Abstract
The human "26-kd protein' is a secreted glycoprotein expressed, for example, in (blood) leukocytes, in epithelial cells treated with various inducers, but most strongly in interleukin-1 (IL-1)-treated fibroblasts. After finding it has antiviral and 2-5A synthetase-inducing activity, one group of authors called this protein IFN-beta 2. However, recently the full-length 26-kd cDNA sequence was shown to be identical with that of a B-cell-differentiating lymphokine called BSF-2, and another report suggested that the 26-kd protein could support the growth of some transformed murine B cell lines. To define its biological activities, we expressed the recombinant 26-kd protein by translating in Xenopus laevis oocytes a pure, synthetic chimeric mRNA containing the 26-kd protein coding region surrounded by Xenopus laevis beta-globin untranslated regions. A similar construction, but containing the HuIFN-beta cDNA coding region, was used to produce HuIFN-beta by the same procedure. Both recombinant glycoproteins were secreted, glycosylated, and their amounts were measured by [35S]methionine incorporation by the oocyte. Here we show that the recombinant 26-kd protein exhibits a high growth factor activity when assayed on an IL-HP1-dependent murine B cell hybridoma (sp. act. approximately 2 X 10(8) U/mg) as well as a potent differentiating activity on human CESS cells (sp. act. approximately 5 X 10(7) U/mg). While rHuIFN-beta was inactive in the latter two assays, it had the expected antiviral activity of 1-5 X 10(8) U/mg. The parallel recombinant 26-kd protein preparations had no detectable antiviral activity (i.e. a maximal specific activity of 1-3 X 10(2) U/mg, if any). The 26-kd protein is thus clearly an interleukin, and considering the confusing nomenclature now in use, this factor may better be renamed "interleukin 6'.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chebath J., Merlin G., Metz R., Benech P., Revel M. Interferon-induced 56,000 Mr protein and its mRNA in human cells: molecular cloning and partial sequence of the cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1213–1226. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Content J., De Wit L., Pierard D., Derynck R., De Clercq E., Fiers W. Secretory proteins induced in human fibroblasts under conditions used for the production of interferon beta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2768–2772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
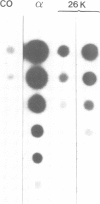
- Content J., De Wit L., Poupart P., Opdenakker G., Van Damme J., Billiau A. Induction of a 26-kDa-protein mRNA in human cells treated with an interleukin-1-related, leukocyte-derived factor. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Oct 15;152(2):253–257. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09191.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Cheroutre H., Degrave W., Fiers W. Simple, efficient in vitro synthesis of capped RNA useful for direct expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6353–6362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Remaut E., Saman E., Stanssens P., De Clercq E., Content J., Fiers W. Expression of human fibroblast interferon gene in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):193–197. doi: 10.1038/287193a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B. Changes in somatic cell nuclei inserted into growing and maturing amphibian oocytes. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1968 Nov;20(3):401–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegeman G., Content J., Volckaert G., Derynck R., Tavernier J., Fiers W. Structural analysis of the sequence coding for an inducible 26-kDa protein in human fibroblasts. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):625–632. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Taga T., Nakano N., Yasukawa K., Kashiwamura S., Shimizu K., Nakajima K., Pyun K. H., Kishimoto T. Purification to homogeneity and characterization of human B-cell differentiation factor (BCDF or BSFp-2). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5490–5494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano T., Yasukawa K., Harada H., Taga T., Watanabe Y., Matsuda T., Kashiwamura S., Nakajima K., Koyama K., Iwamatsu A. Complementary DNA for a novel human interleukin (BSF-2) that induces B lymphocytes to produce immunoglobulin. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):73–76. doi: 10.1038/324073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight E., Jr, Hunkapiller M. W., Korant B. D., Hardy R. W., Hood L. E. Human fibroblast interferon: amino acid analysis and amino terminal amino acid sequence. Science. 1980 Feb 1;207(4430):525–526. doi: 10.1126/science.7352259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohase M., Henriksen-DeStefano D., May L. T., Vilcek J., Sehgal P. B. Induction of beta 2-interferon by tumor necrosis factor: a homeostatic mechanism in the control of cell proliferation. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):659–666. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90780-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegren U. Measurement of cell numbers by means of the endogenous enzyme hexosaminidase. Applications to detection of lymphokines and cell surface antigens. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poupart P., De Wit L., Content J. Induction and regulation of the 26-kDa protein in the absence of synthesis of beta-interferon mRNA in human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;143(1):15–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08332.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinderknecht E., O'Connor B. H., Rodriguez H. Natural human interferon-gamma. Complete amino acid sequence and determination of sites of glycosylation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6790–6797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Wakefield L. M., Roche N. S., Stern D. F., Sporn M. B. Type beta transforming growth factor: a bifunctional regulator of cellular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):119–123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Cayphas S., Vink A., Uyttenhove C., Coulie P. G., Rubira M. R., Simpson R. J. Purification and NH2-terminal amino acid sequence of a T-cell-derived lymphokine with growth factor activity for B-cell hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9679–9683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Snick J., Vink A., Cayphas S., Uyttenhove C. Interleukin-HP1, a T cell-derived hybridoma growth factor that supports the in vitro growth of murine plasmacytomas. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):641–649. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaquero C., Sanceau J., Weissenbach J., Beranger F., Falcoff R. Regulation of human gamma-interferon and beta-interferon gene expression in PHA-activated lymphocytes. J Interferon Res. 1986 Apr;6(2):161–170. doi: 10.1089/jir.1986.6.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wathelet M., Moutschen S., Defilippi P., Cravador A., Collet M., Huez G., Content J. Molecular cloning, full-length sequence and preliminary characterization of a 56-kDa protein induced by human interferons. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09452.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Chernajovsky Y., Zeevi M., Shulman L., Soreq H., Nir U., Wallach D., Perricaudet M., Tiollais P., Revel M. Two interferon mRNAs in human fibroblasts: in vitro translation and Escherichia coli cloning studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7152–7156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissenbach J., Zeevi M., Landau T., Revel M. Identification of the translation products of human fibroblast interferon mRNA in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):1–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13153.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Ruggieri R., Korn J. H., Revel M. Structure and expression of cDNA and genes for human interferon-beta-2, a distinct species inducible by growth-stimulatory cytokines. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2529–2537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04531.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]