., Kvist S. Complete nucleotide sequence of the murine H-2Kk gene. Comparison of three H-2K locus alleles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9473–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Burgert H. G., Hamann U., Hämmerling G., Kees U., Kvist S. Cytolytic T cells recognize the two amino-terminal domains of H-2 K antigens in tandem in influenza A infected cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90528-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B., Horstmann U., Kuon W., Burgert H. G., Hämmerling G. J., Kvist S. Alloreactive cytolytic T-cell clones preferentially recognize conformational determinants on histocompatibility antigens: analysis with genetically engineered hybrid antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7030–7034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. G. Construction of a fusion gene that confers resistance against hygromycin B to mammalian cells in culture. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90446-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat B. M., Wold W. S. Genetic analysis of mRNA synthesis in adenovirus region E3 at different stages of productive infection by RNA-processing mutants. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):54–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.54-63.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
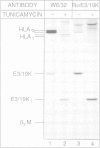
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Maryanski J. L., Kvist S. "E3/19K" protein of adenovirus type 2 inhibits lysis of cytolytic T lymphocytes by blocking cell-surface expression of histocompatibility class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin W. W., Maizel J. V., Jr The polypeptides of adenovirus. VII. Further studies of early polypeptides in vivo and localization of E2 and E2A to the cell plasma membrane. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):518–530. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90378-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
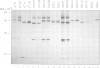
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., Rudersdorf R., Chang C., Petersen J., Strandtmann J., Korn N., Sidwell B., Orr H. T. Mutations that impair a posttranscriptional step in expression of HLA-A and -B antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8183–8187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
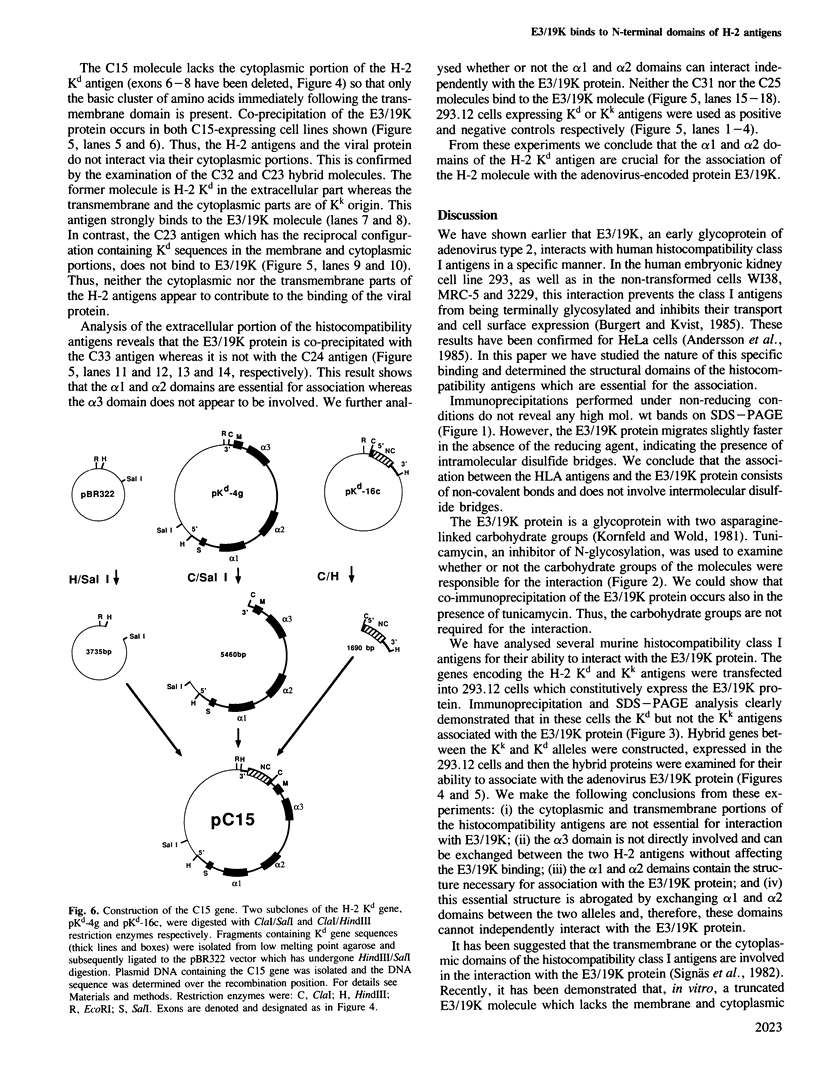
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J. The major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):516–521. doi: 10.1126/science.104386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Wold W. S. Structures of the oligosaccharides of the glycoprotein coded by early region E3 of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.440-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Lodish H. F. Oligomerization is essential for transport of vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein to the cell surface. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90075-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Ostberg L., Persson H., Philipson L., Peterson P. A. Molecular association between transplantation antigens and cell surface antigen in adenovirus-transformed cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5674–5678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Roberts L., Dobberstein B. Mouse histocompatibility genes: structure and organisation of a Kd gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):245–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kvist S., Wiman K., Claesson L., Peterson P. A., Dobberstein B. Membrane insertion and oligomeric assembly of HLA-DR histocompatibility antigens. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kämpe O., Bellgrau D., Hammerling U., Lind P., Päbo S., Severinsson L., Peterson P. A. Complex formation of class I transplantation antigens and a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10594–10598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff T., Elkaim R., Goding C. R., Jalinot P., Sassone-Corsi P., Perricaudet M., Kédinger C., Chambon P. Individual products of the adenovirus 12S and 13S EIa mRNAs stimulate viral EIIa and EIII expression at the transcriptional level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4381–4385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew A. M., Lillehoj E. P., Cowan E. P., Maloy W. L., van Schravendijk M. R., Coligan J. E. Class I genes and molecules: an update. Immunology. 1986 Jan;57(1):3–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki J., Appella E., Ozato K. Intracellular transport blockade caused by disruption of the disulfide bridge in the third external domain of major histocompatibility complex class I antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):757–761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathenson S. G., Geliebter J., Pfaffenbach G. M., Zeff R. A. Murine major histocompatibility complex class-I mutants: molecular analysis and structure-function implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:471–502. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.002351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Jörnvall H., Zabielski J. Multiple mRNA species for the precursor to an adenovirus-encoded glycoprotein: identification and structure of the signal sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Philipson L. Regulation of adenovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;97:157–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68318-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploegh H. L., Orr H. T., Strominger J. L. Major histocompatibility antigens: the human (HLA-A, -B, -C) and murine (H-2K, H-2D) class I molecules. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):287–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90318-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Kämpe O., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Association between transplantation antigens and a viral membrane protein synthesized from a mammalian expression vector. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):445–453. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90426-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Weber F., Nilsson T., Schaffner W., Peterson P. A. Structural and functional dissection of an MHC class I antigen-binding adenovirus glycoprotein. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1921–1927. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss C. S., Evans G. A., Margulies D. H., Seidman J. G., Burakoff S. J. Allospecific and virus-specific cytolytic T lymphocytes are restricted to the N or C1 domain of H-2 antigens expressed on L cells after DNA-mediated gene transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2709–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S., Levine A. J. The genomic map position of the adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):427–430. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salter R. D., Cresswell P. Impaired assembly and transport of HLA-A and -B antigens in a mutant TxB cell hybrid. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):943–949. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schøller J., Shimonkevitz R., MacDonald H. R., Kvist S. Different structural constraints for recognition of mouse H-2Kd and -Kk antigens by alloimmune cytolytic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1986 Dec 1;164(6):1823–1834. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinsson L., Martens I., Peterson P. A. Differential association between two human MHC class I antigens and an adenoviral glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):1003–1009. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Williams J. Genetic analysis of adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;111:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69549-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Katze M. G., Persson H., Philipson L. An adenovirus glycoprotein binds heavy chains of class I transplantation antigens from man and mouse. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):175–178. doi: 10.1038/299175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townsend A. R., Rothbard J., Gotch F. M., Bahadur G., Wraith D., McMichael A. J. The epitopes of influenza nucleoprotein recognized by cytotoxic T lymphocytes can be defined with short synthetic peptides. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):959–968. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. B., Swiedler S. J., Hart G. W. Intracellular transport of membrane glycoproteins: two closely related histocompatibility antigens differ in their rates of transit to the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):725–734. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wold W. S., Cladaras C., Deutscher S. L., Kapoor Q. S. The 19-kDa glycoprotein coded by region E3 of adenovirus. Purification, characterization, and structural analysis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2424–2431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]