Abstract
Background
Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM) is a fulminant disease of the brain caused by Naegleria fowleri. Although the disease is rare, the case fatality rate is very high. In this report, we describe the first case of PAM in Zambia.
Case presentation
The patient presented with sudden onset of seizures and fever on admission. On physical examination he was febrile, comatose and with a stiff neck. Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) collected on admission did not reveal any organism on microscopy or culture but showed elevated white cell count. A working diagnosis of severe septicemia with acute meningoencephalitis was then made and the patient was started on IV Cephtriaxone (2 g) twice daily. Despite receiving treatment, his condition deteriorated. A second CSF sample collected on day 3 was also negative for bacteria and other organisms. However, a repeat CSF sample collected on day 8 revealed numerous motile organisms that were identified as Naegleria on microscopy and confirmed to be N. fowleri on polymerase chain reaction. The patient died on day 8 of hospital admission after having received one dose of Amphotericin B (50 mg). Features consistent with PAM were detected on autopsy.
Conclusion
The isolation of N. fowleri in this patient calls for increased awareness among clinical and laboratory staff on suspected PAM cases to promptly diagnose and effectively manage the disease.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2638-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis, Naegleria fowleri, Zambia
Background
Naegleria fowleri is a pathogenic free living thermophilic amoeba mainly found in fresh water bodies such as lakes, hot springs, ponds and recreational spas [1]. N fowleri causes primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), a fulminant disease affecting the brain [2]. The amoeba also known as “brain eating amoeba” enters the olfactory nerve and migrates to the brain through the cribriform form plate [3]. Majority of the infections are acquired during swimming or diving in fresh water [1, 4], although few infections acquired through nasal irrigation and use of piped household water have been documented [5].
PAM is a rare disease with current estimates of recorded cases worldwide standing at just less than 300 [6]. Due to rapid disease progression and delayed treatment in most cases, the fatality rate of PAM is very high with about 95% of those infected succumbing to the infection. If not promptly treated, death occurs within a week of acquiring the infection [2]. Unlike other free living amoeba such as Acanthamoeba and Balamunthia that cause disease mainly in immunocompromised people, majority of N. fowleri PAM cases are observed in young immunocompetent individuals [2]. In this report, we present and discuss the first recorded case of PAM due to N. fowleri in a young Zambian male patient.
Case presentation
A 24 year old male police recruit from a training camp in Kafue district, in the Southern part of Lusaka Province was admitted to the University Teaching Hospital in Lusaka, Zambia. He presented with sudden-onset seizures and fever for 1 day with no prior history of ill health. Two days before presenting to our hospital, he was reported to have gone swimming in the Kafue River. On physical examination, the patient was febrile, anicteric and comatose with a Glasgow Coma Scale of 6 out of 15. He also presented with a stiff neck and decorticate posturing. His blood pressure was 104/60 with a pulse rate of 126 bpm and body temperature of 39 °C. Chest and abdominal examination were unremarkable. A rapid diagnostic test for falciparum malaria was negative. There were no features of chronic illness and no palpable lymph nodes were observed. A working diagnosis of severe septicemia with acute meningoencephalitis was made and the patient was started on IV Cephtriaxone (2 g) twice daily. The patient was immediately transferred to the intensive care ward. No bacterial or fungal pathogens were detected in CSF collected on admission (Day 1). Due to poor response to antibiotics, a repeat CSF sample was collected on the third day of treatment but no organisms were detected on direct microscopy or stained preparations. A computerized tomography (CT) scan of the brain did not show any abnormalities. The patient continued to have high fevers with generalized seizures and depression of consciousness, requiring endotracheal intubation and ventilatory support. A direct wet mount microscopic examination of the CSF sample collected on day 8 showed numerous highly motile amoebic trophozoites and cysts (Fig. 1a–d) which was later confirmed to be the pathogenic N. fowleri on polymerase chain reaction (Fig. 2). The patient was started on 50 mg of Amphotericin B IV but no improvement was noted. Despite several resuscitations, he died on the same day treatment was commenced (Day 8). Laboratory findings for this case are shown in Table 1 and Table 2. A summary of the patient management is shown in the timeline (Additional file 1).
Fig. 1.
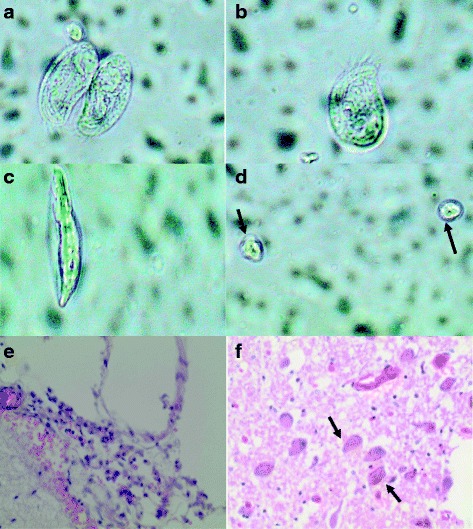
Different stages of N. fowleri in cerebral spinal fluid of a 24 year old Zambian male Different forms of Amoeba (a, b, c) and and cysts (d) in CSF. Fibrino-purulent material on the leptomeninges, consisting of lymphocytes, neutrophils and congested blood vessels (e) and Multiple N. fowleri amoeba (f) present in the brain parenchyma with hemosiderin pigment
Fig. 2.
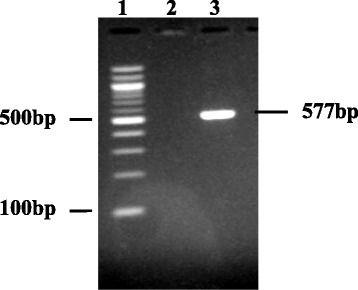
Gel documentation of Naegleria fowleri from the Zambia patient’s CSF. Lane 1: Molecular marker. Lane 2: Negative control and Lane 3 showing a 577 bp product of the internal transcribed spacer region of the rRNA N. fowleri gene
Table 1.
Blood Investigations performed on the day of admission (Day 1)
| Investigations | Laboratory Finding |
|---|---|
| Total White blood cell count | 16.51 × 109/L |
| Neutrophils | 86.4% |
| Lymphocytes | 5.2% |
| Monocytes | 6.3% |
| Eosinophils | 1.9% |
| Basophils | 0.2% |
| Random blood sugar | 2.99 mmols/L |
| Malaria Test | No malaria parasites seen |
| Other blood parasites | No Trypanosomes seen |
| HIV Test | Negative |
| Blood culture | No growth detected |
Table 2.
Cerebral spinal fluid findings for Day 1, Day 3 and Day 8 specimens
| Cerebrospinal Fluid | Day 1a | Day 3 | Day 8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| White cell count | 1120/ mm3 (92% neutrophils) | 70/mm3(82% neutrophils) | 200/mm3 (90% neutrophils) |
| Red blood cells | 5250/mm3 | 820 /mm3 | 5000/mm3 |
| Gram Stain | No organisms seen | No organisms seen | No organisms seen |
| Indian Ink | No Cryptococcus Spp. seen | No Cryptococcus Spp. seen | No Cryptococcus Spp. seen |
| Cryptococcal Antigen Test | Non-Reactive | Non-Reactive | Non-Reactive |
| CSF Culture | No growth | No growth | No growth |
| Direct CSF Microscopic Examination | No organisms seen | No organisms seen | Amoeba present |
aDay 1: Day of patient admission to the hospital
Glucose and protein levels were not measured on all the three CSF samples
On Autopsy, the leptomeninges were thin and transparent with vascular congestion, fibrinopurulent exudates (Fig. 1e). There was no displacement of the cingulate gyrus, medial temporal lobe, or cerebellar tonsils. Histology showed edema, lymphocytes and neutrophils features consistent with meningitis. Multiple amoeba were present in the brain parenchyma (Fig. 1f).
To confirm that PAM was due to N. fowleri, DNA was amplified with primers NF-ITS-F1 [5′-GAC TTC ATT CGT TCT TGT AGA-3′] and NF-ITSR1 [5′-CTC TTG CGA GGT CCA GAC-3′] that targeted a 577 bp region of the internal transcribed spacer of the rRNA gene [7].
Discussion
The PAM case described in this paper is the first to be reported in Zambia. This case was detected during one of the hot months with spiking temperatures supporting observations that N. fowleri infections are associated with hot seasonality [8]. As has been reported elsewhere, the diagnosis of PAM possesses challenges in that its clinical presentation is similar to that of bacterial meningitis. Due to its rapid progression, death usually occurs within 6–17 days of initial exposure if not promptly diagnosed [9].
The lack of information on PAM in Zambia indicates that there is limited or no awareness among clinical and laboratory staff leading to misdiagnosis of cases. In the few cases of PAM successfully managed [10, 11] in other regions, correct and prompt diagnosis was done and treatment commenced without delay. In the absence of a detailed history of exposure, it is very difficult to clinically diagnose PAM as the infection presents like other types of meningitis. Our case presented with clinical signs and symptoms similar to those that have been previously documented [7, 12]. Symptoms such as severe headache, high grade fever, photophobia, lethargy, confusion with altered levels of consciousness and seizures are commonly observed in patients with PAM. Death in most of the cases is due to increased intracranial pressure [7].
Laboratory findings in PAM patients are consistent and are mostly characterized with increased leucocytes which are predominantly polymorphonuclear cells. CSF may also be purulent with marked leucocytosis, increased protein and reduced glucose levels [7, 12]. In most cases, neuro-imaging investigations in early stages of the disease do not reveal any brain abnormalities [13]. However, a strong suspicion of PAM with history of water exposure should guide the management of patients with such presentations in the absence of bacteria or fungi in CSF specimens.
Critical to survival of PAM patients is prompt detection and aggressive treatment. Currently, the drug of choice is Amphotericin B, an antifungal agent with very low cure rate especially when used as a single drug [14]. The sensitivity of Amphotericin B on N. fowleri was demonstrated as far back as the late 1960’s [15]. Other drugs given alongside Amphotericin B are Rifampicin and Fluconazole. In cases where treatment has been successful, aggressive therapy with a combination of antibacterial and antifungal agents was given [8, 16]. Coupled with the use of the above mentioned drugs, management of intracranial pressure, inflammation and induced mild-moderate hypothermia (32 °C-34 °C) are key to successful recovery [16].
Even though the parasite is present in almost all the continents [6, 7], very few cases of PAM have been recorded since it was discovered in 1962. According to the centre for disease control and prevention (CDC), only 138 cases of PAM in the United States have been reported from 1962 to 2015. Recently, there has been an increase in the number of reported PAM cases in Asian countries [14, 17, 18] perhaps due to increased awareness.
In Africa, however, less than 10 cases have been recorded despite having weather conditions such as high temperature that favor the propagation of the parasite. The first reported case of PAM was in an 8 month old baby in Zaria state, Nigeria with no prior exposure to swimming [19]. Following this case, another PAM patient was reported 2 years later in the same country [20]. In addition, there is documentation of N. fowleri isolation from environmental sources [21–23]. N. fowleri has also been isolated from nasal passages during the dry, windy and dusty months (hamarrtan season) affecting parts of the West African coast [23]. While most of the cases in Africa are from Nigeria, only one case has been documented in Southern Africa [24]. The only case of suspected amoebic meningoencephalitis in a Zambian male gardener was reported in 1974 [25]. In this case, the authors concluded that the infection was not as a result of Naegleria but rather another free living amoeba belonging to the hartmannellid family which has been classified as Acanthamoeba. It is conceivable therefore, to suggest that PAM cases are high in Africa and go undiagnosed due to lack of awareness among clinical and laboratory staff.
Conclusion
This is the first confirmed case of PAM in Zambia. Our case highlights the difficulty of making correct diagnosis when clinical features are suggestive of bacterial meningitis. However, the absence of organisms on gram stain, the lack of response to antibiotics and a recent history of swimming exposure should alert clinicians to the possibility of a diagnosis of PAM. In addition, there is need to raise awareness in both clinical and laboratory personnel on the importance of prompt diagnosis and effective management of patients with suspected PAM.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Mr. Sandie Sianongo for laboratory technical assistance. We are also thankful to the clinicians and nurses who managed this patient. The relative to the deceased is also acknowledged for consenting to have this case published.
Funding
No funding was received to publish this case report.
Availability of data and materials
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within this article.
Abbreviations
- CSF
Cerebral spinal fluid
- HIV
Human immunodeficiency virus
- PAM
Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis
Additional file
Case report timeline. (DOC 60 kb)
Authors’ contributions
MC and FS were involved in the clinical care of the patient. MAL performed the autopsy. NJ and MMM performed the laboratory tests. All authors were actively involved in the preparation of the manuscript and approved the final draft.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Written consent was obtained from the relative of the deceased to publish the case report and accompanying images.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Footnotes
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2638-8) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Contributor Information
Mashina Chomba, Email: mashinachomba@gmail.com.
Luchenga A. Mucheleng’anga, Email: Luchengam@gmail.com
Sombo Fwoloshi, Email: sombofwoloshi@gmail.com.
Joseph Ngulube, Email: joze22jozef@gmail.com.
Mable M. Mutengo, Email: mmutengo@yahoo.com
References
- 1.Heggie TW. Swimming with death: Naegleria Fowleri infections in recreational waters. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2010;8(4):201–206. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2010.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Visvesvara GS, Moura H, Schuster FL. Pathogenic and opportunistic free-living amoebae: Acanthamoeba spp., Balamuthia mandrillaris, Naegleria Fowleri, and Sappinia diploidea. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2007;50(1):1–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2007.00232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jarolim KL, McCosh JK, Howard MJ, John DT. A light microscopy study of the migration of Naegleria Fowleri from the nasal submucosa to the central nervous system during the early stage of primary amebic meningoencephalitis in mice. J Parasitol. 2000;86(1):50–55. doi: 10.1645/0022-3395(2000)086[0050:ALMSOT]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Craun GF, Calderon RL, Craun MF. Outbreaks associated with recreational water in the United States. Int J Environ Health Res. 2005;15(4):243–262. doi: 10.1080/09603120500155716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yoder JS, Straif-Bourgeois S, Roy SL, Moore TA, Visvesvara GS, Ratard RC, Hill VR, Wilson JD, Linscott AJ, Crager R, et al. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis deaths associated with sinus irrigation using contaminated tap water. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;55(9):e79–e85. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.De Jonckheere JF. What do we know by now about the genus Naegleria? Exp Parasitol. 2014;145(Suppl):S2–S9. doi: 10.1016/j.exppara.2014.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cogo PE, Scagli M, Gatti S, Rossetti F, Alaggio R, Laverda AM, Zhou L, Xiao L, Visvesvara GS. Fatal Naegleria Fowleri meningoencephalitis, Italy. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004;10(10):1835–1837. doi: 10.3201/eid1010.040273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brown RL. Successful treatment of primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Arch Intern Med. 1991;151(6):1201–1202. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1991.00400060121021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lopez C, Budge P, Chen J, Bilyeu S, Mirza A, Custodio H, Irazuzta J, Visvesvara G, Sullivan KJ. Primary amebic meningoencephalitis: a case report and literature review. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2012;28(3):272–276. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182495589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cope JR, Conrad DA, Cohen N, Cotilla M, DaSilva A, Jackson J, Visvesvara GS. Use of the novel therapeutic agent Miltefosine for the treatment of primary Amebic Meningoencephalitis: report of 1 fatal and 1 surviving case. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(6):774–776. doi: 10.1093/cid/civ1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dunn AL, Reed T, Stewart C, Levy RA. Naegleria Fowleri that induces primary amoebic Meningoencephalitis: rapid diagnosis and rare case of survival in a 12-year-old Caucasian girl. Lab Med. 2016;47(2):149–154. doi: 10.1093/labmed/lmw008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fowler M, Carter RF. Acute pyogenic meningitis probably due to Acanthamoeba sp.: a preliminary report. Br Med J. 1965;2(5464):740–742. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5464.734-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Barnett ND, Kaplan AM, Hopkin RJ, Saubolle MA, Rudinsky MF. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis with Naegleria Fowleri: clinical review. Pediatr Neurol. 1996;15(3):230–234. doi: 10.1016/S0887-8994(96)00173-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Siddiqui R, Khan NA. Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis caused by Naegleria Fowleri: an old enemy presenting new challenges. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8(8):e3017. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Carter RF. Sensitivity to amphotericin B of a Naegleria sp. isolated from a case of primary amoebic meningoencephalitis. J Clin Pathol. 1969;22(4):470–474. doi: 10.1136/jcp.22.4.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Linam WM, Ahmed M, Cope JR, Chu C, Visvesvara GS, da Silva AJ, Qvarnstrom Y, Green J. Successful treatment of an adolescent with Naegleria Fowleri primary amebic meningoencephalitis. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):e744–e748. doi: 10.1542/peds.2014-2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Panda A, Khalil S, Mirdha BR, Singh Y, Kaushik S. Prevalence of Naegleria Fowleri in environmental samples from northern part of India. PLoS One. 2015;10(10):e0137736. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zahid MF, Saad Shaukat MH, Ahmed B, Beg MA, Kadir MM, Mahmood SF. Comparison of the clinical presentations of Naegleria Fowleri primary amoebic meningoencephalitis with pneumococcal meningitis: a case-control study. Infection. 2016;44(4):505–511. doi: 10.1007/s15010-016-0878-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lawande RV, John I, Dobbs RH, Egler LJ. A case of primary amebic meningoencephalitis in Zaria, Nigeria. Am J Clin Pathol. 1979;71(5):591–594. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/71.5.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lawande RV, Macfarlane JT, Weir WR, Awunor-Renner C. A case of primary amebic meningoencephalitis in a Nigerian farmer. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1980;29(1):21–25. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1980.29.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Baquero RA, Reyes-Batlle M, Nicola GG, Martin-Navarro CM, Lopez-Arencibia A, Guillermo Esteban J, Valladares B, Martinez-Carretero E, Pinero JE, Lorenzo-Morales J. Presence of potentially pathogenic free-living amoebae strains from well water samples in Guinea-Bissau. Pathog Global Health. 2014;108(4):206–211. doi: 10.1179/2047773214Y.0000000143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sadaka HA, el-Nassery SF, abou Samra LM, Awadalla HN. Isolation and identification of free-living amoebae from some water sources in Alexandria. J Egypt Soc Parasitol. 1994;24(2):247–257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lawande RV. Recovery of soil amoebae from the air during the harmattan in Zaria, Nigeria. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1983;77(1):45–49. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1983.11811671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Schoeman CJ, van der Vyver AE, Visvesvara GS. Primary amoebic meningo-encephalitis in southern Africa. J Infect. 1993;26(2):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0163-4453(93)93085-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Bhagwandeen SB, Carter RF, Naik KG, Levitt D. A case of hartmannellid amebic meningoencephalitis in Zambia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1975;63(4):483–492. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/63.4.483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the conclusions of this article are included within this article.


