Abstract
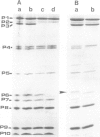
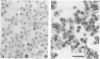
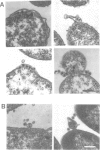
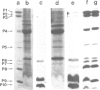
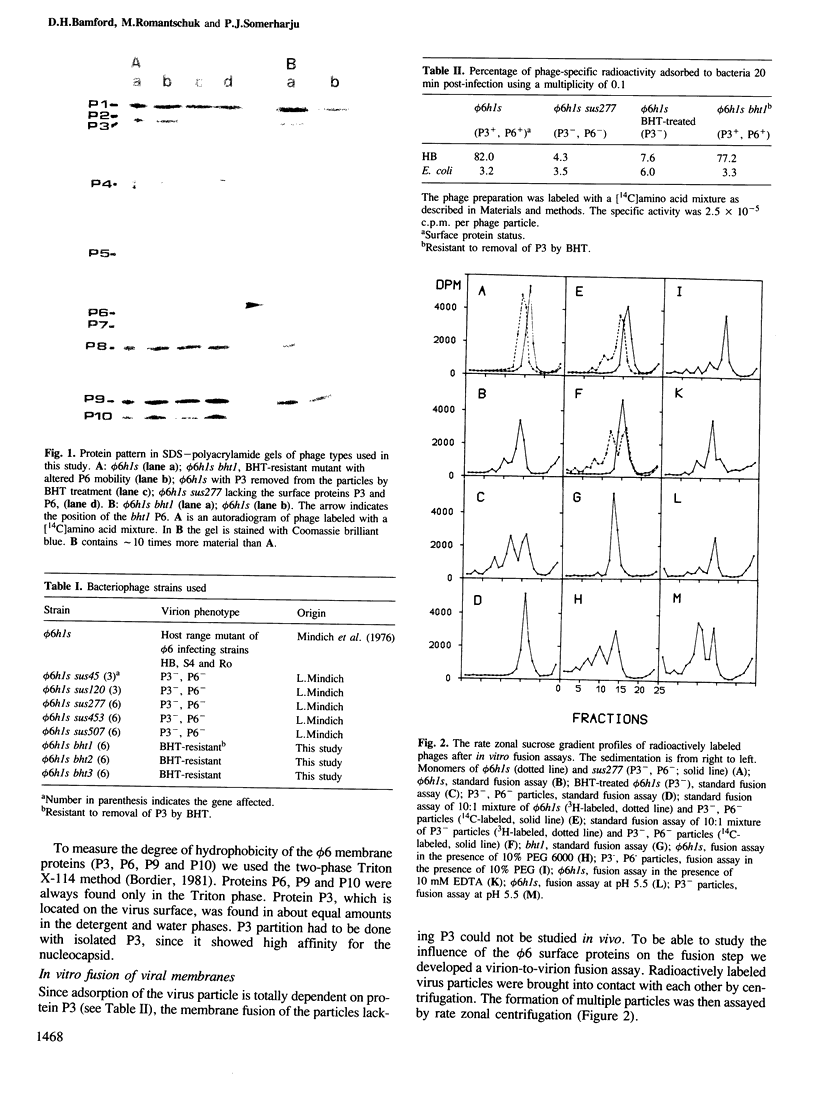
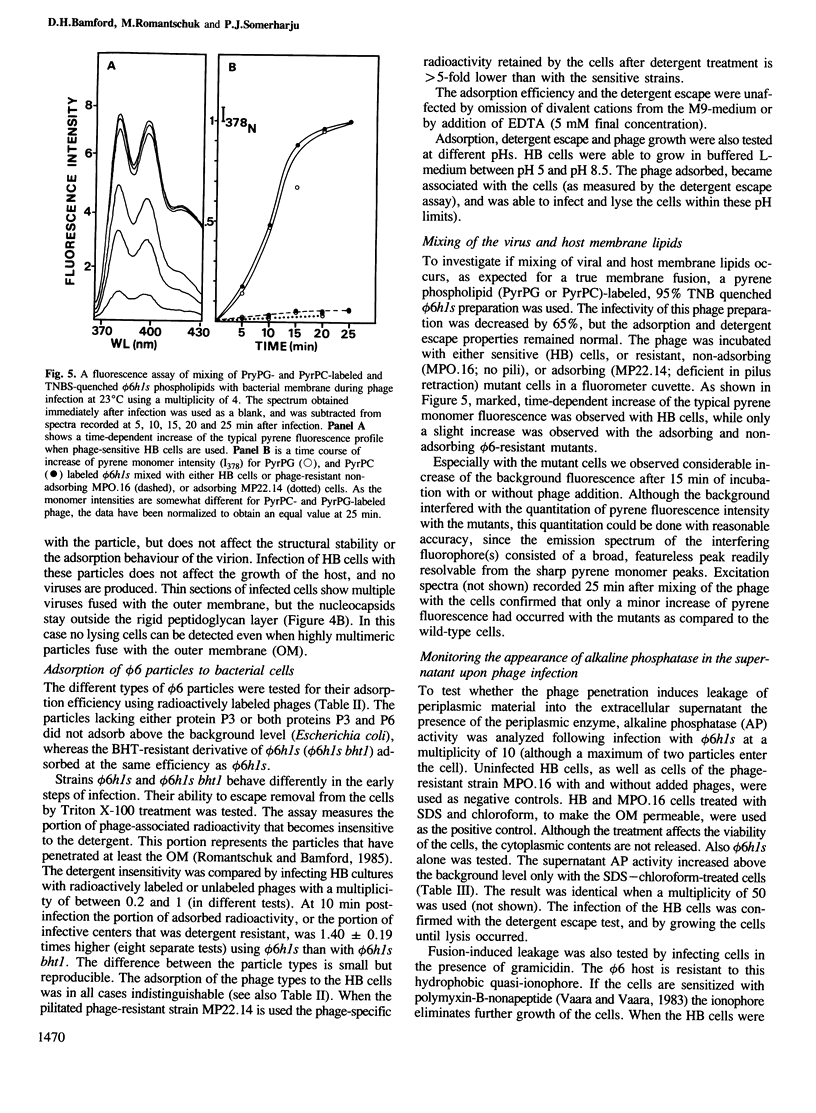
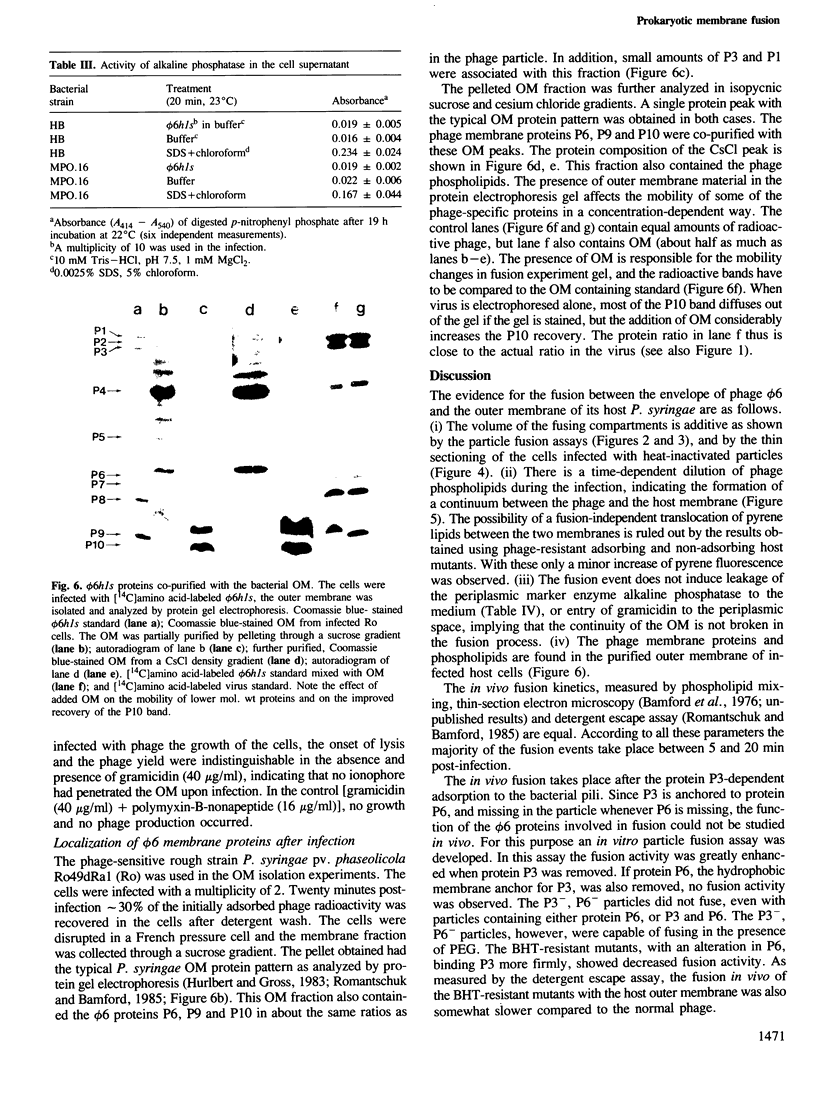
Protein-triggered membrane fusion in the prokaryotic system is described using the lipid-containing enveloped bacterial virus phi 6 and its host, the Gram-negative bacterium Pseudomonas syringae. Bacteriophage particles can be fused to form multiple particles where two or more nucleocapsids are surrounded by a single membrane vesicle with a volume proportional to the number of fused particles. For fusion to occur, a fusogenic protein is required in the membrane of the participating phage particles. Upon infection of the host cell, fusion of the viral membrane with the bacterial membrane takes place without leakage of the periplasmic enzyme alkaline phosphatase to the extracellular supernatant. There is a time-dependent mixing of fluorescent phage phospholipids with the bacterial membrane lipids between 5 and 20 min post-infection. The phage membrane proteins and phospholipids co-purify with the bacterial outer membrane of infected cells. The fusion is independent of divalent cations and pH, resembling Sendai virus fusion with the plasma membrane. This is the first targeted, protein-dependent fusion event described in prokaryotes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Mindich L. Electron microscopy of cells infected with nonsense mutants of bacteriophage phi 6. Virology. 1980 Nov;107(1):222–228. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90287-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Palva E. T., Lounatmaa K. Ultrastructure and life cycle of the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. J Gen Virol. 1976 Aug;32(2):249–259. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-2-249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamford D. H., Palva E. T. Structure of the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. Disruption by Triton X-100 treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 18;601(2):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90530-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger H., Kennedy K. Physical measurements on the lipid-containing bacteriophage phi 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 17;633(1):68–76. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain R. C., Zilversmit D. B. Two nonspecific phospholipid exchange proteins from beef liver. I. Purification and characterization. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 1;19(7):1433–1439. doi: 10.1021/bi00548a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIDSON F. M., LONG C. The structure of the naturally occurring phosphoglycerides. 4. Action of cabbage-leaf phospholipase D on ovolecithin and related substances. Biochem J. 1958 Jul;69(3):458–466. doi: 10.1042/bj0690458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day L. A., Mindich L. The molecular weight of bacteriophage phi 6 and its nucleocapsid. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doms R. W., Helenius A., White J. Membrane fusion activity of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. The low pH-induced conformational change. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2973–2981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Hoekstra D., Scherphof G., Kalicharan R. D., Wilschut J. Low pH-induced fusion of liposomes with membrane vesicles derived from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10880–10887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Massalski A., Schindler H., Dorset D. L., Rosenbusch J. P. Porin channel triplets merge into single outlets in Escherichia coli outer membranes. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):643–645. doi: 10.1038/317643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etten J. V., Lane L., Gonzalez C., Partridge J., Vidaver A. Comparative properties of bacteriophage phi6 and phi6 nucleocapsid. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):652–658. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.652-658.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordesky S. E., Marinetti G. V. The asymetric arrangement of phospholipids in the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1027–1031. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. Activation of the Sendai virus fusion protein (f) involves a conformational change with exposure of a new hydrophobic region. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3557–3563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M. C., Helenius A. Role of cholesterol in fusion of Semliki Forest virus with membranes. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):281–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.281-283.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kielian M., Helenius A. pH-induced alterations in the fusogenic spike protein of Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2284–2291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw T., Mindich L., Frangione B. Nucleotide sequence of the small double-stranded RNA segment of bacteriophage phi 6: novel mechanism of natural translational control. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):142–151. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.142-151.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Hunt J. F., Beckwith J. Effects of signal sequence mutations on the kinetics of alkaline phosphatase export to the periplasm in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):160–167. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.160-167.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Cohen J., Weisburd M. Isolation of nonsense suppressor mutants in Pseudomonas. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):177–182. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.177-182.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Lehman J. Cell wall lysin as a component of the bacteriophage phi 6 virion. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):489–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.489-496.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Lehman J., Huang R. Temperature-dependent compositional changes in the envelope of phi 6. Virology. 1979 Aug;97(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., MacKenzie G., Strassman J., McGraw T., Metzger S., Romantschuk M., Bamford D. cDNA cloning of portions of the bacteriophage phi 6 genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jun;162(3):992–999. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.3.992-999.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mindich L., Sinclair J. F., Cohen J. The morphogenesis of bacteriophage phi6: particles formed by nonsense mutants. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):224–231. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku N., Nojima S., Inoue K. Studies on the interaction of HVJ (Sendai Virus) with liposomal membranes. HVJ-induced permeability increase of liposomes containing glycophorin. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romantschuk M., Bamford D. H. Function of pili in bacteriophage phi 6 penetration. J Gen Virol. 1985 Nov;66(Pt 11):2461–2469. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-11-2461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romantschuk M., Bamford D. H. phi 6-resistant phage-producing mutants of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. J Gen Virol. 1981 Oct;56(Pt 2):287–295. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-2-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SINGLETON W. S., GRAY M. S., BROWN M. L., WHITE J. L. CHROMATOGRAPHICALLY HOMOGENEOUS LECITHIN FROM EGG PHOSPHOLIPIDS. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1965 Jan;42:53–56. doi: 10.1007/BF02558256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands J. A., Lowlicht R. A. Temporal origin of viral phospholipids of the enveloped bacteriophage phi 6. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Feb;22(2):154–158. doi: 10.1139/m76-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair J. F., Cohen J., Mindich L. The isolation of suppressible nonsence mutants of bacteriophage phi6. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):198–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerharju P. J., Virtanen J. A., Eklund K. K., Vainio P., Kinnunen P. K. 1-Palmitoyl-2-pyrenedecanoyl glycerophospholipids as membrane probes: evidence for regular distribution in liquid-crystalline phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 May 21;24(11):2773–2781. doi: 10.1021/bi00332a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L., Mindich L. The structure of bacteriophage phi 6: protease digestion of phi 6 virions. Virology. 1983 Jun;127(2):459–462. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Rauch B., Roseman S. Periplasmic space in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7850–7861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaara M., Vaara T. Sensitization of Gram-negative bacteria to antibiotics and complement by a nontoxic oligopeptide. Nature. 1983 Jun 9;303(5917):526–528. doi: 10.1038/303526a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaver A. K., Koski R. K., Van Etten J. L. Bacteriophage phi6: a Lipid-Containing Virus of Pseudomonas phaseolicola. J Virol. 1973 May;11(5):799–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.5.799-805.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Kielian M., Helenius A. Membrane fusion proteins of enveloped animal viruses. Q Rev Biophys. 1983 May;16(2):151–195. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500005072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]