Abstract
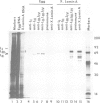
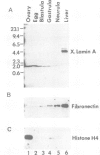
The nuclear lamina of vertebrates is composed of several major polypeptides that range in mol. wt from 60 to 80 kd. In mammals, the three major lamin proteins are designated A, B and C. Two major lamins have been described in Xenopus somatic tissues; two other lamins are expressed primarily in germ cells. We have analysed a cDNA clone encoding a Xenopus lamin that is highly homologous to human lamins A and C. The predicted protein has the carboxy-terminal domain characteristic of human lamin A and is thus a lamin A homologue. Surprisingly, the lamin encoded by the cDNA clone is not one of the known Xenopus lamins. The encoded protein is distinct in size from the oocyte lamin LIII and the two somatic lamins LI and LII. Monoclonal antibodies specific for LII, LIII and LIV (the lamin of male germ cells) do not recognize the protein encoded by the cDNA clone; conversely, a polyclonal antibody against the encoded protein does not recognize any of the known Xenopus lamins. This lamin is expressed late in embryonic development, and is present in all adult somatic cells examined, except erythrocytes. Thus frogs and mammals are similar in having three major somatic lamins that fall into distinct structural classes.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi U., Cohn J., Buhle L., Gerace L. The nuclear lamina is a meshwork of intermediate-type filaments. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):560–564. doi: 10.1038/323560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavente R., Krohne G., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific expression of nuclear lamina proteins during development of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):177–190. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90072-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benavente R., KrohneG Change of karyoskeleton during spermatogenesis of Xenopus: expression of lamin LIV, a nuclear lamina protein specific for the male germ line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6176–6180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Gerace L. A cell free system to study reassembly of the nuclear envelope at the end of mitosis. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):639–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese R., Melton D., Tranquilla T., Smith J. D. Cloning of nematode tRNA genes and their expression in the frog oocyte. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4593–4611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dwyer N., Blobel G. A modified procedure for the isolation of a pore complex-lamina fraction from rat liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1976 Sep;70(3):581–591. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett D. W. On the occurrence of a fibrous lamina on the inner aspect of the nuclear envelope in certain cells of vertebrates. Am J Anat. 1966 Jul;119(1):129–145. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001190108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Scheer U., Krohne G., Jarasch E. D. The nuclear envelope and the architecture of the nuclear periphery. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 2):39s–50s. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.39s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Hanukoglu I. Unraveling the structure of the intermediate filaments. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):332–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blum A., Blobel G. Immunocytochemical localization of the major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex-lamina fraction. Interphase and mitotic distribution. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):546–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Repasky E. A., Lazarides E. Synemin and vimentin are components of intermediate filaments in avian erythrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):299–312. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilly M. N., Danon F., Brouet J. C., Bornens M., Courvalin J. C. Autoantibodies to nuclear lamin B in a patient with thrombopenia. Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;43(2):266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann W., Franz J. K., Franke W. W. Amino acid sequence microheterogeneities of basic (type II) cytokeratins of Xenopus laevis epidermis and evolutionary conservativity of helical and non-helical domains. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90315-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas E., Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Epidermal keratin gene expressed in embryos of Xenopus laevis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5413–5417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Developmental regulation of a gastrula-specific gene injected into fertilized Xenopus eggs. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3463–3471. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04105.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Benavente R. The nuclear lamins. A multigene family of proteins in evolution and differentiation. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90421-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Dabauvalle M. C., Franke W. W. Cell type-specific differences in protein composition of nuclear pore complex-lamina structures in oocytes and erythrocytes of Xenopus laevis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 5;151(1):121–141. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90224-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W. Proteins of pore complex--lamina structures from nuclei and nuclear membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:597–608. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Franke W. W., Scheer U. The major polypeptides of the nuclear pore complex. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 1;116(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Wolin S. L., McKeon F. D., Franke W. W., Kirschner M. W. Nuclear lamin LI of Xenopus laevis: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and binding specificity of a member of the lamin B subfamily. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Laemmli U. K. Evidence for two levels of DNA folding in histone-depleted HeLa interphase nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., Kurer V., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. The nuclear lamin protein family in higher vertebrates. Identification of quantitatively minor lamin proteins by monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13293–13301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner C. F., Stick R., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Differential expression of nuclear lamin proteins during chicken development. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):577–587. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Tuffanelli D. L., Fukuyama K., Kirschner M. W. Autoimmune response directed against conserved determinants of nuclear envelope proteins in a patient with linear scleroderma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4374–4378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miake-Lye R., Newport J., Kirschner M. Maturation-promoting factor induces nuclear envelope breakdown in cycloheximide-arrested embryos of Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):81–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Autoantibodies to the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in a patient with scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):560–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatani S., Winkles J. A., Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Stage-specific keratins in Xenopus laevis embryos and tadpoles: the XK81 gene family. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1957–1965. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: I. characterization and timing of cellular changes at the midblastula stage. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):675–686. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman J. V., Woodland H. R., Sturgess E. A. Modulations of histone messenger RNA during the early development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1979 Jul;71(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatten G., Maul G. G., Schatten H., Chaly N., Simerly C., Balczon R., Brown D. L. Nuclear lamins and peripheral nuclear antigens during fertilization and embryogenesis in mice and sea urchins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4727–4731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stick R., Hausen P. Changes in the nuclear lamina composition during early development of Xenopus laevis. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90073-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner P. C., Woodland H. R. H3 and H4 histone cDNA sequences from Xenopus: a sequence comparison of H4 genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jun 25;10(12):3769–3780. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.12.3769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]