Abstract
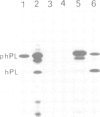
Different wheat germ extracts were tested for the presence of membranes capable of translocating and processing nascent secretory proteins. One lysate was found in which nascent prehuman-placental lactogen (phPL) was translocated and processed to mature human placental lactogen (hPL). Processing was found to occur concomitant with translocation across membranes. Translocation across the wheat germ membrane required a component which is similar to the mammalian signal recognition particle (SRP). It bound to DEAE–Sepharose, had a sedimentation coefficient of 11S and contained a 7S RNA. In addition to hPL, the plant protein zein and the bacterial protein β-lactamase were translocated across and processed by wheat germ membranes. Transport was found to occur only co-translationally. Our results show that the wheat germ protein translocation system is similar to the mammalian one. Unlike the mammalian SRP, the particle purified from wheat germ did not arrest elongation of nascent secretory proteins.
Keywords: plant membranes, protein translocation, signal recognition particle, wheat germ
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassüner R., Wobus U., Rapoport T. A. Signal recognition particle triggers the translocation of storage globulin polypeptides from field beans (Vicia faba L.) across mammalian endoplasmic reticulum membrane. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jan 30;166(2):314–320. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Date T., Wickner W. Isolation of the Escherichia coli leader peptidase gene and effects of leader peptidase overproduction in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6106–6110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G., Walter P. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. I. Detection in the microsomal membrane of a receptor for the signal recognition particle. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):463–469. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen W., Garcia P. D., Walter P. In vitro protein translocation across the yeast endoplasmic reticulum: ATP-dependent posttranslational translocation of the prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90325-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Date T., Wickner W. Synthesis, assembly into the cytoplasmic membrane, and proteolytic processing of the precursor of coliphage M13 coat protein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2123–2130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. C., Blobel G. Post-translational cleavage of presecretory proteins with an extract of rough microsomes from dog pancreas containing signal peptidase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5598–5602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Pedersen K., Handa A. K., Hurkman W. J., Smith L. D. Synthesis and processing of maize storage proteins in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6448–6452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Dobberstein B. Identification and characterization of a membrane component essential for the translocation of nascent proteins across the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1980 Nov;87(2 Pt 1):503–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I. Signal recognition particle (SRP) does not mediate a translational arrest of nascent secretory proteins in mammalian cell-free systems. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2031–2033. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03888.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prehn S., Nürnberg P., Rapoport T. A. A receptor for single segments of secretory proteins in rough endoplasmic reticulum membranes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 12;123(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80024-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapoport T. A. Protein translocation across and integration into membranes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):73–137. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothblatt J. A., Meyer D. I. Secretion in yeast: reconstitution of the translocation and glycosylation of alpha-factor and invertase in a homologous cell-free system. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):619–628. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Translation efficiency of zein mRNA is reduced by hybrid formation between the 5'- and 3'-untranslated region. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2153–2158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03909.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex required for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7112–7116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle: a ribonucleoprotein required for cotranslational translocation of proteins, isolation and properties. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:682–691. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren G., Dobberstein B. Protein transfer across microsomal membranes reassembled from separated membrane components. Nature. 1978 Jun 15;273(5663):569–571. doi: 10.1038/273569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters M. G., Blobel G. Secretory protein translocation in a yeast cell-free system can occur posttranslationally and requires ATP hydrolysis. J Cell Biol. 1986 May;102(5):1543–1550. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.5.1543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]