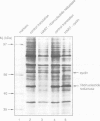
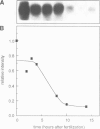
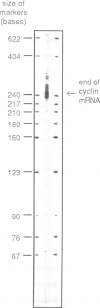
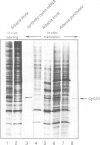
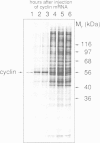
Abstract
We have isolated a cDNA clone encoding sea urchin cyclin and determined its sequence. It contains a single open reading frame of 409 amino acids which shows homology with clam cyclins. RNA transcribed in vitro from this sequence was efficiently translated in reticulocyte lysates, yielding full-length cyclin. Injection of nanogram amounts of this synthetic mRNA into Xenopus oocytes caused them to mature more rapidly than with progesterone treatment. The sea urchin cyclin underwent two posttranslational modifications in the Xenopus oocytes during maturation. The first occurred at about the time that maturation became cycloheximide-resistant, when a small apparent increase in the molecular weight of cyclin was observed. The second modification involved destruction of the cyclin at about the time of white spot appearance, just as would have occurred at the metaphase/anaphase transition in the natural environment of a cleaving sea urchin embryo.
Full text
PDF
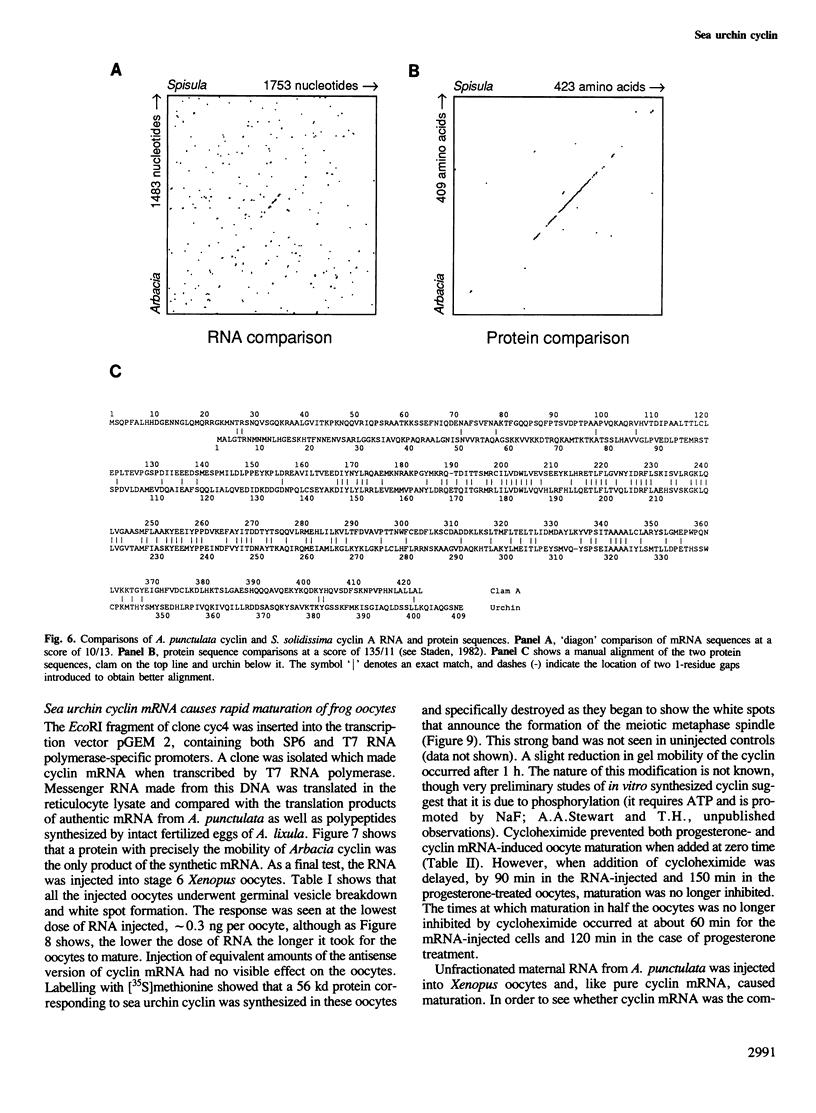
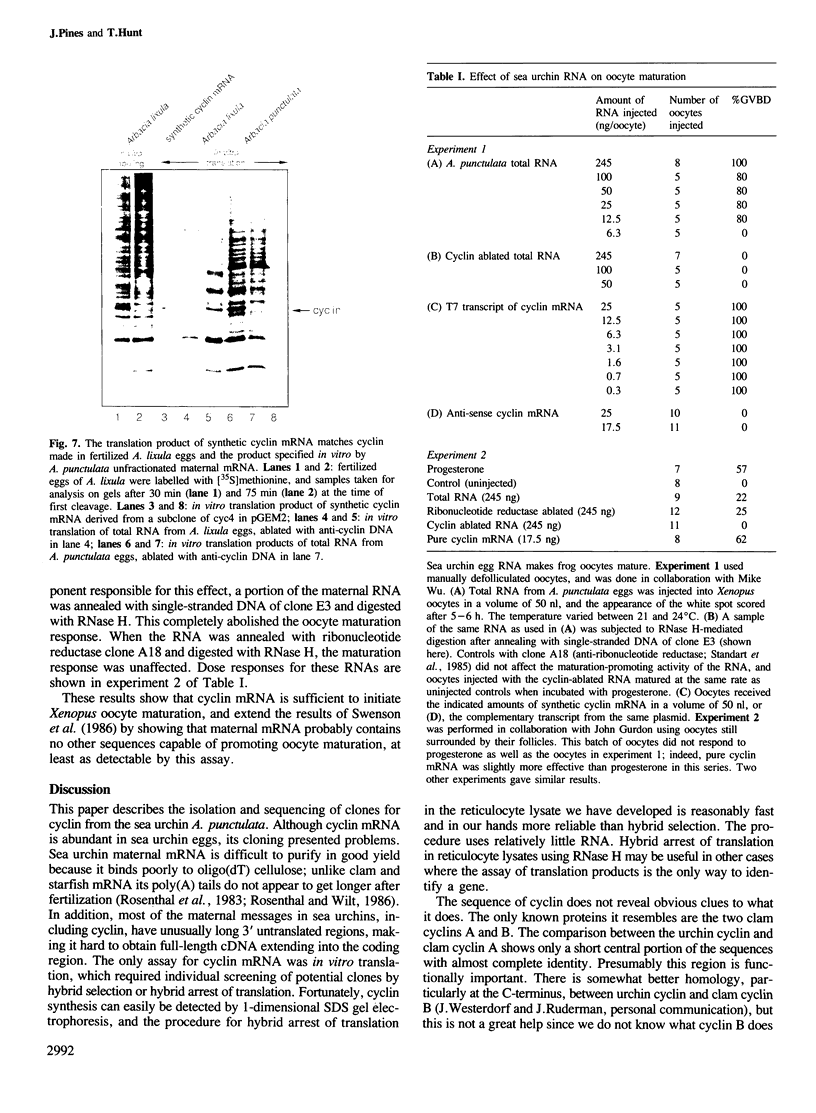
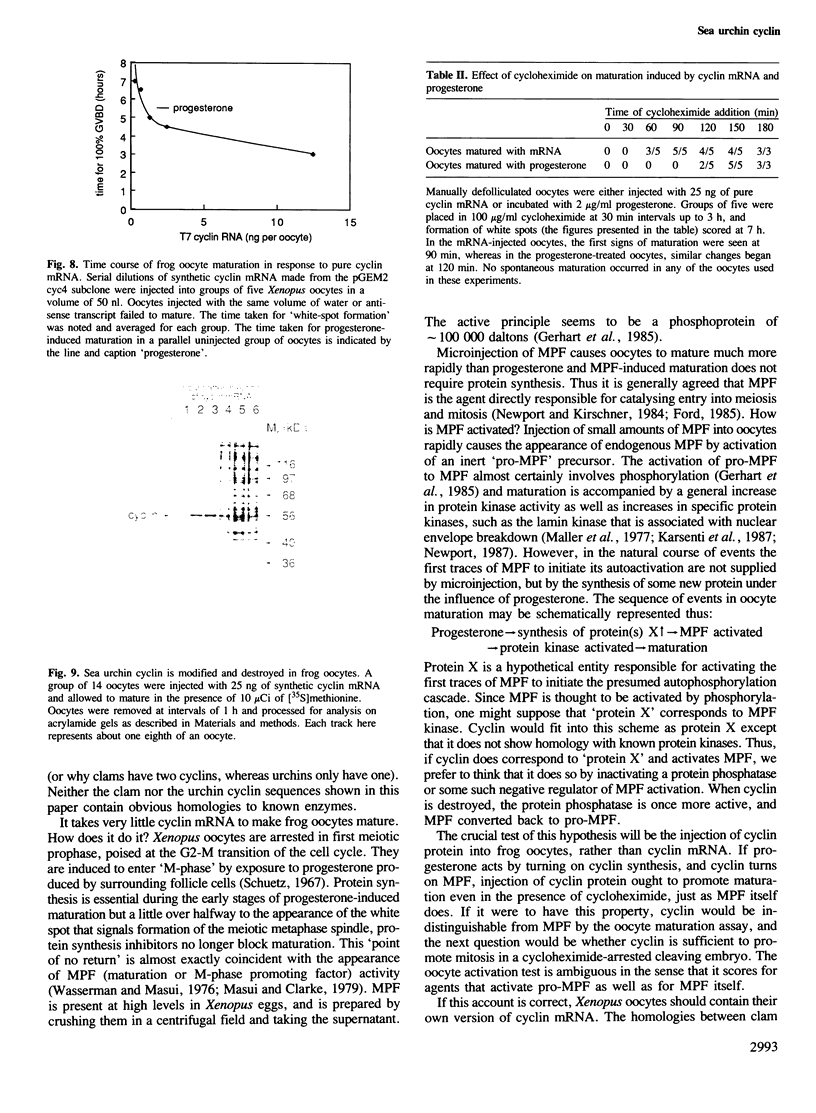


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Rosenthal E. T., Youngblom J., Distel D., Hunt T. Cyclin: a protein specified by maternal mRNA in sea urchin eggs that is destroyed at each cleavage division. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):389–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90420-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford C. C. Maturation promoting factor and cell cycle regulation. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):271–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Cyert M., Kirschner M. M-phase promoting factors from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Cytobios. 1985;43(174S):335–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerhart J., Wu M., Kirschner M. Cell cycle dynamics of an M-phase-specific cytoplasmic factor in Xenopus laevis oocytes and eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1247–1255. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULTIN T. The effect of puromycin on protein metabolism and cell division in fertilized sea urchin eggs. Experientia. 1961 Sep 15;17:410–411. doi: 10.1007/BF02157974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Hunt T. Preparation and use of nuclease-treated rabbit reticulocyte lysates for the translation of eukaryotic messenger RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:50–74. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Bravo R., Kirschner M. Phosphorylation changes associated with the early cell cycle in Xenopus eggs. Dev Biol. 1987 Feb;119(2):442–453. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90048-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
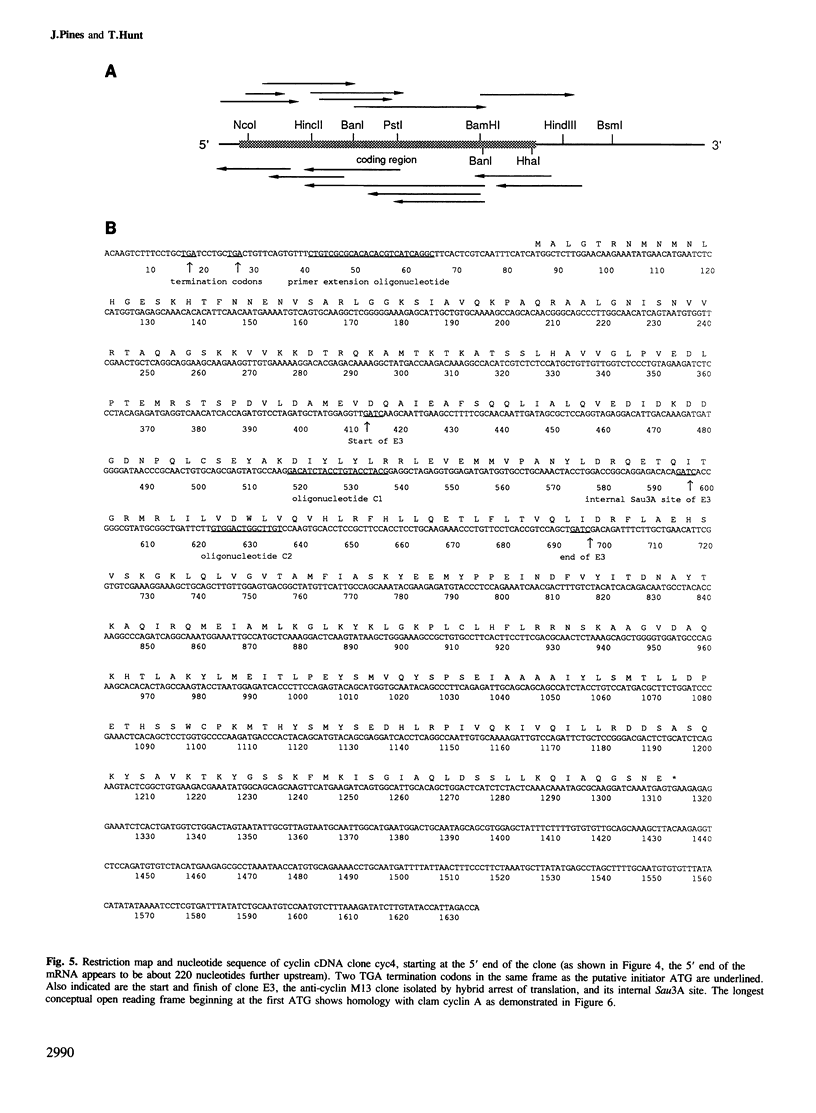
- Kozak M. Analysis of ribosome binding sites from the s1 message of reovirus. Initiation at the first and second AUG codons. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 25;156(4):807–820. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maller J., Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying maturation of Xenopus laevis oocytes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 15;58(2):295–312. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masui Y., Clarke H. J. Oocyte maturation. Int Rev Cytol. 1979;57:185–282. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61464-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
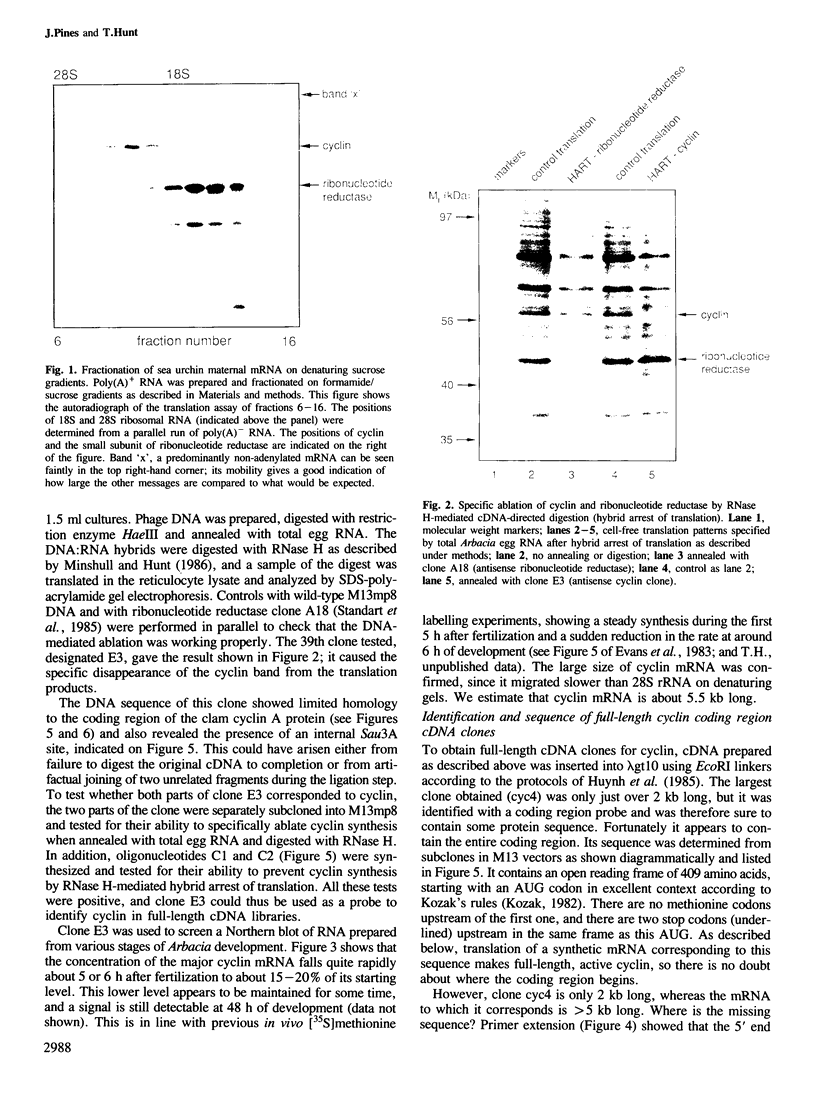
- Minshull J., Hunt T. The use of single-stranded DNA and RNase H to promote quantitative 'hybrid arrest of translation' of mRNA/DNA hybrids in reticulocyte lysate cell-free translations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6433–6451. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. W., Kirschner M. W. Regulation of the cell cycle during early Xenopus development. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J. Nuclear reconstitution in vitro: stages of assembly around protein-free DNA. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):205–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90424-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Peaucellier G., le Bouffant F., Le Peuch C., Dorée M. Role of protein synthesis and proteases in production and inactivation of maturation-promoting activity during meiotic maturation of starfish oocytes. Dev Biol. 1985 Jun;109(2):311–320. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
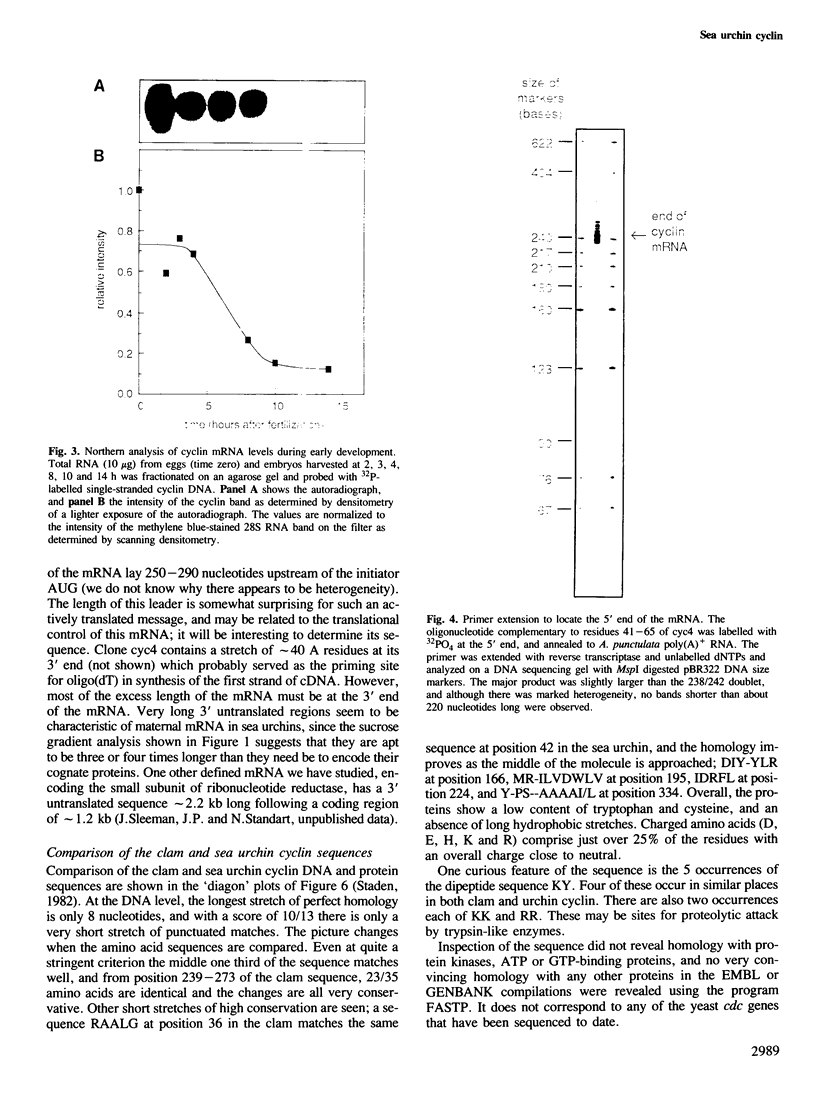
- Rosenthal E. T., Hunt T., Ruderman J. V. Selective translation of mRNA controls the pattern of protein synthesis during early development of the surf clam, Spisula solidissima. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):487–494. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90635-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Tansey T. R., Ruderman J. V. Sequence-specific adenylations and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):309–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Wilt F. H. Patterns of maternal messenger RNA accumulation and adenylation during oogenesis in Urechis caupo. Dev Biol. 1986 Sep;117(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz A. W. Effect of steroids on germinal vesicle of oocytes of the frog (Rana pipiens) in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Apr;124(4):1307–1310. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standart N. M., Bray S. J., George E. L., Hunt T., Ruderman J. V. The small subunit of ribonucleotide reductase is encoded by one of the most abundant translationally regulated maternal RNAs in clam and sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1968–1976. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Farrell K. M., Ruderman J. V. The clam embryo protein cyclin A induces entry into M phase and the resumption of meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90801-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenaar E. B. The timing of synthesis of proteins required for mitosis in the cell cycle of the sea urchin embryo. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Apr 1;144(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman W. J., Masui Y. Effects of cyclohexamide on a cytoplasmic factor initiating meiotic naturation in Xenopus oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 15;91(2):381–388. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90118-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilt F. H., Sakai H., Mazia D. Old and new protein in the formation of the mitotic apparatus in cleaving sea urchin eggs. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90346-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu M., Gerhart J. C. Partial purification and characterization of the maturation-promoting factor from eggs of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):465–477. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]