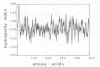
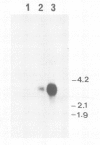
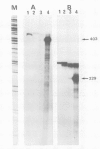
Abstract
A full length dopamine-beta-hydroxylase (DBH) cDNA clone was isolated from a human pheochromocytoma lambda gt11 library. Both structural and functional evidence confirms the authenticity of the clone: (i) antibodies selected with fusion proteins generated by positive clones precipitate DBH activity, (ii) the sequence of three internal DBH tryptic peptides are included in the deduced DBH sequence, (iii) the previously reported N-terminal 15 amino acids of bovine DBH exhibits a nearly complete identity with that predicted for human DBH. The polypeptide chain of DBH comprises 578 amino acids corresponding to an unmodified protein of 64 862 daltons and is preceded by a cleaved signal peptide of 25 residues. DBH exists in both membrane-bound and soluble forms. The hydropathy plot reveals no obvious hydrophobic segment, except the signal peptide. S1 mapping analysis indicates no diversity in the 5' and 3' extremities of the DBH mRNA. Taken together with available biochemical data, these observations suggest that the membrane attachment of DBH probably results from a post-translational modification, glypiation being the most likely candidate. Comparative amino acid sequence analysis establishes that DBH shares no homology with the other catecholamine synthesizing enzymes, tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson A. L., Naujoks K., Thoenen H. Nerve growth factor-mediated enzyme induction in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: specificity and level of regulation. J Neurosci. 1984 Jul;4(7):1771–1780. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-07-01771.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aunis D., Bouclier M., Pescheloche M., Mandel P. Properties of membrane-bound dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in chromaffin granules from bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1977 Sep;29(3):439–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J. Dopamine- -hydroxylase: regulation of its synthesis and release from nerve terminals. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Jun;24(2):233–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baetge E. E., Suh Y. H., Joh T. H. Complete nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequence of bovine phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase: partial amino acid homology with rat tyrosine hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5454–5458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belpaire F., Laduron P. Tissue fractionation and catecholamines. I. Latency and activation properties of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase in adrenal medulla. Biochem Pharmacol. 1968 Mar;17(3):411–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90251-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Baeuerle P. A., Konecki D. S., Frank R., Powell J., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of bovine chromogranin A: a representative of a class of acidic secretory proteins common to a variety of peptidergic cells. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1495–1502. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benedum U. M., Lamouroux A., Konecki D. S., Rosa P., Hille A., Baeuerle P. A., Frank R., Lottspeich F., Mallet J., Huttner W. B. The primary structure of human secretogranin I (chromogranin B): comparison with chromogranin A reveals homologous terminal domains and a large intervening variable region. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1203–1211. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02355.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benlot C., Antreassian J., Henry J. P., Legrand J. C., Gros F., Thibault J. In vitro translation of human pheochromocytoma messenger RNAs: characterization of tyrosine-hydroxylase and dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. Biochimie. 1985 Jun;67(6):589–595. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80198-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biguet N. F., Buda M., Lamouroux A., Samolyk D., Mallet J. Time course of the changes of TH mRNA in rat brain and adrenal medulla after a single injection of reserpine. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):287–291. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjerrum O. J., Helle K. B., Bock E. Immunochemically identical hydrophilic and amphiphilic forms of the bovine adrenomedullary dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):231–237. doi: 10.1042/bj1810231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodde O. E., Arens F., Huvermann K., Schümann H. J. Kinetic studies on soluble and membrane-bound dopamine beta-hydroxylase isolated from storage vesicles of heart and adrenal medulla of different species. Experientia. 1976 Aug 15;32(8):984–986. doi: 10.1007/BF01933925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Geisow M. J. Phosphoproteins of the adrenal chromaffin granule membrane. J Neurochem. 1982 Nov;39(5):1387–1396. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb12582.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciaranello R. D., Wooten G. F., Axwlrod J. Regulation of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in rat adrenal glands. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3204–3211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craine J. E., Daniels G. H., Kaufman S. Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase. The subunit structure and anion activation of the bovine adrenal enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7838–7844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darmon M. C., Grima B., Cash C. D., Maitre M., Mallet J. Isolation of a rat pineal gland cDNA clone homologous to tyrosine and phenylalanine hydroxylases. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhawan S., Duong L. T., Ornberg R. L., Fleming P. J. Subunit exchange between membranous and soluble forms of bovine dopamine beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1869–1875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeland J. A., Gerhard D. S., Pauls D. L., Sussex J. N., Kidd K. K., Allen C. R., Hostetter A. M., Housman D. E. Bipolar affective disorders linked to DNA markers on chromosome 11. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):783–787. doi: 10.1038/325783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Duszenko M., Lamont G. S., Overath P., Cross G. A. Biosynthesis of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. N-glycosylation and addition of a phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer-Colbrie R., Schachinger M., Zangerle R., Winkler H. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase and other glycoproteins from the soluble content and the membranes of adrenal chromaffin granules: isolation and carbohydrate analysis. J Neurochem. 1982 Mar;38(3):725–732. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1982.tb08691.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foldes A., Jeffrey P. L., Preston B. N., Austin L. Some physical properties of bovine adrenal medullary dopamine -hydroxylase. J Neurochem. 1973 May;20(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb00255.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman S., Kaufman S. 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine beta-hydroxylase. Physical properties, copper content, and role of copper in the catalytic acttivity. J Biol Chem. 1965 Dec;240(12):4763–4773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasnier B., Ellory J. C., Henry J. P. Functional molecular mass of binding sites for [3H]dihydrotetrabenazine and [3H]reserpine and of dopamine beta-hydroxylase and cytochrome b561 from chromaffin granule membrane as determined by radiation inactivation. Eur J Biochem. 1987 May 15;165(1):73–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gavine F. S., Pryde J. G., Deane D. L., Apps D. K. Glycoproteins of the chromaffin granule membrane: separation by two-dimensional electrophoresis and identification by lectin binding. J Neurochem. 1984 Nov;43(5):1243–1252. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb05379.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenett H. E., Ledley F. D., Reed L. L., Woo S. L. Full-length cDNA for rabbit tryptophan hydroxylase: functional domains and evolution of aromatic amino acid hydroxylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5530–5534. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Blanot F., Biguet N. F., Mallet J. Complete coding sequence of rat tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):617–621. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grima B., Lamouroux A., Boni C., Julien J. F., Javoy-Agid F., Mallet J. A single human gene encoding multiple tyrosine hydroxylases with different predicted functional characteristics. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):707–711. doi: 10.1038/326707a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Udenfriend S. The application of immunological techniques to the study of enzymes regulating catecholamine synthesis and degradation. Pharmacol Rev. 1972 Jun;24(2):311–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtnagl H., Winkler H., Lochs H. Membrane proteins of chromaffin granules, dopamine -hydroxylase, a major constituent. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):187–195. doi: 10.1042/bj1290187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Baetge E. E., Ross M. E., Reis D. J. Evidence for the existence of homologous gene coding regions for the catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):327–335. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joh T. H., Hwang O. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase: biochemistry and molecular biology. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;493:342–350. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb27217.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN E. Y., LEVENBERG B., KAUFMAN S. The enzymatic conversion of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylamine to norepinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1960 Jul;235:2080–2086. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laduron P. M. Evidence for a localization of dopamine-beta-hydroxylase within the chromaffin granules. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 15;52(1):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80654-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljones T., Skotland T., Flatmark T. Purification and characterization of dopamine beta-hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jan 15;61(2):525–533. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10047.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Saunders G. F. Preparation of pancreatic mRNA: cell-free translation of an insulin-immunoreactive polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):381–391. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man in 't Veld A. J., Boomsma F., Moleman P., Schalekamp M. A. Congenital dopamine-beta-hydroxylase deficiency. A novel orthostatic syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Jan 24;1(8526):183–188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)90002-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis R. K., Finne J., Krusius T., Margolis R. U. Structural studies on glycoprotein oligosaccharides of chromaffin granule membranes and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Feb 1;228(2):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Tsuji A., Katunuma N. Studies on the structure of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase. III. Evidence that the amino terminus of the heavy subunit is the membrane binding segment. J Biochem. 1983 May;93(5):1427–1433. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh E. M., McGee R., Jr, Fleming P. J. Sulfation and constitutive secretion of dopamine beta-hydroxylase from rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 10;260(7):4409–4417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molinoff P. B., Brimijoin S., Weinshilboum R., Axelrod J. Neurally mediated increase in dopamine-beta-hydroxylase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):453–458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno S., Fujisawa H. Purification and characterization of rat dopamine beta-monooxygenase and monoclonal antibodies to the enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jun 29;799(3):260–269. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90269-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Spizz G. Fatty acylation of cellular proteins. Temporal and subcellular differences between palmitate and myristate acylation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2458–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTTER L. T., AXELROD J. SUBCELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF CATECHOLAMINES IN TISSUES OF THE RAT. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1963 Dec;142:291–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson R. B., Woodgett J. R., Cohen P., Kemp B. E. Substrate specificity of a multifunctional calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14471–14476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E. L., Goldstein M. Subcellular site of biosynthesis of the catecholamine biosynthetic enzymes in bovine adrenal medulla. J Neurochem. 1984 Dec;43(6):1663–1668. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb06093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E. L., Greene L. A., Goldstein M. Mechanism of biosynthesis of soluble and membrane-bound forms of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7812–7818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabban E. L., Kuhn L. J., Levin B. E. In vivo biosynthesis of two subunit forms of dopamine beta-hydroxylase in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1987 Jan;7(1):192–200. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-01-00192.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena A., Fleming P. J. Isolation and reconstitution of the membrane-bound form of dopamine beta-hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4147–4152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skotland T., Ljones T., Flatmark T., Sletten K. NH2-terminal sequence of dopamine beta-hydroxylase from bovine adrenal medulla. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Feb 21;74(4):1483–1489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90609-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Zaremba S., Hogue-Angeletti R. A. Purification of membrane-bound dopamine beta-monooxygenase from chromaffin granules: relation to soluble dopamine beta-monooxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 1;211(1):288–296. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoenen H., Angeletti P. U., Levi-Montalcini R., Kettler R. Selective induction by nerve growth factor of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine- -hydroxylase in the rat superior cervical ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1598–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace E. F., Krantz M. J., Lovenberg W. Dopamine-beta-hydroxylase: a tetrameric glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2253–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinshilboum R. M., Thoa N. B., Johnson D. G., Kopin I. J., Axelrod J. Proportional release of norepinephrine and dopamine- -hydroxylase from sympathetic nerves. Science. 1971 Dec 24;174(4016):1349–1351. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4016.1349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Apps D. K., Fischer-Colbrie R. The molecular function of adrenal chromaffin granules: established facts and unresolved topics. Neuroscience. 1986 Jun;18(2):261–290. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90154-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Hörtnagl H., Smith A. D. Membranes of the adrenal medulla. Behaviour of insoluble proteins of chromaffin granules on gel electrophoresis. Biochem J. 1970 Jun;118(2):303–310. doi: 10.1042/bj1180303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. How signal sequences maintain cleavage specificity. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 25;173(2):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]