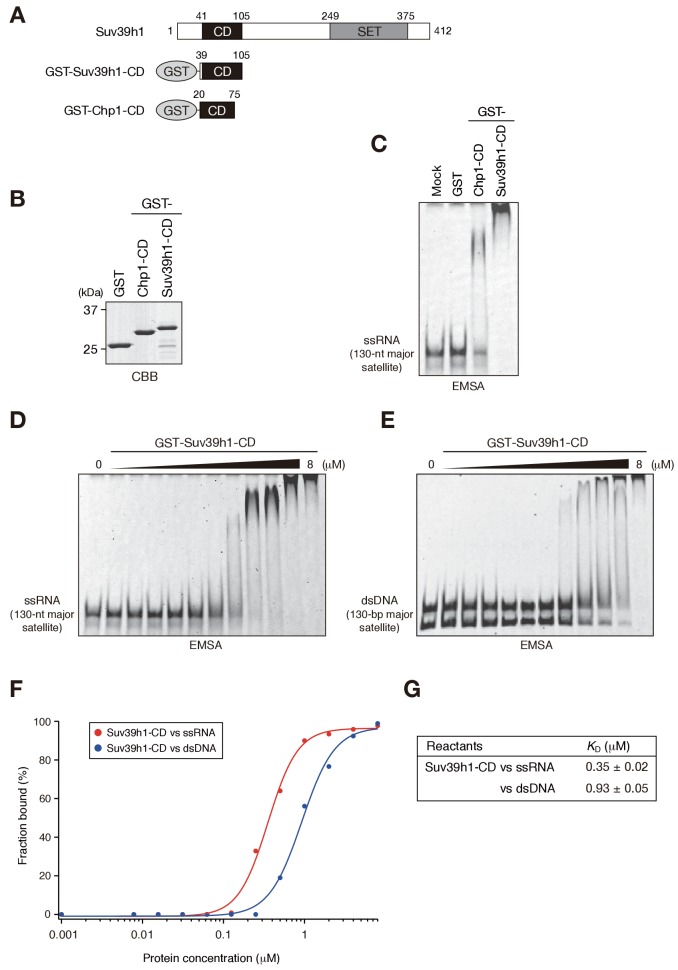
Figure 1. Suv39h1-CD can bind nucleic acids.
(A) Schematic of full-length Suv39h1, GST-fused Suv39h1-CD (39–105), and S. pombe Chp1-CD (20–75). (B) The recombinant GST-fused proteins used in (C); these proteins were visualized by CBB staining. (C) An EMSA using GST-fused proteins. 8 μM of GST or GST-fusion was used in one assay. Fluorescein-labeled 130-nt major satellite ssRNA was used as a probe. (D and E) Titration EMSAs using GST-Suv39h1-CD (0–8 μM with 0.5-fold dilutions) incubated with (D) 130-nt ssRNA or (E) 130 bp dsDNA. DNA probe was detected as doublet bands in gels, because the number of the fluorescent dye, which was conjugated at the single or both 5’-ends, could slightly affect the migration. (F) The binding isotherm of Suv39h1-CD to ssRNA and dsDNA; plots were calculated from the unbound fractions. (G) The dissociation constants measured by titration ssRNA and dsDNA EMSA experiments (D and E).