Abstract
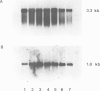
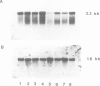
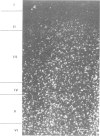
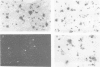
Clones for the amyloid beta protein precursor gene were isolated from a cDNA library prepared from the frontal cortex of a patient who had died with a histologically confirmed diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease; they were used to investigate the tissue and cellular distribution of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA in brain tissues from control patients and from Alzheimer's disease patients. Amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA was expressed in similar amounts in all control human brain regions examined, but a reduction of the mRNA level was observed in the frontal cortex from patients with Alzheimer's disease. By in situ hybridization amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA was present in granule and pyramidal cell bodies in the hippocampal formation and in pyramidal cell bodies in the cerebral cortex. No specific labelling of glial cells or endothelial cells was found. The same qualitative distribution was observed in tissues from control patients and from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Senile plaque amyloid thus probably derives from neurones. The tissue distribution of amyloid beta protein precursor mRNA and its cellular localization demonstrate that its expression is not confined to the brain regions and cells that exhibit the selective neuronal death characteristic of Alzheimer's disease.
Full text
PDF
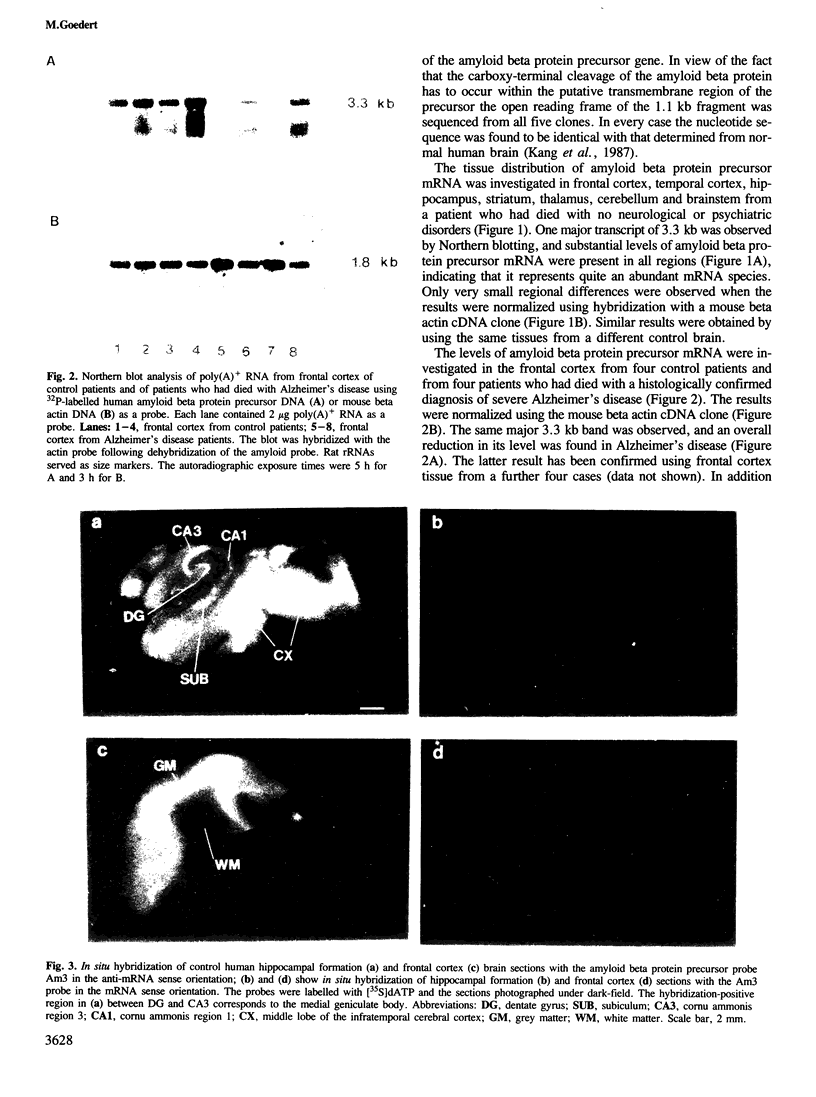



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmanyar S., Higgins G. A., Goldgaber D., Lewis D. A., Morrison J. H., Wilson M. C., Shankar S. K., Gajdusek D. C. Localization of amyloid beta protein messenger RNA in brains from patients with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Jul 3;237(4810):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3299701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball M. J. Neuronal loss, neurofibrillary tangles and granulovacuolar degeneration in the hippocampus with ageing and dementia. A quantitative study. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Feb 28;37(2):111–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00692056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabar J. M., Goldgaber D., Lamour Y., Nicole A., Huret J. L., de Grouchy J., Brown P., Gajdusek D. C., Sinet P. M. Beta amyloid gene duplication in Alzheimer's disease and karyotypically normal Down syndrome. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1390–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2950593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Congophilic microangiopathy in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's syndrome (presenile dementia). Med Hypotheses. 1979 Nov;5(11):1231–1236. doi: 10.1016/0306-9877(79)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE--AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL STUDY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:307–320. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandybur T. I. The incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1975 Feb;25(2):120–126. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.2.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morimatsu M., Hirai S., Muramatsu A., Yoshikawa M. Senile degenerative brain lesions and dementia. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1975 Sep;23(9):390–406. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1975.tb00425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardridge W. M., Vinters H. V., Miller B. L., Tourtellotte W. W., Eisenberg J. B., Yang J. High molecular weight Alzheimer's disease amyloid peptide immunoreactivity in human serum and CSF is an immunoglobulin G. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 May 29;145(1):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91312-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price D. L. New perspectives on Alzheimer's disease. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:489–512. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Wisniewski H. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the cerebrovascular and the neuritic plaque amyloid peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St George-Hyslop P. H., Tanzi R. E., Polinsky R. J., Haines J. L., Nee L., Watkins P. C., Myers R. H., Feldman R. G., Pollen D., Drachman D. The genetic defect causing familial Alzheimer's disease maps on chromosome 21. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):885–890. doi: 10.1126/science.2880399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Peck A., DeTeresa R., Schechter R., Horoupian D. S. Some morphometric aspects of the brain in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1981 Aug;10(2):184–192. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Moretz R. C., Lossinsky A. S. Evidence for induction of localized amyloid deposits and neuritic plaques by an infectious agent. Ann Neurol. 1981 Dec;10(6):517–522. doi: 10.1002/ana.410100605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]