Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the effect of rho kinase inhibitors on oxidative stress in trabecular meshwork (TM) cells.
Methods
TM cells were isolated from the eyes of cynomolgus monkeys. Y-27632 and menadione were used to inhibit rho kinase and induce production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), respectively. The cynomolgus monkey array and 12,613 probes were used in DNA microarray analysis, and the affected genes were categorized using gene ontology analysis. The mRNA levels of the target genes were confirmed by real-time RT-PCR. Intracellular oxidative stress was detected using a fluorescent reagent sensitive to ROS. Cell viability was assessed by the WST-8 assay.
Results
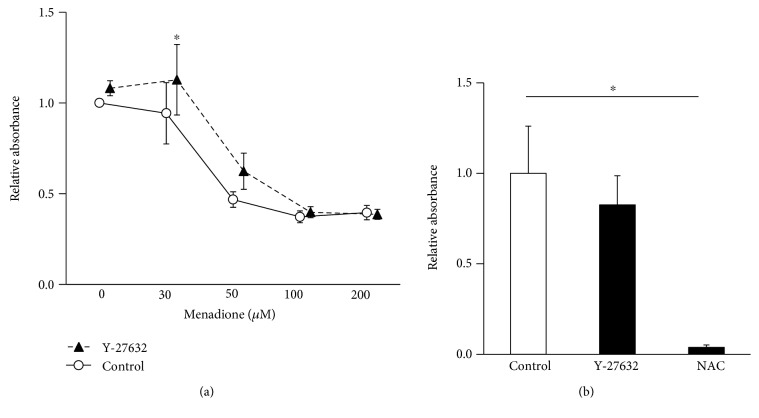
Gene ontology analysis revealed upregulation of genes involved in antioxidant activity, and upregulation of catalase was confirmed by real-time RT-PCR after 30 min treatment with Y-27632. Production of ROS was increased by menadione, and the effect was partly suppressed by pretreatment with Y-27632. At a lower dose of menadione, Y-27632 stimulated TM cells and significantly increased their viability following menadione treatment compared to control cells.
Conclusion
Using microarray analysis, Y-27632 was shown to upregulate antioxidative genes including catalase and partially reduce ROS production and cell death by oxidative stress caused by menadione.
1. Introduction
Oxidative stress is a major physiological phenomenon, mediated through the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), such as peroxides, superoxide, hydroxyl radical, and singlet oxygen. ROS play an important role in cell homeostasis and pathogen response and are therefore essential in biological processes. In contrast, increases in ROS are seen in various age-related diseases including glaucoma [1]. For instance, in the aqueous humor of glaucoma patients, the levels of oxidative stress markers are significantly increased [2–5]. Additionally, oxidative DNA damage is reportedly increased in the trabecular meshwork (TM) of glaucoma patients [6, 7]. These findings indicate that the TM of glaucomatous eyes is continuously exposed to oxidative stress, and therefore, damage to TM may increase outflow resistance and the risk of glaucoma progression. In line with this, lower systemic antioxidant capacity is related to higher intraocular pressure (IOP) levels in open-angle glaucoma patients [8]. Moreover, glaucoma-related genes, such as CYP1B1 and FOXC1, are reportedly linked to oxidative stress in the eyes [9–12]. Taken together, control of oxidative stress in the eye may be a therapeutic target to slow glaucoma progression.
Rho-rho kinase (ROCK) signaling controls polymerization of actin and thereby mediates various cell functions, such as contraction, migration, phagocytosis, and mitosis. Inhibition of ROCK increases aqueous outflow by depolymerizing F-actin in TM cells and Schlemm's canal endothelial cells [13, 14]. A ROCK inhibitor, ripasudil, has been approved as an IOP-lowering drug in Japan [15]. Ripasudil significantly reduces the IOP of glaucoma patients upon either single or multiple administration [16, 17]. However, ROCK inhibitors have drawn attention as antioxidative drugs against cardiovascular diseases and chronic renal injury [18, 19]. Indeed, ripasudil (also known as K-115) has been reported to have a neuroprotective effect on the optic nerve by suppressing oxidative stress in an animal model [20]. Thus, the effect of ROCK inhibitors on oxidative stress in TM cells is of interest from a therapeutic point of view against glaucoma.
Here, we show the results of an exhaustive investigation using a microarray, revealing that treatment with Y-27632, a well-known ROCK inhibitor, upregulates antioxidative molecules in TM cells, inhibits ROS production, and promotes cell survival.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
Trabecular meshwork (TM) cells were isolated from the eyes of cynomolgus monkeys (Shin Nippon Biomedical Laboratories, Kagoshima, Japan) according to the method described previously [21]. Primary TM cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM; Wako, Osaka, Japan) supplemented with 10% FBS, 2 mM glutamine, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/mL streptomycin, and 0.5 μg/mL amphotericin B at 37°C in 5% CO2. These cells were used after 2–5 passages. The character of the isolated cells in the present study was confirmed by expression of specific TM markers (caveolin 1, collagen 4α5, matrix gla protein, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3, and vascular cell adhesion protein 1), phagocytosis function, and myocilin induction by dexamethasone as described previously [22].
2.2. DNA Microarray Analysis
Custom cDNA microarray analysis was performed using a CombiMatrix microarray (CombiMatrix, Mukilteo, WA) as described previously [23]. Briefly, the cynomolgus monkey array was designed to detect directly labeled mRNA from 12,613 probes. Confluent TM cells in 100 mm dishes were treated with 25 μM Y-27632 (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) or vehicle (deionized water) for 30 min. Total RNA was extracted from the cells, and the integrity and concentration of total RNA was measured using an Agilent 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA). Fluorescence-labeled antisense RNA was synthesized by direct incorporation of Cy5-UTP or Cy3-UTP, using each RNA sample and an RNA Transcript SureLABEL Core kit (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). Labeled antisense RNAs were hybridized simultaneously with the microarray chips. DNA microarray preparation, hybridization, processing, scanning, and analyses were performed according to the manufacturer's instructions (Filgen, Nagoya, Japan). Fluorescent images of hybridized microarrays were obtained with a GenePix 4000B Scanner (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Array-Pro Analyzer Ver4.5 (Media Cybernetics, Silver Spring, MD) was used to determine the signal intensity of each spot and its local background. Scanned images were analyzed using Microarray Data Analysis Tool Ver3.2 software (Filgen). Signals from Y-27632 treated cells were compared with those from vehicle-treated cells, and genes that showed greater than 3/2-fold change in expression in at least one of the pairwise probe comparisons were considered upregulated, whereas those that showed a change of expression smaller than 2/3-fold were considered downregulated. These analyses were performed three times using TM cells from three different monkeys independently, and genes with common differences in expression among the three experiments were identified as affected genes. The affected genes were further analyzed by gene ontology, in which putative functions of gene products were categorized as “biological process,” “cellular component,” or “molecular function” by a BLAST homology search of EST sequences available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information.
2.3. Real-Time RT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from cultured TM cells treated with Y-27632 for 30 min using NucleoSpin RNA (Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany). Total RNA was reverse transcribed (PrimeScript RT Master Mix; Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Quantitative real-time RT-PCR was performed using an ABI Prism 7000 (Life Technologies). Reactions were performed in 20 μL of reaction mixture containing 10 μL PCR master mix (SYBR Premix Ex Taq II; Takara Bio Inc.), 0.4 μM primer pairs, and 2 μL cDNA samples. The gene-specific primer pairs were as follows: monkey catalase, forward (F) 5′-GCA AAT CTG TGA GGC CGG GG-3′; reverse (R) 5′-GCG CAT CTA GCA CCG GAG AA-3′ and 18S ribosomal RNA, (F) 5′-GCC CGA AGC GTT TAC TTT GA-3′; (R) 5′-CCG CGG TCC TAT TCC ATT ATT-3′. The thermal cycling conditions were 95°C for 30 s and 40 cycles of 95°C for 5 s and 60°C for 31 s. All PCR reactions were performed in duplicate.
Relative expression of catalase in the Y-27632-treated samples was compared to that in control samples using the comparative CT method (ΔΔCT method); 18S ribosomal RNA was used as an endogenous control. The threshold cycle, CT, was determined after setting the threshold in the linear amplification phase of the PCR reaction and ΔCT was defined as ΔCT = CT (target gene) − CT (18S rRNA). Relative expression of the target gene was calculated as: 2−ΔΔCT, ΔΔCT = ΔCT (treated sample) − ΔCT (control).
2.4. Intracellular Oxidative Stress Detection
The effects of Y-27632 on the production of ROS were evaluated using CellROX® green reagent (Life Technologies) in the TM cells. These cells were cultured on 6 cm dishes in DMEM containing 10% FBS and antibiotics at 37°C in 5% CO2. After cells had grown to confluence, they were pretreated with Y-27632 for 30 min and then stimulated with 100 μM menadione (Sigma, St. Louis, MO) for 1 h. CellROX reagent was then added to each dish to give a final concentration of 5 μM and incubated for 30 min at 37°C. After incubation, TM cells were washed in PBS and detached by trypsin/EDTA solution and centrifuged at 1200 rpm for 3 min. The supernatant was removed, and cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 15 min and then centrifuged twice at 1200 rpm for 3 min, resuspending in PBS after each spin. FITC fluorescence of TM cells was analyzed using a Cell Sorter SH800 (Sony Biotechnology, Tokyo, Japan).
2.5. Cell Viability Assay
The effects of Y-27632 on TM cell viability were evaluated using the WST-8 assay (Cell Counting Kit-8, Dojindo Laboratories, Kumamoto, Japan). Cells were seeded on 96-well plates (1 × 104 cells/well) and incubated at 37°C under 5% CO2 overnight. After pretreatment with Y-27632 for 30 min, cells were stimulated with H2O2 or menadione for 24 h. CCK-8 reagents were added into each well and incubated for 2 h at 37°C. Absorbance at 450 nm was determined using a microplate reader (Multiskan FC, Thermo Fisher Scientific). Cell viability was expressed as a percentage of control (vehicle-treated) cells.
2.6. Direct Antioxidant Activity of Y-27632
Direct antioxidant activity was assessed by 2-methyl-6-p-methoxyphenylethynylimidazopyrazinone (AB-2950 MPEC; ATTO, Tokyo, Japan), a superoxide-sensitive luminescent reagent, and reagents for xanthine-oxidase-induced superoxide production (AB-2970 CLETA-S, ATTO) following the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly, 10 μL of 300 μM MPEC/ethanol and 80 μL of 1.25 unit/mL xanthine oxidase/HEPES were mixed. Then, 10 μL of 25 μM Y-27632 or 20 mM n-acetyl cysteine (positive control) was added into each well of a 96-well plate. Subsequently, 90 μL of the mixture of MPEC and xanthine oxidase and 200 μL of xanthine were added to each well. The luminescent signal was measured for 10 s by a luminometer (AB-2270 Octa; ATTO).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data are presented as means ± standard error. Statistical comparisons of multiple groups were performed using the Tukey-Kramer HSD test and Dunnett's test, and those of two groups were performed using Wilcoxon rank sum test and Wilcoxon signed rank test. Differences were considered statistically significant at P < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Microarray Expression Profile in Y-27632-Treated TM Cells
Among the 12,613 genes analyzed by microarray, the affected genes are listed in Tables 1 and 2; 444 genes were upregulated, and 56 were downregulated. Significantly upregulated and downregulated gene categories based on gene ontology analysis in Y-27632 treated TM cells are listed in Tables 3 and 4. Gene ontology analysis revealed that the upregulated genes were related to various cellular functions including antioxidant activity (P = 0.014), and downregulated genes were related to integrin complexes (P = 0.039), and calcium ion transport into the cytosol (P = 0.008). In the category of antioxidant activity, upregulated genes were homologous to human gene coding catalase (P = 0.046), thioredoxin domain-containing 2 (also known as spermatozoa; P = 0.032), nucleoredoxin (P = 0.017), albumin (probe 1, P = 0.002; probe 2, P = 0.021), and glutathione transferase zeta 1 (P = 0.004). Upregulation of the mRNA of catalase, an extensively investigated antioxidant, was confirmed by real-time RT-PCR and found to be 1.5 times higher in TM cells treated with Y-27632 compared to the control TM cells (P = 0.032; Figure 1(a)). In contrast, four other genes involved in antioxidant activity were not significantly affected after treatment with Y-27632 (data not shown).
Table 1.
Genes that are upregulated in TM cells.
| Accession number | Human RefSeq description | Fold change |
|---|---|---|
| DW528016 | gi|75750485|ref|NM_004773.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger, HIT type 3 (ZNHIT3), mRNA | 6.79928 |
| CJ434702 | gi|20986504|ref|NM_002753.2 Homo sapiens mitogen-activated protein kinase 10 (MAPK10), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 5.85538 |
| AB168851 | gi|224586874|ref|NM_033124.4 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 65 (CCDC65), mRNA | 5.77453 |
| AB169150 | gi|223555972|ref|NR_026827.1 Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC84856 (LOC84856), noncoding RNA | 5.01086 |
| DW523643 | gi|225903398|ref|NM_001146152.1 Homo sapiens cytochrome P450, family 51, subfamily A, polypeptide 1 (CYP51A1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 4.6977 |
| AK240630 | gi|4503754|ref|NM_002021.1 Homo sapiens flavin-containing monooxygenase 1 (FMO1), mRNA | 4.64946 |
| BB894083 | gi|154689768|ref|NM_020840.1 Homo sapiens folliculin-interacting protein 2 (FNIP2), mRNA | 4.52052 |
| AB168218 | gi|85060516|ref|NM_199321.2 Homo sapiens zona pellucida-binding protein 2 (ZPBP2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 4.20286 |
| AB168199 | gi|156523965|ref|NM_001102470.1 Homo sapiens alcohol dehydrogenase 6 (class V) (ADH6), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.89514 |
| AB172502 | gi|50897849|ref|NM_001001936.1 Homo sapiens actin filament-associated protein 1-like 2 (AFAP1L2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.84241 |
| CJ448047 | gi|46909588|ref|NM_002731.2 Homo sapiens protein kinase, cAMP-dependent, catalytic, beta (PRKACB), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 3.75324 |
| DC857227 | gi|239752603|ref|XM_002348257.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to immunoglobulin lambda-like polypeptide 1 (LOC100294459), mRNA | 3.66898 |
| CJ449582 | gi|9506614|ref|NM_019023.1 Homo sapiens protein arginine methyltransferase 7 (PRMT7), mRNA | 3.64058 |
| EF208813 | gi|24797075|ref|NM_002121.4 Homo sapiens major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1 (HLA-DPB1), mRNA | 3.57386 |
| DQ417745 | gi|194,248,050|ref|NM_000839.3 Homo sapiens glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2 (GRM2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.5509 |
| AB049894 | gi|66571326|ref|NM_020914.3 Homo sapiens ring finger protein 213 (RNF213), mRNA | 3.51068 |
| DC850932 | gi|117676364|ref|NM_014350.2 Homo sapiens tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.47535 |
| BB877436 | gi|142360165|ref|NM_005123.2 Homo sapiens nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group H, member 4 (NR1H4), mRNA | 3.46906 |
| AB174726 | gi|22208962|ref|NM_016150.3 Homo sapiens ankyrin repeat and SOCS box-containing 2 (ASB2), mRNA | 3.30479 |
| AB174122 | gi|209862773|ref|NM_002483.4 Homo sapiens carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (nonspecific cross-reacting antigen) (CEACAM6), mRNA | 3.27904 |
| AB173773 | gi|38569483|ref|NM_017641.2 Homo sapiens kinesin family member 21A (KIF21A), mRNA | 3.26679 |
| DK578446 | gi|15718677|ref|NM_033257.2 Homo sapiens DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 6 like (DGCR6L), mRNA | 3.26114 |
| AB168950 | gi|38261961|ref|NM_018179.3 Homo sapiens activating transcription factor 7-interacting protein (ATF7IP), mRNA | 3.25607 |
| CJ488707 | gi|45333915|ref|NM_178456.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 20 open reading frame 85 (C20orf85), mRNA | 3.24156 |
| DC639327 | gi|154800442|ref|NM_005074.3 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 17 (sodium phosphate), member 1 (SLC17A1), mRNA | 3.23693 |
| BB895966 | gi|32483409|ref|NM_000583.2 Homo sapiens group-specific component (vitamin D-binding protein) (GC), mRNA | 3.22662 |
| DQ417744 | gi|194248050|ref|NM_000839.3 Homo sapiens glutamate receptor, metabotropic 2 (GRM2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.1862 |
| AB168486 | gi|195972893|ref|NM_152764.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 16 open reading frame 73 (C16orf73), mRNA | 3.17552 |
| AB047624 | gi|45446748|ref|NM_004984.2 Homo sapiens kinesin family member 5A (KIF5A), mRNA | 3.1749 |
| CJ446015 | gi|187761371|ref|NM_004044.5 Homo sapiens 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide formyltransferase/IMP cyclohydrolase (ATIC), mRNA | 3.17026 |
| AB171508 | gi|89276768|ref|NM_002747.3 Homo sapiens mitogen-activated protein kinase 4 (MAPK4), mRNA | 3.12296 |
| DC639656 | gi|148596946|ref|NM_001098483.1 Homo sapiens chromosome 10 open reading frame 125 (C10orf125), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.11887 |
| AB048996 | gi|211938419|ref|NM_002898.3 Homo sapiens RNA-binding motif, single stranded interacting protein 2 (RBMS2), mRNA | 3.11444 |
| DC630823 | gi|215422360|ref|NM_004786.2 Homo sapiens thioredoxin-like 1 (TXNL1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.09601 |
| AB173283 | gi|197927150|ref|NM_006158.3 Homo sapiens neurofilament, light polypeptide (NEFL), mRNA | 3.09117 |
| DC633065 | gi|34486089|ref|NM_004152.2 Homo sapiens ornithine decarboxylase antizyme 1 (OAZ1), mRNA | 3.0599 |
| AB174730 | gi|115387109|ref|NM_017831.3 Homo sapiens ring finger protein 125 (RNF125), mRNA | 3.03611 |
| AB046044 | gi|170650673|ref|NM_000440.2 Homo sapiens phosphodiesterase 6A, cGMP-specific, rod, alpha (PDE6A), mRNA | 3.03568 |
| AB179171 | gi|82546851|ref|NM_175605.3 Homo sapiens intraflagellar transport 88 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (IFT88), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 3.029 |
| AB051155 | gi|35493712|ref|NM_017890.3 Homo sapiens vacuolar protein sorting 13 homolog B (yeast) (VPS13B), transcript variant 5, mRNA | 3.00764 |
| AB072740 | gi|155029549|ref|NM_178828.4 Homo sapiens chromosome 9 open reading frame 79 (C9orf79), mRNA | 3.00753 |
| BB881371 | gi|162809333|ref|NM_002864.2 Homo sapiens pregnancy-zone protein (PZP), mRNA | 2.99069 |
| CJ463711 | gi|215272411|ref|NM_001142334.1 Homo sapiens ataxin 2-binding protein 1 (A2BP1), transcript variant 6, mRNA | 2.98758 |
| AB170648 | gi|5174424|ref|NM_006052.1 Homo sapiens Down syndrome critical region gene 3 (DSCR3), mRNA | 2.9606 |
| AB220465 | gi|58331245|ref|NM_000817.2 Homo sapiens glutamate decarboxylase 1 (brain, 67 kDa) (GAD1), transcript variant GAD67, mRNA | 2.95173 |
| AB062990 | gi|33149330|ref|NM_022463.3 Homo sapiens nucleoredoxin (NXN), mRNA | 2.94787 |
| AB220509 | gi|139394620|ref|NM_006574.3 Homo sapiens chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 5 (neuroglycan C) (CSPG5), mRNA | 2.92569 |
| AB070086 | gi|22538813|ref|NM_002985.2 Homo sapiens chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 (CCL5), mRNA | 2.92446 |
| AB173147 | gi|194294550|ref|NM_015989.4 Homo sapiens cysteine sulfinic acid decarboxylase (CSAD), mRNA | 2.91509 |
| AB051133 | gi|28329444|ref|NM_014379.2 Homo sapiens potassium channel, subfamily V, member 1 (KCNV1), mRNA | 2.87085 |
| AB174705 | gi|51477720|ref|NM_001003811.1 Homo sapiens testis-expressed 11 (TEX11), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.86731 |
| CJ469703 | gi|169646771|ref|NM_002064.2 Homo sapiens glutaredoxin (thioltransferase) (GLRX), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.85957 |
| AB220438 | gi|109633045|ref|NM_001042437.1 Homo sapiens ST3 beta-galactoside alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase 5 (ST3GAL5), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.85364 |
| BB881475 | gi|170650673|ref|NM_000440.2 Homo sapiens phosphodiesterase 6A, cGMP-specific, rod, alpha (PDE6A), mRNA | 2.84456 |
| AB168610 | gi|62632749|ref|NM_014616.1 Homo sapiens ATPase, class VI, type 11B (ATP11B), mRNA | 2.84449 |
| AB173806 | gi|134031964|ref|NR_003491.1 Homo sapiens myocardial infarction associated transcript (nonprotein coding) (MIAT), noncoding RNA | 2.82677 |
| AB063045 | gi|190570175|ref|NM_152906.4 Homo sapiens chromosome 22 open reading frame 25 (C22orf25), mRNA | 2.80672 |
| AB168446 | gi|223278411|ref|NR_026782.1 Homo sapiens chromosome 1 open reading frame 175 (C1orf175), transcript variant 2, transcribed RNA | 2.79215 |
| CJ473171 | gi|215490055|ref|NM_001142434.1 Homo sapiens meningioma-expressed antigen 5 (hyaluronidase) (MGEA5), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.78342 |
| CJ450383 | gi|83641894|ref|NM_031157.2 Homo sapiens heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (HNRNPA1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.78321 |
| DW528650 | gi|58430810|ref|NM_148912.2 Homo sapiens abhydrolase domain-containing 11 (ABHD11), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.77238 |
| AB362499 | gi|48255911|ref|NM_012338.3 Homo sapiens tetraspanin 12 (TSPAN12), mRNA | 2.76878 |
| AB173195 | gi|196049386|ref|NM_002198.2 Homo sapiens interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1), mRNA | 2.76544 |
| AB168743 | gi|188536107|ref|NM_001127458.1 Homo sapiens cardiolipin synthase 1 (CRLS1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.76042 |
| CJ444006 | gi|157151724|ref|NM_001004333.3 Homo sapiens ribonuclease, RNase K (RNASEK), mRNA | 2.75719 |
| DK583186 | gi|156631002|ref|NM_006913.3 Homo sapiens ring finger protein 5 (RNF5), mRNA | 2.75394 |
| AB168582 | gi|239757151|ref|XM_002345145.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC100292623 (LOC100292623), mRNA | 2.75285 |
| BB884235 | gi|70906436|ref|NM_000509.4 Homo sapiens fibrinogen gamma chain (FGG), transcript variant gamma-A, mRNA | 2.74831 |
| AB070088 | gi|148613875|ref|NM_144715.3 Homo sapiens EF-hand domain family, member B (EFHB), mRNA | 2.74738 |
| AB174502 | gi|239757416|ref|XM_002345385.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2019710 (LOC100294049), mRNA | 2.73964 |
| AB172306 | gi|196162714|ref|NM_024786.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger, DHHC-type-containing 11 (ZDHHC11), mRNA | 2.72049 |
| BB878691 | gi|19743563|ref|NM_000766.3 Homo sapiens cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily A, polypeptide 13 (CYP2A13), mRNA | 2.72031 |
| AB174483 | gi|55775474|ref|NM_194326.2 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein S19-binding protein 1 (RPS19BP1), mRNA | 2.68579 |
| DC632651 | gi|22538474|ref|NM_018955.2 Homo sapiens ubiquitin B (UBB), mRNA | 2.66418 |
| AB168353 | gi|197927266|ref|NM_004388.2 Homo sapiens chitobiase, di-N-acetyl (CTBS), mRNA | 2.64444 |
| AB169323 | gi|156616291|ref|NM_018100.3 Homo sapiens EF-hand domain (C-terminal)-containing 1 (EFHC1), mRNA | 2.6433 |
| AB048961 | gi|209413742|ref|NM_005458.6 Homo sapiens gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) B receptor, 2 (GABBR2), mRNA | 2.63945 |
| AB173162 | gi|73747880|ref|NM_015113.3 Homo sapiens zinc finger, ZZ-type with EF-hand domain 1 (ZZEF1), mRNA | 2.63631 |
| AB179192 | gi|237681201|ref|NM_019644.3 Homo sapiens ankyrin repeat domain 7 (ANKRD7), mRNA | 2.62211 |
| CJ469417 | gi|169790802|ref|NM_005271.2 Homo sapiens glutamate dehydrogenase 1 (GLUD1), mRNA | 2.62134 |
| AB172772 | gi|61835190|ref|NM_006578.3 Homo sapiens guanine nucleotide-binding protein (G protein), beta 5 (GNB5), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.61592 |
| DC857715 | gi|169234652|ref|NM_007360.2 Homo sapiens killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily K, member 1 (KLRK1), mRNA | 2.6139 |
| AB179131 | gi|40807356|ref|NM_005094.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 27 (fatty acid transporter), member 4 (SLC27A4), mRNA | 2.61058 |
| DC647811 | gi|92091576|ref|NM_015533.3 Homo sapiens dihydroxyacetone kinase 2 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (DAK), mRNA | 2.60217 |
| AB171456 | gi|197927256|ref|NM_001134664.1 Homo sapiens sterile alpha motif domain-containing 13 (SAMD13), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 2.59522 |
| CJ490832 | gi|169205007|ref|XM_001714899.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC100131988 (LOC100131988), mRNA | 2.58063 |
| DC635714 | gi|57013275|ref|NM_006082.2 Homo sapiens tubulin, alpha 1b (TUBA1B), mRNA | 2.57848 |
| AB055358 | gi|225735571|ref|NR_027416.1 Homo sapiens nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 3 pseudogene (LOC100272146), noncoding RNA | 2.57079 |
| CJ458955 | gi|197382308|ref|NM_183394.2 Homo sapiens Ca++-dependent secretion activator (CADPS), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.55777 |
| DC636940 | gi|54112387|ref|NM_001005738.1 Homo sapiens formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.54881 |
| CJ493104 | gi|56676323|ref|NM_001001552.3 Homo sapiens LEM domain-containing 1 (LEMD1), mRNA | 2.5487 |
| AB172122 | gi|239754513|ref|XM_001716238.2 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC100128081 (LOC100128081), mRNA | 2.54837 |
| CJ469678 | gi|197304748|ref|NM_032727.3 Homo sapiens internexin neuronal intermediate filament protein, alpha (INA), mRNA | 2.53491 |
| AB070172 | gi|32490571|ref|NM_012307.2 Homo sapiens erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1-like 3 (EPB41L3), mRNA | 2.52667 |
| DW528013 | gi|225735571|ref|NR_027416.1 Homo sapiens nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 3 pseudogene (LOC100272146), noncoding RNA | 2.52479 |
| AB171587 | gi|161169016|ref|NM_001111019.1 Homo sapiens neuron navigator 2 (NAV2), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 2.5209 |
| BB888693 | gi|49574509|ref|NM_016013.2 Homo sapiens NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, assembly factor 1 (NDUFAF1), mRNA | 2.51576 |
| BB897871 | gi|207113180|ref|NM_001097577.2 Homo sapiens angiogenin, ribonuclease, RNase A family, 5 (ANG), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.50309 |
| AB168153 | gi|222352148|ref|NM_018665.2 Homo sapiens DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 43 (DDX43), mRNA | 2.50236 |
| AB173823 | gi|148225856|ref|NM_001097579.1 Homo sapiens G protein-coupled receptor 34 (GPR34), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 2.49912 |
| AB168907 | gi|194688136|ref|NM_002358.3 Homo sapiens MAD2 mitotic arrest deficient-like 1 (yeast) (MAD2L1), mRNA | 2.49825 |
| DK583616 | gi|18390348|ref|NM_000972.2 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein L7a (RPL7A), mRNA | 2.49444 |
| CJ471599 | gi|197245445|ref|NM_024958.2 Homo sapiens neurensin 2 (NRSN2), mRNA | 2.49281 |
| AB179111 | gi|118572587|ref|NM_001761.2 Homo sapiens cyclin F (CCNF), mRNA | 2.49071 |
| AB060886 | gi|23199979|ref|NM_022470.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger, matrin type 3 (ZMAT3), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.48362 |
| AB056810 | gi|126131101|ref|NM_138694.3 Homo sapiens polycystic kidney and hepatic disease 1 (autosomal recessive) (PKHD1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.48299 |
| DC645529 | gi|4501988|ref|NM_001134.1 Homo sapiens alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), mRNA | 2.46808 |
| AB050420 | gi|189095267|ref|NM_000554.4 Homo sapiens cone-rod homeobox (CRX), mRNA | 2.45627 |
| AB243403 | gi|116235483|ref|NM_002701.4 Homo sapiens POU class 5 homeobox 1 (POU5F1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.4534 |
| AB173020 | gi|94420687|ref|NM_004233.3 Homo sapiens CD83 molecule (CD83), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.44967 |
| DC643036 | gi|50409862|ref|NM_017584.5 Homo sapiens myoinositol oxygenase (MIOX), mRNA | 2.44791 |
| BB897024 | gi|142976728|ref|NM_016245.3 Homo sapiens hydroxysteroid (17-beta) dehydrogenase 11 (HSD17B11), mRNA | 2.43894 |
| DW522619 | gi|34147617|ref|NM_138807.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 3 open reading frame 31 (C3orf31), mRNA | 2.43416 |
| DC645828 | gi|16332359|ref|NM_033487.1 Homo sapiens cell division cycle 2-like 1 (PITSLRE proteins) (CDC2L1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 2.43092 |
| AB050260 | gi|203098333|ref|NM_032133.4 Homo sapiens MYCBP-associated protein (MYCBPAP), mRNA | 2.41286 |
| CJ436262 | gi|150010638|ref|NM_015276.1 Homo sapiens ubiquitin specific peptidase 22 (USP22), mRNA | 2.39886 |
| AB056381 | gi|225735571|ref|NR_027416.1 Homo sapiens nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 3 pseudogene (LOC100272146), noncoding RNA | 2.39471 |
| CJ443349 | gi|83367079|ref|NM_003801.3 Homo sapiens glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor attachment protein 1 homolog (yeast) (GPAA1), mRNA | 2.39333 |
| AB171767 | gi|126273571|ref|NM_144586.5 Homo sapiens LY6/PLAUR domain-containing 1 (LYPD1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.393 |
| AB056817 | gi|58535452|ref|NM_001011649.1 Homo sapiens CDK5 regulatory subunit-associated protein 2 (CDK5RAP2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.39285 |
| AB174345 | gi|145208007|ref|NM_173688.2 Homo sapiens Na+/K+-transporting ATPase interacting 3 (NKAIN3), mRNA | 2.39236 |
| DC648733 | gi|134133239|ref|NM_032151.4 Homo sapiens pterin-4 alpha-carbinolamine dehydratase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (TCF1) 2 (PCBD2), mRNA | 2.39231 |
| CJ435057 | gi|189083855|ref|NM_000815.4 Homo sapiens gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) A receptor, delta (GABRD), mRNA | 2.38598 |
| AB172049 | gi|41281366|ref|NM_001440.2 Homo sapiens exostoses (multiple)-like 3 (EXTL3), mRNA | 2.37312 |
| CJ489397 | gi|71143136|ref|NM_005342.2 Homo sapiens high-mobility group box 3 (HMGB3), mRNA | 2.36471 |
| AB170096 | gi|42741653|ref|NM_007375.3 Homo sapiens TAR DNA-binding protein (TARDBP), mRNA | 2.36217 |
| AB056391 | gi|169216999|ref|XM_001720515.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to pro-pol protein (LOC100129323), mRNA | 2.3496 |
| AB071089 | gi|167900475|ref|NM_001080850.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 30 (CCDC30), mRNA | 2.34558 |
| DK579603 | gi|84626579|ref|NM_025108.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 16 open reading frame 59 (C16orf59), mRNA | 2.34371 |
| CJ431113 | gi|226246632|ref|NR_027451.1 Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC647979 (LOC647979), noncoding RNA | 2.34265 |
| DK580610 | gi|34335291|ref|NM_003312.4 Homo sapiens thiosulfate sulfurtransferase (rhodanese) (TST), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 2.3426 |
| AB168450 | gi|81295815|ref|NM_012337.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 19 (CCDC19), mRNA | 2.34063 |
| DQ159931 | gi|163659857|ref|NM_000828.4 Homo sapiens glutamate receptor, ionotrophic, AMPA 3 (GRIA3), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.33939 |
| AB173516 | gi|36287116|ref|NM_014319.3 Homo sapiens LEM domain-containing 3 (LEMD3), mRNA | 2.33925 |
| AB173575 | gi|56550100|ref|NM_020978.3 Homo sapiens amylase, alpha 2B (pancreatic) (AMY2B), mRNA | 2.33548 |
| AB169015 | gi|93277104|ref|NM_173812.4 Homo sapiens dpy-19-like 2 (C. elegans) (DPY19L2), mRNA | 2.33006 |
| BB898675 | gi|70906438|ref|NM_021870.2 Homo sapiens fibrinogen gamma chain (FGG), transcript variant gamma-B, mRNA | 2.32385 |
| DK579646 | gi|153791317|ref|NM_032332.3 Homo sapiens mitogen-activated protein kinase organizer 1 (MORG1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.32308 |
| AB071115 | gi|111548669|ref|NM_153376.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 96 (CCDC96), mRNA | 2.31559 |
| DC632824 | gi|23110926|ref|NM_002799.2 Homo sapiens proteasome (prosome, macropain) subunit, beta type, 7 (PSMB7), mRNA | 2.31501 |
| BB896362 | gi|188595719|ref|NM_005141.3 Homo sapiens fibrinogen beta chain (FGB), mRNA | 2.3131 |
| AB292416 | gi|143770740|ref|NM_001083899.1 Homo sapiens glycoprotein VI (platelet) (GP6), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.311 |
| AB055350 | gi|67782353|ref|NM_001024844.1 Homo sapiens CD82 molecule (CD82), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.31014 |
| AB168962 | gi|210147405|ref|NM_152621.5 Homo sapiens sphingomyelin synthase 2 (SGMS2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.30806 |
| AB168166 | gi|156415985|ref|NM_014579.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 39 (zinc transporter), member 2 (SLC39A2), mRNA | 2.30287 |
| AB172981 | gi|73695942|ref|NM_001010927.2 Homo sapiens T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 2 (TIAM2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.29903 |
| CJ441025 | gi|153252025|ref|NM_001830.3 Homo sapiens chloride channel 4 (CLCN4), mRNA | 2.29786 |
| CJ445440 | gi|42764686|ref|NM_022652.2 Homo sapiens dual specificity phosphatase 6 (DUSP6), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.29536 |
| AB179072 | gi|156119614|ref|NM_006901.2 Homo sapiens myosin IXA (MYO9A), mRNA | 2.28584 |
| AB060229 | gi|239756940|ref|XM_001718053.2 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to CD300C antigen (LOC100130520), mRNA | 2.28415 |
| CJ480802 | gi|71772428|ref|NM_001021.3 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein S17 (RPS17), mRNA | 2.28212 |
| DK581053 | gi|63054873|ref|NM_001615.3 Homo sapiens actin, gamma 2, smooth muscle, enteric (ACTG2), mRNA | 2.27782 |
| AB046030 | gi|169210010|ref|XR_040492.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC440386 (LOC440386), miscRNA | 2.27371 |
| AB174638 | gi|44680147|ref|NM_203327.1 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 23 (nucleobase transporters), member 2 (SLC23A2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.2635 |
| CJ469779 | gi|95147340|ref|NM_004603.2 Homo sapiens syntaxin 1A (brain) (STX1A), mRNA | 2.25959 |
| DC632108 | gi|225637497|ref|NR_003286.2 Homo sapiens 18S ribosomal RNA (LOC100008588), noncoding RNA | 2.25815 |
| AB170956 | gi|65506441|ref|NM_000282.2 Homo sapiens propionyl coenzyme A carboxylase, alpha polypeptide (PCCA), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.25785 |
| DC858184 | gi|13569959|ref|NM_030980.1 Homo sapiens interferon stimulated exonuclease gene 20 kDa-like 2 (ISG20L2), mRNA | 2.25755 |
| CJ470090 | gi|169790838|ref|NM_004172.4 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 1 (glial high affinity glutamate transporter), member 3 (SLC1A3), mRNA | 2.24996 |
| DW522847 | gi|215983055|ref|NM_031471.5 Homo sapiens fermitin family homolog 3 (Drosophila) (FERMT3), transcript variant URP2SF, mRNA | 2.23483 |
| DK577957 | gi|186910295|ref|NM_001126102.1 Homo sapiens haptoglobin (HP), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.23107 |
| AB168531 | gi|162951880|ref|NM_001112707.1 Homo sapiens tousled-like kinase 2 (TLK2), transcript variant B, mRNA | 2.22872 |
| AB047603 | gi|149363673|ref|NM_012194.1 Homo sapiens chromosome 11 open reading frame 41 (C11orf41), mRNA | 2.22681 |
| DC642489 | gi|66392201|ref|NM_002512.2 Homo sapiens nonmetastatic cells 2, protein (NM23B) expressed in (NME2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.22176 |
| AB072760 | gi|91754184|ref|NM_152763.3 Homo sapiens chromosome 1 open reading frame 62 (C1orf62), mRNA | 2.2183 |
| AB168708 | gi|36287109|ref|NM_194429.1 Homo sapiens FGFR1 oncogene partner (FGFR1OP), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.21393 |
| AB168136 | gi|93004101|ref|NM_005730.3 Homo sapiens CTD (carboxy-terminal domain, RNA polymerase II, polypeptide A) small phosphatase 2 (CTDSP2), mRNA | 2.20887 |
| DC641033 | gi|108389126|ref|NM_001042353.1 Homo sapiens family with sequence similarity 110, member A (FAM110A), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 2.20687 |
| CJ453010 | gi|19743893|ref|NM_133480.1 Homo sapiens transcriptional adaptor 3 (NGG1 homolog, yeast)-like (TADA3L), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.20608 |
| AB168419 | gi|32996736|ref|NM_173083.2 Homo sapiens lin-9 homolog (C. elegans) (LIN9), mRNA | 2.20292 |
| AB169251 | gi|148727318|ref|NM_001098529.1 Homo sapiens thioredoxin domain-containing 2 (spermatozoa) (TXNDC2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.2019 |
| AB173492 | gi|31542657|ref|NM_018099.3 Homo sapiens fatty acyl CoA reductase 2 (FAR2), mRNA | 2.20171 |
| CJ443285 | gi|62955828|ref|NM_033428.1 Homo sapiens chromosome 9 open reading frame 123 (C9orf123), mRNA | 2.19894 |
| AB169808 | gi|20336295|ref|NM_018380.2 Homo sapiens DEAD (Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp) box polypeptide 28 (DDX28), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 2.1907 |
| AB169213 | gi|125625349|ref|NM_001790.3 Homo sapiens cell division cycle 25 homolog C (S. pombe) (CDC25C), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.18403 |
| CJ491693 | gi|21361889|ref|NM_021633.2 Homo sapiens Kelch-like 12 (Drosophila) (KLHL12), mRNA | 2.1801 |
| BB876451 | gi|109389366|ref|NM_000312.2 Homo sapiens protein C (inactivator of coagulation factors Va and VIIIa) (PROC), mRNA | 2.17421 |
| AB171871 | gi|153070253|ref|NM_001099680.1 Homo sapiens MAGI family member, X-linked (MAGIX), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.17287 |
| AB173097 | gi|198041927|ref|NM_139241.2 Homo sapiens FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain-containing 4 (FGD4), mRNA | 2.16791 |
| AB046632 | gi|136255215|ref|NM_207351.3 Homo sapiens proline-rich transmembrane protein 3 (PRRT3), mRNA | 2.16598 |
| DK577943 | gi|84872083|ref|NR_002798.1 Homo sapiens napsin B aspartic peptidase pseudogene (NAPSB), noncoding RNA | 2.16578 |
| AB168792 | gi|141802709|ref|NM_145263.2 Homo sapiens spermatogenesis associated 18 homolog (rat) (SPATA18), mRNA | 2.16491 |
| BB881148 | gi|189458840|ref|NM_005942.3 Homo sapiens molybdenum cofactor synthesis 1 (MOCS1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.16393 |
| CJ472360 | gi|24497456|ref|NM_139136.2 Homo sapiens potassium voltage-gated channel, Shaw-related subfamily, member 2 (KCNC2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.15994 |
| CJ430900 | gi|94721262|ref|NM_001040446.1 Homo sapiens myotubularin-related protein 12 (MTMR12), mRNA | 2.15957 |
| AB171550 | gi|19913413|ref|NM_014203.2 Homo sapiens adaptor-related protein complex 2, alpha 1 subunit (AP2A1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.1589 |
| AB173954 | gi|188595678|ref|NM_014959.2 Homo sapiens caspase recruitment domain family, member 8 (CARD8), mRNA | 2.13719 |
| AB071125 | gi|89903024|ref|NM_001031735.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 19 open reading frame 36 (C19orf36), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.13665 |
| AB063014 | gi|170650671|ref|NM_001122769.1 Homo sapiens Leber congenital amaurosis 5 (LCA5), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.13524 |
| DC631520 | gi|189163527|ref|NM_001127700.1 Homo sapiens serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 1 (SERPINA1), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 2.1306 |
| AY742821 | gi|59806358|ref|NM_006011.3 Homo sapiens ST8 alpha-N-acetyl-neuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase 2 (ST8SIA2), mRNA | 2.12885 |
| AK240628 | gi|160298141|ref|NM_000668.4 Homo sapiens alcohol dehydrogenase 1B (class I), beta polypeptide (ADH1B), mRNA | 2.12458 |
| AB174195 | gi|30794215|ref|NM_030961.1 Homo sapiens tripartite motif-containing 56 (TRIM56), mRNA | 2.12446 |
| DC646861 | gi|91807120|ref|NM_033087.3 Homo sapiens asparagine-linked glycosylation 2, alpha-1,3-mannosyltransferase homolog (S. cerevisiae) (ALG2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.12291 |
| AY650365 | gi|27436932|ref|NM_172337.1 Homo sapiens orthodenticle homeobox 2 (OTX2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.11514 |
| DW527197 | gi|219555668|ref|NM_052855.3 Homo sapiens ankyrin repeat domain 40 (ANKRD40), mRNA | 2.115 |
| AB171287 | gi|188497721|ref|NM_001127385.1 Homo sapiens cortexin 3 (CTXN3), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.11438 |
| AB173764 | gi|219879811|ref|NM_005475.2 Homo sapiens SH2B adaptor protein 3 (SH2B3), mRNA | 2.10791 |
| DK582787 | gi|221316657|ref|NM_004811.2 Homo sapiens leupaxin (LPXN), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.10555 |
| AB070128 | gi|217416373|ref|NM_145038.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 2 open reading frame 39 (C2orf39), mRNA | 2.10225 |
| AB070165 | gi|226491198|ref|NM_182496.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 38 (CCDC38), mRNA | 2.10075 |
| DK577398 | gi|52426772|ref|NM_002122.3 Homo sapiens major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1 (HLA-DQA1), mRNA | 2.09004 |
| AB169904 | gi|34147601|ref|NM_004309.3 Homo sapiens rho GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) alpha (ARHGDIA), mRNA | 2.08484 |
| AB220503 | gi|237681178|ref|NM_001160260.1 Homo sapiens cannabinoid receptor 1 (brain) (CNR1), transcript variant 6, mRNA | 2.08434 |
| AB173401 | gi|239750034|ref|XR_039406.2 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to yippee-like 5 (Drosophila) (LOC100132562), miscRNA | 2.08407 |
| AB171785 | gi|253970447|ref|NM_014253.3 Homo sapiens odz, odd Oz/ten-m homolog 1(Drosophila) (ODZ1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 2.08184 |
| AB171491 | gi|117938287|ref|NM_004171.3 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 1 (glial high affinity glutamate transporter), member 2 (SLC1A2), mRNA | 2.08087 |
| AB174571 | gi|182765446|ref|NM_001031711.2 Homo sapiens endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) 1 (ERGIC1), mRNA | 2.07886 |
| AB063092 | gi|34577113|ref|NM_015576.1 Homo sapiens ELKS/RAB6-interacting/CAST family member 2 (ERC2), mRNA | 2.07171 |
| AB056378 | gi|189163523|ref|NM_033064.4 Homo sapiens ataxia, cerebellar, Cayman type (ATCAY), mRNA | 2.06758 |
| AB055299 | gi|163644324|ref|NM_001112732.1 Homo sapiens MCF.2 cell line derived transforming sequence-like (MCF2L), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.06139 |
| AB172748 | gi|119220563|ref|NM_004852.2 Homo sapiens one cut homeobox 2 (ONECUT2), mRNA | 2.05909 |
| AB172478 | gi|239746981|ref|XR_078603.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to putative p150 (LOC100288106), miscRNA | 2.05792 |
| AB170807 | gi|236459850|ref|NM_173569.3 Homo sapiens ubinuclein 2 (UBN2), mRNA | 2.05471 |
| EF208824 | gi|239740919|ref|XM_002344047.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ beta 1, transcript variant 2 (LOC100294318), mRNA | 2.05031 |
| AB169481 | gi|150417992|ref|NM_033312.2 Homo sapiens CDC14 cell division cycle 14 homolog A (S. cerevisiae) (CDC14A), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 2.04992 |
| AB171520 | gi|56243494|ref|NM_004586.2 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein S6 kinase, 90 kDa, polypeptide 3 (RPS6KA3), mRNA | 2.0465 |
| DC629151 | gi|215982788|ref|NM_000477.5 Homo sapiens albumin (ALB), mRNA | 2.04345 |
| DC640591 | gi|208609965|ref|NM_001135664.1 Homo sapiens RAB7, member RAS oncogene family-like 1 (RAB7L1), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 2.04167 |
| BB887273 | gi|215,982,788|ref|NM_000477.5 Homo sapiens albumin (ALB), mRNA | 2.0414 |
| CJ435276 | gi|75,812,975|ref|NM_001033574.1 Homo sapiens archaelysin family metallopeptidase 2 (AMZ2), transcript variant 6, mRNA | 2.04064 |
| DC643114 | gi|33519462|ref|NM_004544.2 Homo sapiens NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 10, 42 kDa (NDUFA10), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 2.03575 |
| CJ436048 | gi|62865867|ref|NM_004102.3 Homo sapiens fatty acid-binding protein 3, muscle and heart (mammary-derived growth inhibitor) (FABP3), mRNA | 2.03528 |
| AB179303 | gi|196162694|ref|NM_003401.3 Homo sapiens X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 4 (XRCC4), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 2.03322 |
| AB171313 | gi|146219840|ref|NM_020709.1 Homo sapiens PNMA-like 2 (PNMAL2), mRNA | 2.02925 |
| AB173369 | gi|149363694|ref|NM_001009984.1 Homo sapiens chromosome 20 open reading frame 194 (C20orf194), mRNA | 2.01079 |
| AB171481 | gi|18496982|ref|NM_015526.1 Homo sapiens CAP-GLY domain-containing linker protein 3 (CLIP3), mRNA | 2.00151 |
| AB174068 | gi|84872123|ref|NR_002833.1 Homo sapiens dpy-19-like 2 pseudogene 1 (C. elegans) (DPY19L2P1), noncoding RNA | 1.99958 |
| AB050434 | gi|239753181|ref|XM_002345525.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2041348 (LOC100293610), mRNA | 1.99905 |
| DK577438 | gi|88999575|ref|NM_002622.4 Homo sapiens prefoldin subunit 1 (PFDN1), mRNA | 1.99519 |
| AB172315 | gi|239753426|ref|XR_038411.2 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 beta 2 (LOC646973), miscRNA | 1.99372 |
| BB895222 | gi|38372939|ref|NM_001185.2 Homo sapiens alpha-2-glycoprotein 1, zinc-binding (AZGP1), mRNA | 1.99214 |
| AB173728 | gi|111154086|ref|NM_020631.3 Homo sapiens pleckstrin homology domain-containing, family G (with RhoGef domain) member 5 (PLEKHG5), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.98959 |
| DC647709 | gi|28416926|ref|NM_002560.2 Homo sapiens purinergic receptor P2X, ligand-gated ion channel, 4 (P2RX4), mRNA | 1.98692 |
| AB048919 | gi|156766083|ref|NM_031418.2 Homo sapiens anoctamin 3 (ANO3), mRNA | 1.98684 |
| AB179103 | gi|18860913|ref|NM_021818.2 Homo sapiens salvador homolog 1 (Drosophila) (SAV1), mRNA | 1.97681 |
| AB046073 | gi|118498342|ref|NM_014861.2 Homo sapiens ATPase, Ca++ transporting, type 2C, member 2 (ATP2C2), mRNA | 1.97604 |
| AB172144 | gi|190341103|ref|NM_015163.5 Homo sapiens tripartite motif-containing 9 (TRIM9), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.97599 |
| DK583369 | gi|171460955|ref|NM_005800.4 Homo sapiens ubiquitin-specific peptidase like 1 (USPL1), mRNA | 1.9752 |
| AB174098 | gi|110815799|ref|NM_024345.3 Homo sapiens DDB1 and CUL4-associated factor 10 (DCAF10), mRNA | 1.97309 |
| DW526268 | gi|31083173|ref|NM_181078.1 Homo sapiens interleukin 21 receptor (IL21R), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.97258 |
| AB171701 | gi|20544144|ref|NM_139062.1 Homo sapiens casein kinase 1, delta (CSNK1D), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.96537 |
| CJ493302 | gi|17136150|ref|NM_004724.2 Homo sapiens ZW10, kinetochore associated, homolog (Drosophila) (ZW10), mRNA | 1.96534 |
| DK577545 | gi|24797075|ref|NM_002121.4 Homo sapiens major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP beta 1 (HLA-DPB1), mRNA | 1.96346 |
| CJ458429 | gi|71067335|ref|NM_031462.2 Homo sapiens CD99 molecule-like 2 (CD99L2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.96208 |
| AB172752 | gi|32698785|ref|NM_182490.1 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 227 (ZNF227), mRNA | 1.95671 |
| AB171668 | gi|40385866|ref|NM_199227.1 Homo sapiens methionine aminopeptidase 1D (MAP1D), mRNA | 1.95399 |
| AB051117 | gi|82617625|ref|NM_001037293.1 Homo sapiens paralemmin 2 (PALM2), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.9528 |
| AB169059 | gi|91992151|ref|NM_000616.3 Homo sapiens CD4 molecule (CD4), mRNA | 1.95226 |
| CJ443230 | gi|46094085|ref|NM_022758.4 Homo sapiens chromosome 6 open reading frame 106 (C6orf106), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.95082 |
| AB178987 | gi|38045951|ref|NM_021030.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 14 (ZNF14), mRNA | 1.94816 |
| AB172387 | gi|163659919|ref|NM_052839.3 Homo sapiens pannexin 2 (PANX2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.94536 |
| AB168775 | gi|223468671|ref|NM_001145135.1 Homo sapiens carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1B (muscle) (CPT1B), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 6, mRNA | 1.94062 |
| DC633198 | gi|206725531|ref|NM_001826.2 Homo sapiens CDC28 protein kinase regulatory subunit 1B (CKS1B), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.93773 |
| AB172044 | gi|25168266|ref|NM_170709.1 Homo sapiens serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase family, member 3 (SGK3), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.93543 |
| DK578185 | gi|239754745|ref|XM_002346052.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC100293771 (LOC100293771), mRNA | 1.93421 |
| AB171597 | gi|113951732|ref|NM_012095.4 Homo sapiens adaptor-related protein complex 3, mu 1 subunit (AP3M1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.93313 |
| AB179405 | gi|31543301|ref|NM_032600.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 54 (CCDC54), mRNA | 1.93038 |
| AB179267 | gi|37594443|ref|NM_015896.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger, MYND-type-containing 10 (ZMYND10), mRNA | 1.92859 |
| DC640525 | gi|35493837|ref|NM_004902.2 Homo sapiens RNA-binding motif protein 39 (RBM39), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.92337 |
| AB049869 | gi|239753181|ref|XM_002345525.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2041348 (LOC100293610), mRNA | 1.92159 |
| DW528250 | gi|52487034|ref|NM_004618.3 Homo sapiens topoisomerase (DNA) III alpha (TOP3A), mRNA | 1.91924 |
| DC636463 | gi|78214521|ref|NM_001035258.1 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein L38 (RPL38), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.91826 |
| AB179052 | gi|115511031|ref|NM_004432.2 Homo sapiens ELAV- (embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila-) like 2 (Hu antigen B) (ELAVL2), mRNA | 1.91696 |
| AB168809 | gi|37622352|ref|NM_003551.2 Homo sapiens nonmetastatic cells 5, protein expressed in nucleoside-diphosphate kinase (NME5), mRNA | 1.91336 |
| CJ435007 | gi|115527063|ref|NM_004859.3 Homo sapiens clathrin, heavy chain (Hc) (CLTC), mRNA | 1.91318 |
| AB171499 | gi|50845406|ref|NM_031444.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 22 open reading frame 13 (C22orf13), mRNA | 1.91088 |
| DC647333 | gi|118600974|ref|NM_007269.2 Homo sapiens syntaxin-binding protein 3 (STXBP3), mRNA | 1.90575 |
| AB172403 | gi|142976637|ref|NM_017420.3 Homo sapiens SIX homeobox 4 (SIX4), mRNA | 1.89362 |
| AB174282 | gi|31543080|ref|NM_016210.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 3 open reading frame 18 (C3orf18), mRNA | 1.89271 |
| DC648759 | gi|6382072|ref|NM_005258.2 Homo sapiens GTP cyclohydrolase I feedback regulator (GCHFR), mRNA | 1.88951 |
| AB169033 | gi|195927038|ref|NM_001786.3 Homo sapiens cell division cycle 2, G1 to S and G2 to M (CDC2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.88515 |
| AB173309 | gi|209447072|ref|NM_001135806.1 Homo sapiens synaptotagmin I (SYT1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.88194 |
| AB063003 | gi|116063563|ref|NM_018218.2 Homo sapiens ubiquitin-specific peptidase 40 (USP40), mRNA | 1.88102 |
| AB171041 | gi|86787650|ref|NM_014800.9 Homo sapiens engulfment and cell motility 1 (ELMO1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.87945 |
| CJ470094 | gi|209364624|ref|NM_001822.4 Homo sapiens chimerin (chimaerin) 1 (CHN1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.87132 |
| AB171236 | gi|19743893|ref|NM_133480.1 Homo sapiens transcriptional adaptor 3 (NGG1 homolog, yeast)-like (TADA3L), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.86897 |
| BB885210 | gi|32484974|ref|NM_006721.2 Homo sapiens adenosine kinase (ADK), transcript variant ADK-long, mRNA | 1.86865 |
| AB169067 | gi|188528615|ref|NM_182911.3 Homo sapiens testis-specific, 10 (TSGA10), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.86706 |
| CJ464698 | gi|221307560|ref|NR_026669.1 Homo sapiens synaptosomal-associated protein, 91 kDa homolog (mouse) (SNAP91), transcript variant 2, transcribed RNA | 1.86542 |
| AB179482 | gi|51173716|ref|NM_006720.3 Homo sapiens actin-binding LIM protein 1 (ABLIM1), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 1.85972 |
| CJ442615 | gi|239745120|ref|XR_015162.2 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC727880 (LOC727880), miscRNA | 1.85021 |
| CJ435208 | gi|170650722|ref|NM_014236.3 Homo sapiens glyceronephosphate O-acyltransferase (GNPAT), mRNA | 1.8499 |
| AY650307 | gi|51599155|ref|NM_001273.2 Homo sapiens chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 4 (CHD4), mRNA | 1.84509 |
| DW525872 | gi|77404354|ref|NM_003908.3 Homo sapiens eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 2 beta, 38 kDa (EIF2S2), mRNA | 1.84501 |
| DW529999 | gi|78190459|ref|NM_000978.3 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein L23 (RPL23), mRNA | 1.84409 |
| AB174451 | gi|223941821|ref|NM_014342.3 Homo sapiens mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 (C. elegans) (MTCH2), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 1.84017 |
| AB066534 | gi|188528627|ref|NM_033109.3 Homo sapiens polyribonucleotide nucleotidyltransferase 1 (PNPT1), mRNA | 1.83655 |
| BB888999 | gi|160298191|ref|NM_000507.3 Homo sapiens fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase 1 (FBP1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.8352 |
| DC637318 | gi|209977038|ref|NM_016074.3 Homo sapiens bolA homolog 1 (E. coli) (BOLA1), mRNA | 1.83477 |
| AB169205 | gi|109948303|ref|NM_018225.2 Homo sapiens smu-1 suppressor of mec-8 and unc-52 homolog (C. elegans) (SMU1), mRNA | 1.82627 |
| CJ441961 | gi|19913444|ref|NM_016257.2 Homo sapiens hippocalcin-like 4 (HPCAL4), mRNA | 1.8159 |
| AY650384 | gi|141803509|ref|NM_058164.2 Homo sapiens olfactomedin 2 (OLFM2), mRNA | 1.81587 |
| DC647305 | gi|38372918|ref|NM_001728.2 Homo sapiens basigin (Ok blood group) (BSG), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.8093 |
| AB172260 | gi|112382251|ref|NM_178313.2 Homo sapiens spectrin, beta, nonerythrocytic 1 (SPTBN1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.80742 |
| AB173850 | gi|194097340|ref|NM_002616.2 Homo sapiens period homolog 1 (Drosophila) (PER1), mRNA | 1.80415 |
| AB168762 | gi|242247096|ref|NM_001340.3 Homo sapiens cylicin, basic protein of sperm head cytoskeleton 2 (CYLC2), mRNA | 1.80079 |
| AB173856 | gi|60302919|ref|NM_001752.2 Homo sapiens catalase (CAT), mRNA | 1.79676 |
| AB060862 | gi|221219051|ref|NM_031924.4 Homo sapiens radial spoke 3 homolog (Chlamydomonas) (RSPH3), mRNA | 1.79563 |
| CJ470793 | gi|224586819|ref|NR_027265.1 Homo sapiens Golgi apparatus protein 1 (GLG1), transcript variant 5, transcribed RNA | 1.79405 |
| DW528583 | gi|239787833|ref|NM_015139.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 35 (UDP-glucuronic acid/UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine dual transporter), member D1 (SLC35D1), mRNA | 1.79359 |
| DK580881 | gi|194394144|ref|NM_145870.2 Homo sapiens glutathione transferase zeta 1 (GSTZ1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.792 |
| AB173997 | gi|225543100|ref|NR_027378.1 Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC643763 (LOC643763), noncoding RNA | 1.79131 |
| AY650356 | gi|223718142|ref|NM_173054.2 Homo sapiens reelin (RELN), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.78729 |
| DK584117 | gi|15967154|ref|NM_016558.2 Homo sapiens SCAN domain-containing 1 (SCAND1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.78008 |
| DC621384 | gi|15431296|ref|NM_000977.2 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein L13 (RPL13), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.77763 |
| DK577712 | gi|109148541|ref|NM_001605.2 Homo sapiens alanyl-tRNA synthetase (AARS), mRNA | 1.77723 |
| AB174251 | gi|253314435|ref|NR_027995.1 Homo sapiens ankyrin repeat domain 20 family, member A2 pseudogene (LOC284232), noncoding RNA | 1.77027 |
| AB174247 | gi|50897295|ref|NM_001002923.1 Homo sapiens IGF-like family member 4 (IGFL4), mRNA | 1.76977 |
| CJ490195 | gi|78190459|ref|NM_000978.3 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein L23 (RPL23), mRNA | 1.76786 |
| AB171831 | gi|167466275|ref|NM_152542.3 Homo sapiens protein phosphatase 1K (PP2C domain containing) (PPM1K), mRNA | 1.76709 |
| DK582810 | gi|90652856|ref|NM_032818.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 9 open reading frame 100 (C9orf100), mRNA | 1.765 |
| AB170534 | gi|108773786|ref|NM_000321.2 Homo sapiens retinoblastoma 1 (RB1), mRNA | 1.76182 |
| AB171096 | gi|110347436|ref|NM_001042545.1 Homo sapiens latent transforming growth factor beta-binding protein 4 (LTBP4), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.75594 |
| AB168611 | gi|21071068|ref|NM_004865.2 Homo sapiens TBP-like 1 (TBPL1), mRNA | 1.74839 |
| CJ492188 | gi|30181234|ref|NM_003447.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 165 (ZNF165), mRNA | 1.74573 |
| AB171700 | gi|115527063|ref|NM_004859.3 Homo sapiens clathrin, heavy chain (Hc) (CLTC), mRNA | 1.74566 |
| AB171366 | gi|22748942|ref|NM_152445.1 Homo sapiens family with sequence similarity 161, member B (FAM161B), mRNA | 1.74405 |
| AB168566 | gi|148664196|ref|NM_017950.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 40 (CCDC40), mRNA | 1.74135 |
| AB171657 | gi|221316692|ref|NM_198449.2 Homo sapiens embigin homolog (mouse) (EMB), mRNA | 1.73933 |
| AB056808 | gi|71772767|ref|NM_152826.2 Homo sapiens-sorting nexin 1 (SNX1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.73686 |
| AB168849 | gi|156766042|ref|NM_001103146.1 Homo sapiens GRB10-interacting GYF protein 2 (GIGYF2), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.73412 |
| AB172848 | gi|95113665|ref|NM_018157.2 Homo sapiens resistance to inhibitors of cholinesterase 8 homolog B (C. elegans) (RIC8B), mRNA | 1.72749 |
| AB048894 | gi|148727250|ref|NM_007137.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 81 (ZNF81), mRNA | 1.71845 |
| DW524469 | gi|239753181|ref|XM_002345525.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2041348 (LOC100293610), mRNA | 1.71582 |
| AB173566 | gi|89242130|ref|NM_014305.2 Homo sapiens TDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (TGDS), mRNA | 1.71406 |
| DC634783 | gi|116812576|ref|NM_016019.2 Homo sapiens LUC7-like 2 (S. cerevisiae) (LUC7L2), mRNA | 1.71163 |
| AB168438 | gi|64276485|ref|NM_005869.2 Homo sapiens serologically defined colon cancer antigen 10 (SDCCAG10), mRNA | 1.71108 |
| AB174725 | gi|169194555|ref|XR_040716.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC439950 (LOC439950), miscRNA | 1.70933 |
| AB170786 | gi|208879448|ref|NM_006265.2 Homo sapiens RAD21 homolog (S. pombe) (RAD21), mRNA | 1.70551 |
| CJ431422 | gi|117938253|ref|NM_001077441.1 Homo sapiens BCL2-associated transcription factor 1 (BCLAF1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.70446 |
| AB048954 | gi|148596971|ref|NM_014951.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 365 (ZNF365), transcript variant A, mRNA | 1.70334 |
| AB173447 | gi|40288292|ref|NM_000361.2 Homo sapiens thrombomodulin (THBD), mRNA | 1.70293 |
| AB173287 | gi|242117988|ref|NM_014702.4 Homo sapiens KIAA0408 (KIAA0408), mRNA | 1.70162 |
| CJ489820 | gi|218505834|ref|NM_001142782.1 Homo sapiens membrane-associated guanylate kinase, WW, and PDZ domain-containing 3 (MAGI3), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.68381 |
| AB173372 | gi|78190481|ref|NM_025221.5 Homo sapiens Kv channel-interacting protein 4 (KCNIP4), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.68058 |
| AB172865 | gi|31795545|ref|NM_012450.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 13 (sodium/sulfate symporters), member 4 (SLC13A4), mRNA | 1.67878 |
| AB168329 | gi|223468562|ref|NM_005628.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 1 (neutral amino acid transporter), member 5 (SLC1A5), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.67642 |
| AB171546 | gi|55956903|ref|NM_005922.2 Homo sapiens mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 (MAP3K4), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.67151 |
| AB063093 | gi|194248055|ref|NM_002045.3 Homo sapiens growth-associated protein 43 (GAP43), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.66805 |
| AB220449 | gi|23510394|ref|NM_138966.2 Homo sapiens neuropilin- (NRP-) and tolloid- (TLL-) like 1 (NETO1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.66789 |
| AB169208 | gi|22547155|ref|NM_002018.2 Homo sapiens flightless I homolog (Drosophila) (FLII), mRNA | 1.66361 |
| AB168324 | gi|116014337|ref|NM_030981.2 Homo sapiens RAB1B, member RAS oncogene family (RAB1B), mRNA | 1.66298 |
| AB169835 | gi|50726964|ref|NM_013392.2 Homo sapiens nuclear receptor-binding protein 1 (NRBP1), mRNA | 1.65785 |
| AB173501 | gi|195539333|ref|NM_018176.3 Homo sapiens leucine-rich repeat LGI family, member 2 (LGI2), mRNA | 1.6574 |
| DC630946 | gi|183227689|ref|NM_002049.3 Homo sapiens GATA-binding protein 1 (globin transcription factor 1) (GATA1), mRNA | 1.65657 |
| AB063075 | gi|239743824|ref|XM_001128647.3 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical LOC728701 (LOC728701), mRNA | 1.65564 |
| AB169782 | gi|38261964|ref|NM_198399.1 Homo sapiens cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein, 21 kD (ARPP-21), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.65067 |
| CJ477467 | gi|133778911|ref|NM_003309.2 Homo sapiens TSPY-like 1 (TSPYL1), mRNA | 1.65062 |
| BB900725 | gi|31542685|ref|NM_025125.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 10 open reading frame 57 (C10orf57), mRNA | 1.64409 |
| AB220555 | gi|208973250|ref|NM_003702.3 Homo sapiens regulator of G-protein signaling 20 (RGS20), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.64376 |
| AB171804 | gi|66932910|ref|NM_014676.2 Homo sapiens pumilio homolog 1 (Drosophila) (PUM1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.63724 |
| DC625559 | gi|4557320|ref|NM_000039.1 Homo sapiens apolipoprotein A-I (APOA1), mRNA | 1.631 |
| AB172266 | gi|170932491|ref|NM_030770.2 Homo sapiens transmembrane protease, serine 5 (TMPRSS5), mRNA | 1.62995 |
| AB173763 | gi|62953115|ref|NM_001017523.1 Homo sapiens BTB (POZ) domain-containing 11 (BTBD11), transcript variant b, mRNA | 1.62499 |
| AB172974 | gi|111161293|ref|NM_005746.2 Homo sapiens nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (NAMPT), mRNA | 1.62078 |
| AB179155 | gi|187608347|ref|NM_145046.3 Homo sapiens calreticulin 3 (CALR3), mRNA | 1.6111 |
| AB169148 | gi|153792481|ref|NM_033048.4 Homo sapiens CPX chromosome region, candidate 1 (CPXCR1), mRNA | 1.60985 |
| AB171264 | gi|130977817|ref|NM_024549.4 Homo sapiens tectonic family member 1 (TCTN1), transcript variant 3, mRNA | 1.60704 |
| AB172446 | gi|193083128|ref|NM_001128920.1 Homo sapiens MAP/microtubule affinity-regulating kinase 3 (MARK3), transcript variant 4, mRNA | 1.60471 |
| DC852298 | gi|195972796|ref|NM_001130917.1 Homo sapiens leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor, subfamily A (with TM domain), member 2 (LILRA2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.59852 |
| AB046637 | gi|209571546|ref|NM_018095.4 Homo sapiens Kelch repeat and BTB (POZ) domain-containing 4 (KBTBD4), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.58107 |
| CJ445723 | gi|90903230|ref|NM_002111.6 Homo sapiens huntingtin (HTT), mRNA | 1.57689 |
| DC630899 | gi|83641894|ref|NM_031157.2 Homo sapiens heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (HNRNPA1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.5766 |
| AB168476 | gi|219555742|ref|NM_015335.3 Homo sapiens mediator complex subunit 13-like (MED13L), mRNA | 1.57355 |
| DC642541 | gi|20357546|ref|NM_004231.2 Homo sapiens ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 14 kDa, V1 subunit F (ATP6V1F), mRNA | 1.57215 |
| AB170370 | gi|224177554|ref|NM_002340.5 Homo sapiens lanosterol synthase (2,3-oxidosqualene-lanosterol cyclase) (LSS), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.57006 |
| DC636538 | gi|71164876|ref|NM_001014.3 Homo sapiens ribosomal protein S10 (RPS10), mRNA | 1.56413 |
| DC648258 | gi|4557818|ref|NM_000277.1 Homo sapiens phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), mRNA | 1.56396 |
| AB168688 | gi|75709218|ref|NM_001324.2 Homo sapiens cleavage stimulation factor, 3′ pre-RNA, subunit 1, 50 kDa (CSTF1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.56349 |
| CJ486539 | gi|194018543|ref|NM_031451.4 Homo sapiens testis expressed 101 (TEX101), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.55338 |
| AB173591 | gi|56699472|ref|NM_006298.2 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 192 (ZNF192), mRNA | 1.54892 |
| AB168460 | gi|56090619|ref|NM_001007531.1 Homo sapiens NFKB-activating protein-like (NKAPL), mRNA | 1.54807 |
| AB046102 | gi|215272394|ref|NM_001080475.2 Homo sapiens pleckstrin homology domain containing, family M, member 3 (PLEKHM3), mRNA | 1.53926 |
| AB097526 | gi|46409303|ref|NM_207332.1 Homo sapiens glutamate-rich 1 (ERICH1), mRNA | 1.53642 |
| AB052134 | gi|227430412|ref|NM_024827.3 Homo sapiens histone deacetylase 11 (HDAC11), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.53543 |
| AB170181 | gi|21265090|ref|NM_007208.2 Homo sapiens mitochondrial ribosomal protein L3 (MRPL3), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 1.52903 |
| AB171241 | gi|116235443|ref|NM_138421.2 Homo sapiens serum amyloid A-like 1 (SAAL1), mRNA | 1.52713 |
| AB171237 | gi|48675815|ref|NM_015723.2 Homo sapiens patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 8 (PNPLA8), mRNA | 1.52587 |
| DC625517 | gi|47578120|ref|NM_177947.2 Homo sapiens armadillo repeat containing, X-linked 3 (ARMCX3), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 1.52547 |
| AB168964 | gi|87159814|ref|NM_001696.3 Homo sapiens ATPase, H+ transporting, lysosomal 31 kDa, V1 subunit E1 (ATP6V1E1), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.52424 |
| DC631115 | gi|239752151|ref|XM_002348112.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to immunoglobulin lambda locus (LOC100290481), mRNA | 1.51711 |
| DC640134 | gi|208609986|ref|NM_014655.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 25, member 44 (SLC25A44), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 1.51672 |
| AB173691 | gi|94536855|ref|NM_013301.2 Homo sapiens coiled-coil domain-containing 106 (CCDC106), mRNA | 1.50477 |
| AB168370 | gi|154744869|ref|NM_022752.5 Homo sapiens zinc finger protein 574 (ZNF574), mRNA | 1.50452 |
Table 2.
Genes that are downregulated in TM cells.
| Accession number | Human RefSeq description | Fold change |
|---|---|---|
| DC624859 | gi|215982788|ref|NM_000477.5 Homo sapiens albumin (ALB), mRNA | 0.11952 |
| AB171761 | gi|148271103|ref|NM_173495.2 Homo sapiens patched domain-containing 1 (PTCHD1), mRNA | 0.13543 |
| AB047615 | gi|70780382|ref|NM_004285.3 Homo sapiens hexose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (glucose 1-dehydrogenase) (H6PD), mRNA | 0.17649 |
| DC621007 | gi|38016905|ref|NR_001578.1 Homo sapiens L-threonine dehydrogenase (TDH), noncoding RNA | 0.20061 |
| CJ443677 | gi|38327038|ref|NM_002154.3 Homo sapiens heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 (HSPA4), mRNA | 0.2086 |
| DC622138 | gi|145386530|ref|NM_001084392.1 Homo sapiens D-dopachrome tautomerase (DDT), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.21345 |
| BB891761 | gi|33519462|ref|NM_004544.2 Homo sapiens NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex, 10, 42 kDa (NDUFA10), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, mRNA | 0.23147 |
| CJ444181 | gi|226437566|ref|NM_001018060.2 Homo sapiens apoptosis-inducing factor, mitochondrion-associated 3 (AIFM3), nuclear gene encoding mitochondrial protein, transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.24045 |
| AB171890 | gi|118572602|ref|NM_001079514.1 Homo sapiens ubinuclein 1 (UBN1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.24676 |
| AB174511 | gi|153792041|ref|NM_020823.1 Homo sapiens transmembrane protein 181 (TMEM181), mRNA | 0.29472 |
| AB168319 | gi|116256484|ref|NM_006781.3 Homo sapiens chromosome 6 open reading frame 10 (C6orf10), mRNA | 0.3105 |
| DW526909 | gi|20302159|ref|NM_005999.2 Homo sapiens translin-associated factor X (TSNAX), mRNA | 0.32949 |
| AB173471 | gi|154354995|ref|NM_002222.4 Homo sapiens inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor, type 1 (ITPR1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.33892 |
| BB898986 | gi|167003944|ref|NM_000204.3 Homo sapiens complement factor I (CFI), mRNA | 0.34234 |
| DK578390 | gi|56788350|ref|NM_001008695.1 Homo sapiens THAP domain-containing 7 (THAP7), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.35502 |
| CJ444326 | gi|209413724|ref|NM_003692.3 Homo sapiens transmembrane protein with EGF-like and two follistatin-like domains 1 (TMEFF1), mRNA | 0.3719 |
| AB048874 | gi|239753181|ref|XM_002345525.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2041348 (LOC100293610), mRNA | 0.38524 |
| DC635743 | gi|239750740|ref|XM_002347480.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens similar to hCG2038941 (LOC100290006), mRNA | 0.3882 |
| CJ442045 | gi|96975096|ref|NM_016577.3 Homo sapiens RAB6B, member RAS oncogene family (RAB6B), mRNA | 0.39034 |
| BB897881 | gi|31542685|ref|NM_025125.2 Homo sapiens chromosome 10 open reading frame 57 (C10orf57), mRNA | 0.39308 |
| AB168422 | gi|194306536|ref|NM_144594.2 Homo sapiens gametocyte-specific factor 1 (GTSF1), mRNA | 0.43061 |
| DW524779 | gi|226342870|ref|NR_027449.1 Homo sapiens TBC1 domain family, member 15 (TBC1D15), transcript variant 4, transcribed RNA | 0.44075 |
| DC630545 | gi|39812105|ref|NM_198941.1 Homo sapiens serine incorporator 3 (SERINC3), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.44508 |
| AB172901 | gi|42544225|ref|NM_020857.2 Homo sapiens vacuolar protein sorting 18 homolog (S. cerevisiae) (VPS18), mRNA | 0.44872 |
| DW528888 | gi|40068463|ref|NM_020732.2 Homo sapiens AT-rich interactive domain 1B (SWI1-like) (ARID1B), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.44985 |
| DC636880 | gi|17738314|ref|NM_006835.2 Homo sapiens cyclin I (CCNI), mRNA | 0.45196 |
| AB220379 | gi|185134767|ref|NM_002524.3 Homo sapiens neuroblastoma RAS viral (v-ras) oncogene homolog (NRAS), mRNA | 0.46121 |
| AB055316 | gi|226437631|ref|NM_001004339.2 Homo sapiens zyg-11 homolog A (C. elegans) (ZYG11A), mRNA | 0.46399 |
| DC641070 | gi|58331227|ref|NM_005223.3 Homo sapiens deoxyribonuclease I (DNASE1), mRNA | 0.46575 |
| AB056428 | gi|49574533|ref|NM_032782.3 Homo sapiens hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 (HAVCR2), mRNA | 0.46705 |
| AB168577 | gi|146260272|ref|NM_001085451.1 Homo sapiens leukemia NUP98 fusion partner 1 (LNP1), mRNA | 0.46891 |
| AB048999 | gi|225735571|ref|NR_027416.1 Homo sapiens nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 3 pseudogene (LOC100272146), noncoding RNA | 0.47824 |
| AB174085 | gi|142360382|ref|NM_176815.3 Homo sapiens dihydrofolate reductase-like 1 (DHFRL1), mRNA | 0.49049 |
| DC642335 | gi|148491081|ref|NM_001343.2 Homo sapiens-disabled homolog 2, mitogen-responsive phosphoprotein (Drosophila) (DAB2), mRNA | 0.4971 |
| AB173771 | gi|38176290|ref|NM_001233.3 Homo sapiens caveolin 2 (CAV2), transcript variant 1, mRNA | 0.49863 |
| DW523198 | gi|145312264|ref|NM_033266.3 Homo sapiens endoplasmic reticulum to nucleus signaling 2 (ERN2), mRNA | 0.50158 |
| AF492282 | gi|52630343|ref|NM_021983.4 Homo sapiens major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR beta 4 (HLA-DRB4), mRNA | 0.50533 |
| AB047937 | gi|194097480|ref|NM_020412.4 Homo sapiens chromatin-modifying protein 1B (CHMP1B), mRNA | 0.51198 |
| AB179165 | gi|118136291|ref|NM_006465.2 Homo sapiens AT-rich interactive domain 3B (bright-like) (ARID3B), mRNA | 0.51349 |
| AJ585530 | gi|75709168|ref|NM_002260.3 Homo sapiens killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily C, member 2 (KLRC2), mRNA | 0.52335 |
| AB170944 | gi|40255250|ref|NM_144635.3 Homo sapiens family with sequence similarity 131, member A (FAM131A), mRNA | 0.55244 |
| AB171281 | gi|154759258|ref|NM_003127.2 Homo sapiens spectrin, alpha, nonerythrocytic 1 (alpha-fodrin) (SPTAN1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.555 |
| AB172429 | gi|224994204|ref|NM_001145853.1 Homo sapiens Wolfram syndrome 1 (wolframin) (WFS1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.57755 |
| AB171421 | gi|110611175|ref|NM_000843.3 Homo sapiens glutamate receptor, metabotropic 6 (GRM6), mRNA | 0.58226 |
| AB096987 | gi|239750853|ref|XR_079356.1 PREDICTED: Homo sapiens hypothetical protein LOC100130855 (LOC100130855), miscRNA | 0.59997 |
| AB049000 | gi|209977116|ref|NM_080872.2 Homo sapiens unc-5 homolog D (C. elegans) (UNC5D), mRNA | 0.60066 |
| BB893759 | gi|194018407|ref|NM_178148.2 Homo sapiens solute carrier family 35, member B2 (SLC35B2), mRNA | 0.61849 |
| AB056791 | gi|162951883|ref|NM_014925.3 Homo sapiens R3H domain-containing 2 (R3HDM2), mRNA | 0.64652 |
| AB070176 | gi|221307501|ref|NM_001143976.1 Homo sapiens WEE1 homolog (S. pombe) (WEE1), transcript variant 2, mRNA | 0.64704 |
| AB048962 | gi|154146186|ref|NM_152634.2 Homo sapiens transcription elongation factor A (SII) N-terminal and central domain containing (TCEANC), mRNA | 0.65673 |
| DK578501 | gi|24797073|ref|NM_033554.2 Homo sapiens major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1 (HLA-DPA1), mRNA | 0.65963 |
Table 3.
Gene ontology of upregulated genes in Y-27632-treated TM cells.
| Ontology | Term | Changed genes | Total genes | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular component | Cell projection | 31 (1) | 331 (38) | 0.0000306 |
| Cellular component | Neuron projection | 20 (6) | 180 (28) | 0.0000901 |
| Cellular component | Cell projection part | 17 (0) | 142 (0) | 0.000135 |
| Biological process | Regulation of neurotransmitter levels | 8 (0) | 47 (2) | 0.00148 |
| Molecular function | Calcium channel regulator activity | 4 (3) | 11 (9) | 0.00225 |
| Cellular component | Presynaptic membrane | 5 (5) | 20 (20) | 0.0024 |
| Cellular component | Plasma membrane part | 45 (0) | 706 (2) | 0.00259 |
| Biological process | Synaptic transmission | 16 (10) | 170 (66) | 0.00374 |
| Molecular function | Channel regulator activity | 5 (0) | 23 (0) | 0.00421 |
| Biological process | Cellular nitrogen compound biosynthetic process | 21 (0) | 255 (0) | 0.00443 |
| Biological process | L-Glutamate import | 3 (3) | 6 (4) | 0.00456 |
| Cellular component | Platelet alpha granule | 5 (1) | 24 (2) | 0.00472 |
| Biological process | Transmission of nerve impulse | 17 (0) | 189 (3) | 0.00563 |
| Molecular function | Anion:cation symporter activity | 4 (0) | 15 (0) | 0.00565 |
| Molecular function | Sodium:dicarboxylate symporter activity | 3 (3) | 7 (7) | 0.00585 |
| Biological process | L-Amino acid import | 3 (0) | 7 (0) | 0.00632 |
| Biological process | Amino acid import | 3 (0) | 7 (0) | 0.00632 |
| Cellular component | Axon part | 6 (0) | 38 (2) | 0.00665 |
| Biological process | Regulation of mitotic cell cycle | 8 (1) | 62 (6) | 0.00683 |
| Molecular function | Anion transmembrane transporter activity | 8 (0) | 66 (5) | 0.00813 |
| Biological process | Cell-cell signaling | 21 (4) | 268 (74) | 0.00841 |
| Molecular function | High-affinity glutamate transmembrane transporter activity | 2 (2) | 2 (2) | 0.00875 |
| Cellular component | Cytoplasmic vesicle part | 9 (0) | 83 (2) | 0.00918 |
| Biological process | Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process | 2 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.00923 |
| Biological process | Response to calcium ion | 5 (4) | 28 (25) | 0.00969 |
| Molecular function | Rho guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity | 5 (5) | 29 (29) | 0.00984 |
| Biological process | Carboxylic acid transport | 9 (0) | 81 (1) | 0.01005 |
| Molecular function | Phosphatidylinositol binding | 3 (3) | 9 (9) | 0.01012 |
| Molecular function | Dicarboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity | 3 (0) | 9 (0) | 0.01012 |
| Biological process | Organic acid transport | 9 (0) | 82 (0) | 0.01077 |
| Biological process | Glutamate metabolic process | 3 (0) | 9 (4) | 0.01091 |
| Biological process | Dicarboxylic acid transport | 3 (3) | 9 (7) | 0.01091 |
| Cellular component | Axoneme | 4 (2) | 19 (5) | 0.01104 |
| Molecular function | Structural constituent of cytoskeleton | 5 (5) | 31 (31) | 0.01251 |
| Cellular component | Cytoplasmic membrane-bounded vesicle lumen | 4 (0) | 20 (0) | 0.01285 |
| Cellular component | Platelet alpha granule lumen | 4 (4) | 20 (20) | 0.01285 |
| Cellular component | Dendritic spine | 4 (4) | 20 (20) | 0.01285 |
| Cellular component | Neuron spine | 4 (0) | 20 (0) | 0.01285 |
| Cellular component | Axon | 9 (6) | 89 (62) | 0.01361 |
| Cellular component | Neurofilament | 2 (2) | 3 (3) | 0.01394 |
| Molecular function | Antioxidant activity | 5 (2) | 32 (12) | 0.01401 |
| Biological process | Rho protein signal transduction | 7 (1) | 57 (15) | 0.01403 |
| Molecular function | Phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase activity | 2 (2) | 3 (3) | 0.0142 |
| Biological process | ER to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | 4 (4) | 20 (20) | 0.01457 |
| Cellular component | Vesicle lumen | 4 (0) | 21 (1) | 0.01484 |
| Biological process | D-Amino acid transport | 2 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.01497 |
| Biological process | D-Aspartate import | 2 (2) | 3 (3) | 0.01497 |
| Biological process | D-Aspartate transport | 2 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.01497 |
| Biological process | Glutamate biosynthetic process | 2 (2) | 3 (3) | 0.01497 |
| Biological process | 2′-Deoxyribonucleotide biosynthetic process | 2 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.01497 |
| Biological process | Fatty acid transport | 4 (1) | 21 (6) | 0.01681 |
| Molecular function | Ras guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity | 5 (0) | 34 (3) | 0.01737 |
| Biological process | Regulation of cell cycle process | 6 (0) | 47 (0) | 0.01912 |
| Biological process | Nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process | 8 (1) | 76 (3) | 0.0195 |
| Molecular function | Transporter activity | 34 (8) | 556 (147) | 0.01993 |
| Molecular function | Monocarboxylic acid binding | 4 (0) | 23 (0) | 0.02002 |
| Cellular component | Neurofilament cytoskeleton | 2 (0) | 4 (1) | 0.02037 |
| Biological process | Pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process | 3 (0) | 12 (0) | 0.02063 |
| Biological process | Pyrimidine nucleoside triphosphate metabolic process | 3 (0) | 12 (0) | 0.02063 |
| Molecular function | Oxidoreductase activity, acting on paired donors, with incorporation or reduction of molecular oxygen, reduced pteridine as one donor, and incorporation of one atom of oxygen | 2 (1) | 4 (2) | 0.02075 |
| Molecular function | Thioredoxin-disulfide reductase activity | 2 (2) | 4 (4) | 0.02075 |
| Biological process | Regulation of secretion | 8 (0) | 77 (0) | 0.0208 |
| Biological process | Neurotransmitter biosynthetic process | 2 (2) | 4 (4) | 0.02186 |
| Biological process | Tetrahydrobiopterin metabolic process | 2 (1) | 4 (1) | 0.02186 |
| Biological process | Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate metabolic process | 2 (0) | 4 (1) | 0.02186 |
| Cellular component | Clathrin coat | 4 (1) | 24 (1) | 0.02193 |
| Biological process | Response to metal ion | 8 (0) | 78 (3) | 0.02216 |
| Cellular component | Transport vesicle membrane | 3 (0) | 13 (0) | 0.02236 |
| Biological process | Neurotransmitter metabolic process | 3 (1) | 13 (3) | 0.02465 |
| Biological process | Long-chain fatty acid transport | 3 (2) | 13 (4) | 0.02465 |
| Molecular function | Oxidoreductase activity, acting on sulfur group of donors | 4 (0) | 25 (0) | 0.02549 |
| Molecular function | Organic acid:sodium symporter activity | 3 (0) | 14 (0) | 0.02707 |
| Molecular function | Phosphoinositide binding | 6 (2) | 53 (30) | 0.02738 |
| Molecular function | Carboxylic acid binding | 8 (0) | 84 (5) | 0.02754 |
| Cellular component | MHC protein complex | 4 (0) | 26 (0) | 0.02764 |
| Molecular function | DNA topoisomerase type I activity | 2 (2) | 5 (5) | 0.02831 |
| Molecular function | Solute:sodium symporter activity | 4 (0) | 26 (0) | 0.02853 |
| Cellular component | Synapse | 13 (10) | 167 (116) | 0.0289 |
| Biological process | L-Amino acid transport | 3 (0) | 14 (1) | 0.02906 |
| Biological process | Cilium morphogenesis | 3 (1) | 14 (3) | 0.02906 |
| Cellular component | Secretory granule | 8 (3) | 86 (27) | 0.02929 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of myeloid leukocyte differentiation | 2 (0) | 5 (0) | 0.0298 |
| Biological process | Glutamate catabolic process | 2 (0) | 5 (0) | 0.0298 |
| Biological process | Sulfate transport | 2 (2) | 5 (5) | 0.0298 |
| Biological process | Deoxyribonucleotide biosynthetic process | 2 (0) | 5 (2) | 0.0298 |
| Cellular component | Endomembrane system | 26 (1) | 416 (14) | 0.03019 |
| Cellular component | External side of plasma membrane | 6 (5) | 55 (49) | 0.03035 |
| Cellular component | Plasma membrane | 64 (48) | 1224 (935) | 0.03044 |
| Cellular component | Endocytic vesicle membrane | 3 (3) | 15 (12) | 0.03078 |
| Cellular component | Clathrin coated vesicle membrane | 4 (0) | 27 (3) | 0.0308 |
| Cellular component | Intrinsic to organelle membrane | 8 (0) | 87 (0) | 0.03095 |
| Biological process | Regulation of rho protein signal transduction | 5 (5) | 39 (29) | 0.03101 |
| Biological process | Neurotransmitter secretion | 4 (3) | 26 (11) | 0.03114 |
| Cellular component | Synapse part | 10 (0) | 117 (2) | 0.03187 |
| Biological process | Vitamin transport | 3 (1) | 15 (1) | 0.03386 |
| Molecular function | Symporter activity | 6 (6) | 57 (44) | 0.03631 |
| Molecular function | Syntaxin-1 binding | 2 (2) | 6 (6) | 0.03678 |
| Molecular function | Ion channel inhibitor activity | 2 (1) | 6 (2) | 0.03678 |
| Biological process | Cell communication | 34 (4) | 562 (40) | 0.03717 |
| Cellular component | Endocytic vesicle | 4 (1) | 29 (10) | 0.03772 |
| Biological process | Regulation of mitosis | 4 (2) | 28 (7) | 0.03839 |
| Biological process | Regulation of nuclear division | 4 (0) | 28 (0) | 0.03839 |
| Biological process | Response to inorganic substance | 10 (1) | 118 (8) | 0.03843 |
| Biological process | Phosphatidylcholine biosynthetic process | 2 (2) | 6 (5) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Interleukin-1 beta secretion | 2 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Interleukin-1 secretion | 2 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Regulation of interleukin-1 beta secretion | 2 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Regulation of interleukin-1 secretion | 2 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Cdc42 protein signal transduction | 2 (1) | 6 (3) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | L-Phenylalanine catabolic process | 2 (2) | 6 (6) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | L-Phenylalanine metabolic process | 2 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Tyrosine metabolic process | 2 (0) | 6 (1) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Multicellular organismal aging | 2 (1) | 6 (2) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Aspartate transport | 2 (0) | 6 (3) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway | 2 (2) | 6 (6) | 0.03869 |
| Biological process | Neurofilament cytoskeleton organization | 2 (1) | 6 (5) | 0.03869 |
| Molecular function | Chloride ion binding | 4 (4) | 29 (29) | 0.0389 |
| Biological process | L-Glutamate transport | 3 (0) | 16 (7) | 0.03904 |
| Biological process | Platelet activation | 3 (2) | 16 (11) | 0.03904 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of secretion | 5 (0) | 42 (1) | 0.03976 |
| Molecular function | Substrate-specific transporter activity | 28 (0) | 463 (0) | 0.04034 |
| Biological process | Nucleotide biosynthetic process | 12 (0) | 151 (7) | 0.04052 |
| Cellular component | Microtubule basal body | 3 (3) | 17 (17) | 0.04062 |
| Molecular function | Calcium-dependent protein binding | 3 (3) | 17 (17) | 0.04164 |
| Biological process | Anion transport | 7 (0) | 73 (10) | 0.04185 |
| Molecular function | Solute:cation symporter activity | 5 (0) | 44 (0) | 0.04201 |
| Biological process | Purine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthetic process | 7 (0) | 74 (0) | 0.0443 |
| Biological process | Acidic amino acid transport | 3 (0) | 17 (0) | 0.04461 |
| Biological process | Pyrimidine nucleoside metabolic process | 3 (0) | 17 (1) | 0.04461 |
| Biological process | Pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthetic process | 3 (0) | 17 (4) | 0.04461 |
| Cellular component | MHC class II protein complex | 3 (3) | 18 (18) | 0.04607 |
| Molecular function | Oxidoreductase activity, acting on sulfur group of donors, NAD, or NADP as acceptor | 2 (0) | 7 (2) | 0.04608 |
| Molecular function | Fatty acid transporter activity | 2 (1) | 7 (3) | 0.04608 |
| Molecular function | Channel inhibitor activity | 2 (0) | 7 (1) | 0.04608 |
| Molecular function | DNA topoisomerase activity | 2 (1) | 7 (2) | 0.04608 |
| Biological process | Regulation of cytokine production | 7 (0) | 75 (0) | 0.04684 |
| Molecular function | NADP or NADPH binding | 3 (3) | 18 (17) | 0.04721 |
| Biological process | Nucleobase, nucleoside, and Nucleotide biosynthetic process | 12 (0) | 157 (0) | 0.04725 |
| Biological process | Nucleobase, nucleoside, nucleotide, and nucleic acid biosynthetic process | 12 (0) | 157 (0) | 0.04725 |
| Biological process | G1 phase | 2 (1) | 7 (1) | 0.04845 |
| Cellular component | Lamellipodium | 4 (4) | 32 (32) | 0.04965 |
| Cellular component | Transport vesicle | 4 (1) | 32 (11) | 0.04965 |
Table 4.
Gene ontology of downregulated genes in Y-27632-treated TM cells.
| Ontology | Term | Changed genes | Total genes | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular function | Endonuclease activity, active with either ribo- or deoxyribonucleic acids and producing 5′-phosphomonoesters | 2 (0) | 13 (0) | 0.00279 |
| Biological process | Antigen processing and presentation of peptide or polysaccharide antigen via MHC class II | 2 (2) | 16 (14) | 0.00421 |
| Cellular component | MHC class II protein complex | 2 (2) | 18 (18) | 0.00606 |
| Molecular function | D-Dopachrome decarboxylase activity | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01065 |
| Molecular function | Glucose 1-dehydrogenase activity | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01065 |
| Molecular function | Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01065 |
| Molecular function | Deoxyribonuclease I activity | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01065 |
| Molecular function | 3′-Phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate transmembrane transporter activity | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01065 |
| Biological process | Olfactory behavior | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01091 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01091 |
| Biological process | Regulation of dopamine receptor signaling pathway | 1 (0) | 1 (0) | 0.01091 |
| Biological process | 3′-Phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate transport | 1 (1) | 1 (1) | 0.01091 |
| Biological process | Negative regulation of neuron apoptosis | 2 (2) | 28 (28) | 0.01148 |
| Cellular component | MHC protein complex | 2(0) | 26(0) | 0.01171 |
| Molecular function | Toxin binding | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | C2H2 zinc finger domain binding | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | Dopachrome isomerase activity | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | 6-Phosphogluconolactonase activity | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | Hedgehog receptor activity | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | Dihydrofolate reductase activity | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01594 |
| Molecular function | Purine nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity | 1 (0) | 2 (1) | 0.01594 |
| Biological process | Cytolysis by symbiont of host cells | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Cytolysis of cells in other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Cytolysis of cells of another organism | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Disruption by symbiont of host cells | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Hemolysis by symbiont of host erythrocytes | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Hemolysis of cells in other organism | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Hemolysis of cells in other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Killing by symbiont of host cells | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Maintenance of mitochondrion location | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification by organism of cell membrane in other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification by symbiont of host cell membrane | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification by symbiont of host cellular component | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification by symbiont of host structure | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification of cellular component in other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Modification of structure of other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Caveola assembly | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Membrane raft assembly | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway | 1 (0) | 2 (1) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Chromatin-mediated maintenance of transcription | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of gene expression, epigenetic | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | ncRNA catabolic process | 1 (0) | 2 (0) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | rRNA catabolic process | 1 (1) | 2 (2) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Purine nucleoside transport | 1 (0) | 2 (1) | 0.01632 |
| Biological process | Striated muscle cell differentiation | 2 (1) | 38 (5) | 0.0199 |
| Biological process | Antigen processing and presentation | 2 (2) | 38 (32) | 0.0199 |
| Molecular function | Copper ion binding | 2 (2) | 39 (38) | 0.01996 |
| Molecular function | Endodeoxyribonuclease activity, producing 5′-phosphomonoesters | 1 (0) | 3 (1) | 0.0212 |
| Cellular component | Membrane | 24 (17) | 2769 (1768) | 0.02168 |
| Biological process | Maintenance of organelle location | 1 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Melanin biosynthetic process | 1 (1) | 3 (3) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Melanin metabolic process | 1 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Endoplasmic reticulum calcium ion homeostasis | 1 (1) | 3 (1) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Multicellular organismal water homeostasis | 1 (0) | 3 (0) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Renal water homeostasis | 1 (1) | 3 (1) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of Rac protein signal transduction | 1 (1) | 3 (3) | 0.02171 |
| Biological process | Apoptosis | 7 (3) | 522 (189) | 0.0221 |
| Biological process | Programmed cell death | 7 (0) | 525 (2) | 0.02273 |
| Cellular component | Extrinsic to internal side of plasma membrane | 1 (1) | 3 (3) | 0.02347 |
| Cellular component | Spectrin | 1 (1) | 3 (3) | 0.02347 |
| Molecular function | Endonuclease activity | 2 (2) | 43 (30) | 0.02378 |
| Molecular function | Nucleoside transmembrane transporter activity | 1 (0) | 4 (1) | 0.02643 |
| Biological process | Regulation of neuron apoptosis | 2 (0) | 45 (2) | 0.02693 |
| Biological process | Detection of visible light | 1 (1) | 4 (1) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Chemosensory behavior | 1 (0) | 4 (3) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Protein maturation by protein folding | 1 (1) | 4 (4) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Cellular chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly | 1 (1) | 4 (2) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Mitochondrial outer membrane translocase complex assembly | 1 (1) | 4 (4) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Outer mitochondrial membrane organization | 1 (0) | 4 (0) | 0.02706 |
| Biological process | Glycine biosynthetic process | 1 (1) | 4 (2) | 0.02706 |
| Cellular component | Membrane part | 21 (0) | 2325 (1) | 0.02771 |
| Biological process | Cellular membrane organization | 4 (0) | 212 (30) | 0.02909 |
| Biological process | Membrane organization | 4 (0) | 212 (0) | 0.02909 |
| Biological process | Neuron apoptosis | 2 (0) | 48 (3) | 0.03021 |
| Biological process | Neuron death | 2 (0) | 48 (0) | 0.03021 |
| Biological process | Muscle cell differentiation | 2 (0) | 49 (1) | 0.03134 |
| Biological process | Disruption of cells of other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 5 (0) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Killing of cells in other organism during symbiotic interaction | 1 (0) | 5 (0) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Water homeostasis | 1 (0) | 5 (1) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Endoplasmic reticulum organization | 1 (1) | 5 (5) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Membrane raft organization | 1 (0) | 5 (1) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Pinocytosis | 1 (1) | 5 (2) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Nucleoside transport | 1 (0) | 5 (2) | 0.03239 |
| Biological process | Response to light stimulus | 2 (0) | 51 (8) | 0.03364 |
| Biological process | Cell death | 7 (0) | 578 (68) | 0.03597 |
| Biological process | Vesicle-mediated transport | 5 (2) | 336 (120) | 0.03622 |
| Biological process | Death | 7 (0) | 579 (0) | 0.03626 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of signaling pathway | 3 (0) | 133 (0) | 0.03743 |
| Biological process | Modification by host of symbiont morphology or physiology | 1 (0) | 6 (0) | 0.03769 |
| Biological process | ER overload response | 1 (1) | 6 (5) | 0.03769 |
| Biological process | Regulation of Rac protein signal transduction | 1 (0) | 6 (1) | 0.03769 |
| Molecular function | Actin binding | 3 (3) | 139 (121) | 0.0394 |
| Cellular component | HOPS complex | 1 (1) | 6 (6) | 0.04072 |
| Molecular function | Intramolecular oxidoreductase activity, transposing C=C bonds | 1 (0) | 7 (0) | 0.04196 |
| Biological process | Detection of light stimulus | 1 (0) | 7 (0) | 0.04296 |
| Biological process | Metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling pathway | 1 (1) | 7 (4) | 0.04296 |
| Biological process | Regulation of synaptic transmission, GABAergic | 1 (1) | 7 (2) | 0.04296 |
| Cellular component | Internal side of plasma membrane | 1 (0) | 7 (4) | 0.04641 |
| Molecular function | Scavenger receptor activity | 1 (1) | 8 (8) | 0.04708 |
| Biological process | Interaction with symbiont | 1 (0) | 8 (1) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Modification by symbiont of host morphology or physiology | 1 (0) | 8 (0) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Chaperone-mediated protein complex assembly | 1 (0) | 8 (4) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | 1 (0) | 8 (4) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Positive regulation of small GTPase-mediated signal transduction | 1 (0) | 8 (0) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Synaptic transmission, GABAergic | 1 (0) | 8 (1) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Actin filament capping | 1 (1) | 8 (6) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Pentose-phosphate shunt | 1 (1) | 8 (7) | 0.0482 |
| Biological process | Calcium ion transport | 2 (1) | 63 (41) | 0.04876 |
| Cellular component | Intrinsic to membrane | 17 (0) | 1867 (20) | 0.0491 |
Figure 1.
(a) Quantitative PCR analysis of catalase mRNA. The TM cells were treated with 25 μM Y-27632 for 30 min. The relative expression level of catalase of samples treated with Y-27632 was compared to that of the control sample using the comparative CT method (ΔΔCT method). The 18S ribosomal RNA was used as an endogenous control. Data are shown as mean ± SE from six independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 compared with control by Wilcoxon rank sum test. (b) The effects of Y-27632 on the intracellular production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). The TM cells were treated with or without 25 μM Y-27632 for 30 min, followed by 100 μM menadione stimulated for 1 h. ROS were detected by CellROX reagent, and the fluorescence of the TM cells were measured by cell sorter SH800. Data are shown as mean ± SE from five independent experiments. ∗∗P < 0.01 and ∗P < 0.05 compared with control by the Wilcoxon rank sum test (a) and Tukey Kramer HSD test (b).
3.2. Effects of Y-27632 on the Production of Reactive Oxygen Species in TM Cells
To assess the effects of Y-27632 on the production of ROS in TM cells, we utilized a fluorogenic probe that exhibits bright fluorescence upon oxidation by ROS. In the absence of an oxidative reagent, the fluorescence intensity was not significantly different in TM cells treated with Y-27632 compared to control (3673.2 ± 452.3 versus 5104.5 ± 735.0; Figure 1(b)). In the presence of 100 μM menadione, the fluorescence intensity was significantly elevated (16097.7 ± 1133.0; P < 0.0001); this elevation was partly suppressed by treatment with Y-27632 (11443.6 ± 1332.2; P = 0.0182), suggesting that Y-27632 reduces ROS production in TM cells under oxidative stress.
3.3. Effects of Y-27632 on the Viability of TM Cells under Oxidative Stress
Finally, we investigated the effects of Y-27632 on the viability of TM cells under oxidative stress. As shown in Figure 2(a), menadione reduced TM cell viability in a dose-dependent manner. At a lower dose of menadione, Y-27632-stimulated TM cells regained significant viability against menadione treatment compared to control cells (P = 0.0238). In contrast, the effects of Y-27632 on cell viability were not significant at a higher dose of menadione.
Figure 2.
(a) The effect of Y-27632 on oxidative stress-induced cell death. The TM cells were treated with or without 25 μM Y-27632 for 30 min, followed by menadione stimulation of the cells for 24 h. Cell viabilities were shown as relative value compared with the control. Data are shown as the mean ± SE from six independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 compared with control by Wilcoxon rank sum test. (b) The effect of Y-27632 on extracellular antioxidative activity. The xanthine-oxidase-induced superoxide production was assessed using a superoxide-sensitive luminescent reagent. Data are shown as the mean ± SE from six independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05 compared with the control by Dunnett's test. Nac: n-acetyl cysteine.
3.4. Direct Antioxidant Activity of Y-27632
To confirm the extracellular antioxidant activity of Y-27632, we assessed xanthine oxidase-induced superoxide production using a luminescent reagent. As shown in Figure 2(b), there was no significant difference in ROS production between the control and Y-27632 treatment. Thus, Y-27632 does not appear to affect extracellular oxidants.
4. Discussion
In the present study, we have identified the antioxidative effect of Y-27632 in TM cells by microarray analysis, an exhaustive investigation of gene expression, and shown that Y-27632 partially suppresses ROS production and cell death induced by menadione. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report to show the antioxidant effect of ROCK inhibitor on TM cells. Previously, we presented depolymerization of F-actin before morphometric recovery from oxidative stress in TM cells [24], suggesting a correlation between oxidative stress and regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in TM cells. In other tissues, rho-kinase was identified as a mediator of various diseases associated with inflammation and oxidative stress, and inhibition of rho-kinase has been drawing attention as a promising therapeutic strategy. For instance, activation of the rho/rho-kinase pathway is related to the pathophysiology of chronic renal injury, and long-term fasudil treatment has renoprotective effects in this malignant hypertension model. The mechanism of the renoprotective effect of fasudil, a nonspecific ROCK inhibitor, was suggested to involve a combination of factors, including inhibition of the TGF-β-collagen cascade, control of inflammation, reduction of oxidative stress, and upregulation of eNOS [18]. Clinical studies with fasudil have suggested that it may be useful for the treatment of a wide range of cardiovascular diseases [19]. Importantly, rho-kinase inhibitors block ROS production by suppressing CyPA secretion from vascular smooth muscle cells [25], suggesting the beneficial effect of rho-kinase inhibitors against cardiovascular diseases.
Recently, Yamamoto and colleagues demonstrated the neuroprotective effect of the ROCK inhibitor K-115, a novel IOP-lowering drug, using the mouse optic crush model [20]. They showed the effect was at least partially dependent on suppression of ROS production via inhibition of Nox1 expression in retinal ganglion cells. We also showed that ROCK inhibitors' antioxidant effects are indirect using monkey TM cells. However, in the present study using microarray analysis, Nox family genes were not identified as affected, but catalase was upregulated after treatment with Y-27632. This disagreement might be caused by differences in species and/or tissues. Thus, the precise molecular mechanisms of the antioxidative effect of ROCK inhibitors have not been clarified completely. On the other hand, a recent study reported that Y-27632 induced p-53-mediated apoptosis in hemangioma [26]. In the present study, we indicated that ROCK inhibitor effected cell survival in TM cells. This is interesting point since ROCK inhibitor-induced effects such as cell death or cell protection were changed by differences of cell types.
TM has a critical role in the maintenance of aqueous outflow resistance through the regulation of extracellular matrix metabolism, phagocytosis of debris, and empty space associated with tissue contraction [27, 28]. Indeed, the number of TM cells is decreased in glaucomatous eyes [29], suggesting that functional TM cells are essential in controlling IOP. In this context, oxidative stress is a potential cause of cellular dysregulation in TM, both functionally and numerally, because it has been suggested that the TM of glaucomatous eyes is continuously exposed to oxidative stress [2–7]. Thus, an antioxidant drug might reduce oxidative stress in TM cells, slowing progression of glaucomatous damage in outflow tissues. Though it remains unknown whether clinically used eye-drops containing ripasudil have significant antioxidative effects on TM cells in vivo, the present study's findings may be clinically relevant.
The effect of Y-27632 on cell survival under oxidative stress was significant, but limited. Since glaucoma progresses chronically in the majority of the patients, the acute oxidative damage in the present study may not reflect pathological conditions in glaucomatous TM cells, which is one of the limitations of the present study. Another limitation is that the antioxidative effects of ROCK inhibition were not corroborated in vivo. Further studies are required to acquire more clinically relevant evidence of the effects of ROCK inhibitor on oxidative stress in TM.
5. Conclusion
Microarray analysis reveals that Y-27632 upregulates antioxidative genes including catalase and partially reduces the ROS production and cell death by oxidative stress induced by menadione.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the JSPS KAKENHI Grant nos. 26293375, 15K15636, and 26462664.
Conflicts of Interest
Dr. Hidenobu Tanihara has received consulting fees from Kowa and MSD and board membership fees from Senju Pharmaceutical, Santen Pharmaceutical, Alcon Japan, and Pfizer Japan.
References
- 1.Babizhayev M. A., Vishnyakova K. S., Yegorov Y. E. Oxidative damage impact on aging and age-related diseases: drug targeting of telomere attrition and dynamic telomerase activity flirting with imidazole-containing dipeptides. Recent Patents on Drug Delivery & Formulation. 2014;8(3):163–192. doi: 10.2174/1872211308666140602125505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ferreira S. M., Lerner S. F., Brunzini R., Evelson P. A., Llesuy S. F. Oxidative stress markers in aqueous humor of glaucoma patients. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2004;137(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9394(03)00788-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ghanem A. A., Arafa L. F., El-Baz A. Oxidative stress markers in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Current Eye Research. 2010;35(4):295–301. doi: 10.3109/02713680903548970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zanon-Moreno V., Marco-Ventura P., Lleo-Perez A., et al. Oxidative stress in primary open-angle glaucoma. Journal of Glaucoma. 2008;17(4):263–268. doi: 10.1097/IJG.0b013e31815c3a7f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goyal A., Srivastava A., Sihota R., Kaur J. Evaluation of oxidative stress markers in aqueous humor of primary open angle glaucoma and primary angle closure glaucoma patients. Current eye Research. 2014;39(8):823–829. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2011.556299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Izzotti A., Sacca S. C., Cartiglia C., De Flora S. Oxidative deoxyribonucleic acid damage in the eyes of glaucoma patients. American Journal of Medicine. 2003;114(8):638–646. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(03)00114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sacca S. C., Pascotto A., Camicione P., Capris P., Izzotti A. Oxidative DNA damage in the human trabecular meshwork: clinical correlation in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma. Archives of Ophthalmology. 2005;123(4):458–463. doi: 10.1001/archopht.123.4.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tanito M., Kaidzu S., Takai Y., Ohira A. Correlation between systemic oxidative stress and intraocular pressure level. PLoS One. 2015;10(7, article e0133582) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tang Y., Scheef E. A., Wang S., et al. CYP1B1 expression promotes the proangiogenic phenotype of endothelium through decreased intracellular oxidative stress and thrombospondin-2 expression. Blood. 2009;113(3):744–754. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-03-145219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhao Y., Wang S., Sorenson C. M., et al. Cyp1b1 mediates periostin regulation of trabecular meshwork development by suppression of oxidative stress. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2013;33(21):4225–4240. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00856-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ito Y. A., Goping I. S., Berry F., Walter M. A. Dysfunction of the stress-responsive FOXC1 transcription factor contributes to the earlier-onset glaucoma observed in Axenfeld-Rieger syndrome patients. Cell Death & Disease. 2014;5, article e1069 doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Berry F. B., Skarie J. M., Mirzayans F., et al. FOXC1 is required for cell viability and resistance to oxidative stress in the eye through the transcriptional regulation of FOXO1A. Human Molecular Genetics. 2008;17(4):490–505. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddm326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Honjo M., Tanihara H., Inatani M., et al. Effects of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor Y-27632 on intraocular pressure and outflow facility. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. 2001;42(1):137–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rao P. V., Deng P. F., Kumar J., Epstein D. L. Modulation of aqueous humor outflow facility by the rho kinase-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. 2001;42(5):1029–1037. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Garnock-Jones K. P. Ripasudil: first global approval. Drugs. 2014;74(18):2211–2215. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tanihara H., Inoue T., Yamamoto T., et al. Phase 2 randomized clinical study of a rho kinase inhibitor, K-115, in primary open-angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. American Journal of Ophthalmology. 2013;156(4):731–736. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2013.05.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tanihara H., Inoue T., Yamamoto T., et al. Additive intraocular pressure-lowering effects of the rho kinase inhibitor ripasudil (K-115) combined with timolol or latanoprost: a report of 2 randomized clinical trials. JAMA Ophthalmology. 2015;133(7):755–761. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2015.0525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nishikimi T., Matsuoka H. Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies of chronic renal injury: renoprotective effect of rho-kinase inhibitor in hypertensive glomerulosclerosis. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences. 2006;100(1):22–28. doi: 10.1254/jphs.FMJ05003X5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Satoh K., Fukumoto Y., Shimokawa H. Rho-kinase: important new therapeutic target in cardiovascular diseases. American Journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 2011;301(2):H287–H296. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00327.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yamamoto K., Maruyama K., Himori N., et al. The novel rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitor K-115: a new candidate drug for neuroprotective treatment in glaucoma. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciencies. 2014;55(11):7126–7136. doi: 10.1167/iovs.13-13842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fujimoto T., Inoue T., Kameda T., et al. Involvement of RhoA/Rho-associated kinase signal transduction pathway in dexamethasone-induced alterations in aqueous outflow. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. 2012;53(11):7097–7108. doi: 10.1167/iovs.12-9989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Inoue-Mochita M., Inoue T., Fujimoto T., et al. p38 MAP kinase inhibitor suppresses transforming growth factor-beta2-induced type 1 collagen production in trabecular meshwork cells. PLoS One. 2015;10(3, article e0120774) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0120774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kameda T., Inoue T., Inatani M., et al. The effect of rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor on monkey Schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. 2012;53(6):3092–3103. doi: 10.1167/iovs.11-8018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Awai-Kasaoka N., Inoue T., Kameda T., Fujimoto T., Inoue-Mochita M., Tanihara H. Oxidative stress response signaling pathways in trabecular meshwork cells and their effects on cell viability. Molecular Vision. 2013;19:1332–1340. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Satoh K., Nigro P., Matoba T., et al. Cyclophilin A enhances vascular oxidative stress and the development of angiotensin II-induced aortic aneurysms. Nature Medicine. 2009;15(6):649–656. doi: 10.1038/nm.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Qiu M. K., Wang S. Q., Pan C., et al. ROCK inhibition as a potential therapeutic target involved in apoptosis in hemangioma. Oncology Reports. 2017;37(5):2987–2993. doi: 10.3892/or.2017.5515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Roy Chowdhury U., Hann C. R., Stamer W. D., Fautsch M. P. Aqueous humor outflow: dynamics and disease. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences. 2015;56(5):2993–3003. doi: 10.1167/iovs.15-16744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Vranka J. A., Kelley M. J., Acott T. S., Keller K. E. Extracellular matrix in the trabecular meshwork: intraocular pressure regulation and dysregulation in glaucoma. Experimental eye Research. 2015;133:112–125. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2014.07.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Alvarado J., Murphy C., Juster R. Trabecular meshwork cellularity in primary open-angle glaucoma and nonglaucomatous normals. Ophthalmology. 1984;91(6):564–579. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(84)34248-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]