Abstract
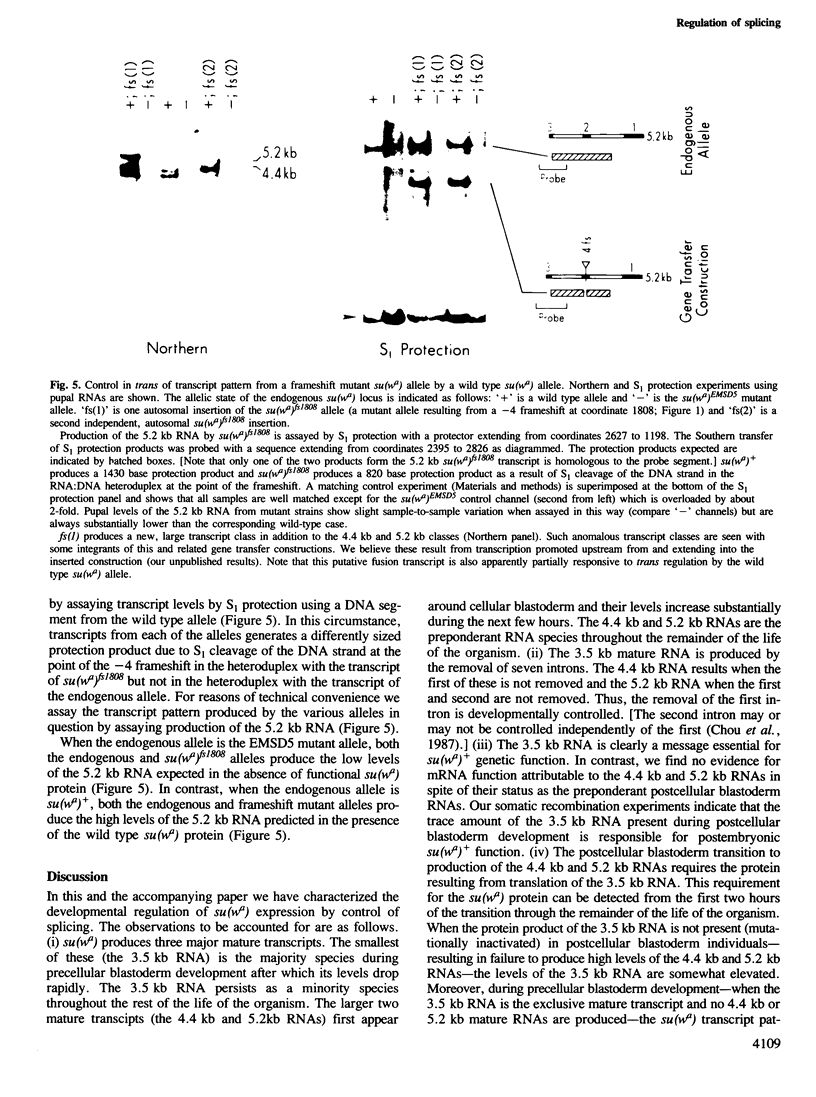
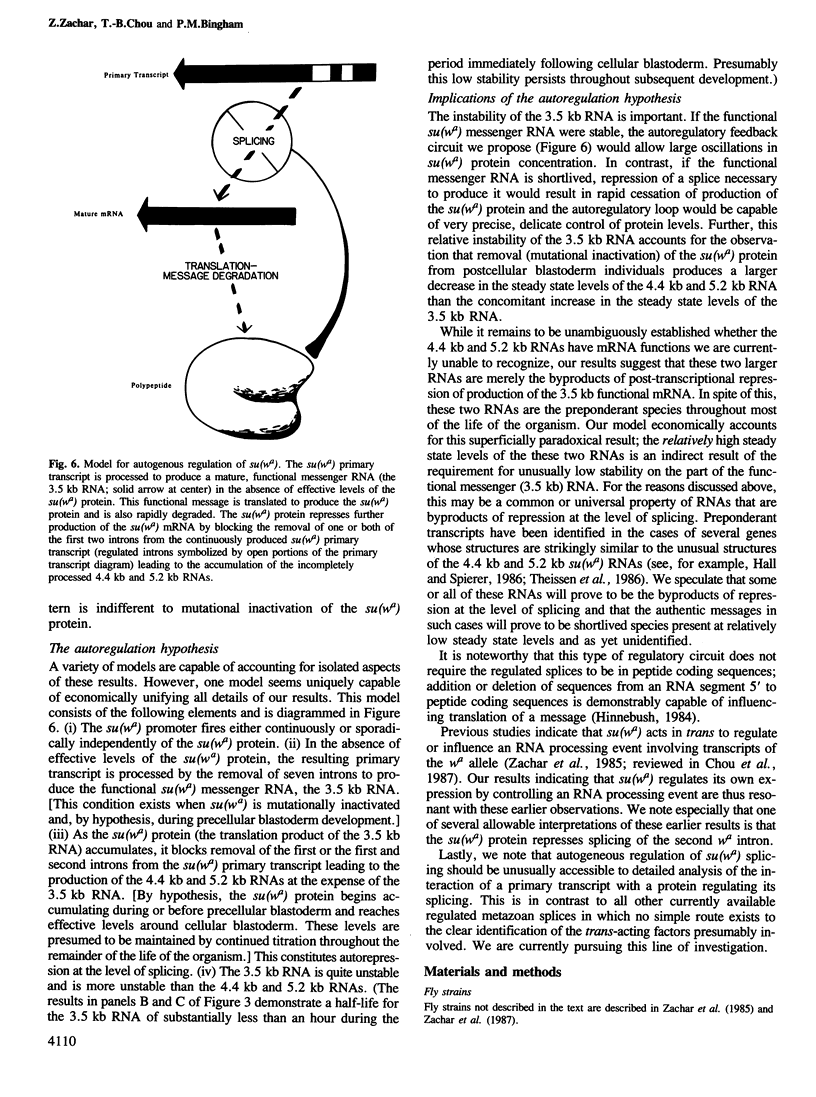
Expression of the presumptive regulatory gene, suppressor-of-white-apricot [su(wa)], is controlled at the level of splicing. Results reported here indicate that this control represents autorepression of su(wa) expression. Specifically, reverse genetic studies demonstrate that the 3.5 kb mature su(wa) RNA (produced by removal of seven introns) is a message essential for su(wa)+ function and indicate that the abundant 4.4 kb and 5.2 kb mature su(wa) RNAs (resulting when the first or first and second of the seven introns are not removed) are, unexpectedly, byproducts of repression of production of the functional 3.5 kb RNA. Moreover, several experiments indicate that this repression of splices necessary to produce the 3.5 kb RNA is dependent on the translation product of the 3.5 kb RNA itself. We propose that this regulatory gene autoregulates its expression by controlling splicing of its primary transcript.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benyajati C., Spoerel N., Haymerle H., Ashburner M. The messenger RNA for alcohol dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster differs in its 5' end in different developmental stages. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90341-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham P. M., Zachar Z. Evidence that two mutations, wDZL and z1, affecting synapsis-dependent genetic behavior of white are transcriptional regulatory mutations. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):819–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou T. B., Zachar Z., Bingham P. M. Developmental expression of a regulatory gene is programmed at the level of splicing. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02755.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison D., Chapman C. H., Wedeen C., Bingham P. M. Genetic and physical studies of a portion of the white locus participating in transcriptional regulation and in synapsis-dependent interactions in Drosophila adult tissues. Genetics. 1985 Jul;110(3):479–494. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.3.479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori Y., Shiba T., Kanaya S., Inouye S., Yuki S., Saigo K. The nucleotide sequences of copia and copia-related RNA in Drosophila virus-like particles. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):773–776. doi: 10.1038/315773a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5' leader. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu N., Messing J. The making of strand-specific M13 probes. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90143-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karess R. E., Rubin G. M. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90534-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., O'Hare K., Rubin G. M. Effects of transposable element insertions on RNA encoded by the white gene of Drosophila. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):471–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90502-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marlor R. L., Parkhurst S. M., Corces V. G. The Drosophila melanogaster gypsy transposable element encodes putative gene products homologous to retroviral proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1129–1134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connell P. O., Rosbash M. Sequence, structure, and codon preference of the Drosophila ribosomal protein 49 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5495–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Bröckl C. Transcription of the Drosophila white locus and some of its mutants. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):563–568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Vectors for P element-mediated gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6341–6351. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theissen H., Etzerodt M., Reuter R., Schneider C., Lottspeich F., Argos P., Lührmann R., Philipson L. Cloning of the human cDNA for the U1 RNA-associated 70K protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3209–3217. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04631.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Davison D., Garza D., Bingham P. M. A detailed developmental and structural study of the transcriptional effects of insertion of the Copia transposon into the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1985 Nov;111(3):495–515. doi: 10.1093/genetics/111.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachar Z., Garza D., Chou T. B., Goland J., Bingham P. M. Molecular cloning and genetic analysis of the suppressor-of-white-apricot locus from Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2498–2505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]