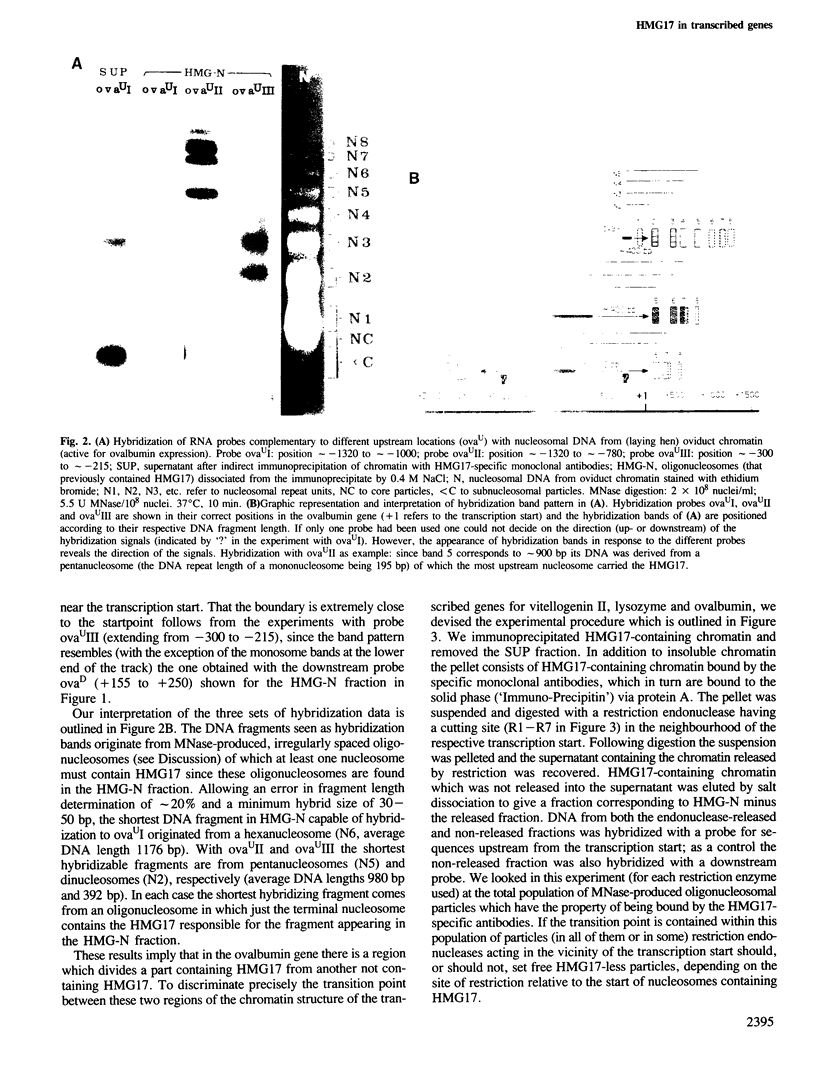
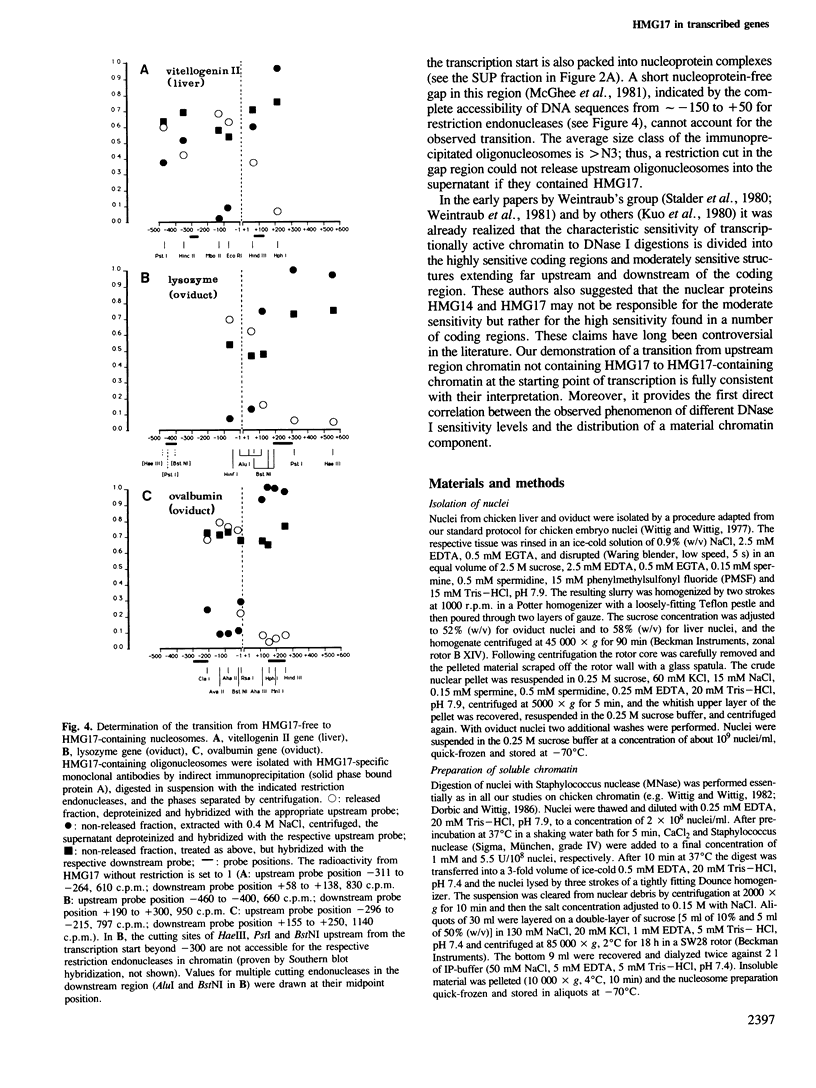
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies specific for the non-histone chromosomal protein HMG17 were used to isolate oligonucleosomes from the transcriptionally active chromatin of chicken liver and oviduct. The distribution of HMG17 with respect to the coding region of three genes was analyzed in these oligonucleosomes by employing two independent experimental approaches. In the vitellogenin II gene (active in liver) and the lysozyme and ovalbumin genes (active in oviduct) HMG17 was found only downstream from the respective starting points of transcription. The transition from HMG17-free to HMG17-containing chromatin is located at the transcription start. This directly demonstrates that the distribution of an abundant nuclear protein correlates with the observation of moderate DNase I-sensitivity in upstream regions and of high sensitivity in the coding regions of active genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. N., Vanderbilt J. N., Lawson G. M., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Chromatin structure of the ovalbumin gene family in the chicken oviduct. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):21–30. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellard M., Dretzen G., Bellard F., Oudet P., Chambon P. Disruption of the typical chromatin structure in a 2500 base-pair region at the 5' end of the actively transcribed ovalbumin gene. EMBO J. 1982;1(2):223–230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01151.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Abmayr S. M., Fleischmann G., Lowenhaupt K., Elgin S. C., Keene M. A., Howard G. C. Chromatin structure and gene activity: the role of nonhistone chromosomal proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1982;13(1):1–86. doi: 10.3109/10409238209108709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorbic T., Wittig B. Isolation of oligonucleosomes from active chromatin using HMG17-specific monoclonal antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3363–3376. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiser M., Mattaj I. W., Wilks A. F., Seldran M., Jost J. P. Structure and sequence of the promoter area and of a 5' upstream demethylation site of the estrogen-regulated chicken vitellogenin ii gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):9024–9030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grez M., Land H., Giesecke K., Schütz G., Jung A., Sippel A. E. Multiple mRNAs are generated from the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):743–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igo-Kemenes T., Hörz W., Zachau H. G. Chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:89–121. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.000513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpov V. L., Preobrazhenskaya O. V., Mirzabekov A. D. Chromatin structure of hsp 70 genes, activated by heat shock: selective removal of histones from the coding region and their absence from the 5' region. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo M. T., Mandel J. L., Chambon P. DNA methylation: correlation with DNase I sensitivity of chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 20;7(8):2105–2113. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.8.2105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Felsenfeld G. Nucleosome structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:1115–1156. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.005343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGhee J. D., Wood W. I., Dolan M., Engel J. D., Felsenfeld G. A 200 base pair region at the 5' end of the chicken adult beta-globin gene is accessible to nuclease digestion. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):45–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90359-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolas R. H., Wright C. A., Cockerill P. N., Wyke J. A., Goodwin G. H. The nuclease sensitivity of active genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):753–772. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L., Annunziato A. T., Smith R. D. High mobility group proteins: abundance, turnover, and relationship to transcriptionally active chromatin. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 11;22(21):5008–5015. doi: 10.1021/bi00290a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Mirzabekov A. D. Primary organization of nucleosomes. Interaction of non-histone high mobility group proteins 14 and 17 with nucleosomes, as revealed by DNA-protein crosslinking and immunoaffinity isolation. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder J., Larsen A., Engel J. D., Dolan M., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Tissue-specific DNA cleavages in the globin chromatin domain introduced by DNAase I. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90631-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein A., Townsend T. HMG 14/17 binding affinities and DNAase I sensitivities of nucleoprotein particles. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6803–6819. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow P. S., Varshavsky A. Affinity of HMG17 for a mononucleosome is not influenced by the presence of ubiquitin-H2A semihistone but strongly depends on DNA fragment size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):387–401. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. On the structure of eukaryotic, prokaryotic, and viral chromatin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):457–473. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Groudine M., Weintraub H. Interaction of HMG 14 and 17 with actively transcribed genes. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):289–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisbrod S., Weintraub H. Isolation of actively transcribed nucleosomes using immobilized HMG 14 and 17 and an analysis of alpha-globin chromatin. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig B., Wittig S. Nucleosome mono, di, tri-, and tetramers from chicken embryo chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):3901–3917. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.3901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittig S., Wittig B. Function of a tRNA gene promoter depends on nucleosome position. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):31–38. doi: 10.1038/297031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wong Y. C., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: II. Disruption of chromatin structure during gene activity. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yau P., Imai B. S., Thorne A. W., Goodwin G. H., Bradbury E. M. Effect of HMG protein 17 on the thermal stability of control and acetylated HeLa oligonucleosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2651–2664. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]