Abstract
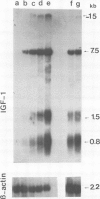
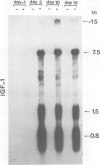
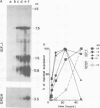
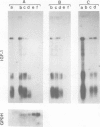
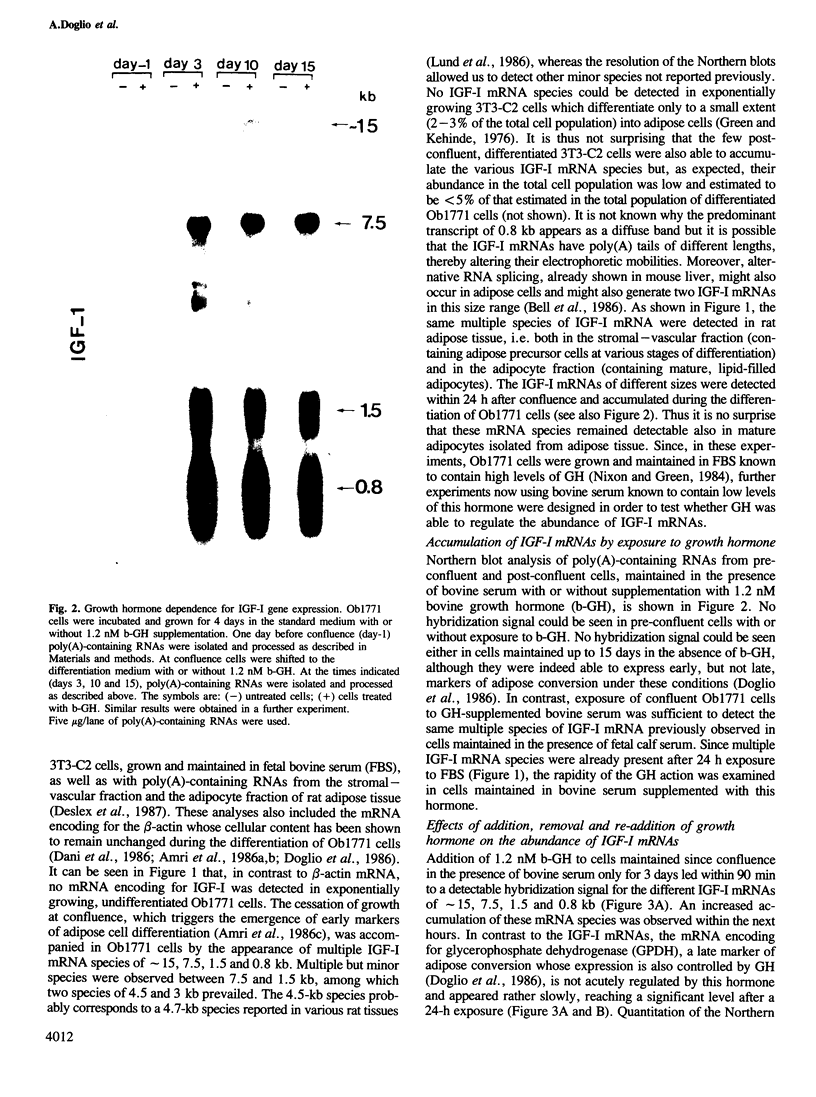
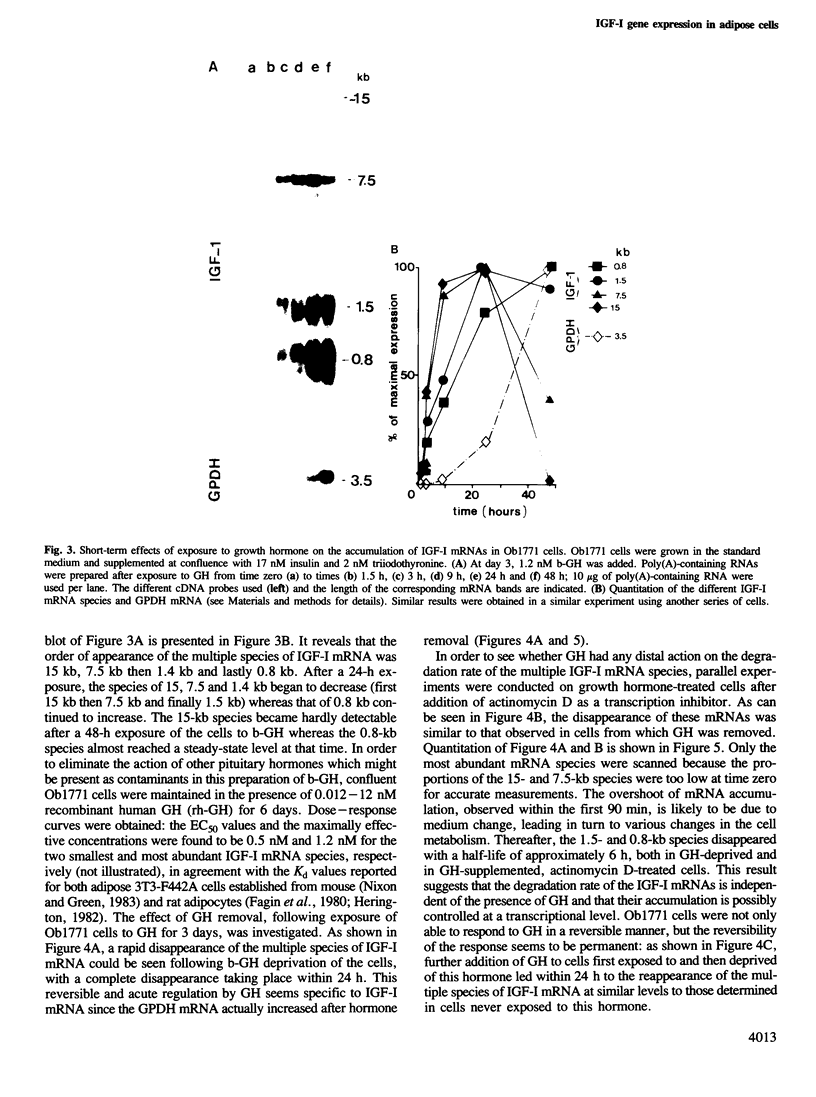
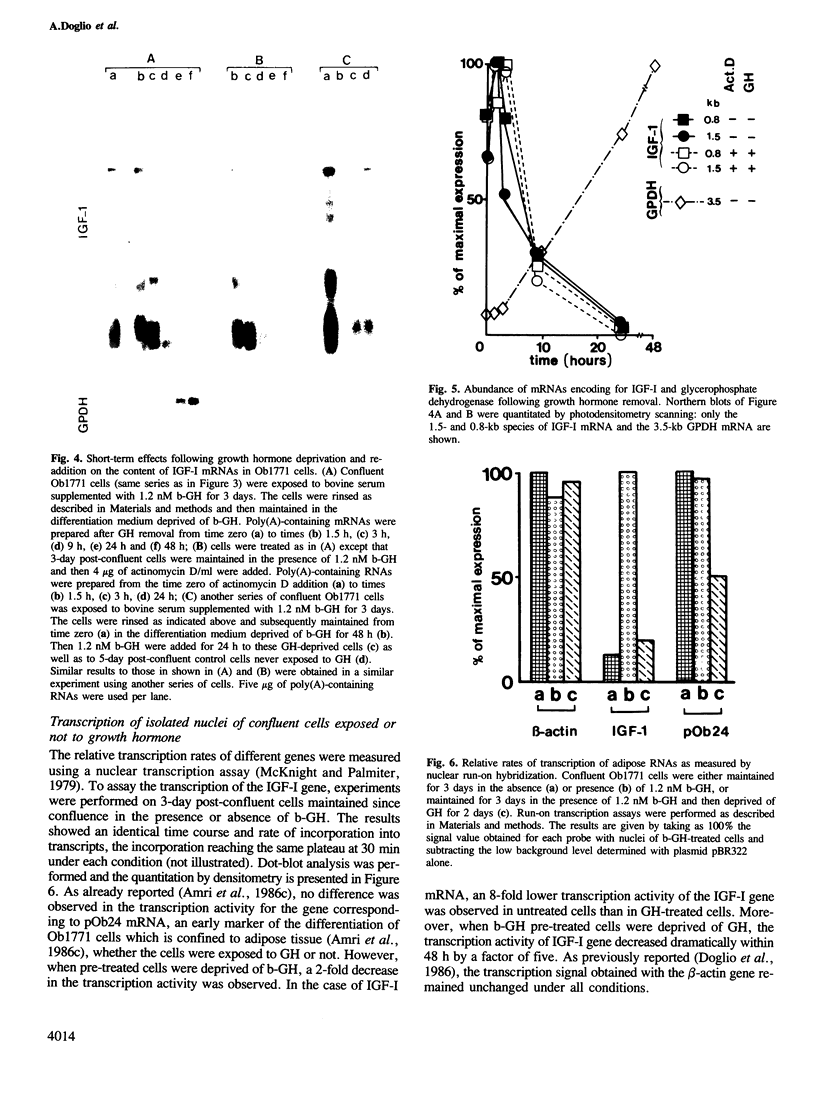
Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) is a mitogenic polypeptide that is thought to play, under the control of growth hormone, a role in fetal development as well as post-natally. The direct effect of growth hormone on the regulation of the expression of IGF-I gene was examined in adipose Ob1771 cells. Growth hormone regulates the abundance of multiple species of IGF-I mRNAs of 15, 7.5, 1.5 and 0.8 kb in a differentiation-dependent manner. The regulation of IGF-I gene expression is strikingly rapid (less than 2 h), reversible and takes place primarily at transcriptional level. Thus growth hormone can increase the cellular content of IGF-I mRNA encoding for a protein which could be involved in a paracrine/autocrine action during adipose tissue development.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amri E. Z., Barbaras R., Doglio A., Dani C., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Role of spermidine in the expression of late markers of adipose conversion. Effects of growth hormone. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):363–370. doi: 10.1042/bj2390363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Etienne J., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Adipose cell differentiation: evidence for a two-step process in the polyamine-dependent Ob1754 clonal line. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):115–122. doi: 10.1042/bj2380115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amri E. Z., Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Coupling of growth arrest and expression of early markers during adipose conversion of preadipocyte cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):903–910. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91165-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Gerhard D. S., Fong N. M., Sanchez-Pescador R., Rall L. B. Isolation of the human insulin-like growth factor genes: insulin-like growth factor II and insulin genes are contiguous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Stempien M. M., Fong N. M., Rall L. B. Sequences of liver cDNAs encoding two different mouse insulin-like growth factor I precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7873–7882. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Ercole A. J., Stiles A. D., Underwood L. E. Tissue concentrations of somatomedin C: further evidence for multiple sites of synthesis and paracrine or autocrine mechanisms of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Doglio A., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Expression of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene and its insulin regulation during differentiation of preadipose cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):468–475. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90304-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deslex S., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Development of a chemically defined serum-free medium for differentiation of rat adipose precursor cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jan;168(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90412-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doglio A., Dani C., Grimaldi P., Ailhaud G. Growth hormone regulation of the expression of differentiation-dependent genes in preadipocyte Ob1771 cells. Biochem J. 1986 Aug 15;238(1):123–129. doi: 10.1042/bj2380123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fagin K. D., Lackey S. L., Reagan C. R., DiGirolamo M. Specific binding of growth hormone by rat adipocytes. Endocrinology. 1980 Aug;107(2):608–615. doi: 10.1210/endo-107-2-608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. E., Rechler M. M., Brown A. L., Frunzio R., Romanus J. A., Bruni C. B., Whitfield H. J., Nissley S. P., Seelig S., Berry S. Coordinate developmental regulation of high and low molecular weight mRNAs for rat insulin-like growth factor II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4519–4523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Kehinde O. Formation of normally differentiated subcutaneous fat pads by an established preadipose cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Oct;101(1):169–171. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Morikawa M., Nixon T. A dual effector theory of growth-hormone action. Differentiation. 1985;29(3):195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1985.tb00316.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi P., Czerucka D., Rassoulzadegan M., Cuzin F., Ailhaud G. ob17 cells transformed by the middle-T-only gene of polyoma virus differentiate in vitro and in vivo into adipose cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5440–5444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi P., Djian P., Forest C., Poli P., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Lipogenic and mitogenic effects of insulin during conversion of Ob17 cells to adipose-like cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1983 Mar;29(3):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(83)90017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi P., Djian P., Negrel R., Ailhaud G. Differentiation of Ob17 preadipocytes to adipocytes: requirement of adipose conversion factor(s) for fat cell cluster formation. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):687–692. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Edén S., Jansson J. O. Mode of action of pituitary growth hormone on target cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:483–499. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaksson O. G., Jansson J. O., Gause I. A. Growth hormone stimulates longitudinal bone growth directly. Science. 1982 Jun 11;216(4551):1237–1239. doi: 10.1126/science.7079756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund P. K., Moats-Staats B. M., Hynes M. A., Simmons J. G., Jansen M., D'Ercole A. J., Van Wyk J. J. Somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor-II mRNAs in rat fetal and adult tissues. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14539–14544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews L. S., Norstedt G., Palmiter R. D. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I gene expression by growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9343–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight G. S., Palmiter R. D. Transcriptional regulation of the ovalbumin and conalbumin genes by steroid hormones in chick oviduct. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):9050–9058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikawa M., Nixon T., Green H. Growth hormone and the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):783–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90440-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon T., Green H. Contribution of growth hormone to the adipogenic activity of serum. Endocrinology. 1984 Feb;114(2):527–532. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-2-527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon T., Green H. Properties of growth hormone receptors in relation to the adipose conversion of 3T3 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):291–296. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. T., Jr, Brown A. L., Graham D. E., Seelig S., Berry S., Gabbay K. H., Rechler M. M. Growth hormone regulates the abundance of insulin-like growth factor I RNA in adult rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10025–10028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Pollock K. M., Didier D. K., Krivi G. G. Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4828–4832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P. Two insulin-like growth factor I messenger RNAs are expressed in human liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(1):77–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell S. M., Spencer E. M. Local injections of human or rat growth hormone or of purified human somatomedin-C stimulate unilateral tibial epiphyseal growth in hypophysectomized rats. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2563–2567. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlechter N. L., Russell S. M., Spencer E. M., Nicoll C. S. Evidence suggesting that the direct growth-promoting effect of growth hormone on cartilage in vivo is mediated by local production of somatomedin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7932–7934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Green H. The generation of insulin-like growth factor-1--sensitive cells by growth hormone action. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.3726546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]