Abstract
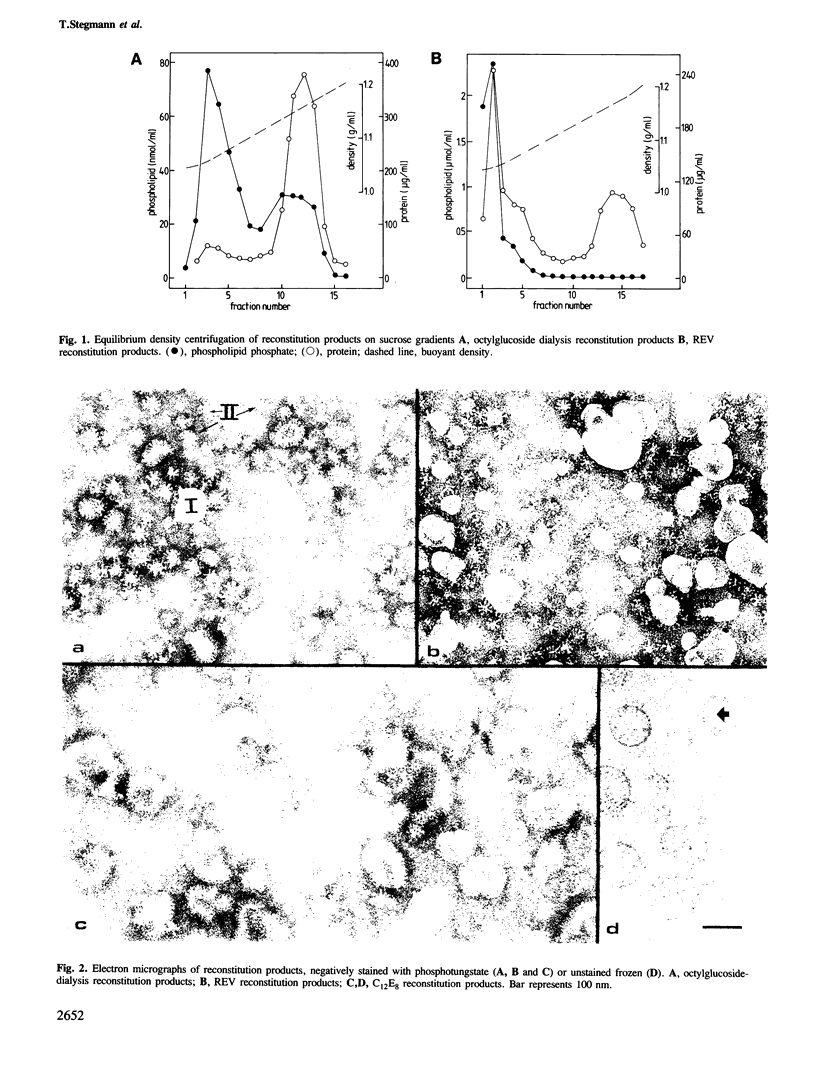
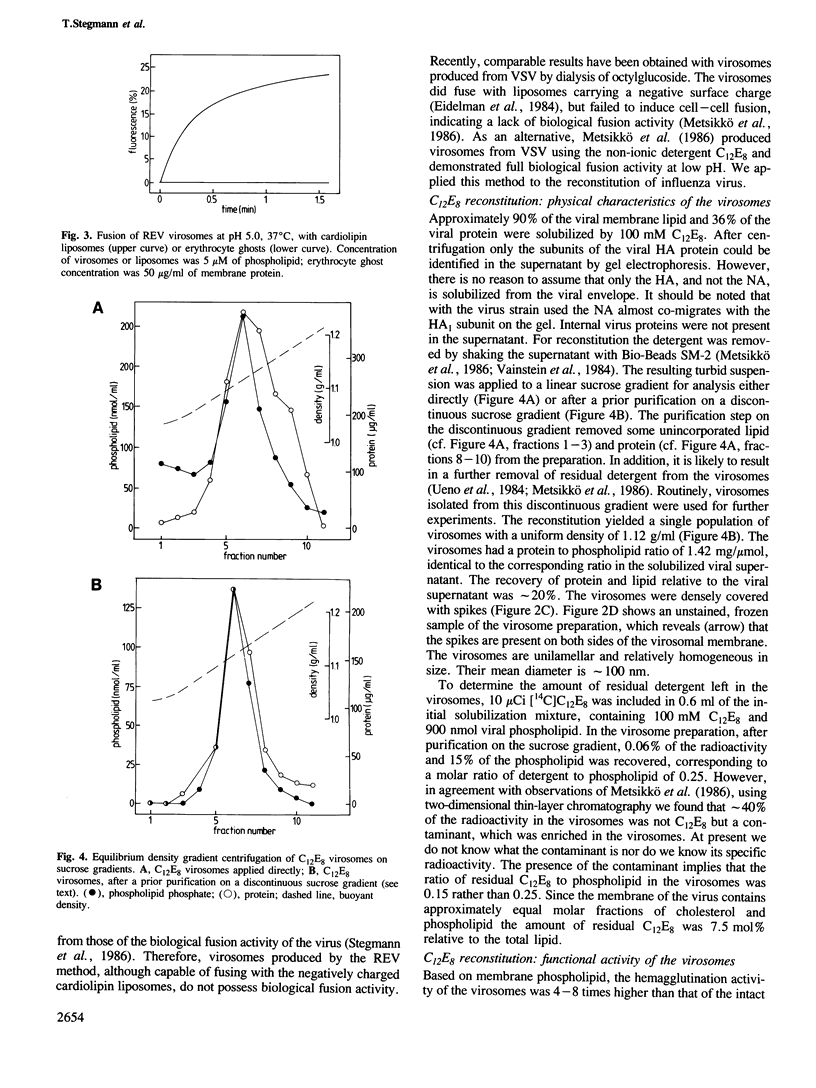
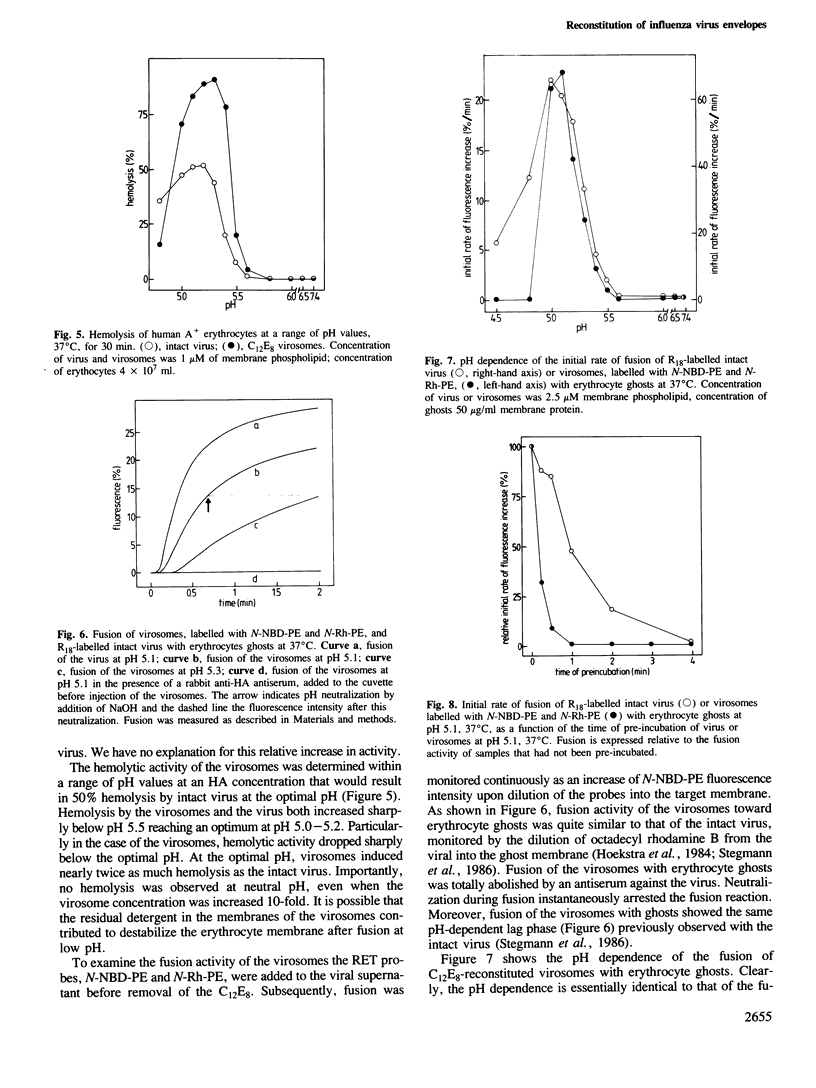
We have examined several procedures for the reconstitution of influenza virus envelopes, based on detergent removal from solubilized viral membranes. With octylglucoside, no functionally active virosomes are formed, irrespective of the rate of detergent removal: in the final preparation the viral spike proteins appear predominantly as rosettes. Protein incorporation in reconstituted vesicles is improved when a method based on reverse-phase evaporation of octylglucoside-solubilized viral membranes in an ether/water system is employed. However, the resulting vesicles do not fuse with biological membranes, but exhibit only a non-physiological fusion reaction with negatively charged liposomes. Functional reconstitution of viral envelopes is achieved after solubilization with octaethyleneglycol mono(n-dodecyl)ether (C12E8), and subsequent detergent removal with Bio-Beads SM-2. The spike protein molecules are quantitatively incorporated in a single population of virosomes of uniform buoyant density and appear on both sides of the membrane. The virosomes display hemagglutination activity and a strictly pH-dependent hemolytic activity. The virosomes fuse with erythrocyte ghosts, as revealed by a fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay. The rate and the pH dependence of fusion are essentially the same as those of the intact virus. The virosomes also fuse with cultured cells, either at the level of the endosomal membrane or directly with the cellular plasma membrane upon a brief exposure to low pH.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Booy F. P., Ruigrok R. W., van Bruggen E. F. Electron microscopy of influenza virus. A comparison of negatively stained and ice-embedded particles. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):667–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90312-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chejanovsky N., Zakai N., Amselem S., Barenholz Y., Loyter A. Membrane vesicles containing the Sendai virus binding glycoprotein, but not the viral fusion protein, fuse with phosphatidylserine liposomes at low pH. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4810–4817. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A., White J. Membrane fusion activity of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. The low pH-induced conformational change. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2973–2981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Hoekstra D., Scherphof G., Kalicharan R. D., Wilschut J. Low pH-induced fusion of liposomes with membrane vesicles derived from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10880–10887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidelman O., Schlegel R., Tralka T. S., Blumenthal R. pH-dependent fusion induced by vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein reconstituted into phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4622–4628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLCH J., LEES M., SLOANE STANLEY G. H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem. 1957 May;226(1):497–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen M. C., Wilschut J., Scherphof G., Hulstaert C., Hoekstra D. Reconstitution and fusogenic properties of Sendai virus envelopes. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 18;149(3):591–599. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08966.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Fries E., Kartenbeck J. Reconstitution of Semliki forest virus membrane. J Cell Biol. 1977 Dec;75(3):866–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.75.3.866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Sarvas M., Simons K. Asymmetric and symmetric membrane reconstitution by detergent elimination. Studies with Semliki-Forest-virus spike glycoprotein and penicillinase from the membrane of Bacillus licheniformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmeland L. M. A nondenaturing zwitterionic detergent for membrane biochemistry: design and synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6368–6370. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra D., de Boer T., Klappe K., Wilschut J. Fluorescence method for measuring the kinetics of fusion between biological membranes. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5675–5681. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosaka Y., Yasuda Y., Fukai K. Hemolysis by liposomes containing influenza virus hemagglutinins. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1014–1017. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1014-1017.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Wahn K., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Association of the envelope glycoproteins of influenza virus with liposomes--a model study on viral envelope assembly. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):212–217. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90390-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang R. T., Wahn K., Klenk H. D., Rott R. Fusion between cell membrane and liposomes containing the glycoproteins of influenza virus. Virology. 1980 Jul 30;104(2):294–302. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90334-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. L., Litman B. J. Rhodopsin-egg phosphatidylcholine reconstitution by an octyl glucoside dilution procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 25;812(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M. L., Litman B. J. Rhodopsin-phospholipid reconstitution by dialysis removal of octyl glucoside. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5601–5608. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junankar P. R., Cherry R. J. Temperature and pH dependence of the haemolytic activity of influenza virus and of the rotational mobility of the spike glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 29;854(2):198–206. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki K., Sato S. B., Ohnishi S. Membrane fusion activity of reconstituted vesicles of influenza virus hemagglutinin glycoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):286–290. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90534-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenard J., Compans R. W. The membrane structure of lipid-containing viruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 8;344(1):51–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(74)90008-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepault J., Booy F. P., Dubochet J. Electron microscopy of frozen biological suspensions. J Microsc. 1983 Jan;129(Pt 1):89–102. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1983.tb04163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I., Fuchs R., Helenius A. Acidification of the endocytic and exocytic pathways. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:663–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., van Meer G., Simons K. Reconstitution of the fusogenic activity of vesicular stomatitis virus. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3429–3435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04665.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. R., Hammond G. T., Noble A. D., Rushton L., Letchworth A. T. Late complications of sterilisation by laparoscopy and tubal ligation. A controlled study. Lancet. 1975 Oct 11;2(7937):699–700. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)90789-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson F., Hunt C. A., Szoka F. C., Vail W. J., Papahadjopoulos D. Preparation of liposomes of defined size distribution by extrusion through polycarbonate membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 19;557(1):9–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90085-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petri W. A., Jr, Wagner R. R. Reconstitution into liposomes of the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus by detergent dialysis. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4313–4316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skehel J. J., Bayley P. M., Brown E. B., Martin S. R., Waterfield M. D., White J. M., Wilson I. A., Wiley D. C. Changes in the conformation of influenza virus hemagglutinin at the pH optimum of virus-mediated membrane fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):968–972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L., Kant J. A. Preparation of impermeable ghosts and inside-out vesicles from human erythrocyte membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:172–180. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Hoekstra D., Scherphof G., Wilschut J. Fusion activity of influenza virus. A comparison between biological and artificial target membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):10966–10969. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stegmann T., Hoekstra D., Scherphof G., Wilschut J. Kinetics of pH-dependent fusion between influenza virus and liposomes. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 18;24(13):3107–3113. doi: 10.1021/bi00334a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Hoekstra D., Pagano R. E. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4093–4099. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szoka F., Jr, Papahadjopoulos D. Procedure for preparation of liposomes with large internal aqueous space and high capture by reverse-phase evaporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4194–4198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai K. H., Lenard J. Asymmetry of influenza virus membrane bilayer demonstrated with phospholipase C. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):554–555. doi: 10.1038/253554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tycko B., Maxfield F. R. Rapid acidification of endocytic vesicles containing alpha 2-macroglobulin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno M., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Phospholipid vesicle formation using nonionic detergents with low monomer solubility. Kinetic factors determine vesicle size and permeability. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):3070–3076. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vainstein A., Hershkovitz M., Israel S., Rabin S., Loyter A. A new method for reconstitution of highly fusogenic Sendai virus envelopes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 27;773(2):181–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(84)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky D. J., Loyter A. An efficient method for reassembly of fusogenic Sendai virus envelopes after solubilization of intact virions with Triton X-100. FEBS Lett. 1978 Aug 15;92(2):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80751-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Helenius A., Gething M. J. Haemagglutinin of influenza virus expressed from a cloned gene promotes membrane fusion. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):658–659. doi: 10.1038/300658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilschut J., Düzgüneş N., Fraley R., Papahadjopoulos D. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: kinetics of calcium ion induced fusion of phosphatidylserine vesicles followed by a new assay for mixing of aqueous vesicle contents. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):6011–6021. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Gerhard W., Bachi T. Monoclonal anti-hemagglutinin antibodies detect irreversible antigenic alterations that coincide with the acid activation of influenza virus A/PR/834-mediated hemolysis. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.239-248.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura A., Ohnishi S. Uncoating of influenza virus in endosomes. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):497–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.497-504.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Davoust J., Simons K. Parameters affecting low-pH-mediated fusion of liposomes with the plasma membrane of cells infected with influenza virus. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3593–3602. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




