Abstract
Neutral endopeptidase (EC 3.4.24.11) is a major constituent of kidney brush border membranes. It is also present in the brain where it has been shown to be involved in the inactivation of opioid peptides, methionine- and leucine-enkephalins. For this reason this enzyme is often called 'enkephalinase'. In order to characterize the primary structure of the enzyme, oligonucleotide probes were designed from partial amino acid sequences and used to isolate clones from kidney cDNA libraries. Sequencing of the cDNA inserts revealed the complete primary structure of the enzyme. Neutral endopeptidase consists of 750 amino acids. It contains a short N-terminal cytoplasmic domain (27 amino acids), a single membrane-spanning segment (23 amino acids) and an extracellular domain that comprises most of the protein mass. The comparison of the primary structure of neutral endopeptidase with that of thermolysin, a bacterial Zn-metallopeptidase, indicates that most of the amino acid residues involved in Zn coordination and catalytic activity in thermolysin are found within highly honmologous sequences in neutral endopeptidase.
Full text
PDF


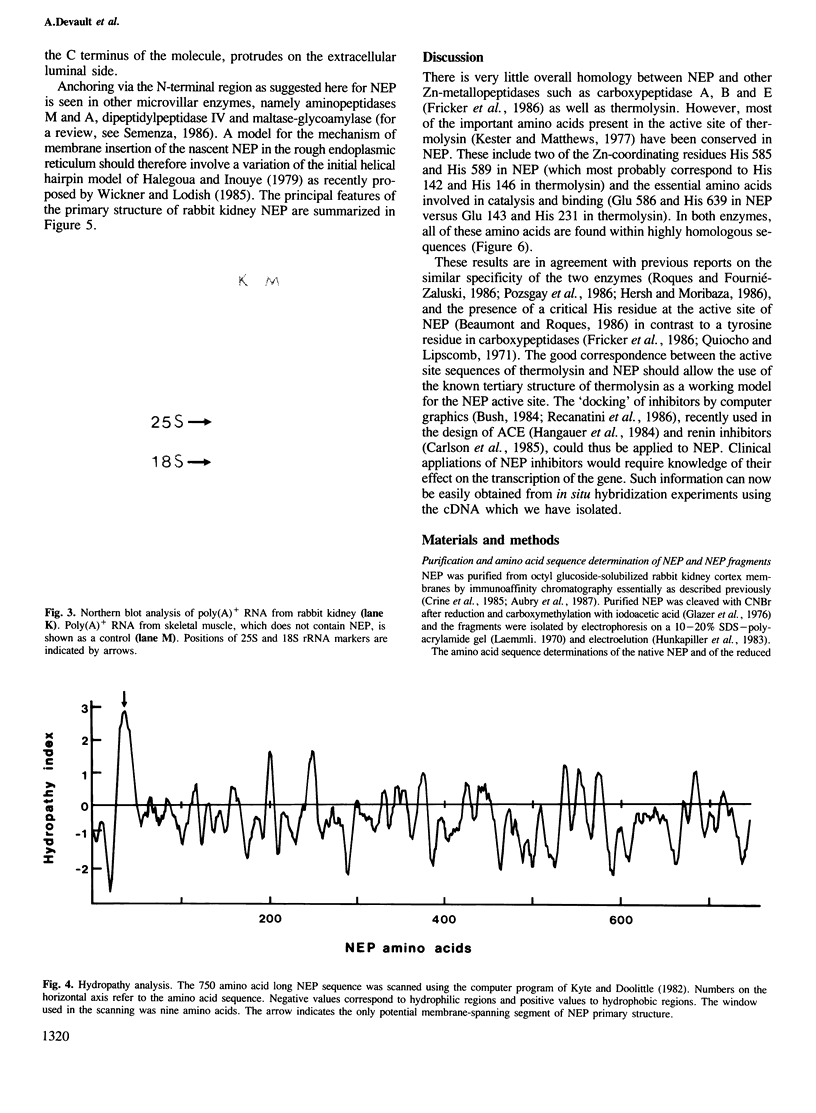
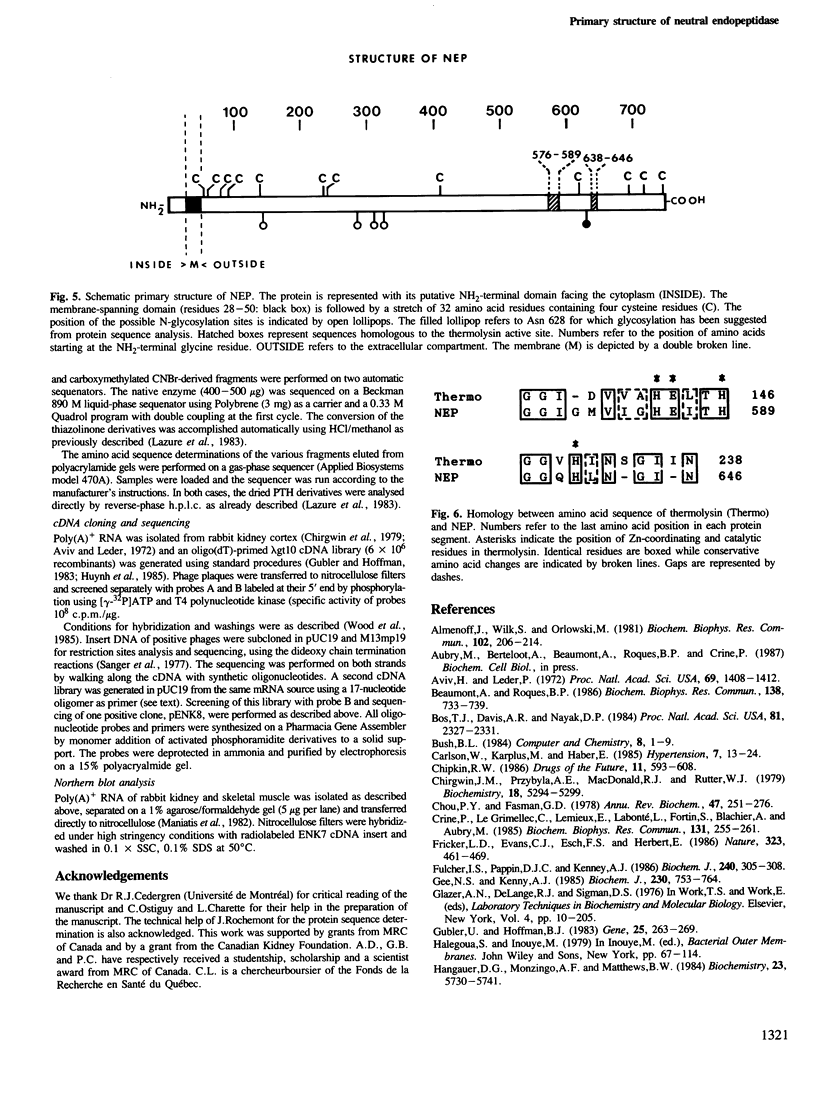

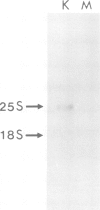
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almenoff J., Wilk S., Orlowski M. Membrane bound pituitary metalloendopeptidase: apparent identity to enkephalinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Sep 16;102(1):206–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91508-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaumont A., Roques B. P. Presence of a histidine at the active site of the neutral endopeptidase-24.11. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 14;139(2):733–739. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. NH2-terminal hydrophobic region of influenza virus neuraminidase provides the signal function in translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2327–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson W., Karplus M., Haber E. Construction of a model for the three-dimensional structure of human renal renin. Hypertension. 1985 Jan-Feb;7(1):13–26. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crine P., LeGrimellec C., Lemieux E., Labonté L., Fortin S., Blachier A., Aubry M. The production and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for the 94,000 dalton enkephalin-degrading peptidase from rabbit kidney brush border. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):255–261. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91796-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fricker L. D., Evans C. J., Esch F. S., Herbert E. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine carboxypeptidase E. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):461–464. doi: 10.1038/323461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulcher I. S., Pappin D. J., Kenny A. J. The N-terminal amino acid sequence of pig kidney endopeptidase-24.11 shows homology with pro-sucrase-isomaltase. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):305–308. doi: 10.1042/bj2400305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gee N. S., Kenny A. J. Proteins of the kidney microvillar membrane. The 130 kDa protein in pig kidney, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK5C1, is an ectoenzyme with aminopeptidase activity. Biochem J. 1985 Sep 15;230(3):753–764. doi: 10.1042/bj2300753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hangauer D. G., Monzingo A. F., Matthews B. W. An interactive computer graphics study of thermolysin-catalyzed peptide cleavage and inhibition by N-carboxymethyl dipeptides. Biochemistry. 1984 Nov 20;23(24):5730–5741. doi: 10.1021/bi00319a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hersh L. B., Morihara K. Comparison of the subsite specificity of the mammalian neutral endopeptidase 24.11 (enkephalinase) to the bacterial neutral endopeptidase thermolysin. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6433–6437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Lujan E., Ostrander F., Hood L. E. Isolation of microgram quantities of proteins from polyacrylamide gels for amino acid sequence analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:227–236. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunziker W., Spiess M., Semenza G., Lodish H. F. The sucrase-isomaltase complex: primary structure, membrane-orientation, and evolution of a stalked, intrinsic brush border protein. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):227–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90739-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Codon usage and tRNA content in unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mol Biol Evol. 1985 Jan;2(1):13–34. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kester W. R., Matthews B. W. Comparison of the structures of carboxypeptidase A and thermolysin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7704–7710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laperche Y., Bulle F., Aissani T., Chobert M. N., Aggerbeck M., Hanoune J., Guellaën G. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of rat kidney gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):937–941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathe R. Synthetic oligonucleotide probes deduced from amino acid sequence data. Theoretical and practical considerations. J Mol Biol. 1985 May 5;183(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90276-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazure C., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Lallier R., St-Pierre S. Primary structure determination of Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin of porcine origin. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 May;61(5):287–292. doi: 10.1139/o83-039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfroy B., Swerts J. P., Guyon A., Roques B. P., Schwartz J. C. High-affinity enkephalin-degrading peptidase in brain is increased after morphine. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):523–526. doi: 10.1038/276523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsas R., Kenny A. J., Turner A. J. An immunohistochemical study of endopeptidase-24.11 ("enkephalinase") in the pig nervous system. Neuroscience. 1986 Aug;18(4):991–1012. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondetti M. A., Rubin B., Cushman D. W. Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science. 1977 Apr 22;196(4288):441–444. doi: 10.1126/science.191908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozsgay M., Michaud C., Liebman M., Orlowski M. Substrate and inhibitor studies of thermolysin-like neutral metalloendopeptidase from kidney membrane fractions. Comparison with bacterial thermolysin. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1292–1299. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quiocho F. A., Lipscomb W. N. Carboxypeptidase A: a protein and an enzyme. Adv Protein Chem. 1971;25:1–78. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60278-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recanatini M., Klein T., Yang C. Z., McClarin J., Langridge R., Hansch C. Quantitative structure-activity relationships and molecular graphics in ligand receptor interactions: amidine inhibition of trypsin. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Apr;29(4):436–446. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournie-Zaluski M. C. Enkephalin degrading enzyme inhibitors: a physiological way to new analgesics and psychoactive agents. NIDA Res Monogr. 1986;70:128–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Soroca E., Lecomte J. M., Malfroy B., Llorens C., Schwartz J. C. The enkephalinase inhibitor thiorphan shows antinociceptive activity in mice. Nature. 1980 Nov 20;288(5788):286–288. doi: 10.1038/288286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roques B. P., Lucas-Soroca E., Chaillet P., Costentin J., Fournié-Zaluski M. C. Complete differentiation between enkephalinase and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition by retro-thiorphan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3178–3182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Schwartz A. L., Lodish H. F. Sequence of human asialoglycoprotein receptor cDNA. An internal signal sequence for membrane insertion. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1979–1982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tam L. T., Engelbrecht S., Talent J. M., Gracy R. W., Erdös E. G. The importance of disulfide bridges in human endopeptidase (enkephalinase) after proteolytic cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):1187–1192. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Furthmayr H., Marchesi V. T. Primary structure of human erythrocyte glycophorin A. Isolation and characterization of peptides and complete amino acid sequence. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 31;17(22):4756–4770. doi: 10.1021/bi00615a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waksman G., Hamel E., Fournié-Zaluski M. C., Roques B. P. Autoradiographic comparison of the distribution of the neutral endopeptidase "enkephalinase" and of mu and delta opioid receptors in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1523–1527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W. T., Lodish H. F. Multiple mechanisms of protein insertion into and across membranes. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):400–407. doi: 10.1126/science.4048938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]