Abstract
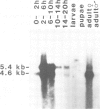
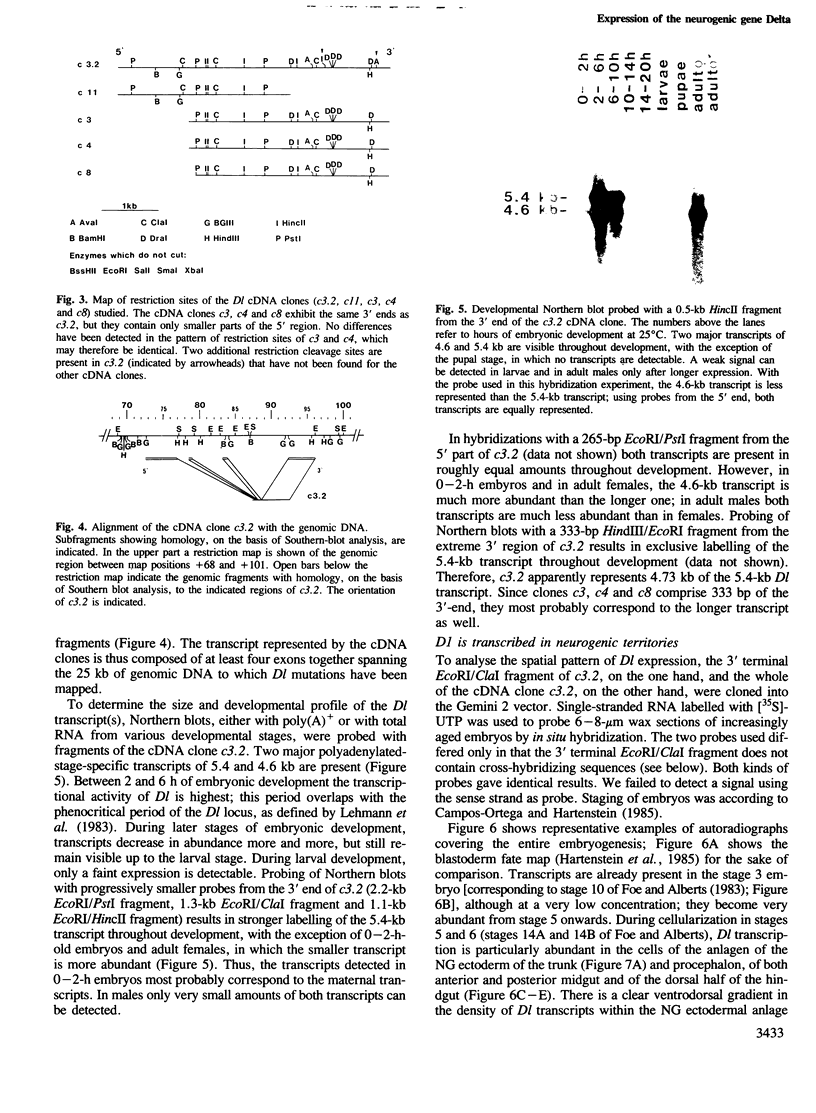
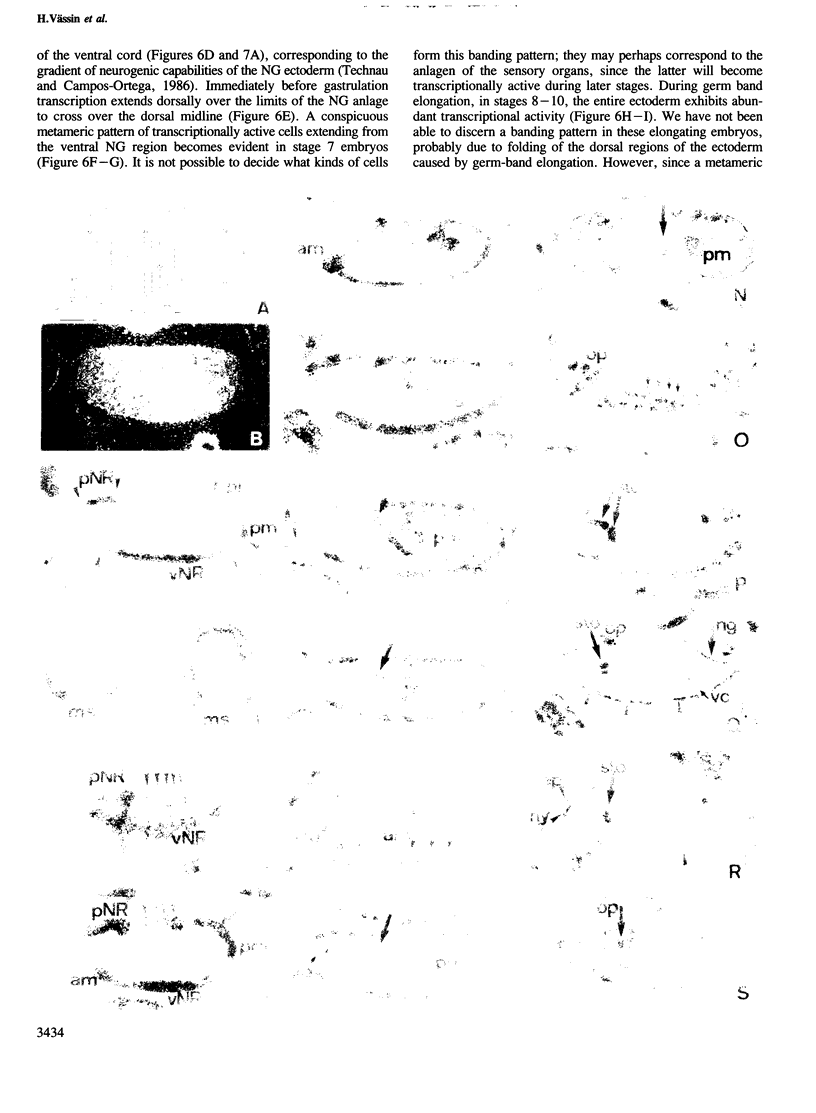
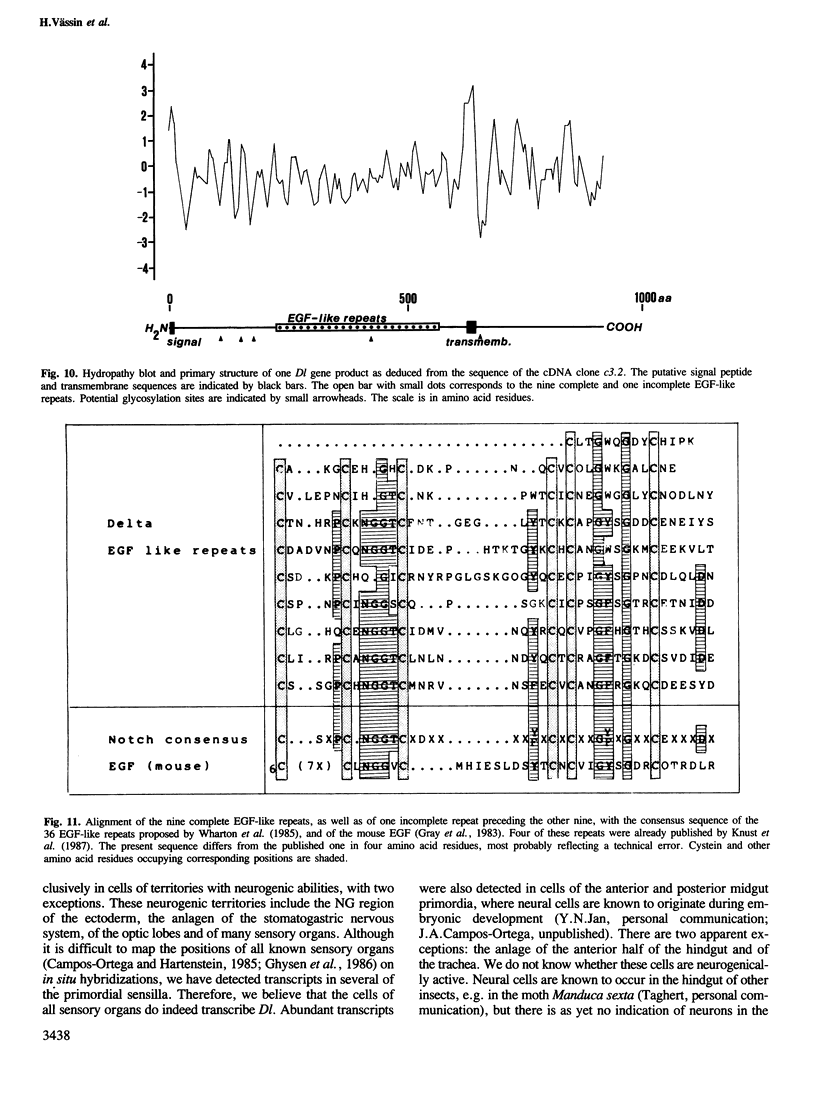
The decision of an ectodermal cell to take on a neural or an epidermal fate depends on its interactions with the neighbouring cells. In Drosophila melanogaster, the available evidence suggests that a regulatory signal necessary for epidermal commitment is built by the products of the so-called neurogenic genes. We have cloned 180 kb of genomic DNA surrounding the neurogenic gene Delta (Dl). Restriction fragment-length polymorphisms were mapped to a region of 25 kb. These 25 kb of DNA are assumed to contain essential parts, or all, of the Dl gene. Northern blots detect two developmentally regulated transcripts, of 5.4 and 4.6 kb, which are associated with the region where the mutants map. Serveral cDNA clones were recovered from embryonic cDNA libraries by homology to the 25 kb of genomic DNA. The complete sequence of a cDNA clone containing an insert of 4.73 kb was determined. The conceptual translation of the longest open reading frame yields a protein of 880 amino acids. This protein displays characteristics of a membrane protein, with intercellular, transmembrane and extracellular domains. The extracellular domain contains a tandem array of nine EGF-like repeats. In in situ hybridizations to tissue sections, transcripts homologous to Dl are detected in all territories with neurogenic abilities, e.g. the neurogenic ectoderm and the primordia of the sensory organs. Initially all cells of these neurogenic territories express Dl, but later on transcription of Dl becomes restricted to the cells that have adopted the neural fate. The topological specificity in the transcription of Dl corresponds to the one expected for a regulatory signal that mediates epidermal commitment.
Keywords: Drosophila, neurogenesis, Delta, expression, sequence
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavener D. R. Comparison of the consensus sequence flanking translational start sites in Drosophila and vertebrates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1353–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis C. G., Goldstein J. L., Südhof T. C., Anderson R. G., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Acid-dependent ligand dissociation and recycling of LDL receptor mediated by growth factor homology region. Nature. 1987 Apr 23;326(6115):760–765. doi: 10.1038/326760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich U., Campos-Ortega J. A. The expression of neurogenic loci in imaginal epidermal cells of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurogenet. 1984 Dec;1(4):315–332. doi: 10.3109/01677068409107094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doe C. Q., Goodman C. S. Early events in insect neurogenesis. I. Development and segmental differences in the pattern of neuronal precursor cells. Dev Biol. 1985 Sep;111(1):193–205. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E., Alberts B. M. Studies of nuclear and cytoplasmic behaviour during the five mitotic cycles that precede gastrulation in Drosophila embryogenesis. J Cell Sci. 1983 May;61:31–70. doi: 10.1242/jcs.61.1.31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf J., Iwamoto Y., Sasaki M., Martin G. R., Kleinman H. K., Robey F. A., Yamada Y. Identification of an amino acid sequence in laminin mediating cell attachment, chemotaxis, and receptor binding. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):989–996. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90707-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. lin-12, a nematode homeotic gene, is homologous to a set of mammalian proteins that includes epidermal growth factor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):583–590. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90230-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kidd S., Kelley M. R., Young M. W. Sequence of the notch locus of Drosophila melanogaster: relationship of the encoded protein to mammalian clotting and growth factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3094–3108. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knust E., Dietrich U., Tepass U., Bremer K. A., Weigel D., Vässin H., Campos-Ortega J. A. EGF homologous sequences encoded in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster, and their relation to neurogenic genes. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):761–766. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04818.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Hadfield C., Pretorius G. H. Microdissection and cloning of the white locus and the 3B1-3C2 region of the Drosophila X chromosome. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):927–934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole S. J., Kauvar L. M., Drees B., Kornberg T. The engrailed locus of Drosophila: structural analysis of an embryonic transcript. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):37–43. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulson D. F. Chromosomal Deficiencies and the Embryonic Development of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1937 Mar;23(3):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.23.3.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kato S., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding the laminin B1 chain reveals a multidomain protein containing cysteine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg P. W., Horvitz H. R. The genetic control of cell lineage during nematode development. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:489–524. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Technau G. M., Campos-Ortega J. A. Cell autonomy of expression of neurogenic genes of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4500–4504. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vässin H., Campos-Ortega J. A. Genetic Analysis of Delta, a Neurogenic Gene of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1987 Jul;116(3):433–445. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vässin H., Vielmetter J., Campos-Ortega J. A. Genetic interactions in early neurogenesis of Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurogenet. 1985 Nov;2(5):291–308. doi: 10.3109/01677068509102325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. R. The genetics of embryogenesis in Drosophila. Adv Genet. 1970;15:261–395. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60075-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yedvobnick B., Muskavitch M. A., Wharton K. A., Halpern M. E., Paul E., Grimwade B. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Molecular genetics of Drosophila neurogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:841–854. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]