Abstract
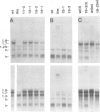
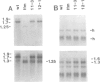
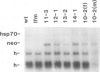
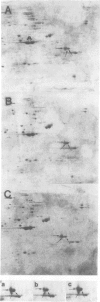
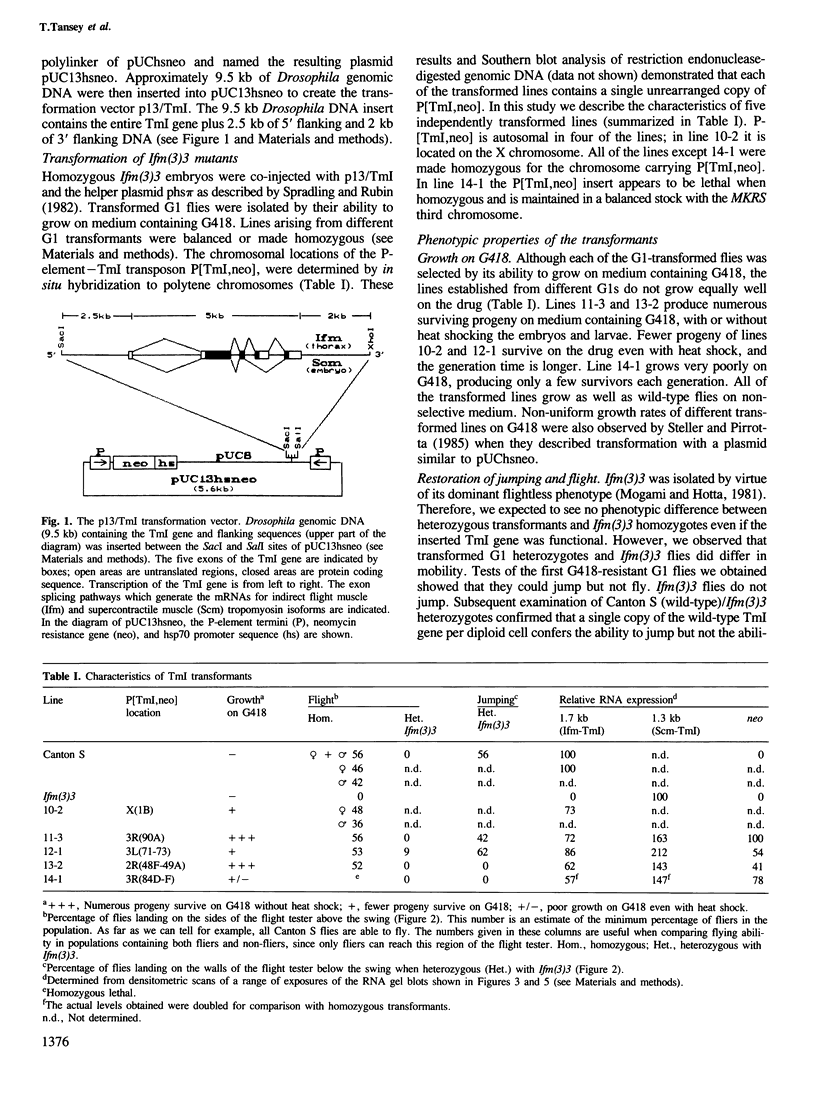
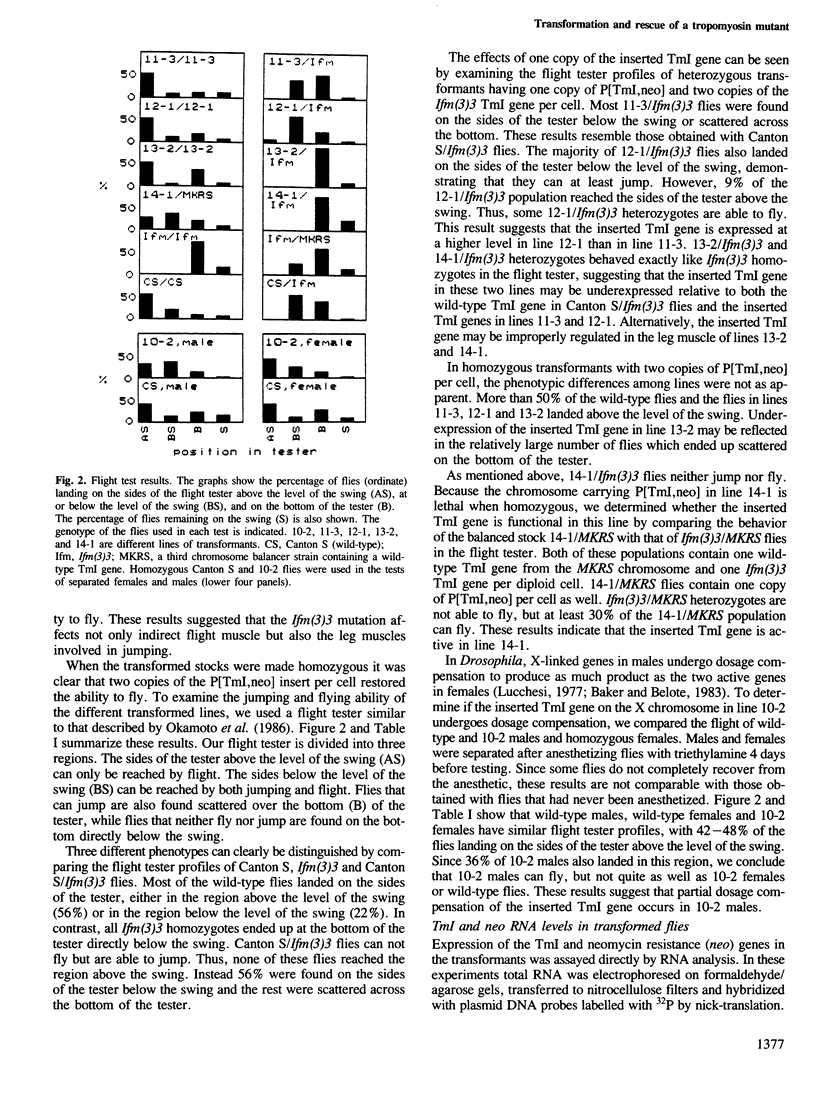
In the Drosophila flightless mutant Ifm(3)3, a transposable element inserted into the alternatively spliced fourth exon of the tropomyosin I (TmI) gene prevents proper expression of Ifm-TmI, the tropomyosin isoform found in indirect flight muscle. We have rescued the flightless phenotype of Ifm(3)3 flies using P-element-mediated transformation with a segment of the Drosophila genome containing the wild-type TmI gene plus 2.5 kb of 5' flanking and 2 kb of 3' flanking DNA. The inserted TmI gene is expressed with the proper developmental and tissue specificity, although its level of expression varies among the five transformed lines examined. These conclusions are based on analyses of flight, myofibrillar morphology, and TmI RNA and protein levels. A minimum of two copies of the inserted TmI gene per cell is necessary to restore flight to most of the flies in each line. We also show that the Ifm-TmI isoform is expressed in the leg muscle of wild-type flies and is decreased in Ifm(3)3 leg muscle. Homozygous Ifm(3)3 mutants do not jump. The ability to jump can be restored with a single copy of the wild-type TmI gene per cell.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker B. S., Belote J. M. Sex determination and dosage compensation in Drosophila melanogaster. Annu Rev Genet. 1983;17:345–393. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.17.120183.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Boardman M., Storti R. V. Alternative splicing of a Drosophila tropomyosin gene generates muscle tropomyosin isoforms with different carboxy-terminal ends. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2828–2836. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basi G. S., Storti R. V. Structure and DNA sequence of the tropomyosin I gene from Drosophila melanogaster. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):817–827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L., Storti R. V. Identification of a cytoplasmic tropomyosin gene linked to two muscle tropomyosin genes in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7123–7127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bautch V. L., Storti R. V., Mischke D., Pardue M. L. Organization and expression of Drosophila tropomyosin genes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 5;162(2):231–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., Mogami K., Donady J. J., Emerson C. P., Jr Drosophila muscle myosin heavy chain encoded by a single gene in a cluster of muscle mutations. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):393–397. doi: 10.1038/302393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boardman M., Basi G. S., Storti R. V. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a Drosophila tropomyosin gene are used to generate functional mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1763–1776. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourouis M., Richards G. Remote regulatory sequences of the Drosophila glue gene sgs3 as revealed by P-element transformation. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90149-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Ritchie K. A., Hammer R. E., O'Brien R. L., Arp B., Storb U. Expression of a microinjected immunoglobulin gene in the spleen of transgenic mice. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):332–336. doi: 10.1038/306332a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chada K., Magram J., Raphael K., Radice G., Lacy E., Costantini F. Specific expression of a foreign beta-globin gene in erythroid cells of transgenic mice. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):377–380. doi: 10.1038/314377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. H., Chovnick A. Studies of normal and position-affected expression of rosy region genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Nov;114(3):819–840. doi: 10.1093/genetics/114.3.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Meselson M. Separate regulatory elements for the heat-inducible and ovarian expression of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):737–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. B., McCarron M., Love C., Chovnick A. Dysgenesis-induced instability of rosy locus transformation in Drosophila melanogaster: analysis of excision events and the selective recovery of control element deletions. Genetics. 1985 Jan;109(1):95–117. doi: 10.1093/genetics/109.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels S. B., McCarron M., Love C., Clark S. H., Chovnick A. The underlying bases of gene expression differences in stable transformants of the rosy locus in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):265–285. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deak I. I., Bellamy P. R., Bienz M., Dubuis Y., Fenner E., Gollin M., Rähmi A., Ramp T., Reinhardt C. A., Cotton B. Mutations affecting the indirect flight muscles of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1982 Jun;69:61–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer J. A., Maniatis T. Regulatory elements involved in Drosophila Adh gene expression are conserved in divergent species and separate elements mediate expression in different tissues. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1275–1289. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04357.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garabedian M. J., Shepherd B. M., Wensink P. C. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer from the Drosophila yolk protein 1 gene. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):859–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90560-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geyer P. K., Fyrberg E. A. 5'-flanking sequence required for regulated expression of a muscle-specific Drosophila melanogaster actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3388–3396. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T. Correct developmental expression of a cloned alcohol dehydrogenase gene transduced into the Drosophila germ line. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Kedes L., Hickey R. J., Skoultchi A. I. Expression of human cardiac actin in mouse L cells: a sarcomeric actin associates with a nonmuscle cytoskeleton. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90351-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey R., Skoultchi A., Gunning P., Kedes L. Regulation of a human cardiac actin gene introduced into rat L6 myoblasts suggests a defect in their myogenic program. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3287–3290. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Hotta Y. Actin gene mutations in Drosophila; heat shock activation in the indirect flight muscles. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1681–1687. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03837.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Okamoto H., Gehring W. J., Hotta Y. Germline transformation with Drosophila mutant actin genes induces constitutive expression of heat shock genes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):293–301. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90763-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodgetts R. B. The response of dopa decarboxylase activity to variations in gene dosage in Drosophila: a possible location of the structural gene. Genetics. 1975 Jan;79(1):45–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/79.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Fyrberg E. A. An insertion within a variably spliced Drosophila tropomyosin gene blocks accumulation of only one encoded isoform. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Fyrberg E. A. Two Drosophila melanogaster tropomyosin genes: structural and functional aspects. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1965–1973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koana T., Hotta Y. Isolation and characterization of flightless mutants in Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Jun;45:123–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacy E., Roberts S., Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Costantini F. D. A foreign beta-globin gene in transgenic mice: integration at abnormal chromosomal positions and expression in inappropriate tissues. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Effects of genomic position on the expression of transduced copies of the white gene of Drosophila. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):558–561. doi: 10.1126/science.2992080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Separable cis-acting control elements for expression of the white gene of Drosophila. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3489–3499. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahaffey J. W., Coutu M. D., Fyrberg E. A., Inwood W. The flightless Drosophila mutant raised has two distinct genetic lesions affecting accumulation of myofibrillar proteins in flight muscles. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):101–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90313-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., Hotta Y. Isolation of Drosophila flightless mutants which affect myofibrillar proteins of indirect flight muscle. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;183(3):409–417. doi: 10.1007/BF00268758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., O'Donnell P. T., Bernstein S. I., Wright T. R., Emerson C. P., Jr Mutations of the Drosophila myosin heavy-chain gene: effects on transcription, myosin accumulation, and muscle function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1393–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamoto H., Hiromi Y., Ishikawa E., Yamada T., Isoda K., Maekawa H., Hotta Y. Molecular characterization of mutant actin genes which induce heat-shock proteins in Drosophila flight muscles. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):589–596. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04251.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Spradling A. C. Drosophila chorion gene amplification requires an upstream region regulating s18 transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4624–4633. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauli D., Spierer A., Tissières A. Several hundred base pairs upstream of Drosophila hsp23 and 26 genes are required for their heat induction in transformed flies. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):755–761. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Fillers J. P., Cohen C. Tropomyosin crystal structure and muscle regulation. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):111–131. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90468-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Steller H., Bozzetti M. P. Multiple upstream regulatory elements control the expression of the Drosophila white gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3501–3508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04109.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G., Cassab A., Bourouis M., Jarry B., Dissous C. The normal developmental regulation of a cloned sgs3 'glue' gene chromosomally integrated in Drosophila melanogaster by P element transformation. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2137–2142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholnick S. B., Morgan B. A., Hirsh J. The cloned dopa decarboxylase gene is developmentally regulated when reintegrated into the Drosophila genome. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Expression and regulation of chicken actin genes introduced into mouse myogenic and nonmyogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific and developmentally regulated expression of a chimeric actin-globin gene in transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2624–2631. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M. Tissue-specific expression of rat myosin light-chain 2 gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Mar 21;314(6008):283–286. doi: 10.1038/314283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. A., Sutton C. A., Lobell R. B., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T. Determinants of heat shock-induced chromosome puffing. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90340-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. The effect of chromosomal position on the expression of the Drosophila xanthine dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90135-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Rubin G. M. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):341–347. doi: 10.1126/science.6289435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H., Pirrotta V. A transposable P vector that confers selectable G418 resistance to Drosophila larvae. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):167–171. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02332.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Cicco D. V., Spradling A. C. Localization of a cis-acting element responsible for the developmentally regulated amplification of Drosophila chorion genes. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90525-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]