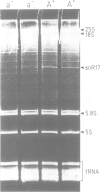
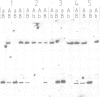
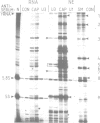
Abstract
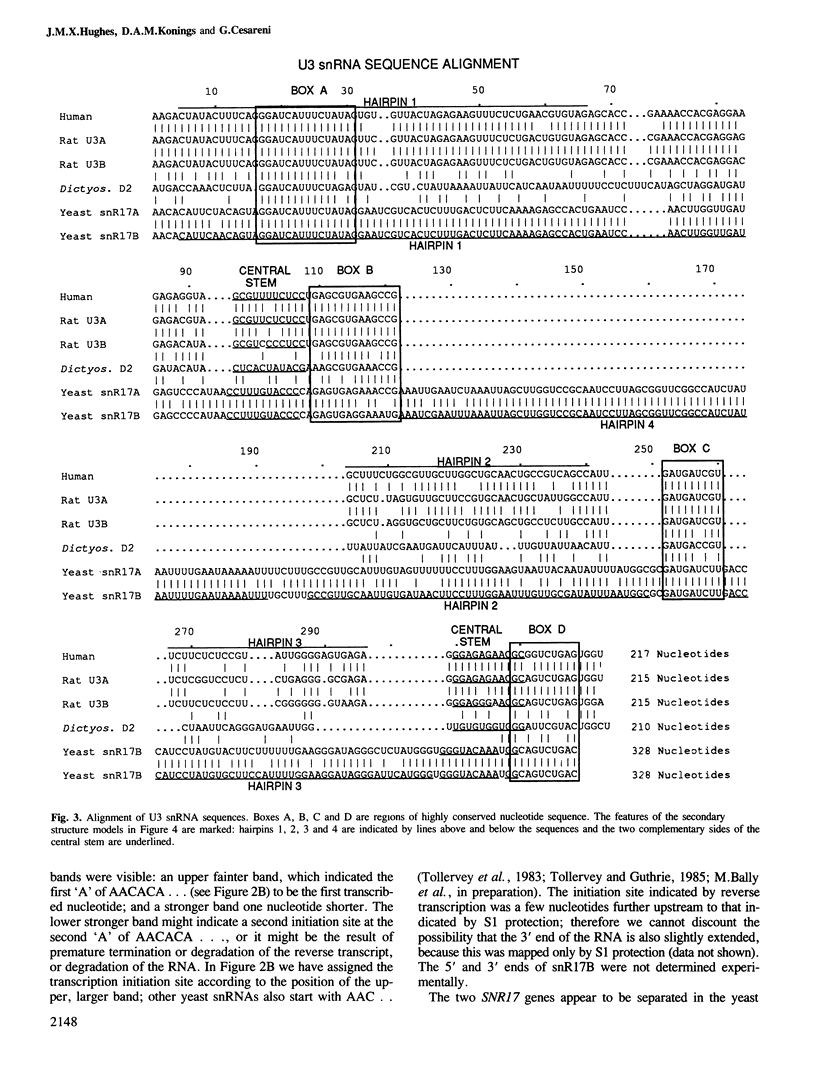
snR17, one of the most abundant capped small nuclear RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, is equivalent to U3 snRNA of other eukaryotes. It is 328 nucleotides in length, 1.5 times as long as other U3 RNAs, but shares significant homology both in nucleotide sequence and in predicted secondary structure. Human scleroderma antiserum specific to nucleolar U3 RNP can enrich snR17 from sonicated yeast nuclear extracts. Unlike other yeast snRNAs which are encoded by single copy genes, snR17 is encoded by two genetically unlinked genes: SNR17A and SNR17B. The RNA snR17A is more abundant than snR17B. Deleting one or other of the genes has no obvious phenotypic effect, except that the steady-state level of snR17B is increased in snr17a- strains. Haploid strains with both genes deleted are inviable, therefore yeast U3 is essential.
Full text
PDF


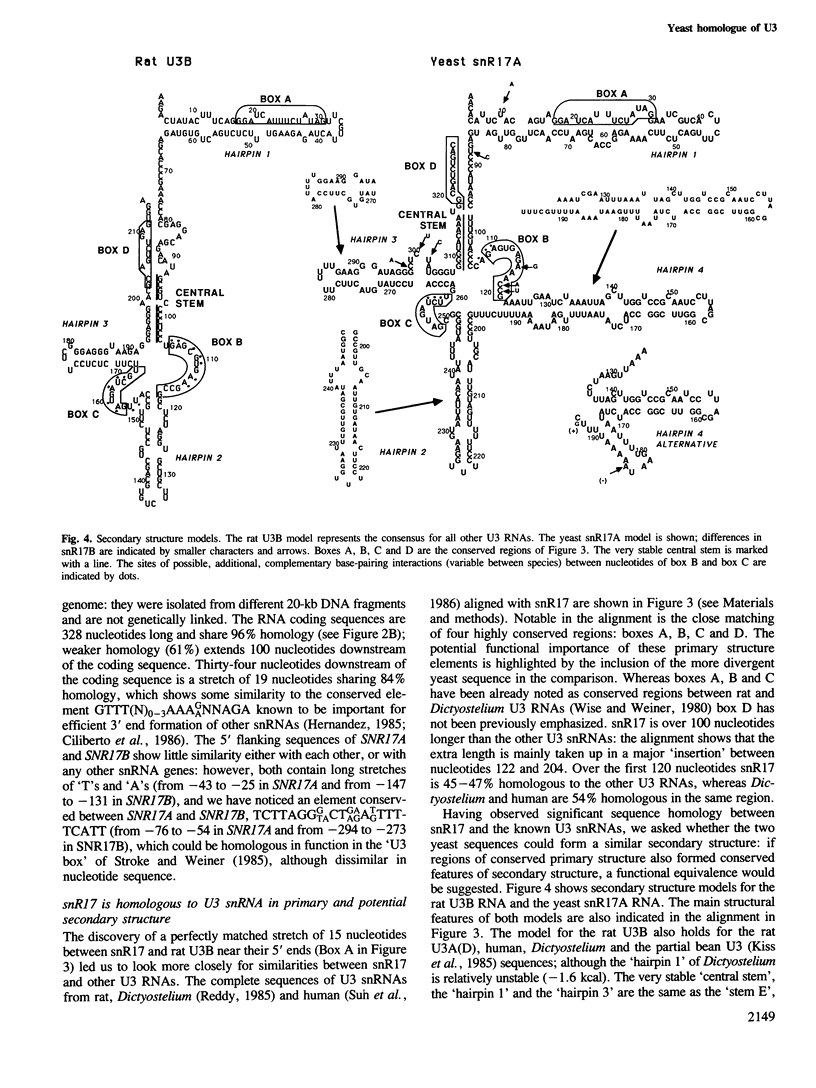

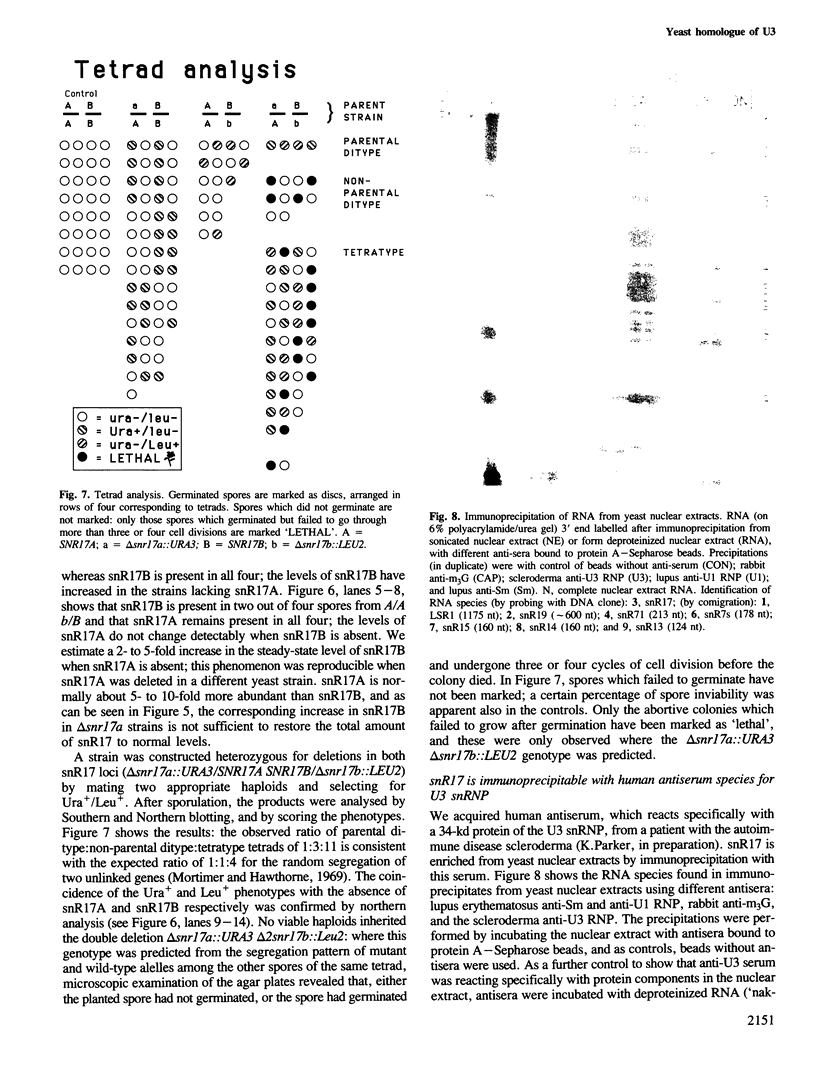




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ares M., Jr U2 RNA from yeast is unexpectedly large and contains homology to vertebrate U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear RNAs. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):49–59. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90365-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachellerie J. P., Michot B., Raynal F. Recognition signals for mouse pre-rRNA processing. A potential role for U3 nucleolar RNA. Mol Biol Rep. 1983 May;9(1-2):79–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00777477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldari C., Cesareni G. Plasmids pEMBLY: new single-stranded shuttle vectors for the recovery and analysis of yeast DNA sequences. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein L. B., Mount S. M., Weiner A. M. Pseudogenes for human small nuclear RNA U3 appear to arise by integration of self-primed reverse transcripts of the RNA into new chromosomal sites. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):461–472. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90466-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Chabot B., Steitz J. A. U2 as well as U1 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins are involved in premessenger RNA splicing. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):737–750. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L., Steitz J. A. Pre-mRNA splicing in vitro requires intact U4/U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):697–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branlant C., Krol A., Ebel J. P., Lazar E., Haendler B., Jacob M. U2 RNA shares a structural domain with U1, U4, and U5 RNAs. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bringmann P., Rinke J., Appel B., Reuter R., Lührmann R. Purification of snRNPs U1, U2, U4, U5 and U6 with 2,2,7-trimethylguanosine-specific antibody and definition of their constituent proteins reacting with anti-Sm and anti-(U1)RNP antisera. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1129–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01557.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Strathern J. N., Hicks J. B. Transformation in yeast: development of a hybrid cloning vector and isolation of the CAN1 gene. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch H., Reddy R., Rothblum L., Choi Y. C. SnRNAs, SnRNPs, and RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:617–654. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvet J. P., Pederson T. Base-pairing interactions between small nuclear RNAs and nuclear RNA precursors as revealed by psoralen cross-linking in vivo. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Tanner N. K., Tinoco I., Jr, Weir B. R., Zuker M., Perlman P. S. Secondary structure of the Tetrahymena ribosomal RNA intervening sequence: structural homology with fungal mitochondrial intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3903–3907. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Black D. L., LeMaster D. M., Steitz J. A. The 3' splice site of pre-messenger RNA is recognized by a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1344–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.2933810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dathan N., Frank R., Philipson L., Mattaj I. W. Formation of the 3' end on U snRNAs requires at least three sequence elements. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England T. E., Uhlenbeck O. C. 3'-terminal labelling of RNA with T4 RNA ligase. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):560–561. doi: 10.1038/275560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Busch H. Multiple states of U3 RNA in Novikoff hepatoma nucleoli. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 6;23(23):5421–5425. doi: 10.1021/bi00318a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Garoff H., Lehrach H. A subcloning strategy for DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5541–5549. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Stunnenberg H. G., Birnstiel M. L. Biochemical complementation with RNA in the Xenopus oocyte: a small RNA is required for the generation of 3' histone mRNA termini. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):823–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90539-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., MacDonald R. J. Cloning of hormone genes from a mixture of cDNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:75–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Halvorson H. O. Methods in sporulation and germination of yeasts. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:45–69. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60316-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA is directed by a conserved sequence located downstream of the coding region. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1827–1837. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03857.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogeweg P., Hesper B. The alignment of sets of sequences and the construction of phyletic trees: an integrated method. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(2):175–186. doi: 10.1007/BF02257378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacob M., Lazar E., Haendler B., Gallinaro H., Krol A., Branlant C. A family of small nucleoplasmic RNAs with common structural features. Biol Cell. 1984;51(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00278.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Tóth M., Solymosy F. Plant small nuclear RNAs. Nucleolar U3 snRNA is present in plants: partial characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):259–266. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09192.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T. Multiple factors including the small nuclear ribonucleoproteins U1 and U2 are necessary for pre-mRNA splicing in vitro. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):725–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer A., Keller W., Appel B., Lührmann R. The 5' terminus of the RNA moiety of U1 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles is required for the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90551-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A. Antibodies to small nuclear RNAs complexed with proteins are produced by patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5495–5499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. J., Newman A. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Yeast mRNA splicing in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14780–14792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lischwe M. A., Ochs R. L., Reddy R., Cook R. G., Yeoman L. C., Tan E. M., Reichlin M., Busch H. Purification and partial characterization of a nucleolar scleroderma antigen (Mr = 34,000; pI, 8.5) rich in NG,NG-dimethylarginine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14304–14310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Reed R. The role of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles in pre-mRNA splicing. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):673–678. doi: 10.1038/325673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W. Cap trimethylation of U snRNA is cytoplasmic and dependent on U snRNP protein binding. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):905–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90072-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., De Robertis E. M. Nuclear segregation of U2 snRNA requires binding of specific snRNP proteins. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90314-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Habets W. J., van Venrooij W. J. Monospecific antibodies reveal details of U2 snRNP structure and interaction between U1 and U2 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):997–1002. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04314.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matter L., Schopfer K., Wilhelm J. A., Nyffenegger T., Parisot R. F., De Robertis E. M. Molecular characterization of ribonucleoprotein antigens bound by antinuclear antibodies. A diagnostic evaluation. Arthritis Rheum. 1982 Nov;25(11):1278–1283. doi: 10.1002/art.1780251102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M., Pettersson I., Hinterberger M., Karmas A., Steitz J. A. The U1 small nuclear RNA-protein complex selectively binds a 5' splice site in vitro. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):509–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Guthrie C. A point mutation in the conserved hexanucleotide at a yeast 5' splice junction uncouples recognition, cleavage, and ligation. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. Specific small nuclear RNAs are associated with yeast spliceosomes. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):869–877. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90561-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prestayko A. W., Tonato M., Busch H. Low molecular weight RNA associated with 28 s nucleolar RNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):505–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90318-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Busch H. Small nuclear RNAs and RNA processing. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;30:127–162. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60685-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Henning D., Busch H. Primary and secondary structure of U8 small nuclear RNA. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10930–10935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wise J. A., Swerdlow H., Mak A., Guthrie C. Small nuclear RNAs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: unexpected diversity in abundance, size, and molecular complexity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8097–8101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Wolin S., Guthrie C. A subset of yeast snRNA's contains functional binding sites for the highly conserved Sm antigen. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):328–331. doi: 10.1126/science.2948278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Preparation of RNA and ribosomes from yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:45–64. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60951-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz J. A., Berg C., Gottlieb E., Hardin J. A., Hashimoto C., Hendrick J. P., Hinterberger M., Krikeles M., Lerner M. R., Mount S. M. Structure and function of small ribonucleoproteins from eukaryotic cells. Princess Takamatsu Symp. 1982;12:101–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroke I. L., Weiner A. M. Genes and pseudogenes for rat U3A and U3B small nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jul 20;184(2):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90372-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strub K., Galli G., Busslinger M., Birnstiel M. L. The cDNA sequences of the sea urchin U7 small nuclear RNA suggest specific contacts between histone mRNA precursor and U7 RNA during RNA processing. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2801–2807. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02212.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh D., Busch H., Reddy R. Isolation and characterization of a human U3 small nucleolar RNA gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1133–1140. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90343-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S. Isolation and characterization of small nuclear RNAs from Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biochem. 1981 Aug;90(2):299–308. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Guthrie C. Deletion of a yeast small nuclear RNA gene impairs growth. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3873–3878. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Mattaj I. W. Fungal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins share properties with plant and vertebrate U-snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):469–476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Wise J. A., Guthrie C. A U4-like small nuclear RNA is dispensable in yeast. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):753–762. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A., Penman S. Small molecular weight monodisperse nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Dec;38(3):289–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90387-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. L., Jr, Tinoco I., Jr A dynamic programming algorithm for finding alternative RNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 10;14(1):299–315. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.1.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Tollervey D., Maloney D., Swerdlow H., Dunn E. J., Guthrie C. Yeast contains small nuclear RNAs encoded by single copy genes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):743–751. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90107-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wise J. A., Weiner A. M. Dictyostelium small nuclear RNA D2 is homologous to rat nucleolar RNA U3 and is encoded by a dispersed multigene family. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang V. W., Lerner M. R., Steitz J. A., Flint S. J. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein is required for splicing of adenoviral early RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1371–1375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieve G., Penman S. Small RNA species of the HeLa cell: metabolism and subcellular localization. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):19–31. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90181-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]