Abstract
The lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase pp56lck, encoded by a member of the src gene family, is implicated in the control of T-cell growth and differentiation. Purified resting human T lymphocytes contain appreciable levels of lck mRNA and of pp56lck. Upon activation of these T cells, levels of lck mRNA and of pp56lck promptly decline. These reductions in lck mRNA and protein expression are closely correlated with the induction of lymphokine production. Both require identical stimuli and follow a similar time course of response. Down-regulation of lck expression, however, is not correlated with proliferation. Our results provide an example of regulation of a src-like protein tyrosine kinase in a normal fully differentiated cell population and suggest that modulation of lck RNA and protein expression is an important feature of the lymphocyte activation sequence leading to lymphokine production.
Full text
PDF
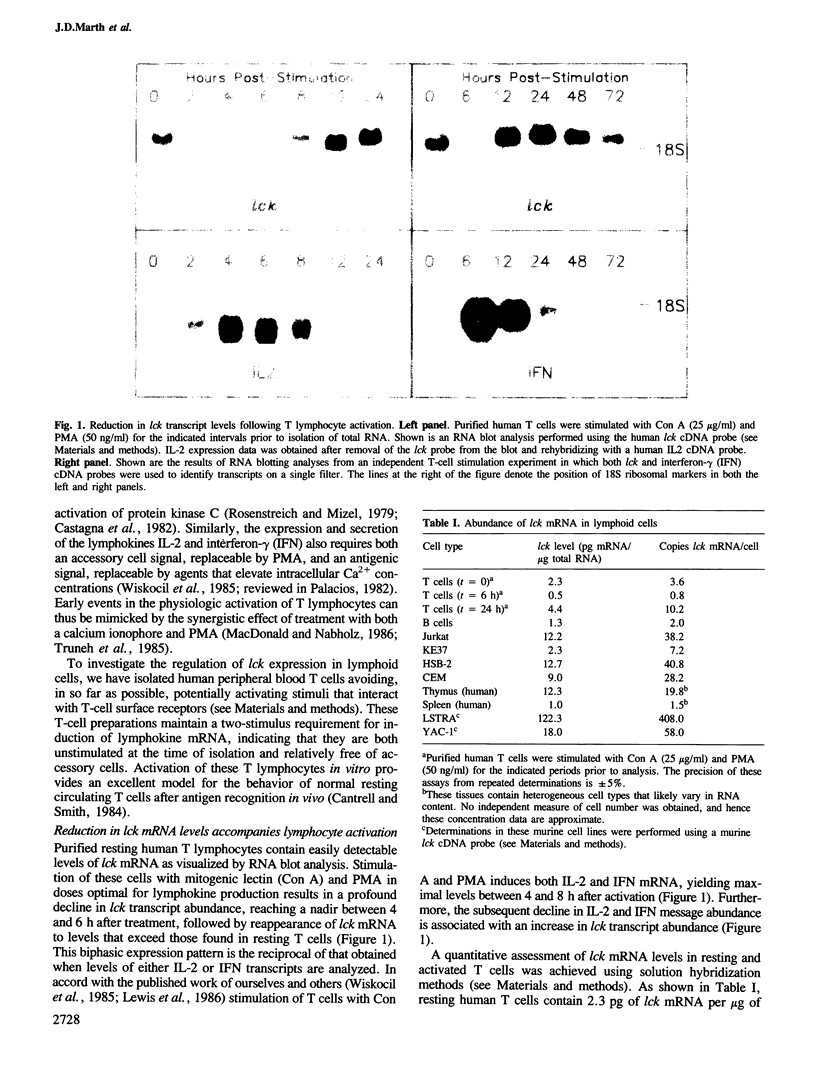
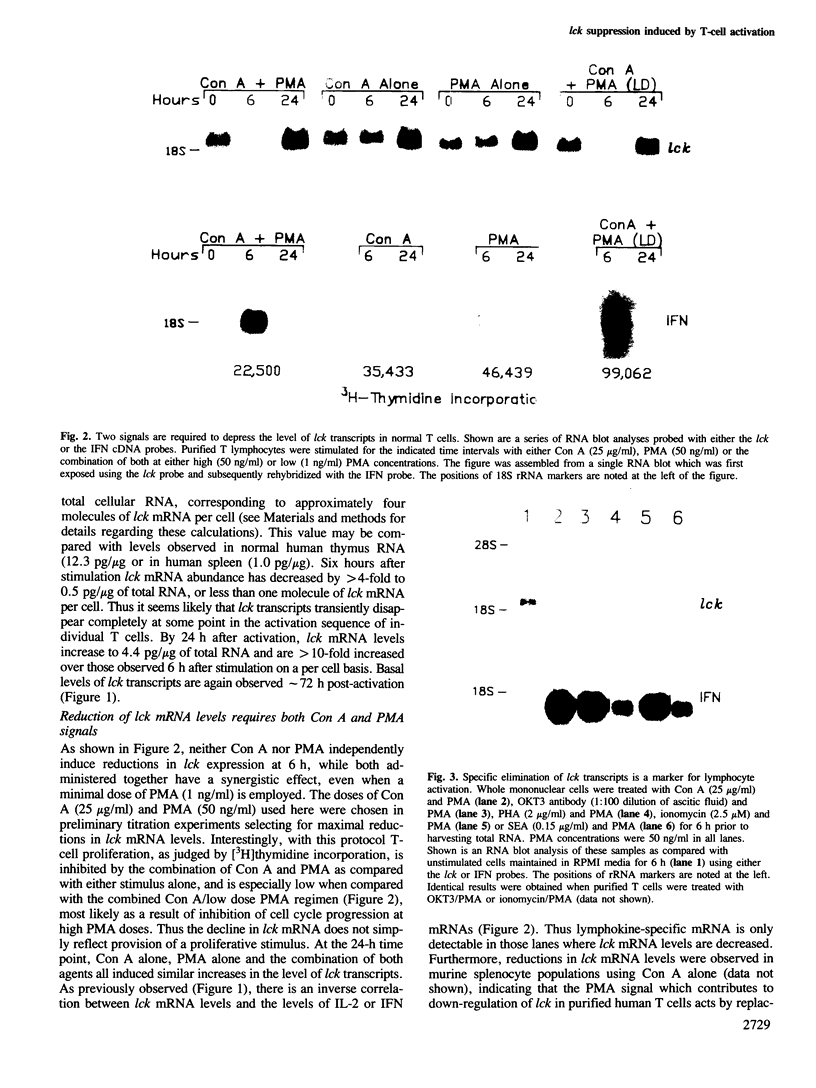





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adkins B., Leutz A., Graf T. Autocrine growth induced by src-related oncogenes in transformed chicken myeloid cells. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):439–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alemà S., Casalbore P., Agostini E., Tatò F. Differentiation of PC12 phaeochromocytoma cells induced by v-src oncogene. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):557–559. doi: 10.1038/316557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allwood G., Asherson G. L., Davey M. J., Goodford P. J. The early uptake of radioactive calcium by human lymphocytes treated with phytohaemagglutinin. Immunology. 1971 Sep;21(3):509–516. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggs D. R. The kinetics of neutrophilic leukocytes in health and in disease. Semin Hematol. 1967 Oct;4(4):359–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Cotton P. C., Queral A. E., Barrett J. N., Nonner D., Keane R. W. Neurones express high levels of a structurally modified, activated form of pp60c-src. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):554–557. doi: 10.1038/316554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Pike L. J., Hellström K. E., Krebs E. G. Phosphorylation of synthetic peptides by a tyrosine protein kinase from the particulate fraction of a lymphoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):282–286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Lamberts R. J. Tumor promoters cause changes in the state of phosphorylation and apparent molecular weight of a tyrosine protein kinase in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4921–4925. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheah M. S., Ley T. J., Tronick S. R., Robbins K. C. fgr proto-oncogene mRNA induced in B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus infection. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):238–240. doi: 10.1038/319238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Martin G. S. Phosphorylation of talin at tyrosine in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):371–378. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. A practical approach for quantitating specific mRNAs by solution hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Yahara I. Temperature-sensitive changes in surface modulating assemblies of fibroblasts transformed by mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2047–2051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Fagard R., Gacon G., Genetet N., Piau J. P., Blaineau C. Stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation in lectin treated human lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):682–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman M. H., Raff M. C. Induction of increased calcium uptake in mouse T lymphocytes by concanavalin A and its modulation by cyclic nucleotides. Nature. 1975 May 29;255(5507):378–382. doi: 10.1038/255378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fults D. W., Towle A. C., Lauder J. M., Maness P. F. pp60c-src in the developing cerebellum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):27–32. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden A., Nemeth S. P., Brugge J. S. Blood platelets express high levels of the pp60c-src-specific tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):852–856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granelli-Piperno A., Andrus L., Steinman R. M. Lymphokine and nonlymphokine mRNA levels in stimulated human T cells. Kinetics, mitogen requirements, and effects of cyclosporin A. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):922–937. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa N., Kaibuchi K., Matsubara T., Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y., Itoh K., Tomioka C. A possible role of protein kinase C in signal-induced lysosomal enzyme release. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):743–750. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90587-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katakami Y., Kaibuchi K., Sawamura M., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic action of protein kinase C and calcium for histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):573–578. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern J. A., Reed J. C., Daniele R. P., Nowell P. C. The role of the accessory cell in mitogen-stimulated human T cell gene expression. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 1;137(3):764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Lippes H., Kojima K., Rasmussen H. Aldosterone secretion: effect of phorbol ester and A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronenberg M., Kraig E., Siu G., Kapp J. A., Kappler J., Marrack P., Pierce C. W., Hood L. Three T cell hybridomas do not contain detectable heavy chain variable gene transcripts. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):210–227. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Coutinho A., Martinez C. A suggested mechanism for T lymphocyte activation: implications on the acquisition of functional reactivities. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:61–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00317.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Larsen A., Wilson C. B. Reduced interferon-gamma mRNA levels in human neonates. Evidence for an intrinsic T cell deficiency independent of other genes involved in T cell activation. J Exp Med. 1986 Apr 1;163(4):1018–1023. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.4.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Nabholz M. T-cell activation. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:231–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchildon G. A., Casnellie J. E., Walsh K. A., Krebs E. G. Covalently bound myristate in a lymphoma tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7679–7682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Disteche C., Pravtcheva D., Ruddle F., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. Localization of a lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase gene (lck) at a site of frequent chromosomal abnormalities in human lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7400–7404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marth J. D., Peet R., Krebs E. G., Perlmutter R. M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine T cell lymphoma LSTRA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):393–404. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90169-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe J. C., Pozzan T., Smith G. A., Hesketh T. R. A calcium hypothesis for the control of cell growth. Biochem Soc Symp. 1980;45:1–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nisbet-Brown E., Cheung R. K., Lee J. W., Gelfand E. W. Antigen-dependent increase in cytosolic free calcium in specific human T-lymphocyte clones. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):545–547. doi: 10.1038/316545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettgen H. C., Terhorst C., Cantley L. C., Rosoff P. M. Stimulation of the T3-T cell receptor complex induces a membrane-potential-sensitive calcium influx. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R. Mechanism of T cell activation: role and functional relationship of HLA-DR antigens and interleukins. Immunol Rev. 1982;63:73–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., Creutz C. E. p60c-src activity detected in the chromaffin granule membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jan 29;134(2):736–742. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80482-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piga A., Taheri M. R., Yaxley J. C., Wickremasinghe R. G., Hoffbrand A. V. Higher tyrosine protein kinase activity in resting lymphocytes than in proliferating normal or leukaemic blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 14;124(3):766–773. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintrell N., Lebo R., Varmus H., Bishop J. M., Pettenati M. J., Le Beau M. M., Diaz M. O., Rowley J. D. Identification of a human gene (HCK) that encodes a protein-tyrosine kinase and is expressed in hemopoietic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2267–2275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Alpers J. D., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Sequential expression of protooncogenes during lectin-stimulated mitogenesis of normal human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3982–3986. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M. Use of glutaraldehyde as a coupling agent for proteins and peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):159–165. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenstreich D. L., Mizel S. B. Signal requirements for T lymphocyte activation. I. Replacement of macrophage function with phorbol myristic acetate. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1749–1754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semba K., Nishizawa M., Miyajima N., Yoshida M. C., Sukegawa J., Yamanashi Y., Sasaki M., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. yes-related protooncogene, syn, belongs to the protein-tyrosine kinase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5459–5463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M. A., Drees B., Kornberg T., Bishop J. M. The nucleotide sequence and the tissue-specific expression of Drosophila c-src. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorge L. K., Levy B. T., Maness P. F. pp60c-src is developmentally regulated in the neural retina. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka C., Taniyama K., Kusunoki M. A phorbol ester and A23187 act synergistically to release acetylcholine from the guinea pig ileum. FEBS Lett. 1984 Sep 17;175(1):165–169. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80591-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truneh A., Albert F., Golstein P., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Early steps of lymphocyte activation bypassed by synergy between calcium ionophores and phorbol ester. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):318–320. doi: 10.1038/313318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vardimon L., Fox L. E., Moscona A. A. Accumulation of c-src mRNA is developmentally regulated in embryonic neural retina. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4109–4111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A. F., Sefton B. M. Expression of a new tyrosine protein kinase is stimulated by retrovirus promoter insertion. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):682–685. doi: 10.1038/319682a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A., Imboden J., Hardy K., Manger B., Terhorst C., Stobo J. The role of the T3/antigen receptor complex in T-cell activation. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:593–619. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Remington J. S. Activity of human blood leukocytes against Toxoplasma gondii. J Infect Dis. 1979 Dec;140(6):890–895. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.6.890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Westall J., Johnston L., Lewis D. B., Dower S. K., Alpert A. R. Decreased production of interferon-gamma by human neonatal cells. Intrinsic and regulatory deficiencies. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):860–867. doi: 10.1172/JCI112383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiskocil R., Weiss A., Imboden J., Kamin-Lewis R., Stobo J. Activation of a human T cell line: a two-stimulus requirement in the pretranslational events involved in the coordinate expression of interleukin 2 and gamma-interferon genes. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1599–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi J., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Castagna M., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of phorbol ester and calcium in serotonin release from human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 29;112(2):778–786. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawalich W., Brown C., Rasmussen H. Insulin secretion: combined effects of phorbol ester and A23187. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):448–455. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91221-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Marth J. D., Lewis D. B., Perlmutter R. M. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase gene (hck) preferentially expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2276–2285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Whitlock C. A., Goff S. P., Gifford A., Witte O. N. Lethal effect of the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming gene product. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pont J. J., Fleuren-Jakobs A. M. Synergistic effect of A23187 and a phorbol ester on amylase secretion from rabbit pancreatic acini. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):64–68. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81369-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









