Abstract
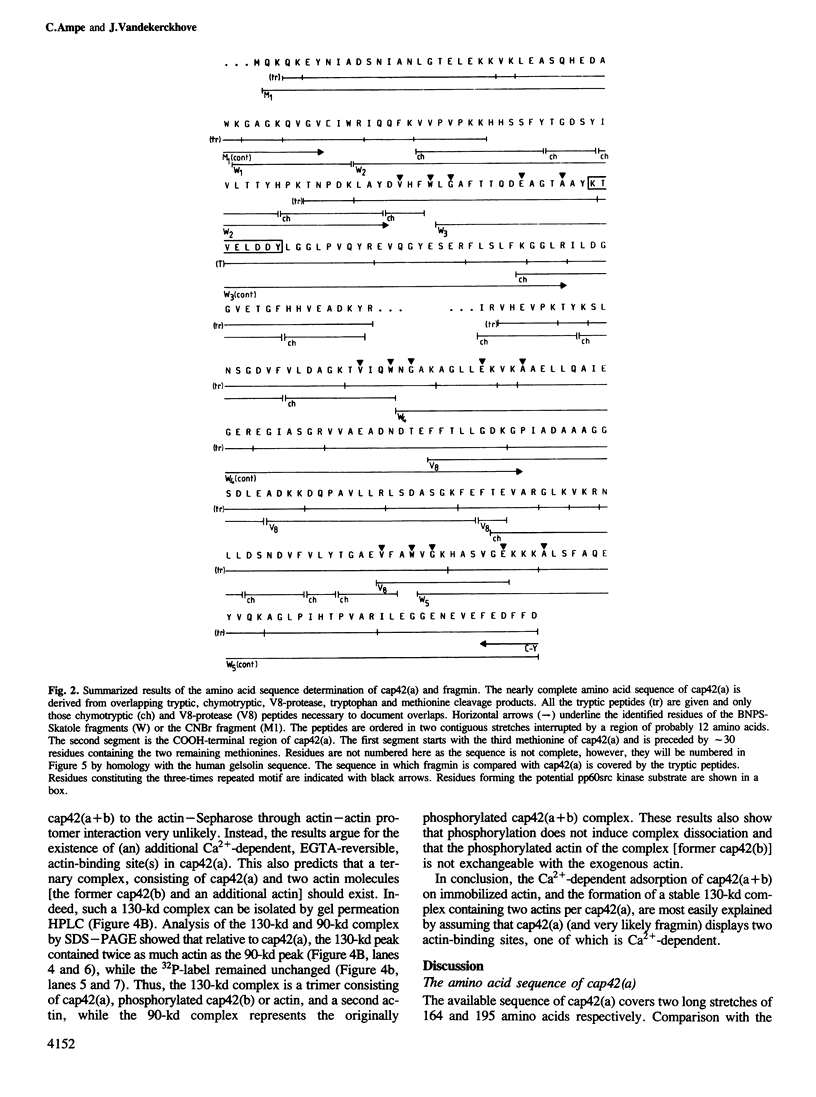
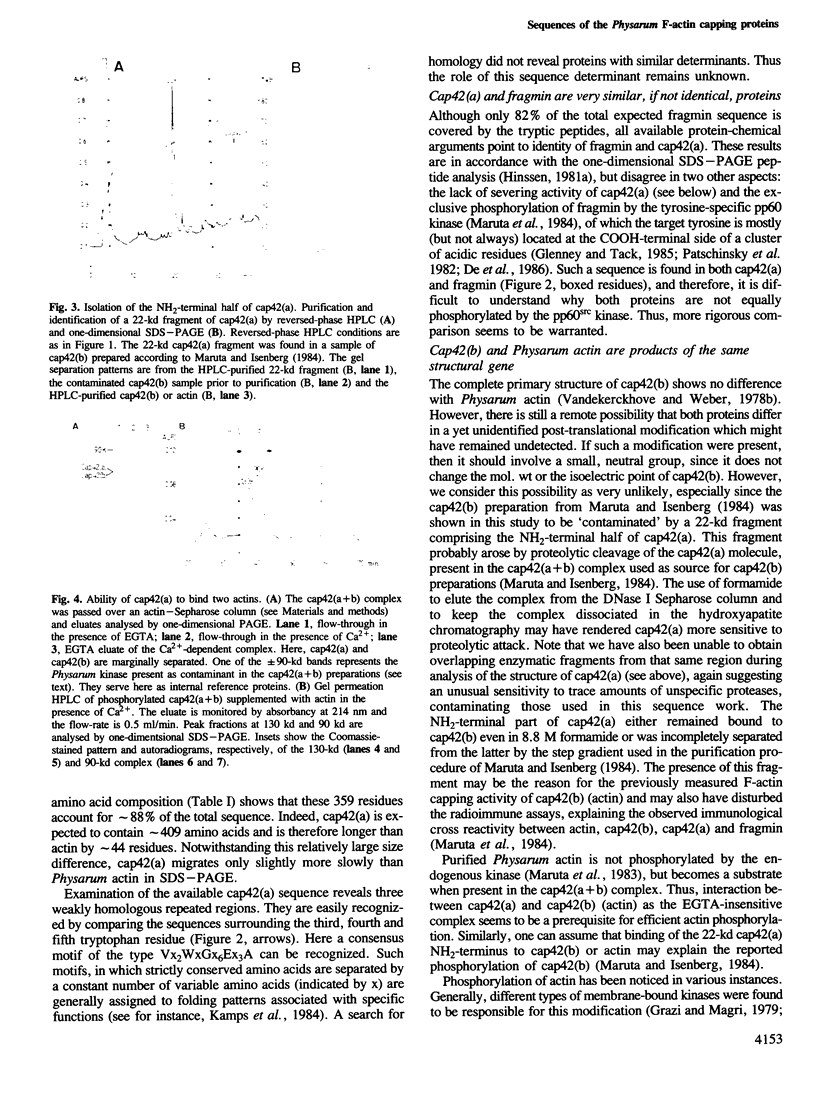
We have carried out a primary structure analysis of the F-actin capping proteins of Physarum polycephalum. Cap42(b) was completely sequenced and was found to be identical with Physarum actin. Approximately 88% of the sequence of cap42(a) was determined. Cap42(a) and fragmin were found to be identical by amino acid composition, isoelectric point, mol. wt, elution time on reversed-phase chromatography and amino acid sequence of their tryptic peptides. The available sequence of cap42(a) is greater than 36% homologous with the NH2-terminal 42-kd domain of human gelsolin. A highly homologous region of 16 amino acids is also shared between cap42(a), gelsolin and the Acanthamoeba profilins. Cap42(a) binds two actin molecules in a similar way to gelsolin suggesting a mechanism of F-actin modulation that has been conserved during evolution.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J., Brenner S. L., Tobacman L., Korn E. D. The amino acid sequence of Acanthamoeba profilin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):834–840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. R., Hare P. E. O-phthalaldehyde: fluorogenic detection of primary amines in the picomole range. Comparison with fluorescamine and ninhydrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):619–622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bidlingmeyer B. A., Cohen S. A., Tarvin T. L. Rapid analysis of amino acids using pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr. 1984 Dec 7;336(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)85133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A., Weber K. Villin is a major protein of the microvillus cytoskeleton which binds both G and F actin in a calcium-dependent manner. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):839–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. S., Yamamoto K., Spudich J. A. A 40,000-dalton protein from Dictyostelium discoideum affects assembly properties of actin in a Ca2+-dependent manner. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):205–210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Hwo S. Definition of an N-terminal actin-binding domain and a C-terminal Ca2+ regulatory domain in human brevin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1439–1446. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J., Kurth M. C. Actin-gelsolin interactions. Evidence for two actin-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7480–7487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaponnier C., Borgia R., Rungger-Brändle E., Weil R., Gabbiani G. An actin-destabilizing factor is present in human plasma. Experientia. 1979 Aug 15;35(8):1039–1041. doi: 10.1007/BF01949928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaponnier C., Janmey P. A., Yin H. L. The actin filament-severing domain of plasma gelsolin. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1473–1481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M. A common philosophy and FORTRAN 77 software package for implementing and searching sequence databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):397–407. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. H., Elzinga M. The primary structure of actin from rabbit skeletal muscle. Completion and analysis of the amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coué M., Korn E. D. Interaction of plasma gelsolin with G-actin and F-actin in the presence and absence of calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15033–15041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De B. K., Misono K. S., Lukas T. J., Mroczkowski B., Cohen S. A calcium-dependent 35-kilodalton substrate for epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase isolated from normal tissue. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13784–13792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSS E., WITKOP B. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: the methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jun;237:1856–1860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Geisler N., Kaulfus P., Weber K. Demonstration of at least two different actin-binding sites in villin, a calcium-regulated modulator of F-actin organization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):8156–8161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Tack B. F. Amino-terminal sequence of p36 and associated p10: identification of the site of tyrosine phosphorylation and homology with S-100. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7884–7888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Eisenberg E., Korn E. D. Characterization of cytoplasmic actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii by a new method. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grazi E., Magri E. Phosphorylation of actin and removal of its inhibitory activity on pancreatic DNAase I by liver plasma membranes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 15;104(2):284–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80833-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., Schwartz J. H. Characterization of brevin, a serum protein that shortens actin filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6798–6802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasegawa T., Takahashi S., Hayashi H., Hatano S. Fragmin: a calcium ion sensitive regulatory factor on the formation of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2677–2683. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi R., Moore S., Stein W. H. Carboxypeptidase from yeast. Large scale preparation and the application to COOH-terminal analysis of peptides and proteins. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 10;248(7):2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Hunkapiller M. W., Hood L. E., Dreyer W. J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7990–7997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinssen H. An actin-modulating protein from Physarum polycephalum. I. Isolation and purification. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;23(2):225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinssen H. An actin-modulating protein from Physarum polycephalum. II. Ca++-dependence and other properties. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;23(2):234–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstein R., Hershkowitz M., Gozes I., Samuel D. The characterization and phosphorylation of an actin-like protein in synaptosomal membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jul 24;624(1):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(80)90234-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang K. S., Wallner B. P., Mattaliano R. J., Tizard R., Burne C., Frey A., Hession C., McGray P., Sinclair L. K., Chow E. P. Two human 35 kd inhibitors of phospholipase A2 are related to substrates of pp60v-src and of the epidermal growth factor receptor/kinase. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90736-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurny A. C., Wnuk W. A novel 40,000 Da Ca2+-dependent actin modulator from bovine brain. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 29;206(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81344-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Chaponnier C., Lind S. E., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P., Yin H. L. Interactions of gelsolin and gelsolin-actin complexes with actin. Effects of calcium on actin nucleation, filament severing, and end blocking. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3714–3723. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Stossel T. P., Lind S. E. Sequential binding of actin monomers to plasma gelsolin and its inhibition by vitamin D-binding protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):72–79. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90878-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Taylor S. S., Sefton B. M. Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase have homologous ATP-binding sites. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):589–592. doi: 10.1038/310589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M. I. Los Alamos sequence analysis package for nucleic acids and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 11;10(1):183–196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.1.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwiatkowski D. J., Stossel T. P., Orkin S. H., Mole J. E., Colten H. R., Yin H. L. Plasma and cytoplasmic gelsolins are encoded by a single gene and contain a duplicated actin-binding domain. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):455–458. doi: 10.1038/323455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machicao F., Urumow T., Wieland O. H. Evidence for phosphorylation of actin by the insulin receptor-associated protein kinase from human placenta. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):76–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. II. Ca2+-dependent f-actin-capping activity of subunit a and its regulation by phosphorylation of subunit b. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10151–10158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. Subunit b is a DNase I-binding and F-actin capping protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5208–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G., Schreckenbach T., Hallmann R., Risse G., Shibayama T., Hesse J. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. I. Ca2+/actin-dependent inhibition of its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10144–10150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Knoerzer W., Hinssen H., Isenberg G. Regulation of actin polymerization by non-polymerizable actin-like proteins. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):424–427. doi: 10.1038/312424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Graves T. A., Wharton K. A., Falco N., Howe C. L. Regulation of microvillus structure: calcium-dependent solation and cross-linking of actin filaments in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):809–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norberg R., Thorstensson R., Utter G., Fagraeus A. F-Actin-depolymerizing activity of human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):575–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström L. E., Lindberg U., Kendrick-Jones J., Jakes R. The amino acid sequence of profilin from calf spleen. FEBS Lett. 1979 May 1;101(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnuma M., Mabuchi I. The 45K molecular weight actin-modulating protein from sea urchin eggs forms a complex with actin in the presence of calcium ions. J Biochem. 1986 Sep;100(3):817–820. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Esch F. S., Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sequence of amino acids surrounding sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Actin and actin-binding proteins. A critical evaluation of mechanisms and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:987–1035. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Cooper J. A. Quantitative analysis of the effect of Acanthamoeba profilin on actin filament nucleation and elongation. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6631–6641. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saris C. J., Tack B. F., Kristensen T., Glenney J. R., Jr, Hunter T. The cDNA sequence for the protein-tyrosine kinase substrate p36 (calpactin I heavy chain) reveals a multidomain protein with internal repeats. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):201–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90737-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonobe S., Takahashi S., Hatano S., Kuroda K. Phosphorylation of Amoeba G-actin and its effect on actin polymerization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14837–14843. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southwick F. S., DiNubile M. J. Rabbit alveolar macrophages contain a Ca2+-sensitive, 41,000-dalton protein which reversibly blocks the "barbed" ends of actin filaments but does not sever them. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14191–14195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg R. A. Actin nascent chains are substrates for cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stossel T. P., Chaponnier C., Ezzell R. M., Hartwig J. H., Janmey P. A., Kwiatkowski D. J., Lind S. E., Smith D. B., Southwick F. S., Yin H. L. Nonmuscle actin-binding proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:353–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.002033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawata M., Kobayashi R., Mace M. L., Nielsen T. B., Field J. B. Isolation of an actin polymerization stimulator from bovine thyroid plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Mar 16;111(2):415–423. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J. S., Sandoval I. V. Purification and characterization of a new mammalian serum protein with the ability to inhibit actin polymerization and promote depolymerization of actin filaments. Biochemistry. 1982 Aug 17;21(17):3983–3991. doi: 10.1021/bi00260a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Chordate muscle actins differ distinctly from invertebrate muscle actins. The evolution of the different vertebrate muscle actins. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 5;179(3):391–413. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Mammalian cytoplasmic actins are the products of at least two genes and differ in primary structure in at least 25 identified positions from skeletal muscle actins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of Physarum actin. Nature. 1978 Dec 14;276(5689):720–721. doi: 10.1038/276720a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh T. P., Weber A., Higgins J., Bonder E. M., Mooseker M. S. Effect of villin on the kinetics of actin polymerization. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 5;23(12):2613–2621. doi: 10.1021/bi00307a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegner A. Head to tail polymerization of actin. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):139–150. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Kwiatkowski D. J., Mole J. E., Cole F. S. Structure and biosynthesis of cytoplasmic and secreted variants of gelsolin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5271–5276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Control of cytoplasmic actin gel-sol transformation by gelsolin, a calcium-dependent regulatory protein. Nature. 1979 Oct 18;281(5732):583–586. doi: 10.1038/281583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin H. L., Stossel T. P. Purification and structural properties of gelsolin, a Ca2+-activated regulatory protein of macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9490–9493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]