Abstract
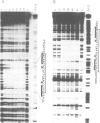
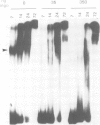
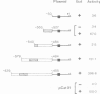
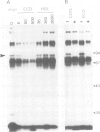
It has previously been shown that a region of ˜100 bp in the Drosophila hsp27 promoter is sufficient to confer ecdysone inducibility on a heterologous gene. We now show, using binding and DNase I footprinting assays, that a 23-bp hyphenated dyad within this sequence forms a protein-binding site, and that this is sufficient for inducibility. The sequence shows partial homology with mammalian steroid receptor binding sites. UV crosslinking identifies an 80- to 90-kd protein that binds specifically to this sequence and is thus a candidate for the ecdysone receptor.
Keywords: ecdysone, Drosophila, hsp27, transcription
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly A., Le Page C., Rauch M., Milgrom E. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the progesterone receptor to the uteroglobin gene: effects of hormone, antihormone and receptor phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3235–3241. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04634.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groyer A., Schweizer-Groyer G., Cadepond F., Mariller M., Baulieu E. E. Antiglucocorticosteroid effects suggest why steroid hormone is required for receptors to bind DNA in vivo but not in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):624–626. doi: 10.1038/328624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Segui P., Evans R. M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ireland R. C., Berger E., Sirotkin K., Yund M. A., Osterbur D., Fristrom J. Ecdysterone induces the transcription of four heat-shock genes in Drosophila S3 cells and imaginal discs. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):498–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Sequence requirement for expression of the Drosophila melanogaster heat shock protein hsp22 gene during heat shock and normal development. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2011–2019. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mestril R., Schiller P., Amin J., Klapper H., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Heat shock and ecdysterone activation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp23 gene; a sequence element implied in developmental regulation. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1667–1673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that define a small region sufficient for enhancer activation. Science. 1987 Apr 24;236(4800):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.3563519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miesfeld R., Rusconi S., Godowski P. J., Maler B. A., Okret S., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90659-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morganelli C. M., Berger E. M., Pelham H. R. Transcription of Drosophila small hsp-tk hybrid genes is induced by heat shock and by ecdysterone in transfected Drosophila cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5865–5869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redeuilh G., Moncharmont B., Secco C., Baulieu E. E. Subunit composition of the molybdate-stabilized "8-9 S" nontransformed estradiol receptor purified from calf uterus. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6969–6975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddihough G., Pelham H. R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1653–1658. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04408.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusconi S., Yamamoto K. R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1309–1315. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02369.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Meshinchi S., Tienrungroj W., Schlesinger M. J., Toft D. O., Pratt W. B. Relationship of the 90-kDa murine heat shock protein to the untransformed and transformed states of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6986–6991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Walker P., Martinez E., Mérillat A. M., Givel F., Wahli W. Identification of estrogen-responsive DNA sequences by transient expression experiments in a human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8755–8770. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Purification and characterization of a heat-shock element binding protein from yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):3035–3041. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02609.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]