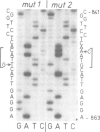
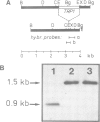
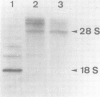
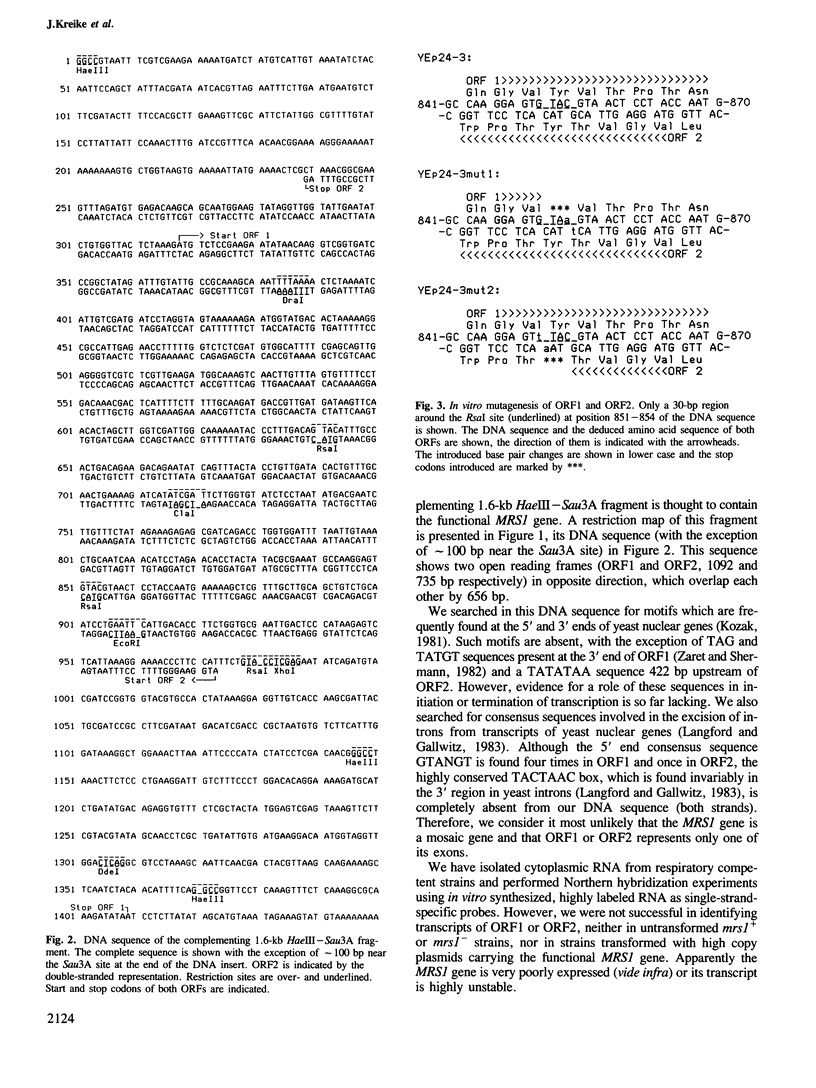
Abstract
We have cloned a 1.6-kb fragment of yeast nuclear DNA, which complements pet- mutant MK3 (mrs1). This mutant was shown to be defective in mitochondrial RNA splicing: the excision of intron 3 from the mitochondrial COB pre-RNA is blocked. The DNA sequence of the nuclear DNA fragment revealed two open reading frames (ORF1 with 1092 bp; ORF2 with 735 bp) on opposite strands, which overlap by 656 bp. As shown by in vitro mutagenesis, ORF1, but not ORF2, is responsible for complementation of the splice defect. Hence, ORF1 represents the nuclear MRS1 gene. Disruption of the gene (both ORFs) in the chromosomal DNA of the respiratory competent yeast strain DBY747 (long form COB gene) leads to a stable pet- phenotype and to the accumulation of the same mitochondrial RNA precursors as in strain MK3. The amino acid sequence of the putative ORF1 product does not exhibit any homology with other known proteins, except for a small region of homology with the gene product of another nuclear yeast gene involved in mitochondrial RNA splicing, CBP2. The function of the MRS1 (ORF1) gene in mitochondrial RNA splicing and the significance of the overlapping ORFs in this gene are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belfort M., Maley G., Pedersen-Lane J., Maley F. Primary structure of the Escherichia coli thyA gene and its thymidylate synthase product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4914–4918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M., Pedersen-Lane J. Genetic system for analyzing Escherichia coli thymidylate synthase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):371–378. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.371-378.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellisario R. L., Maley G. F., Guarino D. U., Maley F. The primary structure of Lactobacillus casei thymidylate synthetase. II. The complete amino acid sequence of the active site peptide, CNBr 4. J Biol Chem. 1979 Feb 25;254(4):1296–1300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casino A., Cipollaro M., Guerrini A. M., Mastrocinque G., Spena A., Scarlato V. Coding capacity of complementary DNA strands. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 25;9(6):1499–1518. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.6.1499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R. The generality of self-splicing RNA: relationship to nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):207–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90751-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasiolo F., Bonnet J., Lacroute F. Cloning of the yeast methionyl-tRNA synthetase gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2324–2328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garriga G., Lambowitz A. M. RNA splicing in neurospora mitochondria: self-splicing of a mitochondrial intron in vitro. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90470-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. A mutation in yeast mitochondrial DNA results in a precise excision of the terminal intron of the cytochrome b gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3235–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreike J., Schulze M., Pillar T., Körte A., Rödel G. Cloning of a nuclear gene MRS1 involved in the excision of a single group I intron (bI3) from the mitochondrial COB transcript in S. cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;11(3):185–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00420605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruger K., Grabowski P. J., Zaug A. J., Sands J., Gottschling D. E., Cech T. R. Self-splicing RNA: autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of Tetrahymena. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90414-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. F., Burger G. A collection of programs for nucleic acid and protein analysis, written in FORTRAN 77 for IBM-PC compatible microcomputers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):455–465. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang B. F. The mitochondrial genome of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: highly homologous introns are inserted at the same position of the otherwise less conserved cox1 genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Aspergillus nidulans. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2129–2136. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the processing of the cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9459–9468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Pape L. K., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2087–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. MSW, a yeast gene coding for mitochondrial tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15371–15377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Normark S., Bergström S., Edlund T., Grundström T., Jaurin B., Lindberg F. P., Olsson O. Overlapping genes. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:499–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles C. L., Perlman P. S., Mecklenburg K. L., Petrillo M. L., Tabor J. H., Jarrell K. A., Cheng H. L. A self-splicing RNA excises an intron lariat. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90755-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pillar T., Lang B. F., Steinberger I., Vogt B., Kaudewitz F. Expression of the "split gene" cob in yeast mtDNA. Nuclear mutations specifically block the excision of different introns from its primary transcript. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7954–7959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schmidt C., May K., Schweyen R. J. Determination of functional domains in intron bI1 of yeast mitochondrial RNA by studies of mitochondrial mutations and a nuclear suppressor. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2047–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01698.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Isolation and characterisation of a yeast chromosomal replicator. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):39–43. doi: 10.1038/282039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring R. B., Davies R. W. Assessment of a model for intron RNA secondary structure relevant to RNA self-splicing--a review. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):277–291. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90145-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Rödel G., Schweyen R. J., Kaudewitz F. Expression of the split gene cob in yeast: evidence for a precursor of a "maturase" protein translated from intron 4 and preceding exons. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90169-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]