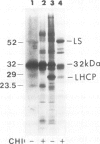
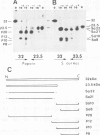
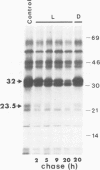
Abstract
The 32 kd photosystem II protein of plant chloroplasts is rapidly turned over in the light. The initial events in the degradation of the 32 kd protein were studied. A 23.5 kd breakdown product was identified in Spirodela oligorrhiza membranes using immunological analysis. The 23.5 kd polypeptide was shown to be derived from the amino-terminal portion of the 32 kd protein using partial proteolytic fingerprinting. An in vivo precursor--product relationship between the 32 kd protein and the 23.5 kd polypeptide was kinetically demonstrated by radiolabeling and pulse-chase experiments. The cleavage site yielding the 23.5 kd polypeptide was localized to a functionally active region (between helices IV and V) of the 32 kd protein. We propose that an alpha-helix-destabilizing 'degradation' sequence, bordered by arginine residues 225 and 238, is involved in the formation of the 23.5 kd polypeptide.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chua N. H., Gillham N. W. The sites of synthesis of the principal thylakoid membrane polypeptides in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1977 Aug;74(2):441–452. doi: 10.1083/jcb.74.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. The ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic pathway and mechanisms of energy-dependent intracellular protein degradation. J Cell Biochem. 1984;24(1):27–53. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240240104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D., Mets L. Herbicide resistance and cross-resistance: changes at three distinct sites in the herbicide-binding protein. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):204–207. doi: 10.1126/science.228.4696.204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaba V., Marder J. B., Greenberg B. M., Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Degradation of the 32 kD Herbicide Binding Protein in Far Red Light. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):348–352. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner G. Azidoatrazine: photoaffinity label for the site of triazine herbicide action in chloroplasts. Science. 1981 Feb 27;211(4485):937–940. doi: 10.1126/science.211.4485.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Davis F. E., Palade G. E. Protein blotting in uniform or gradient electric fields. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jan;144(1):32–40. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90080-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels to a positively charged membrane filter. Anal Biochem. 1982 Aug;124(2):396–405. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden S. S., Haselkorn R. Mutation to herbicide resistance maps within the psbA gene of Anacystis nidulans R2. Science. 1985 Sep 13;229(4718):1104–1107. doi: 10.1126/science.3929379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goloubinoff P., Edelman M., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast-coded atrazine resistance in Solanum nigrum: psbA loci from susceptible and resistant biotypes are isogenic except for a single codon change. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9489–9496. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebanier A. E., Steinback K. E., Bogorad L. Comparison of the Molecular Weights of Proteins Synthesized by Isolated Chloroplasts with Those Which Appear during Greening in Zea mays. Plant Physiol. 1979 Mar;63(3):436–439. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.3.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. Ubiquitin: roles in protein modification and breakdown. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):11–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90131-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschberg J., McIntosh L. Molecular Basis of Herbicide Resistance in Amaranthus hybridus. Science. 1983 Dec 23;222(4630):1346–1349. doi: 10.1126/science.222.4630.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Falk H., Mattoo A. K., Marder J. B., Edelman M., Ellis R. J. General occurrence and structural similarity of the rapidly synthesized, 32,000-dalton protein of the chloroplast membrane. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4583–4587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder J. B., Goloubinoff P., Edelman M. Molecular architecture of the rapidly metabolized 32-kilodalton protein of photosystem II. Indications for COOH-terminal processing of a chloroplast membrane polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3900–3908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Intramembrane translocation and posttranslational palmitoylation of the chloroplast 32-kDa herbicide-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1497–1501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Hoffman-Falk H., Marder J. B., Edelman M. Regulation of protein metabolism: Coupling of photosynthetic electron transport to in vivo degradation of the rapidly metabolized 32-kilodalton protein of the chloroplast membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1380–1384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattoo A. K., Pick U., Hoffman-Falk H., Edelman M. The rapidly metabolized 32,000-dalton polypeptide of the chloroplast is the "proteinaceous shield" regulating photosystem II electron transport and mediating diuron herbicide sensitivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1572–1576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohana Rao J. K., Argos P. A conformational preference parameter to predict helices in integral membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 30;869(2):197–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller O. M., Gerber H. B. Circadian changes of the rat pancreas acinar cell. A quantitative morphological investigation. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1985;112:12–19. doi: 10.3109/00365528509092208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanba O., Satoh K. Isolation of a photosystem II reaction center consisting of D-1 and D-2 polypeptides and cytochrome b-559. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):109–112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohad I., Kyle D. J., Hirschberg J. Light-dependent degradation of the Q(B)-protein in isolated pea thylakoids. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1655–1659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03833.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisfeld A., Mattoo A. K., Edelman M. Processing of a chloroplast-translated membrane protein in vivo. Analysis of the rapidly synthesized 32 000-dalton shield protein and its precursor in Spirodela oligorrhiza. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):125–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayre R. T., Andersson B., Bogorad L. The topology of a membrane protein: the orientation of the 32 kd Qb-binding chloroplast thylakoid membrane protein. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90624-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Ellis R. J. Protein synthesis in chloroplasts. VIII. Differential synthesis of chloroplast proteins during spinach leaf development. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 30;607(2):319–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinback K. E., McIntosh L., Bogorad L., Arntzen C. J. Identification of the triazine receptor protein as a chloroplast gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7463–7467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolber P. K., Eilmann M., Steinback K. E. Mapping of the triazine binding site to a highly conserved region of the QB-protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Jul;248(1):224–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bohnert H. J., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for the M(r) 32,000 thylakoid membrane protein from Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi predicts a totally conserved primary translation product of M(r) 38,950. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7699–7703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]