Abstract
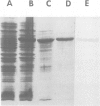
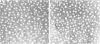
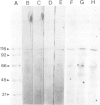
We have constructed a plasmid, pLM8, containing the coding sequence of the mature human apoA-1 fused to the coding sequence of the IgG-binding domains of protein A (PA) from Staphylococcus aureus. The hybrid gene is transcribed in Escherichia coli under the control of a heat-sensitive repressor, leading to the synthesis of large amounts of hybrid protein (apoA-1--PA). The hybrid protein was purified by denaturation with urea and alkali, renaturation and affinity chromatography on an IgG Sepharose column. ApoA-1--PA is soluble and has an Mr of 316 kd, as determined by gel filtration. This is five times the monomer size of 62 kd, predicted from the sequence and found by SDS-PAGE analysis. Cell surface binding activity of the hybrid protein was tested using two different cell types (J774 macrophages and Fao hepatocytes) and compared to human high density lipoprotein (HDL). High-affinity binding was found for both ligands in both cell lines (Kd = 3.4 X 10(-8)M in Fao cells, 4.9 X 10(-8) M in J774 cells for apoA-1--PA and 3.0 X 10(-8) M in Fao cells, 2.8 X 10(-8) M in J774 cells for HDL), with approximately 2 X 10(5) high-affinity binding sites per cell. ApoA-1--PA and HDL effectively competed with each other for binding to the cell surface. Additionally, they both bound to a 110-kd polypeptide on a ligand blot, identifying an HDL receptor. The binding parameters of HDL were very similar to those of apoA-1--PA.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachorik P. S., Franklin F. A., Virgil D. G., Kwiterovich P. O., Jr High-affinity uptake and degradation of apolipoprotein E free high-density lipoprotein and low-density lipoprotein in cultured porcine hepatocytes. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5675–5684. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biesbroeck R., Oram J. F., Albers J. J., Bierman E. L. Specific high-affinity binding of high density lipoproteins to cultured human skin fibroblasts and arterial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Mar;71(3):525–539. doi: 10.1172/JCI110797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinton E. A., Kenagy R. D., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Regulation of high density lipoprotein binding activity of aortic endothelial cells by treatment with acetylated low density lipoprotein. Arteriosclerosis. 1985 Jul-Aug;5(4):329–335. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.5.4.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko G. K. Characterization of high-density lipoprotein binding sites in rat liver and testis membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):417–426. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko G. K. Human high density lipoprotein (HDL3) binding to rat liver plasma membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jul 20;712(1):129–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(82)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chacko G. K. Modification of human high density lipoprotein (HDL3) with tetranitromethane and the effect on its binding to isolated rat liver plasma membranes. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jun;26(6):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Kraemer F. B., Reaven G. M. Identification of specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites in rat testis and regulation of binding by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9162–9167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschatrette J., Weiss M. C. Characterization of differentiated and dedifferentiated clones from a rat hepatoma. Biochimie. 1974;56(11-12):1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80286-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvorin E., Gorder N. L., Benson D. M., Gotto A. M., Jr Apolipoprotein A-IV. A determinant for binding and uptake of high density lipoproteins by rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15714–15718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. High density lipoprotein metabolism. J Lipid Res. 1984 Oct;25(10):1017–1058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N. H., Nestel P. J. Identification of apolipoproteins involved in the interaction of human high density lipoprotein3 with receptors on cultured cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3570–3575. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidge N., Kagami A., O'Connor M. Identification of a high density lipoprotein binding protein from adrenocortical membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jun 28;129(3):759–765. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91957-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. L., Oram J. F. Identification and characterization of a high density lipoprotein-binding protein in cell membranes by ligand blotting. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7439–7442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havekes L., Schouten D., van Hinsbergh V., de Wit E. Characterisation of the binding of apolipoprotein E-free high density lipoprotein to cultured human endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):785–790. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang J., Menon K. M. Binding of apolipoprotein A-I and A-II after recombination with phospholipid vesicles to the high density lipoprotein receptor of luteinized rat ovary. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5660–5668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagami A., Fidge N., Suzuki N., Nestel P. Characteristics of the binding of high-density lipoprotein3 by intact cells and membrane preparations of rat intestinal mucosa. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Sep 12;795(2):179–190. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(84)90064-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Van Renswoude J., Ashwell G., Kempf C., Schechter A. N., Dean A., Bridges K. R. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of transferrin in K562 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4715–4724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langley K. E., Villarejo M. R., Fowler A. V., Zamenhof P. J., Zabin I. Molecular basis of beta-galactosidase alpha-complementation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1254–1257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzetti R., Sidoli A., Palomba R., Monaco L., Martineau D., Lappi D. A., Soria M. Expression of the human apolipoprotein AI gene fused to the E. coli gene for beta-galactosidase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):343–346. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80114-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottspeich F. Identification of the phenylthiohydantoin derivatives of amino acids by high pressure liquid chromatography, using a ternary, isocratic solvent system. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1980 Dec;361(12):1829–1834. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1980.361.2.1829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D., Reggio H., Warren G. Antibodies to the Golgi complex and the rough endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):92–107. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Innerarity T. L. Lipoprotein receptors and cholesterol homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 May 24;737(2):197–222. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(83)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendel C. M., Kunitake S. T., Kane J. P. Discrimination between subclasses of human high-density lipoproteins by the HDL binding sites of bovine liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 3;875(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90011-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B., Abrahmsén L., Uhlén M. Immobilization and purification of enzymes with staphylococcal protein A gene fusion vectors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1075–1080. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03741.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Brinton E. A., Bierman E. L. Regulation of high density lipoprotein receptor activity in cultured human skin fibroblasts and human arterial smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest. 1983 Nov;72(5):1611–1621. doi: 10.1172/JCI111120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. C., Glass C. K., Atkinson D., Small D. M. Synthetic high density lipoprotein particles. Application to studies of the apoprotein specificity for selective uptake of cholesterol esters. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 25;262(6):2435–2442. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralph P., Prichard J., Cohn M. Reticulum cell sarcoma: an effector cell in antibody-dependent cell-mediated immunity. J Immunol. 1975 Feb;114(2 Pt 2):898–905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifici V. A., Eder H. A. A hepatocyte receptor for high-density lipoproteins specific for apolipoprotein A-I. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13814–13818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz G., Niemann R., Brennhausen B., Krause R., Assmann G. Regulation of high density lipoprotein receptors in cultured macrophages: role of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2773–2779. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoulders C. C., Kornblihtt A. R., Munro B. S., Baralle F. E. Gene structure of human apolipoprotein A1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2827–2837. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabas I., Tall A. R. Mechanism of the association of HDL3 with endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells, and fibroblasts. Evidence against the role of specific ligand and receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13897–13905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadros M. H., Suter F., Seydewitz H. H., Witt I., Zuber H., Drews G. Isolation and complete amino-acid sequence of the small polypeptide from light-harvesting pigment-protein complex I (B870) of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):209–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadros M. H., Zuber H., Drews G. The polypeptide components from light-harvesting pigment-protein complex II (B800-850) of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Solubilization, purification and sequence studies. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):315–318. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06872.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Goldminz D., Vlodavsky I., Gospodarowicz D. The interaction of the high-density lipoprotein with cultured cells of bovine vascular endothelium. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Oct;119(2):317–325. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C. Characterization of a monoclonal antibody directed against mouse macrophage and lymphocyte Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):580–596. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Kaplan G., Plutner H., Cohn Z. A. Fc-receptor variants of a mouse macrophage cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1400–1404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zabeau M., Stanley K. K. Enhanced expression of cro-beta-galactosidase fusion proteins under the control of the PR promoter of bacteriophage lambda. EMBO J. 1982;1(10):1217–1224. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb00016.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol A., Dallinga-Thie G. M., van Gent T., van 't Hooft F. M. Specific saturable binding of rat high-density lipoproteins to rat kidney membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 15;876(2):340–351. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol A., Dallinga-Thie G. M., van Gent T., van 't Hooft F. M. Specific saturable binding of rat high-density lipoproteins to rat kidney membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Apr 15;876(2):340–351. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90293-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]