Abstract
Cholesteryl esters of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FAs (Chl-ωOAHFAs) were identified for the first time in vernix caseosa and characterized using chromatography and MS. Chl-ωOAHFAs were isolated using adsorption chromatography on silica gel and magnesium hydroxide. Their general structure was established using high-resolution and tandem MS of intact lipids, and products of their transesterification and derivatizations. Individual molecular species were characterized using nonaqueous reversed-phase HPLC coupled to atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. The analytes were detected as protonated molecules, and their structures were elucidated in the negative ion mode using controlled thermal decomposition and data-dependent fragmentation. About three hundred molecular species of Chl-ωOAHFAs were identified in this way. The most abundant Chl-ωOAHFAs contained 32:1 ω-hydroxy FA (ω-HFA) and 14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 16:1, and 18:1 FAs. The double bond in the 32:1 ω-HFA was in the n-7 and n-9 positions. Chl-ωOAHFAs are estimated to account for approximately 1–2% of vernix caseosa lipids.
Keywords: skin lipids, neutral lipids, cholesterol, lipidomics, mass spectrometry
Vernix caseosa is a white cheese-like naturally occurring biofilm that coats the skin of the fetus during the last trimester of gestation and usually remains present on the skin during delivery. It is a highly cellular material consisting of hydrophilic desquamated corneocytes embedded in a lipid matrix. Vernix caseosa is essential for skin development in utero, as well as post-birth adaptation, providing multiple functions (1–3).
Vernix caseosa consists of water (80%), proteins (10%), and a complex mixture of lipids (10%). Although investigations of its lipid composition started more than seventy years ago (4), the entire lipidome of vernix caseosa has not yet been described comprehensively. Lipids exist in intercellular space as free (extractable) components, or they are covalently bound to the cornified envelope. About 90% of the free lipids are nonpolar species like squalene, sterol esters, wax esters, diesters, and triacylglycerols, and the remaining 10% are barrier lipids, mostly cholesterol, free FAs, and ceramides. The lipids covalently linked to the cornified envelope consist of ω-hydroxy FAs (ωHFAs) and ω-hydroxyceramides (5).
Nonpolar diesters form 3–9% of the total vernix caseosa lipids (6, 7). The first report (6) characterized them as esters of an alkane 1,2-diol with two FAs [later described as type II diesters or 1,2-diol diesters (1,2-DDEs)] with a small amount of esters of a HFA with a fatty alcohol and an FA (type I diesters). Four years later, type II diesters were confirmed as the main constituents of the diester fraction (8, 9). The analyses of hydrolysis products also disclosed α-hydroxy FAs (αHFAs), sterols, and fatty alcohols, which prompted the authors to hypothesize on the existence of additional types of diesters, type I diesters, and type I diesters with the fatty alcohol having been replaced by a sterol (9). However, the existence of the additional type of diesters in vernix caseosa has never been substantiated. No diester lipids have been detected in adult human sebum or epidermal surface, where triacylglycerols and their breakdown products (monoacylglycerols, diacylglycerols, and free FAs) are found instead (10, 11). On the contrary, the skin surface lipids of many animals are rich in diesters. Mammals like rabbit, cat, or cow biosynthesize type I diesters, whereas mouse, hamster, guinea-pig, or gerbil produce mostly type II diesters (1,2-DDE) (8, 12–14). A special sort of type II diester, with one FA replaced by isovaleric acid, has been found in the dog (15) and macaque (16). Uropygial (preen) glands of birds mostly produce 2,3-DDE (17). The existence of various types of esters in the sebum of humans and animals has been discussed in terms of the physicochemical properties of the lipids and their likely roles in the skin protection and control of the microbiome (10, 11).
Recently, we reported on the analysis of molecular species of 1,2-DDE (18) from vernix caseosa. Diesters were isolated from a total lipid extract using TLC and separated by nonaqueous reversed-phase HPLC. The 1,2-DDE molecular species were identified using tandem MS with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI). In addition to 1,2-DDE, molecular species of an unknown lipid class appeared in the chromatogram at higher retention times. In this work, we isolated the unknown lipids from a fresh material using multistep chromatography and identified them as cholesteryl esters of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FAs (Chl-ωOAHFAs). To the best of our knowledge, these diesters represent a new lipid class for vernix caseosa. A HPLC/APCI-MS2 method was developed and applied for comprehensive characterization of Chl-ωOAHFA molecular species in vernix caseosa.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Vernix caseosa (1–2 g) was collected from healthy newborn subjects delivered at full term (gestation weeks 39–42) immediately after the delivery. The samples were stored in amber glass vials at −80°C. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the General University Hospital, Prague (910/09 S-IV) and the samples were collected with a written informed parental consent.
Chemicals
LC-MS grade acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, methanol, and propan-2-ol (Sigma-Aldrich) were used as received. Chloroform, hexane, and dichloromethane (Penta, Czech Republic) were distilled in glass from analytical-grade solvents. Rhodamine 6G and silica gel were both from Merck & Co. N,N-dimethylformamide (Acros Organics, part of Thermo Fisher Scientific, San Jose, CA), anhydrous magnesium sulfate, magnesium hydroxide, primuline, (Z)-octadec-9-enoyl chloride, 16-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid, hydrochloric acid, sodium bicarbonate, pyridine, N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, N,O-bis(TMS)acetamide, dichloromethane, 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine, cholesterol, pyridinium dichloroformate, acetyl chloride, and silver carbonate (all from Sigma-Aldrich) were of reagent grade and used as purchased.
Standard synthesis
Cholesteryl ester of 16-{[(9Z)-octadec-9-enoyl]oxy}hexadecanoic acid was synthesized by stirring (Z)-octadec-9-enoyl chloride and 16-hydroxyhexadecanoic acid in anhydrous pyridine. The oily product was purified by flash chromatography and treated with cholesterol in dichloromethane in the presence of N,N’-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine (19). The final purified product was obtained in 39% overall yield and its structure was verified by NMR. The details on the synthetic procedure and NMR data are given in the supplemental data (Section 1).
Isolation of total lipids
Lipids were extracted from 20 samples equally representing gender of newborns (10 boys, 10 girls). Each sample was processed separately as follows: The sample (300 mg) was suspended in methanol:chloroform (2:1, by volume; 3 ml) in a conical-bottom glass centrifuge tube, and homogenized using a vortex shaker followed by a 2 min treatment in an ultrasonic bath. Then, chloroform (1 ml) and water (1.8 ml) were added and the suspension was shaken for 1 h. The mixture was centrifuged at 400 g for 5 min. The chloroform layer was transferred into a new glass tube, vortexed with 1.8 ml of water and collected after centrifugation. The water layer was re-extracted with 1 ml of chloroform. The chloroform extracts were combined, treated with anhydrous magnesium sulfate to remove the water residues, and filtered through precleaned cotton wool. The lipid extracts from all 20 samples were combined and concentrated on a rotary evaporator (37°C, 170 mbar) to approximately one-third of the original volume. The rest of the solvent was evaporated under a stream of nitrogen. In total, 6.0 g of vernix caseosa yielded 561.1 mg of total lipids. The lipids were reconstituted in chloroform:methanol (19:1 by vol) at the concentration of 30 mg/ml and stored at −20°C.
Fractionation of lipids
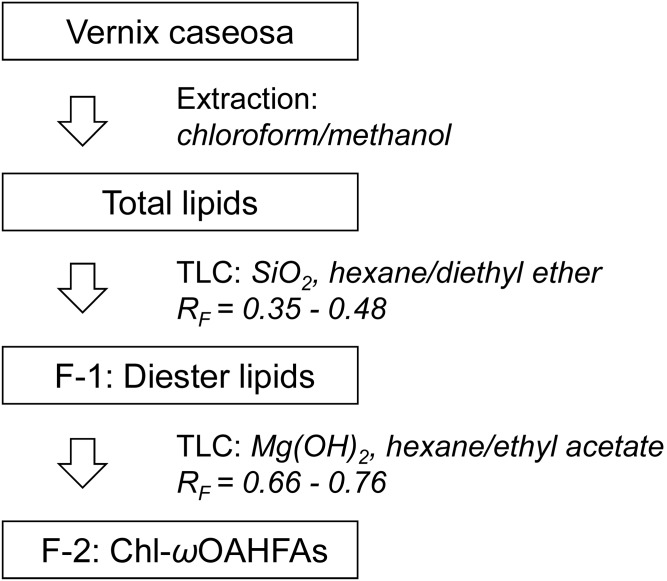
Approximately half of the total lipid extract was fractionated in two steps using semi-preparative TLC. In the first step, lipids were separated on glass plates coated with silica gel using hexane:diethyl ether (93:7, by volume) mobile phase. The zones were visualized under UV light after spraying with rhodamine 6G (0.05% in ethanol). Silica gel with diesters (Rf = 0.35–0.48) was scraped off the plates and the lipids were extracted with freshly distilled diethyl ether. The solvent was evaporated under a nitrogen stream. The procedure was used repeatedly (approximately 3 mg of lipids separated in each step) and yielded 27.6 mg of diesters (F-1).
In the second step, F-1 was reconstituted in chloroform:methanol (2:1, by volume) at a concentration of 30 mg/ml and separated on glass plates coated with magnesium hydroxide (for details on the TLC plate preparation, see supplemental data, Section 2). Hexane:ethyl acetate (99.95:0.05, by volume) was used as a mobile phase. Prior to the separation, a filter paper was inserted into the developing chamber. After the filter paper was fully soaked with the solvent, each plate was developed twice to focus the zones; in the first step to 3/4 of the plate height and then, after air-drying, to the top. After air-drying, the zones were sprayed with 0.05% primuline in ethanol and then visualized under UV light. A synthesized standard [18:1(n-9)/16:0-Chl] was used to verify the Rf of Chl-ωOAHFAs. The sorbent layer corresponding to Rf = 0.66–0.76 was collected and extracted with diethyl ether. The procedure was used repeatedly to process the whole F-1 (approximately 3 mg separated in each step) and yielded 5.8 mg of Chl-ωOAHFAs (F-2). The lipids were dissolved in chloroform:methanol (9:1, by volume) at a concentration of 5 mg/ml and stored at −20°C. The whole isolation and fractionation procedure is depicted in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
Scheme of the isolation and fractionation procedure.
Transesterification
Chl-ωOAHFAs were transesterified using an acid catalyst (20). Briefly, F-2 was dissolved in chloroform:methanol (2:3, by volume) in a small glass ampoule. After adding acetyl chloride, the ampoule was sealed and heated at 70°C for 60 min. The reaction mixture was neutralized with silver carbonate and the organic layer was used for further analyses.
Trimethylsilylation
TMS derivatives of HFA were prepared according to a published procedure (21). FA methyl esters (FAMEs) were dissolved in dried acetonitrile (0.4 mg/ml) and treated with excess of N,O-bis(TMS)acetamide at 40°C for 10 min. The solvent was evaporated under a stream of nitrogen, the residues were dissolved in chloroform (250 μl), and the sample was injected onto the GC column.
Oxidation with pyridinium dichromate in DMF
HFAs were oxidized with pyridinium dichromate (PDC) in N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) (22). The solution of FAMEs in chloroform:methanol, 2:3, by volume (100 μl) was shaken with 5 mg of PDC and 50 μl of DMF for 24 h at laboratory temperature. The reaction mixture was transferred into a small glass column with silica gel, and the reaction products were eluted with chloroform (2 × 200 μl). The sample volume was reduced to 30 μl under a stream of nitrogen.
GC/EI-MS
The analyses were performed on a 7890N gas chromatograph coupled to a 5975C mass spectrometer, equipped with EI and quadrupole analyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). The sample (2 μl) was injected in the split mode with a split ratio of 5:1. The injector and transfer line temperatures were set to 350°C and 340°C, respectively. A DB-5HT fused silica capillary column (15 m × 250 μm; a film thickness 0.10 μm) from Agilent Technologies was used. The carrier gas was helium at a constant flow rate of 1.5 ml/min. The temperature program was set as follows: 100°C (2 min), then 6°C/min to 370°C (3 min). The ion source and quadrupole temperatures were 230°C and 150°C, respectively. EI spectra (70 eV) were recorded from m/z 20 to 700.
Direct infusion MS and HPLC/APCI-MS
Direct infusion and HPLC/MS experiments were performed using an LTQ Orbitrap XL hybrid FT mass spectrometer equipped with an Ion Max source and controlled by Xcalibur (all Thermo Fisher Scientific). The mass spectrometer was coupled to a HPLC system consisting of a Rheos 2200 quarternary gradient pump (Flux Instruments, Reinach, Switzerland), a PAL HTS autosampler (CTC Analytics, Zwingen, Switzerland), and a DeltaChrom CTC 100 column oven (Watrex, Prague, Czech Republic). Molecular species of Chl-ωOAHFAs were separated in nonaqueous reversed-phase HPLC and detected by APCI-MS2 using the conditions as follows: The temperature of the sample tray was set at 10°C. The autosampler injected 5 μl of the sample and the injection system was washed with chloroform/acetonitrile (1:1, by volume). Two Nova-Pak C18 stainless-steel columns connected in series (150 and 300 mm × 3.9 mm, particle size 4 μm; Waters, Milford, MA) were placed in a column oven set at 40°C. The mobile phase was prepared from acetonitrile (A) and ethyl acetate (B) using the following linear gradient program: 0 min, 30% of A and 70% of B; 74.5 min, 67.25% of B; 75 min, 67.5% of B; 140 min, 100% of B; 140.5 min, 100% of B; 154 min, 100% of B. The mobile phase flow rate was set as follows: 0–74.5 min, 0.6 ml/min; 75–140 min, 0.15 ml/min; and 140.5–154 min, 0.6 ml/min. The APCI corona discharge current, vaporizer, and heated capillary temperatures were 5 μA, 500°C, and 170°C, respectively. The sheath and auxiliary gas (nitrogen) were set at the flow rate of 52 and 22 arbitrary units, respectively. The MS method encompassed three scan events: 1) the Orbitrap full MS scan event in the m/z 300–1,600 range, in the positive ion mode at a resolution of 30,000; 2) the linear ion trap full MS scan event in the m/z 200–1,600 range in the negative ion mode; and 3) the collision-induced dissociation (CID) MS2 scan event of the first most intense ion from the parent mass list with a normalized collision energy of 21.5% and isolation window 2 Da in the negative ion mode. The CID MS2 parent mass list was calculated for [M − H − Chl + H2O]− (i.e., [OAHFA]−) ions of all possible Chl-ωOAHFAs with the total number of carbons and double bonds in the range of 37–60 and 0–3, respectively. The HPLC/MS2 data were interpreted manually, with the help of an in-house developed Excel macro.
Shorthand nomenclature
Considering previous literature (23, 24), sterol esters of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FAs are abbreviated St-ωOAHFAs. In the case of cholesterol, Chl-ωOAHFAs is used. Molecular species within this class are abbreviated using a FA/ωHFA-Chl format, which is consistent with the established shorthand nomenclature for ωOAHFAs (25) and reflects the chemical structure of Chl-ωOAHFAs. Thus, for instance, a molecular species identified in this work as 16:0/32:1-Chl corresponds to cholesteryl ester of ωHFA with 32 carbons and 1 double bond, with the hydroxyl esterified to a saturated FA with 16 carbons. In the ion description, “Chl” is considered a neutral cholesterol molecule. Thus, for instance, protonated ωOAHFA, which is an ion resulting by neutral loss of dehydrated cholesterol from Chl-ωOAHFA (M), is [M − Chl + H2O]+.
RESULTS
General structure elucidation
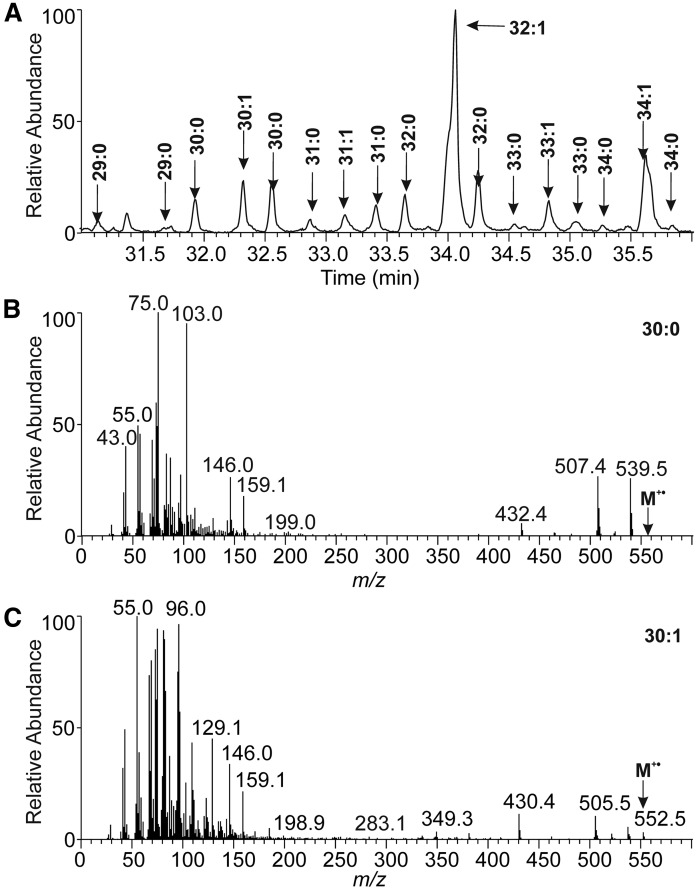
As shown in our previous report (18), the unknown lipids eluted in the reversed-phase HPLC at higher retention times than aliphatic 1,2-DDEs. For protonated molecules, high-resolution APCI mass spectra revealed elemental compositions, CnH2n−xO4, where x = 11, 13, 15, or 17. The existence of four oxygen atoms and similar retention on silica gel as 1,2-DDE pointed out diester lipids. The formulas corresponded to ring plus double bond equivalents (RDBEs) of 6.5–9.5, showing an unusually high degree of unsaturation and/or presence of rings (the RDBE values for 1,2-DDEs ranged from 1.5 to 3.5). Protonated molecules of unknown lipids were found at higher m/z values (m/z 1,000–1,250) than 1,2-DDE (m/z 800–1,000). The APCI spectra of all molecular species showed neutral loss of 368 Da, typical for sterol-containing compounds. The occurrence of a sterol corresponded well with the high RDBE values. The presence of a sterol in the unknown diesters and its absence in 1,2-DDE made it possible to separate these two diester lipid classes from each other using TLC on magnesium-based sorbents (26, 27). Commercial production of such sorbents was mostly discontinued, which forced us to use common reagent-grade chemicals. Nevertheless, a fraction of unknown sterol-containing diesters with satisfactory purity was obtained. In the next step, the unknown lipids were transesterified and analyzed by high-temperature GC/EI-MS and high-resolution MS. The GC/EI-MS data showed cholesterol and a rich mixture of FAMEs (supplemental Fig. S4). A group of FAMEs at unusually high retention times was identified as methyl esters of HFAs (HFAMEs). Their TMS derivatives (Fig. 2) provided spectra consistent with a hydroxy group at the terminal carbon (28, 29) and revealed saturated and monounsaturated ωHFAs with 29–34 carbons. Interestingly, saturated ωHFAs eluted in two chromatographically separated peaks, obviously differing by chain branching. The mass spectra of earlier eluting isomers of 30:0 and 32:0 showed significantly more abundant m/z 103, which could indicate methyl branching in the iso position. The chromatographic peaks of TMS derivatives of monounsaturated ωHFAMEs were distorted, likely because of double bond positional isomers. The original transesterified mixture was also analyzed by high-resolution APCI-MS (supplemental Fig. S5a). The positive ion spectra displayed abundant m/z 369.3510 (cholesterol; [Chl + H − H2O]+) and showed ions consistent with protonated molecules of saturated and monounsaturated hydroxy FAMEs (exact masses within 2 ppm error). To confirm the position of the hydroxy group in an independent experiment, oxidation with PDC in DMF was performed. As known from the literature (22), the oxidation of primary alcohol gives carboxyl, whereas the reaction of secondary alcohol provides a carbonyl group. High-resolution electrospray mass spectrum of negative ions showed reaction products with one extra oxygen, i.e., carboxyl derivatives (supplemental Fig. S5b). Therefore, the hydroxy group on the terminal carbons of HFAs was confirmed. Double bond position in unsaturated ωHFAs was investigated using our previously developed method based on gas phase reactions of acetonitrile (30–32). CID MS/MS spectra of the [M + 55]+• adduct of ωHFAME (32:1) revealed double bonds in two positions, n-7 (more abundant) and n-9 (less abundant), see supplemental Fig. S5c. The existence of two isomers corresponded well with the distorted peaks in GC chromatogram discussed above. The entire analytical strategy used for the lipid class identification is summarized on a flowchart in supplemental Fig. S6.
Fig. 2.
A section of GC/MS chromatogram reconstructed for m/z 75 showing TMS derivatives of HFAMEs from Chl-ωOAHFAs (A). The EI-MS (70 eV) spectrum of TMS derivative of HFAME 30:0 (tR = 31.9 min) (B). The EI-MS (70 eV) spectrum of TMS derivative of HFAME 30:1 (tR = 32.3 min) (C).
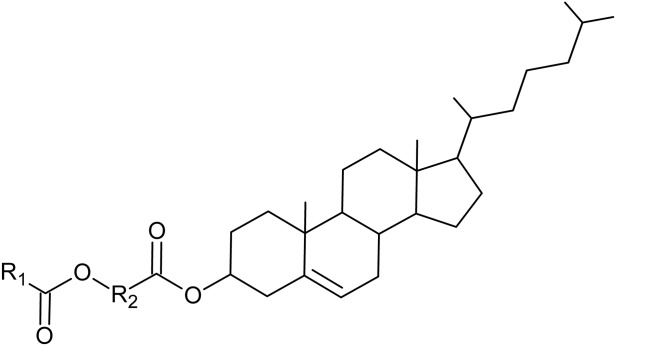
All the results directed us to a hypothesis of diesters composed of ωHFAs having cholesterol attached to the carboxyl and common FA to the hydroxyl. The unknown diester lipids in vernix caseosa were identified as Chl-ωOAHFAs with the general structure shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
The general structure of Chl-ωOAHFAs (R1, aliphatic chain of FA; R2, aliphatic chain of HFA).
Optimization of HPLC/APCI-MS
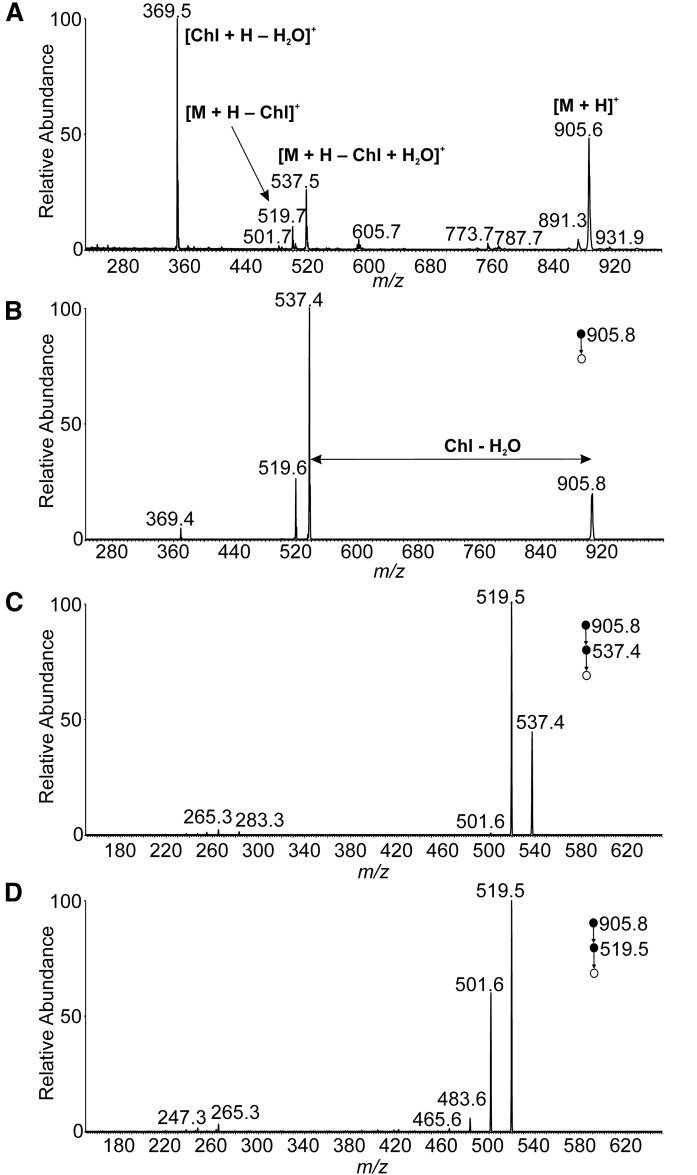
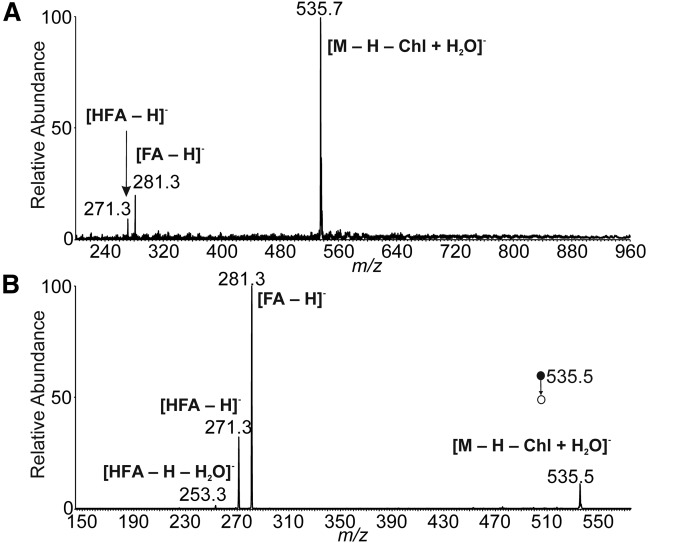
The mass spectra of a synthetic standard were studied with the aim to develop an HPLC/MS method for comprehensive characterization of Chl-ωOAHFA molecular species. The APCI spectrum of 18:1(n-9)/16:0-Chl in the positive ion mode (Fig. 4A) showed protonated molecule (m/z 905.6), protonated and dehydrated cholesterol [Chl + H − H2O]+ (m/z 369.5), and fragments consistent with a neutral loss of dehydrated cholesterol (m/z 537.5) and cholesterol (m/z 519.7). The CID MS/MS spectrum of protonated molecule (Fig. 4B) resembled the full scan spectrum, providing identical fragments. Structural information on the FAs and/or HFAs was searched in the MS3 spectra of [M + H − Chl + H2O]+ (Fig. 4C) and [M + H − Chl]+ (Fig. 4D). Unluckily, the fragmentation channels proceeded almost exclusively via elimination of water. Thus, positive ion mode turned out to be useless for structure elucidation of Chl-ωOAHFAs. The standard did not provide [M − H]− in the negative ion mode because of the absence of groups prone to deprotonation. Fortunately, elevated temperature in the ion source induced thermal degradation to OAHFA that easily deprotonated in the corona discharge (Fig. 5A). The process was not very efficient under the conditions used and required optimization of the ion source parameters. The ion source temperature and the mobile phase flow rate, as well as ion optics voltages, were tuned to maximize signal of deprotonated OAHFA (supplemental data, Section 6). Fragmentation of deprotonated ωOAHFAs is known to give structural information on FAs and HFAs; the MS/MS spectrum of 18:1(n-9)/16:0 (Fig. 5B) showed the same fragments as in previously published work (33).
Fig. 4.
APCI mass spectra of 18:1(n-9)/16:0-Chl in the positive ion mode. Full scan spectrum (A). CID MS2 spectrum of the protonated molecule (m/z 905.8; normalized collision energy 15%) (B). CID MS3 spectrum of [M + H − Chl + H2O]+ (m/z 537.4; normalized collision energy 16%) (C). CID MS3 spectrum of [M + H − Chl]+ (m/z 519.5; normalized collision energy 16%) (D). The chloroform solution (1 mg/ml) delivered by a syringe pump (5 μl/min) was mixed with acetonitrile:ethyl acetate (45:55, by volume) flowing at 150 μl/min. The mixture was directly infused into the ion source.
Fig. 5.
APCI mass spectra of 18:1(n-9)/16:0-Chl in the negative ion mode. Full scan spectrum (A). CID MS2 spectrum of [M − H − Chl + H2O]− (m/z 535.5; normalized collision energy 15%) (B). The chloroform solution (1 mg/ml) delivered by a syringe pump (5 μl/min) was mixed with acetonitrile:ethyl acetate (45:55, by volume) flowing at 150 μl/min. The mixture was directly infused into the ion source.
The chromatography was optimized using the lipid sample from vernix caseosa, with the aim to achieve the highest possible resolution for molecular species in a reasonable time. Based on our previous experience with 1,2-DDEs (18), a nonaqueous reversed-phase system with the two Nova-Pak C18 columns connected in series with a total length of 45 cm was developed. Various binary mobile phases containing methanol, propan-2-ol, acetonitrile, ethyl acetate, and acetone were studied. Finally, we ended up with separation conditions similar to those used for 1,2-DDE (18), i.e., a linear increase of ethyl acetate in acetonitrile in 140 min. The flow rate of the mobile phase in the elution window of Chl-ωOAHFAs was reduced from 0.6 to 0.15 ml/min to increase detection sensitivity.
Chl-ωOAHFAs in vernix caseosa
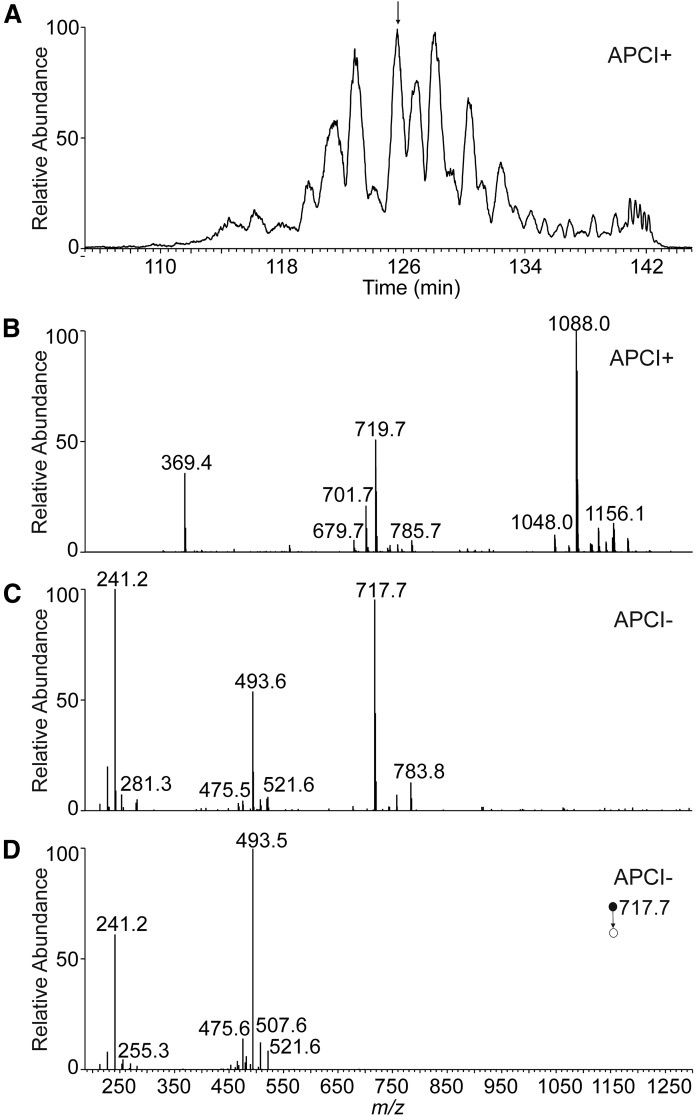
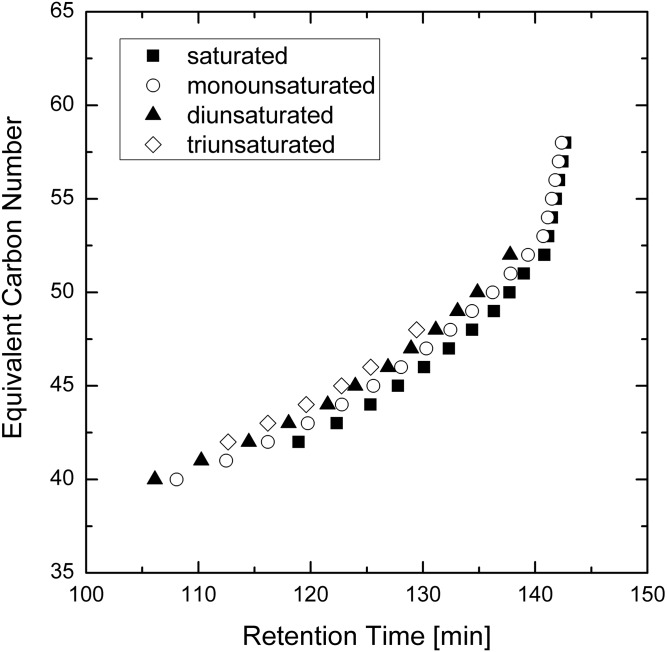
The base peak chromatogram of Chl-ωOAHFAs showed many overlapping peaks (Fig. 6A). The extracted chromatograms displayed up to several peaks for each m/z value, obviously representing isomers. The elution order followed the equivalent carbon number concept (34); retention increased with the length of the chain and decreased with the number of double bonds. As shown in Fig. 7, the molecular species appeared on a band rising almost linearly with the retention time (at higher retention times the curve rose exponentially as the flow rate increased from 150 μl/min back to 600 μl/min).
Fig. 6.
Positive ion base-peak chromatogram (m/z 1,000–1,300) of Chl-ωOAHFAs isolated from vernix caseosa (A) and the APCI mass spectra used for the structure elucidation of a species with tR= 126.0 min (B–D). Full scan spectrum in the positive ion mode (B). Full scan spectrum in the negative ion mode (C). CID MS2 spectrum of m/z 717.7 in the negative ion mode (normalized collision energy 21.5%) (D).
Fig. 7.
Plot of calculated equivalent carbon number (ECN) values versus retention times for the Chl-ωOAHFAs identified in vernix caseosa (ECN = CN-2DB where CN is the total number of carbons and DB is the total number of double bonds in the ωOAHFA part of the molecules).
The molecular species of Chl-ωOAHFAs were detected and identified using APCI-tandem MS with data-dependent scanning. The high-resolution full-scan mass spectra of positively charged ions (Fig. 6B) were used for determining the total number of carbons and double bonds in fatty chains and served for confirmation of the expected elemental composition. The typical mass errors were in the range of 0.5–1.5 ppm. The ion-trap full-scan mass spectra in the negative ion mode (showing deprotonated ωOAHFAs, Fig. 6C) further confirmed the total number of carbons and double bonds in fatty chains and served for data-dependent selection of precursors for MS/MS. The ion-trap MS2 spectra in the negative ion mode (Fig. 6D) revealed FAs and ωHFAs. The deprotonated ωHFA ions ([HFA − H]−) were always accompanied by less abundant water loss peaks ([HFA − H − H2O]−), which made it possible to distinguish them from deprotonated FA ions. In total, 295 molecular species of Chl-ωOAHFAs were fully characterized in 59 chromatographic peaks, and Chl-ωOAHFAs in an additional 11 peaks were characterized by the total number of carbons and double bonds. The list of the 50 most abundant species is given in Table 1 (for all identified Chl-ωOAHFAs see supplemental Table S1). The relative proportions of identified molecular species were estimated from peak areas integrated in the chromatograms reconstructed for [M + H]+ and relative intensities of deprotonated FA ions in MS2 spectra. It is important to note that response factors of lipids depend on the number of double bonds and carbon chain length (35, 36). As neither standards nor response factors were available for quantification, the relative proportions must be considered merely as an estimate.
TABLE 1.
List of 50 abundant Chl-ωOAHFAs identified in vernix caseosa
| tR (min) | m/z of [M + H]++ | m/z of [ωOAHFA]− | Relative Peak Areaa (%) | Identificationb |
| 112.64 | 1,098.02 | 727.66 | 0.53 | 16:1/32:2-Chl |
| 114.50 | 1,072.01 | 701.65 | 1.45 | 16:1/30:1-Chl |
| 114.50 | 1,072.01 | 701.65 | 0.57 | 14:1/32:1-Chl |
| 116.18 | 1,045.99 | 675.63 | 1.46 | 14:0/30:1-Chl |
| 118.04 | 1,086.02 | 715.66 | 0.68 | 16:1/31:1-Chl |
| 118.04 | 1,086.02 | 715.66 | 0.49 | 15:0/32:2-Chl |
| 119.60 | 1,126.05 | 755.69 | 0.75 | 18:2/32:1-Chl |
| 119.74 | 1,060.01 | 689.65 | 2.53 | 15:0/30:1-Chl |
| 119.74 | 1,060.01 | 689.65 | 1.41 | 13:0/32:1-Chl |
| 119.74 | 1,060.01 | 689.65 | 1.29 | 14:0/31:1-Chl |
| 121.51 | 1,100.04 | 729.68 | 5.33 | 16:1/32:1-Chl |
| 121.51 | 1,100.04 | 729.68 | 1.76 | 18:1/30:1-Chl |
| 121.51 | 1,100.04 | 729.68 | 0.53 | 14:0/34:2-Chl |
| 122.78 | 1,074.02 | 703.66 | 5.85 | 14:0/32:1-Chl |
| 122.78 | 1,074.02 | 703.66 | 0.94 | 16:0/30:1-Chl |
| 122.78 | 1,074.02 | 703.66 | 0.62 | 15:0/31:1-Chl |
| 122.78 | 1,074.02 | 703.66 | 0.50 | 16:1/30:0-Chl |
| 123.97 | 1,114.05 | 743.69 | 1.27 | 17:1/32:1-Chl |
| 123.97 | 1,114.05 | 743.69 | 0.72 | 16:1/33:1-Chl |
| 123.97 | 1,114.05 | 743.69 | 0.64 | 15:0/34:2-Chl |
| 123.97 | 1,114.05 | 743.69 | 0.60 | 18:1/31:1-Chl |
| 124.24 | 1,074.02 | 703.66 | 1.17 | 14:0/32:1-Chl |
| 125.33 | 1,048.01 | 677.65 | 0.81 | 14:0/30:0-Chl |
| 125.58 | 1,088.04 | 717.68 | 6.14 | 15:0/32:1-Chl |
| 125.58 | 1,088.04 | 717.68 | 0.81 | 14:0/33:1-Chl |
| 126.41 | 1,088.04 | 717.68 | 0.90 | 15:0/32:1-Chl |
| 126.89 | 1,128.07 | 757.71 | 5.70 | 18:1/32:1-Chl |
| 126.89 | 1,128.07 | 757.71 | 1.97 | 16:1/34:1-Chl |
| 127.77 | 1,062.02 | 691.66 | 0.80 | 15:0/30:0-Chl |
| 128.06 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 4.33 | 16:0/32:1-Chl |
| 128.06 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 2.38 | 14:0/34:1-Chl |
| 128.06 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 0.78 | 15:0/33:1-Chl |
| 128.06 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 0.74 | 18:1/30:0-Chl |
| 128.94 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 1.71 | 16:0/32:1-Chl |
| 128.94 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 0.62 | 18:1/30:0-Chl |
| 128.94 | 1,102.05 | 731.69 | 0.52 | 14:0/34:1-Chl |
| 128.94 | 1,142.08 | 771.72 | 0.67 | 18:1/33:1-Chl |
| 128.94 | 1,142.08 | 771.72 | 0.56 | 17:1/34:1-Chl |
| 130.10 | 1,076.04 | 705.68 | 1.02 | 14:0/32:0-Chl |
| 130.10 | 1,076.04 | 705.68 | 0.58 | 16:0/30:0-Chl |
| 130.30 | 1,116.07 | 745.71 | 0.48 | 18:1/31:0-Chl |
| 130.30 | 1,116.07 | 745.71 | 2.36 | 15:0/34:1-Chl |
| 130.30 | 1,116.07 | 745.71 | 1.74 | 17:0/32:1-Chl |
| 131.14 | 1,156.10 | 785.74 | 2.37 | 18:1/34:1-Chl |
| 132.32 | 1,090.05 | 719.69 | 0.96 | 15:0/32:0-Chl |
| 132.44 | 1,130.08 | 759.72 | 1.77 | 16:0/34:1-Chl |
| 132.44 | 1,130.08 | 759.72 | 0.77 | 18:1/32:0-Chl |
| 133.34 | 1,130.08 | 759.72 | 0.52 | 16:0/34:1-Chl |
| 134.38 | 1,144.10 | 773.74 | 0.70 | 17:0/34:1-Chl |
| 134.38 | 1,104.07 | 733.71 | 0.75 | 16:0/32:0-Chl |
A full list of all 306 Chl-ωOAHFAs can be found in the supplemental Table S1.
The values of relative peak area were calculated in two steps. In the first step, full scan trace in the positive ion mode was used to create reconstructed ion chromatograms for individual m/z values ([M + H]+). The peak areas were integrated and put in relative values. In the second step, relative proportions of the isomers within each peak were established from relative intensities of the deprotonated FA ions in the negative ion MS/MS spectra.
Molecular species with the relative peak area higher than 1.5% are bolded.
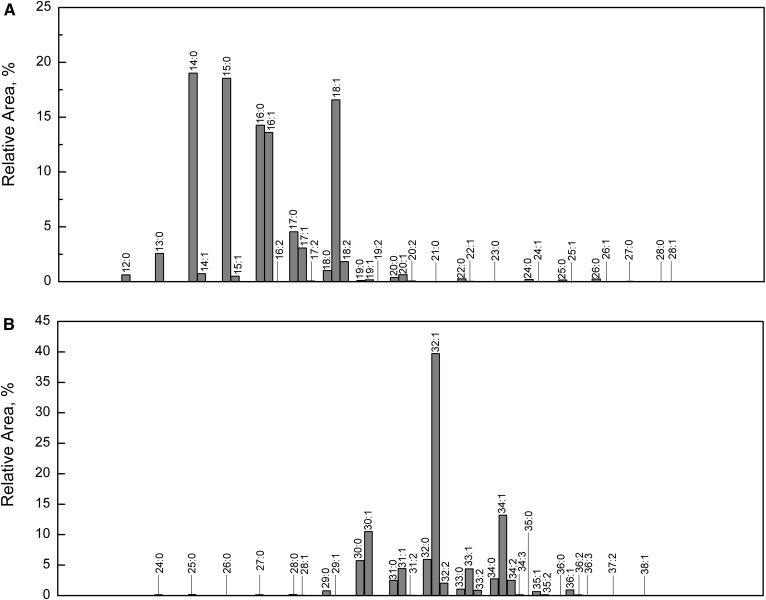
The most abundant molecular species were composed of cholesterol, ωHFA 32:1, and FAs commonly found in skin lipids, namely FA 15:0, FA 14:0, FA 18:1, FA 16:1, and FA 16:0 (15:0/32:1-Chl, 14:0/32:1-Chl, 18:1/32:1-Chl, 16:1/32:1-Chl, and 16:0/32:1-Chl). Relative proportions of FAs and HFAs in Chl-ωOAHFAs calculated from HPLC/APCI-MS2 are shown in Fig. 8. Chl-ωOAHFAs detected in vernix caseosa appeared to contain 34 FAs with 12–28 carbons (up to two double bonds) and 32 ωHFAs with 24–38 carbons (up to three double bonds). All saturated Chl-ωOAHFAs corresponded to 11% of the total integrated signal, whereas monounsaturated, diunsaturated, and triunsaturated species accounted for 55, 30, and 4%, respectively.
Fig. 8.
Histogram showing relative proportions of FAs (A) and ωHFAs (B) in Chl-ωOAHFAs from vernix caseosa. The proportions were calculated using HPLC/MS data given in supplemental Table S1 (the extended version of Table 1).
DISCUSSION
Indirect evidence of cholesterol-containing diesters in vernix caseosa appeared in 1969 when a subclass of type I diesters [also called “type III diester waxes” (11)], composed of αHFAs esterified on the hydroxyl group with an unsubstituted FA and on the carboxyl group with a sterol, was proposed (9). However, a diester lipid class with a sterol moiety has never been substantiated in vernix caseosa. Our work brings evidence that the sterol-containing diesters are, in fact, Chl-ωOAHFAs comprised of long-chain ωHFAs.
ωHFAs form 2–3% of free (unesterified) FAs in vernix caseosa (5). Although they have been identified in hydrolysates of sterol esters, wax esters, diol diesters, and triacylglycerols (5), intact neutral lipids containing ωHFAs have not yet been reported. The detection of ωHFAs in the diol diester fraction (5) was very likely because of Chl-ωOAHFAs co-isolated with diol diesters. As regards more polar lipids, ωHFAs are found in three ceramide subclasses, EOS (Cer 1), EOH (Cer 4), and EOP (Cer 9), which together form about 1/4 of all vernix caseosa ceramides (5, 37, 38). These ceramides are composed of long-chain ωHFAs linked by an amide bond with a sphingoid base (sphingosine in EOS, 6-hydroxy-sphingosine in EOH, and dihydrosphingosine in EOP), with the ω-hydroxyl group esterified with a FA. The ωHFAs in EOS have long aliphatic chains with 28–32 carbons (37). Vernix caseosa ceramides are derived from the fetal epidermis and they represent the key barrier lipids (38). As in the case of stratum corneum, ωHFAs and ceramides with ωHFAs are also covalently linked (esterified through the ω-hydroxyl group) to the cornified cell envelope (39). Whereas covalently bound ω-hydroxyceramides in stratum corneum mostly contain 30:0, 32:1, and 34:1 chains (40, 41), ω-hydroxyeicosanoic acid predominates in vernix caseosa; C30-C34 ωHFAs are present as minor components (5).
Ester lipids containing ωHFAs are important constituents of meibum, which is a secretion of holocrine meibomian glands in the eyelids of humans and most animals. Meibum lipids form the outermost layer of the tear film that protects the ocular surface from desiccating and bacterial infection (42). The existence of long-chain ωHFAs in meibum is known from the early eighties when they were found in steer and human samples (43, 44). Mostly monounsaturated straight-chain ωHFAs with 30–36 carbons formed approximately 10% of the total acids. Soon after, St-ωOAHFAs (ωType I-St) were isolated and identified in steer and human meibum. It was the first report on these diesters in animal samples (45). In addition to the ωHFAs, meibomian St-ωOAHFAs appeared to contain predominantly FAs with 18:1 and 16:1 chains and cholesterol (60%) or lathosterol (35%). St-ωOAHFAs formed approximately 5% of steer meibomian lipids. The interest in St-OAHFAs increased again after discovering ωOAHFAs in meibum (33). The ωOAHFAs are likely either precursors or degradation products of St-ωOAHFAs, and they are considered to be one of the amphiphilic compounds that separate and stabilize the interfacial layer between the very hydrophobic lipids of meibum and the aqueous layer of the tear film (46). They are linked to dry eye disease and might represent biomarkers of the disease progression (47). The complex mixture of ωOAHFAs in human meibum contains molecular species composed mostly of monounsaturated FAs with 18 and 16 carbons and 28:1–34:1 ωHFAs (46, 48). Recently, 61 ωOAHFAs with 34–56 carbon atoms and one to seven double bonds in human meibum have been reported (25). The occurrence of St-ωOAHFAs in meibum was reconfirmed by the analysis of their intact molecules (49). The ωOAHFA moieties of St-ωOAHFAs and ωOAHFAs in meibum are closely related (50). Their abundances are also similar, with each lipid class accounting for 3–5% of meibomian lipids (24, 47). St-ωOAHFAs have also been found in meibum of several animal species, including dogs, mice, and rabbits (23). Very recently, ωOAHFAs similar to the meibomian ones have been detected in equine sperm and the essential role of these amphiphilic lipids in sperm function was hypothesized (51). It is worth noting that mammals also biosynthesize isomeric OAHFAs derived from HFAs with nonterminal hydroxyl. These recently discovered endogenous lipids (also known as fatty acyl esters of hydroxy FAs) exhibit anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic effects (52, 53).
In this work, Chl-ωOAHFAs comprised approximately 20% of the nonpolar diester fraction. As diesters form 3–9% of the total lipids (6, 7), Chl-ωOAHFAs are estimated to account for approximately 1–2% of vernix caseosa lipids, which is less than in human meibum (3–5%) (24, 45, 47). Chl-ωOAHFAs were detected and comprehensively characterized from a pooled sample representing 10 male and 10 female full-term babies. Moreover, some experiments were also performed with samples from individual subjects (data not shown). Chl-ωOAHFAs were detected in all samples at a similar level, suggesting that these esters are commonly present in vernix caseosa and that they are not related to fetus gender. Our experiments showed that the sterol moiety in Chl-ωOAHFAs is represented by cholesterol; lathosterol, reported in addition to cholesterol in meibomian St-ωOAHFAs (45), has been detected in this work only in traces. ωHFAs in Chl-ωOAHFAs from vernix caseosa resembled those existing in meibomian St-ωOAHFAs and ωOAHFAs. The most abundant ωHFAs in vernix caseosa (32:1, 34:1, and 30:1) were also the most abundant in St-ωOAHFAs (44, 45) and ωOAHFAs (25) from meibum. High proportions of these ωHFAs have also been reported for equine sperm (51). Saturated ωHFAs of meibum are both straight chain and methyl branched (44), which is also in agreement with our findings. The level of similarity can be illustrated by i-30:0 and i-32:0 ωHFAs identified in vernix caseosa based on the mass spectra of their TMS derivatives (Fig. 2). The earlier work showed that meibomian even-carbon ωHFAs are iso-methyl branched, whereas odd-carbon ωHFAs are predominantly of the anteiso type (44). As regards double bond position in unsaturated ωHFAs in meibum, the available data are scarce. The action of Δ9-desaturases was proposed (44) and n-9 and n-7 double bonds were assumed (46). We clearly demonstrated that the double bonds in 32:1 ωHFAs in vernix caseosa are in both positions, n-7 (more abundant) and n-9 (less abundant). As regards FAs, the largest signals provided Chl-ωOAHFAs with 14:0, 15:0, 16:0, 16:1, and 18:1 chains, which is not surprising for a sample of vernix caseosa origin (54, 55). The distribution of FAs in Chl-ωOAHFAs (Fig. 8A) was similar to the overall representation of FAs in the vernix caseosa lipidome reported earlier (56) (compare supplemental Fig. S8). The higher levels of 16:1 and 18:1 observed for Chl-ωOAHFAs has to be interpreted with caution because, as discussed above, APCI-MS is somewhat more sensitive to unsaturated lipids (35, 36). Nevertheless, the results indicate that Chl-ωOAHFAs are biosynthesized from a pool of all FAs, likely with a certain preference for 16:1 and 18:1 chains. The meibomian St-ωOAHFAs and ωOAHFAs tend to incorporate fatty acyls with 16 and 18 carbons more exclusively (24, 25, 45, 47). Meibomian ωOAHFAs have been reported to comprise a relatively large proportion of FA 18:2 (24), which is not the case of vernix caseosa Chl-ωOAHFAs. Nevertheless, 18:2 was the most abundant diunsaturated FA in Chl-ωOAHFAs from vernix caseosa. Considering the intact molecules, this study showed the ratio of unsaturated and saturated Chl-ωOAHFAs as 89%:10%, which is in a good agreement with meibum (91 ± 3%:9 ± 1%) (57). The main species in vernix caseosa are represented by 15:0/32:1-Chl, 14:0/32:1-Chl, 18:1/32:1-Chl, 16:1/32:1-Chl, and 16:0/32:1-Chl, which reflects the higher incorporation of saturated shorter chain FAs than in meibum.
The biological role of Chl-ωOAHFAs in vernix caseosa remains to be clarified. The diesters are structurally related to cholesteryl esters, important constituents of neutral lipids in vernix caseosa (6). Chl-ωOAHFAs might be a storage or inactivated form of ωOAHFAs, similarly to cholesteryl esters of very long chain FAs and ωOAHFAs in meibum (46, 58). However, it is not known whether nonesterified ωOAHFAs exist in vernix caseosa (or eventually in amniotic fluid) or not. One can imagine that the amphiphilic properties of ωOAHFAs might be important for proper functions and/or cohesion of vernix caseosa. It seems reasonable to assume that Chl-ωOAHFAs are products of the sebaceous gland, taking into account that they are produced by a meibomian gland (a type of sebaceous gland). Sebaceous glands in the developing skin are a presumed source of structurally related cholesteryl esters in vernix caseosa (2). On the other hand, OAHFA structural motives in certain ceramides (5, 37, 38) cannot be overlooked, and the epidermal origin of Chl-ωOAHFAs should be considered as well.
We finally wish to briefly comment on the analytical methodology used in this work. Although positive ion mode of APCI-MS provided intense signals of protonated Chl-ωOAHFAs, it has turned out to be unusable for detailed structural elucidation because of virtually missing fragments related to FAs and HFAs. Negative ion mode is unlikely to be efficient for diester-type structures lacking easily deprotonatable groups. Although deprotonated molecules of St-OAHFAs have been reported (49), we found the negative ion mode to be insensitive. On-line thermal degradation of Chl-ωOAHFAs to ωOAHFAs in the APCI source worked well and made it possible to detect about 300 molecular species of Chl-ωOAHFAs, by far the highest number of reported Chl-ωOAHFAs to date.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- APCI
- atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
- Chl-ωOAHFA
- cholesteryl ester of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FA
- CID
- collision-induced dissociation
- DMF
- N,N-dimethylformamide
- 1
- 2-DDE, 1,2-diol diester
- FAME
- FA methyl ester
- HFA
- hydroxy FA
- αHFA
- α-hydroxy FA
- ωHFA
- ω-hydroxy FA
- HFAME
- hydroxy FA methyl ester
- ωOAHFA
- ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FA
- PDC
- pyridinium dichromate
- RDBE
- ring plus double bond equivalent
- St-ωOAHFA
- sterol ester of ω-(O-acyl)-hydroxy FA
This work was supported by the Czech Science Foundation (Project P206/12/0750) and Charles University in Prague (Project SVV260440).
The online version of this article (available at http://www.jlr.org) contains a supplement.
REFERENCES
- 1.Haubrich K. A. 2003. Role of vernix caseosa in the neonate: potential application in the adult population. AACN Clin. Issues. 14: 457–464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hoath S. B., Pickens W. L., and Visscher M. O.. 2006. The biology of vernix caseosa. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 28: 319–333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Singh G., and Archana G.. 2008. Unraveling the mystery of vernix caseosa. Indian J. Dermatol. 53: 54–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schmid R. 1939. Notizen zur Kenntnis der Vernix caseosa. Arch. Gynakol. 168: 445–450. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Rissmann R., Groenink H. W. W., Weerheim A. M., Hoath S. B., Ponec M., and Bouwstra J. A.. 2006. New insights into ultrastructure, lipid composition and organization of vernix caseosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 126: 1823–1833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kaerkkaeinen J., Nikkari T., Ruponen S., and Haahti E.. 1965. Lipids of vernix caseosa. J. Invest. Dermatol. 44: 333–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ansari M. N., Fu H. C., and Nicolaides N.. 1970. Fatty acids of the alkane diol diesters of vernix caseosa. Lipids. 5: 279–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nikkari T. 1969. The occurrence of diester waxes in human vernix caseosa and in hair lipids of common laboratory animals. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 29: 795–803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fu H. C., and Nicolaides N.. 1969. The structure of alkane diols of diesters in vernix caseosa lipids. Lipids. 4: 170–175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nicolaides N., Fu H. C., and Rice G. R.. 1968. The skin surface lipids of man compared with those of eighteen species of animals. J. Invest. Dermatol. 51: 83–89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nikkari T. 1974. Comparative chemistry of sebum. J. Invest. Dermatol. 62: 257–267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nicolaides N., Fu H. C., and Ansari M. N.. 1970. Diester waxes in surface lipids of animal skin. Lipids. 5: 299–307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yeung D., Nacht S., and Cover R. E.. 1981. The composition of the skin surface lipids of the gerbil. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 663: 524–535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Schmid P. C., Wedmid Y., and Schmid H. O.. 1978. 15-Methyl-1,2-hexadecanediol, a major constituent of hamster surface wax. Lipids. 13: 825–827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sharaf D. M., Clark S. J., and Downing D. T.. 1977. Skin surface lipids of the dog. Lipids. 12: 786–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Nishimaki-Mogami T., Minegishi K., Takahashi A., Kawasaki Y., Kurokawa Y., and Uchiyama M.. 1988. Characterization of skin-surface lipids from the monkey (Macaca fascicularis). Lipids. 23: 869–877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Haahti E. O. A., and Fales H. M.. 1967. The uropygiols: identification of the unsaponifiable constituent of a diester wax from chicken preen glands. J. Lipid Res. 8: 131–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Šubčíková L., Hoskovec M., Vrkoslav V., Čmelíková T., Háková E., Míková R., Coufal P., Doležal A., Plavka R., and Cvačka J.. 2015. Analysis of 1,2-diol diesters in vernix caseosa by high-performance liquid chromatography - atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 1378: 8–18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Neises B., and Steglich W.. 1978. Simple method for the esterification of carboxylic acids. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 17: 522–524. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Stránský K., and Jursík T.. 1996. Simple quantitative transesterification of lipids. 1. Introduction. Fett/Lipid. 98: 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Carvalho F., Gauthie L. T., Hodgson D. J., Dawson B., and Buist P. H.. 2005. Quantitation of hydroxylated byproduct formation in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Δ9 desaturating system. Org. Biomol. Chem. 3: 3979–3983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Corey E. J., and Schmidt G.. 1979. Useful procedures for the oxidation of alcohols involving pyridinium dichromate in aprotic media. Tetrahedron Lett. 20: 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Butovich I. A., Lu H., McMahon A., and Eule J. C.. 2012. Toward an animal model of the human tear film: biochemical comparison of the mouse, canine, rabbit, and human meibomian lipidomes. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 53: 6881–6896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Butovich I. A. 2013. Tear film lipids. Exp. Eye Res. 117: 4–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mori N., Fukano Y., Arita R., Shirakawa R., Kawazu K., Nakamura M., and Amano S.. 2014. Rapid identification of fatty acids and (O-acyl)-ω-hydroxy fatty acids in human meibum by liquid chromatography/high-resolution mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 1347: 129–136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nicolaides N. 1970. Magnesium oxide as an adsorbent for the chromatographic separation of molecules according to their degree of flatness, e.g. the separation of wax esters from sterol esters. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 8: 717–720. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Stewart M. E., and Downing D. T.. 1981. Separation of wax esters from steryl esters by chromatography on magnesium hydroxide. Lipids. 16: 355–359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nicolaides N., Soukup V. G., and Ruth E. C.. 1983. Mass spectrometric fragmentation patterns of the acetoxy and trimethylsilyl derivatives of all the positional isomers of the methyl hydroxypalmitates. Biol. Mass Spectrom. 10: 441–449. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Christie W. W. 2016. Mass spectrometry of methyl esters: hydroxy fatty acids - trimethylsilyl derivatives. Accessed January 5, 2017, at http://www.lipidhome.co.uk/ms/methesters/me-hydroxy-2/index.htm.
- 30.Vrkoslav V., Háková E., Pecková K., Urbanová K., and Cvačka J.. 2011. Localization of double bonds in wax esters by high-performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry utilizing the fragmentation of acetonitrile-related adducts. Anal. Chem. 83: 2978–2986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Vrkoslav V., and Cvačka J.. 2012. Identification of the double-bond position in fatty acid methyl esters by liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 1259: 244–250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Háková E., Vrkoslav V., Míková R., Schwarzová-Pecková K., Bosáková Z., and Cvačka J.. 2015. Localization of double bonds in triacylglycerols using high-performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization ion-trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 407: 5175–5188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Butovich I. A., Wojtowitz J. C., and Molai M.. 2009. Human tear film and meibum. Very long chain wax esters and (O-acyl)-omega-hydroxy fatty acids of meibum. J. Lipid Res. 50: 2471–2485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Christie W. W. 1987. The separation of molecular species of glycerolipids. In High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Lipids: A Practical Guide. Christie W. W., editor. Pergamon Press, Oxford: 169–210. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Holčapek M., Lísa M., Jandera P., and Kabátová N.. 2005. Quantitation of triacylglycerols in plant oils using HPLC with APCI-MS, evaporative light-scattering, and UV detection. J. Sep. Sci. 28: 1315–1333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vrkoslav V., Urbanová K., and Cvačka J.. 2010. Analysis of wax ester molecular species by high performance liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 1217: 4184–4194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Oku H., Mimura K., Tokitsu Y., Onaga K., Iwasaki H., and Chinen I.. 2000. Biased distribution of the branched-chain fatty acids in ceramides of vernix caseosa. Lipids. 35: 373–381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hoeger P. H., Schreiner V., Klaassen I. A., Enzmann C. C., Friedrichs K., and Bleck O.. 2002. Epidermal barrier lipids in human vernix caseosa: corresponding ceramide pattern in vernix and fetal skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 146: 194–201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Stewart M. E., and Downing D. T.. 2001. The omega-hydroxyceramides of pig epidermis are attached to corneocytes solely through omega-hydroxyl groups. J. Lipid Res. 42: 1105–1110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Swartzendruber D. C., Wertz P. W., Madison K. C., and Downing D. T.. 1987. Evidence that the corneocyte has a chemically bound lipid envelope. J. Invest. Dermatol. 88: 709–713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wertz P. W., Madison K. C., and Downing D. T.. 1989. Covalently bound lipids of human stratum corneum. J. Invest. Dermatol. 92: 109–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Davidson H. J., and Kuonen V. J.. 2004. The tear film and ocular mucins. Vet. Ophthalmol. 7: 71–77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Nicolaides N., and Ruth E. C.. 1982–1983. Unusual fatty acids in the lipids of steer and human meibomian gland excreta. Curr. Eye Res. 2: 93–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nicolaides N., Santos E. C., and Papadakis K.. 1984. Double-bond patterns of fatty acids and alcohols in steer and human meibomian gland lipids. Lipids. 19: 264–277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Nicolaides N., and Santos E. C.. 1985. The di- and triesters of the lipids of steer and human meibomian glands. Lipids. 20: 454–467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Butovich I. A. 2011. Lipidomics of human meibomian gland secretions: chemistry, biophysics, and physiological role of meibomian lipids. Prog. Lipid Res. 50: 278–301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lam S. M., Tong L., Yong S. S., Li B., Chaurasia S. S., Shui G., and Wenk M. R.. 2011. Meibum lipid composition in Asians with dry eye disease. PLoS One. 6: e24339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chen J., Green-Church K. B., and Nichols K. K.. 2010. Shotgun lipidomic analysis of human meibomian gland secretions with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 51: 6220–6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Butovich I. A., Borowiak A. M., and Eule J. C.. 2011. Comparative HPLC-MS analysis of canine and human meibomian lipidomes: many similarities, a few differences. Sci. Rep. 1: 24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Butovich I. A. 2011. On the presence of (O-acyl)-omega-hydroxy fatty acids and of their esters in human meibomian gland secretions. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 52: 639–641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wood P. L., Scoggin K., Ball B. A., Troedsson M. H., and Squires E. L.. 2016. Lipidomics of equine sperm and seminal plasma: identification of amphiphilic (O-acyl)-ω-hydroxy-fatty acids. Theriogenology. 86: 1212–1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Yore M. M., Syed I., Moraes-Vieira P. M., Zhang T., Herman M. A., Homan E. A., Patel R. T., Lee J., Chen S., Peroni O. D., et al. 2014. Discovery of a class of endogenous mammalian lipids with anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. Cell. 159: 318–332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kuda O., Brezinova M., Rombaldova M., Slavikova B., Posta M., Beier P., Janovska P., Veleba J., Kopecky J. Jr., Kudova E., et al. 2016. Docosahexaenoic acid-derived Fatty Acid Esters of Hydroxy Fatty Acids (FAHFAs) with anti-inflammatory properties. Diabetes. 65: 2580–2590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Haahti E., Nikkari T., Salmi A. M., and Laaksonen A. L.. 1961. Fatty acids of vernix caseosa. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 13: 70–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Míková R., Vrkoslav V., Hanus R., Háková E., Habová Z., Doležal A., Plavka R., Coufal P., and Cvačka J.. 2014. Newborn boys and girls differ in the lipid composition of vernix caseosa. PLoS One. 9: e99173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hauff S., and Vetter W.. 2010. Exploring the fatty acids of vernix caseosa in form of their methyl esters by off-line coupling of non-aqueous reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 1217: 8270–8278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chen J., Green K. B., and Nichols K. K.. 2013. Quantitative profiling of major neutral lipid classes in human meibum by direct infusion electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54: 5730–5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Butovich I. A. 2009. Cholesteryl esters as a depot for very long chain fatty acids in human meibum. J. Lipid Res. 50: 501–513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.