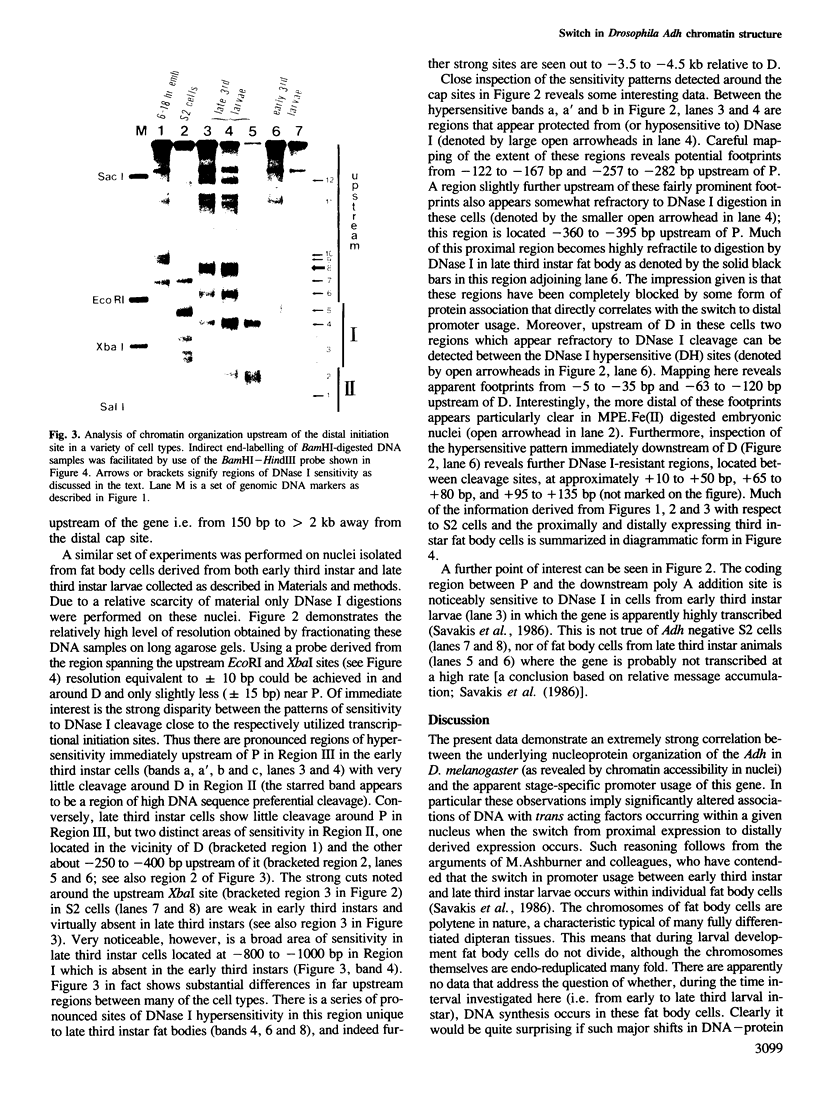
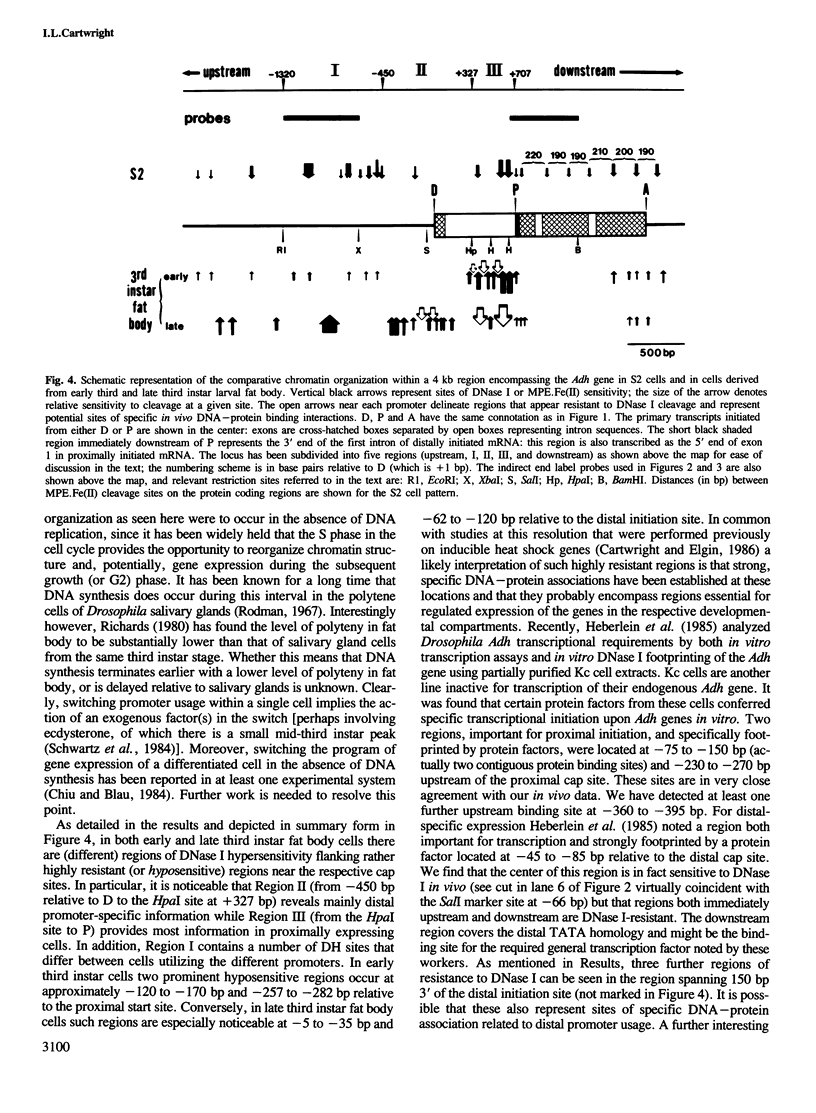
Abstract
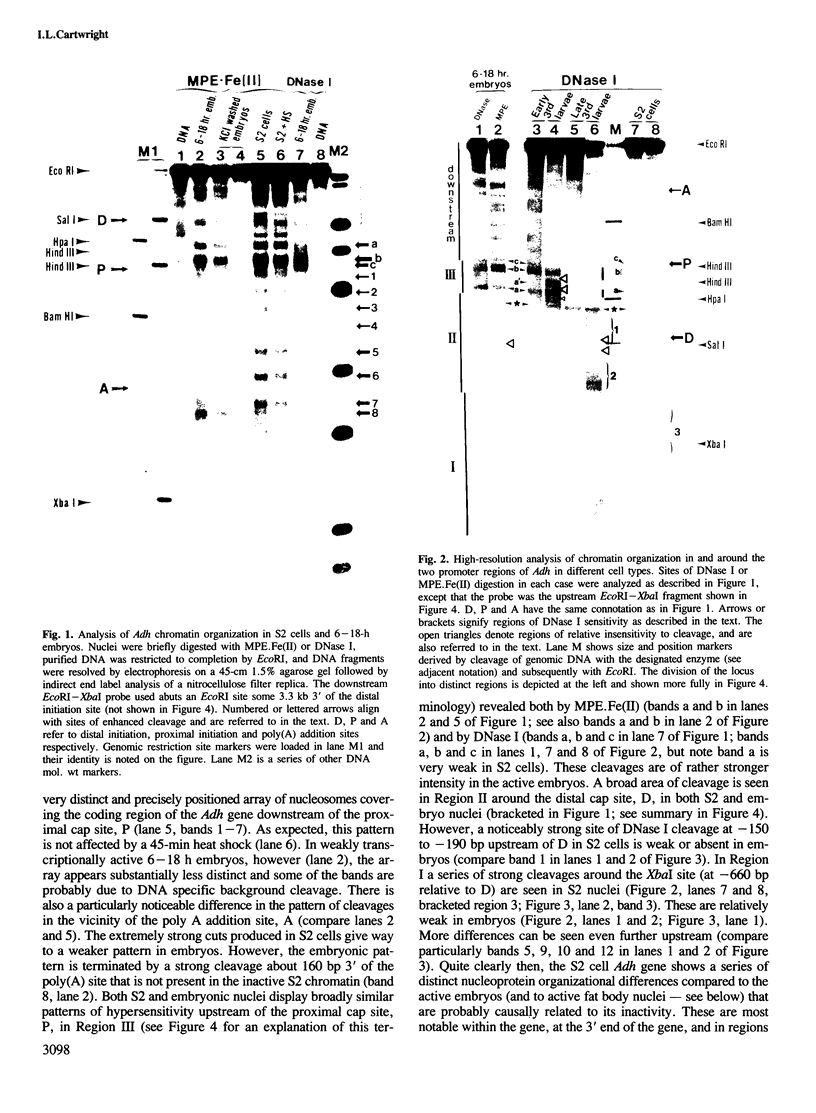
During the development of Drosophila melanogaster a switch in alcohol dehydrogenase gene promoter usage occurs, such that proximally initiated mRNA is replaced by mRNA initiated from a more distal location. Investigation of the nucleo-protein organization at this gene in cells inactive for Adh expression, or derived from tissues active at either the proximal or distal promoter, reveals distinct changes in patterns of nucleosome organization and regions of nuclease sensitivity that are strongly correlated with the activity of the gene and its promoter usage. A positioned array of nucleosomes covers the coding region of the inactive gene, but is partially disassembled on gene activation. A series of proximally located hypersensitive sites, detected in early third instar larval fat body cells, are replaced by new, distally located regions of hypersensitivity in late third instar larval fat body, the change apparently coinciding with the promoter switch. Further developmental stage differences are detected in regions over 1 kb upstream of the distal start site. In addition, for both proximally and distally expressing cells, separate and different regions of apparent resistance to DNase I cleavage in chromatin are detected in locations that, in some instances, were previously demonstrated to bind specific factors in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Batterham P., Lovett J. A., Starmer W. T., Sullivan D. T. Differential regulation of duplicate alcohol dehydrogenase genes in Drosophila mojavensis. Dev Biol. 1983 Apr;96(2):346–354. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90172-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Dray J. F. Cloned Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase genes are correctly expressed after transfection into Drosophila cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1701–1705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer M., Ashburner M. Conservation and change in the DNA sequences coding for alcohol dehydrogenase in sibling species of Drosophila. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):425–430. doi: 10.1038/309425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Elgin S. C. Chemical footprinting of 5S RNA chromatin in embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3101–3108. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02265.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Elgin S. C. Nucleosomal instability and induction of new upstream protein-DNA associations accompany activation of four small heat shock protein genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):779–791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright I. L., Hertzberg R. P., Dervan P. B., Elgin S. C. Cleavage of chromatin with methidiumpropyl-EDTA . iron(II). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu C. P., Blau H. M. Reprogramming cell differentiation in the absence of DNA synthesis. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):879–887. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90423-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Cartwright I. L., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Selected topics in chromatin structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:485–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Structure and transcription of the Drosophila mulleri alcohol dehydrogenase genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6899–6917. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett T. The regulatory domain of a larval serum protein gene in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3789–3795. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04149.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nedospasov S. A., Georgiev G. P. Non-random cleavage of SV40 DNA in the compact minichromosome and free in solution by micrococcal nuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 29;92(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. The polytene chromosomes in the fat body nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1980;79(2):241–250. doi: 10.1007/BF01175189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodman T. C. DNA replication in salivary gland nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster at successive larval and prepupal stages. Genetics. 1967 Mar;55(3):375–386. doi: 10.1093/genetics/55.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowan R. G., Brennan M. D., Dickinson W. J. Developmentally regulated RNA transcripts coding for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila affinidisjuncta. Genetics. 1986 Oct;114(2):405–433. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.2.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. B., Imberski R. B., Kelly T. J. Analysis of metamorphosis in Drosophila melanogaster: characterization of giant, an ecdysteroid-deficient mutant. Dev Biol. 1984 May;103(1):85–95. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shermoen A. W., Beckendorf S. K. A complex of interacting DNAase I-hypersensitive sites near the Drosophila glue protein gene, Sgs4. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):601–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Bingham P. M., Livak K. J., Holmgren R., Elgin S. C. The chromatin structure of specific genes: I. Evidence for higher order domains of defined DNA sequence. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. The 5' ends of Drosophila heat shock genes in chromatin are hypersensitive to DNase I. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):854–860. doi: 10.1038/286854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]