Abstract

Fecal-oral pathogens are transmitted through complex, environmentally mediated pathways. Sanitation interventions that isolate human feces from the environment may reduce transmission but have shown limited impact on environmental contamination. We conducted a study in rural Bangladesh to (1) quantify domestic fecal contamination in settings with high on-site sanitation coverage; (2) determine how domestic animals affect fecal contamination; and (3) assess how each environmental pathway affects others. We collected water, hand rinse, food, soil, and fly samples from 608 households. We analyzed samples with IDEXX Quantitray for the most probable number (MPN) of E. coli. We detected E. coli in source water (25%), stored water (77%), child hands (43%), food (58%), flies (50%), ponds (97%), and soil (95%). Soil had >120 000 mean MPN E. coli per gram. In compounds with vs without animals, E. coli was higher by 0.54 log10 in soil, 0.40 log10 in stored water and 0.61 log10 in food (p < 0.05). E. coli in stored water and food increased with increasing E. coli in soil, ponds, source water and hands. We provide empirical evidence of fecal transmission in the domestic environment despite on-site sanitation. Animal feces contribute to fecal contamination, and fecal indicator bacteria do not strictly indicate human fecal contamination when animals are present.
Introduction
Fecal-oral pathogens are transmitted from feces to new hosts through complex, environmentally mediated pathways. The complexity arises from a multitude of transmission pathways, a broad diversity of pathogens, the influence of environmental conditions and interactions between the environment and human behavior. In the absence of effective sanitation and sewerage facilities that isolate human feces from the environment, human fecal organisms can spread into fields and ambient waters. These are subsequently transported by fomites and vectors (e.g., hands, flies) into drinking water and food as well as ingested through mouth contact with contaminated hands and objects or geophagia (deliberate ingestion of soil) by young children.1,2
Contamination of drinking water, a direct ingestion pathway, has been studied extensively, and water treatment has been shown to improve microbiological water quality as measured by fecal indicator bacteria (FIB) and reduce self-reported diarrhea.3,4 Other transmission pathways remain understudied even though these could present major sources of fecal exposure. For example, complementary foods for young children contain FIB in low-income country settings5 and child diarrhea has been linked to food contamination.6 High FIB levels are found on hands in low-income countries7 and handwashing interventions reduce self-reported diarrhea.8 Flies are known to carry human pathogens9,10 and fly control programs have successfully reduced diarrheal disease.11 FIB and pathogens have been detected in soil12 and geophagia has been associated with diarrhea, markers of environmental enteric dysfunction, and stunting in young children.13,14 However, it has not been documented how soil contamination affects subsequent contamination of ambient and drinking waters, hands and food.
Sanitation interventions are a primary barrier to disease transmission and should block enteric pathogens both by stopping feces from spreading into the environment as well as eliminating fly breeding sites. However, recent sanitation trials have shown limited health impact. Two trials in India found no effect of sanitation improvements on child diarrhea, parasite infections, and growth,15,16 while a trial in Mali demonstrated improved child growth but no diarrhea reduction.17 These trials also found no reduction in FIB measured in source and stored water, and on hands and fomites.15−17 A systematic review identified no overall reductions in environmental contamination in response to sanitation improvements.18 Possible explanations include low latrine uptake and continuing open defecation; Clasen et al. (2014) and Patil et al. (2014) reported that <50% of households in intervention villages had a functional or improved latrine, respectively, and Patil et al. found that >70% of adults in intervention villages reported daily open defecation.15,16
Another potential explanation for the failure of sanitation improvements to reduce domestic fecal contamination and diarrhea is residual contamination from animal feces. Sanitation programs focus on isolating human feces from the environment, typically with no measures to reduce exposure to animal feces. Many households in low-income countries keep livestock in close proximity to living quarters.19 Microbial source tracking studies in rural India and Bangladesh suggest that fecal contamination from animals is more prevalent than human contamination in the domestic environment, including source and stored drinking water, hands, and soil.20−22 Courtyard soil, household floors, and child hands have been shown to contain animal fecal molecular markers.20,23 Presence of animal feces in the compound has been associated with visible dirtiness of caregivers’ and children’s hands and faces.24 There is also increasing evidence that exposure to domestic animals is associated with increased diarrhea.19 However, the contribution of animal feces to fecal contamination along different transmission pathways in settings with on-site sanitation has not been assessed.
The objectives of our study were to (1) characterize levels of fecal contamination along multiple environmental transmission pathways (source, stored and ambient waters, child hands, complementary food, courtyard soil, and flies caught in the compound) in rural Bangladeshi households, (2) determine how the presence of domestic animals, household sanitary infrastructure and ambient climate conditions affect contamination levels, and (3) assess how different environmental pathways affect each other.
Materials and Methods
Data Collection
Our study was nested within a randomized controlled trial in rural central Bangladesh (WASH Benefits).25 We randomly enrolled households from the trial’s control arm between July 2013 and March 2014. During household visits, field workers conducted spot check observations on the presence of human and animal feces in the courtyard; human vs specific animal (cow, goat/sheep, chicken) feces were distinguished based on their visual characteristics. Field workers also administered a structured questionnaire on animal husbandry. Additionally, they observed water, sanitation, and hygiene indicators, including the cover status of the storage containers from which the drinking water and food samples were collected, presence of a handwashing station with soap and water (tubewell, pond, or container with water) within 10 m of the latrine, and presence and number of latrines in the compound and within 10 m of tubewells and ponds. They differentiated improved latrines based on Joint Monitoring Programme (JMP) categories26 and observed whether the latrine drained into a septic tank, pit, or the environment (pond, ditch, etc.). When collecting soil samples, field staff observed whether the sampled area was visibly wet and in the sun or shade.
Sample Collection
Field workers collected samples from the compound, including tubewell water, drinking water stored in the home, pond water, child hand rinses, complementary foods given to young children, flies caught in the food preparation area, and courtyard soil from young children’s outdoor play area. Samples were collected in sterile Whirlpak bags (Nasco Modesto, Salida, CA). To collect source water (tubewell) samples, field staff removed fabric or other materials attached to the tubewell mouth and flushed the tubewell by pumping five times before collecting 250 mL of water. To collect stored water, field workers asked the respondent to provide a glass of water from their primary drinking water storage container as if giving it to their children <5 years and pour 250 mL from the glass into a Whirlpak. Pond samples were collected by dipping a Whirlpak into the pond and collecting 250 mL of water from the area where the household reported most commonly accessing the pond. To sample child hands, field workers asked the respondent to place both hands of the youngest child <5 years, one at a time, into a Whirlpak prefilled with 250 mL of distilled water. Each hand was massaged from outside the bag for 15 s, followed by 15 s of shaking, and the rinsewater was preserved in the Whirlpak.27 To collect soil samples, the respondent was asked to identify the outdoor area where the youngest child <5 years had most recently spent time. Field workers marked a 30 × 30 cm2 area with a sterile stencil, and scraped the top layer of soil within the stencil into a Whirlpak using a sterile scoop to collect approximately 50 g of soil. To sample complementary food, field workers identified stored food to be served to children <5 years and asked the respondent to provide a small amount of food in the same manner they feed their children. Food was scooped to fill a 50 mL sterile plastic tube using a sterile spoon. Finally, field workers identified a suitable location in the food preparation area (away from the stove and smoke, under a roof or protected from rain if possible) and hung three horizontal 1.5-foot strips of nonbaited sticky fly tape. The tape was left in place for 3–6 h to capture flies. Field workers removed one fly from the center of the strip with the most flies using sterile tweezers and placed it into a Whirlpak. Clean gloves were worn to collect pond, hand rinse, soil, and food samples.
Sample Processing
Samples were preserved on ice and processed on the same day, typically within 12 h of collection. Tubewell and stored water samples were analyzed without dilution. Pond samples were diluted 1:100 and hand rinses 1:2 with distilled water. Food and soil were homogenized with distilled water using a sterile blending bag (BagFilter P, 400 mL, Interscience, Saint Nom, France) and a laboratory-scale food processor (BagMixer C, Interscience, Saint Nom, France) for 1 min at a specified mixing speed. A 10 g aliquot of food was homogenized with 100 mL of distilled water and then diluted 1:10. A 20 g aliquot of soil was homogenized with 200 mL of distilled water and then diluted 1:104. An additional 5 g food and soil aliquot was oven-dried overnight to determine the moisture content and dry weight. Flies were homogenized with a pestle from outside the Whirlpak and mixed with 100 mL of distilled water; this slurry was diluted 1:100.
One field blank per sample collector per week, one laboratory blank per laboratory assistant per day, 10% field duplicates (two samples from one household), and 5% laboratory replicates (two aliquots from the same sample) were processed for quality control. Field workers collected two types of field blanks (1) by asking the respondent to pour distilled water from a sterile bottle into a Whirlpak and (2) by opening and shaking a prefilled Whirlpak in the field as if collecting a hand rinse. Samples were analyzed using IDEXX Quantitray with Colilert-18 media (IDEXX Laboratories, Maine, U.S.A.) and incubated at 44.5 °C for 18 h to enumerate E. coli with the most probable number (MPN) method. The Quantitray-2000 system with a wide detection range of 1–2419 MPN per tray was selected to accommodate variability within sample types.
Statistical Methods
We tabulated the presence/absence, log10-transformed counts, and geometric means of E. coli; we substituted the value of 0.5 MPN for samples below and 2420 MPN for samples above the detection limit to calculate the logarithm. We assessed the association between log10-transformed E. coli counts and ambient climate factors (e.g., season, sunlight and visible moisture in soil sampling area, measured soil moisture content), presence of animals, observed human/animal feces, and household sanitary infrastructure. Season was defined as wet vs dry as Bangladesh receives >80% of its rain during the monsoon season from June through October and is typically dry otherwise.28 We also assessed the relationships between different transmission pathways by separately estimating the association of E. coli levels in different sample types (e.g., log10 increase in E. coli on hands for every log10 increase in E. coli in soil). We used generalized linear models with robust standard errors to account for the clustered design of the WASH Benefits trial. We assessed whether housing materials, reported income, land ownership, presence of electricity, and female education (≥1 year of formal schooling) as socioeconomic proxies were associated with the presence of animals and animal feces using chi-square tests; all models controlled for these potential confounders.
Results and Discussion
Household Characteristics
Of the 699 households randomly selected from the control arm of the parent trial, we successfully enrolled 608 (87%) households with 13% lost to follow-up (7% stillbirth, miscarriage, abortion, or death of children in the target age range, 5% relocation, and 1% refusal). Among 608 enrolled households, 97% had a latrine and 68% had an improved latrine as per the JMP definition;26 29% of latrines drained into the environment (Table 1). The presence and number of latrines were positively associated with all proxies of higher socioeconomic status (finished walls, electricity access, above-median reported income, land ownership, ≥1 years of female education, all p-values <0.05) while the presence of an improved latrine was not associated with any of these proxies. Human feces were observed in 4% of compounds. Half (47%) of households had water in the latrine area while 7% had soap. Fewer than 20% of drinking water storage containers were covered in contrast to 85% of food storage containers. At least one fly was caught in the food preparation area in 32% of households.
Table 1. Characteristics of Enrolled Households (N = 608).
| household characteristics | % |
|---|---|
| household water, sanitation, hygiene conditions | |
| latrine in compound | 97 |
| improved latrine in compound (JMP definitiona) | 68 |
| latrine flushes to environment | 29 |
| household owns child potty | 17 |
| human feces observed in courtyard | 4 |
| stored water covered | 17 |
| water present in latrine | 47 |
| soap present in latrine | 7 |
| food container covered | 85 |
| flies captured in food preparation area | 32 |
| presence of domestic animals and animal feces | |
| compound has animals | 94 |
| chickens | 91 |
| cows | 69 |
| goats/sheep | 39 |
| animals roam free in compound | 56 |
| animal feces observed in courtyard | 89 |
| chicken feces | 87 |
| cow feces | 30 |
| goat/sheep feces | 19 |
JMP: Joint Monitoring Programme.
Animals and Animal Feces
Almost all compounds (94%) had domestic animals and the most common animal was chickens, while 89% of compounds had observed animal feces in the courtyard and chicken feces were the most common type of feces observed. Whether or not a household had animals was not associated with socioeconomic proxies; however, households that owned land were more likely to have >1 cow or >10 chickens (p < 0.05). Compounds were more likely to have animal feces in the courtyard if they had unfinished (e.g., bamboo, mud) walls or no electricity (p < 0.05).
Fecal Contamination
We tested 3254 samples and detected E. coli in every sample type, including 25% of source water, 77% of stored water, 43% of child hands, 58% of complementary foods, 50% of flies, 97% of ponds, and 95% of soil (Table 2). Geometric mean E. coli was <10 MPN per reporting unit in drinking water, food and on hands. The geometric mean E. coli for flies was 663 MPN per fly. Ponds and soil had extremely high contamination; geometric mean E. coli was >5000 MPN per 100 mL for ponds and >120 000 MPN per dry gram for soil. Across all samples types, 5% of samples exceeded the detection limit.
Table 2. E. coli Detection among Environmental Pathways.
| type of sample | N | unit | lower detection limit (MPNa) | upper detection limit (MPNa) | geometric mean (MPNa) | % positive |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| soil | 591 | 1 dry gram | 1000–1515b | 2.4 × 106 to 3.7 × 106b | 125 530 | 95 |
| ponds | 277c | 100 mL | 100 | 241 900 | 5918 | 97 |
| tubewells | 563 | 100 mL | 1 | 2419 | 1 | 25 |
| flies | 193d | 1 fly | 100 | 241 900 | 663 | 50 |
| child hands | 584 | 2 hands | 5 | 12 095 | 7 | 43 |
| stored water | 497 | 100 mL | 1 | 2419 | 9 | 77 |
| food | 549 | 1 dry gram | 1–8e | 2426–20 158e | 2 | 58 |
MPN: Most probable number.
Corresponds to lower limit of 1000 MPN and upper limit of 2 419 000 MPN per wet gram given soil moisture content range of 0–34%.
Approximately half of households reported accessing a pond (typically to wash dishes and clothes).
A fly was captured in one-third of households.
Corresponds to lower limit of 1 MPN and upper limit of 2419 MPN per wet gram given food moisture content range of 3–88%.
Ambient Climate Conditions Vs Fecal Contamination
During the rainy season, E. coli was detected significantly more frequently and at higher concentrations along all pathways compared to the dry season (all p < 0.05 except for log10E. coli in soil) (Figure 1). Soil E. coli counts were not affected by whether the soil was visibly wet at the time of sampling. However, soil samples with above-median moisture content (median = 7%, range = 0–34%) had 0.70 log10 MPN higher E. coli per dry gram (p < 0.005). Soil from areas sunlit at the time of collection had 0.48 log10 MPN fewer E. coli per dry gram than soil from shaded areas (p < 0.005).
Figure 1.
E. coli detection during wet season (Jun–Oct) vs dry season (Nov–May). The y-axis shows the percentage of E. coli positive samples. Geometric mean E. coli counts are displayed beneath the bars.
Presence of Animals and Animal Feces Vs Fecal Contamination
Animal presence was associated with higher levels of fecal contamination along multiple pathways; soil contamination in particular was independently associated with the presence of individual animal species (chickens, goats/sheep, cows) as well as the presence of any animal in the compound (Figure 2). Compounds with animals had 0.54 log10 MPN higher E. coli in soil, 0.40 log10 MPN higher E. coli in stored water, and 0.61 log10 MPN higher E. coli in food (all p < 0.05). This was primarily driven by the presence of chickens; compounds with chickens had 0.70 log10 MPN higher E. coli in soil, 0.49 log10 MPN higher E. coli in stored water, and 0.40 log10 MPN higher E. coli in food (all p < 0.05). Compounds where animals roamed freely had 0.22 log10 MPN higher E. coli in soil and 0.27 log10 MPN higher E. coli in ponds (all p < 0.05) than compounds with no animals at all or no free-roaming animals. Food had 0.32 log10 MPN higher E. coli in compounds where ≥1 fly was captured in the food preparation area (p = 0.02).
Figure 2.
Increase in log10E. coli associated with the presence of animals, animal and human feces, and sanitary infrastructure in compound.
Similarly, the presence of animal feces in the courtyard was significantly associated with increased contamination in the domestic environment; especially soil E. coli was independently associated with the presence of feces from individual animal species as well as the presence of any animal feces in the compound (Figure 2). Compounds with animal feces had 0.55 log10 MPN higher soil E. coli; the increase was 0.51 log10 for chicken feces, 0.33 log10 for goat/sheep feces and 0.25 log10 for cow feces (all p < 0.05). Animal feces were associated with higher levels of E. coli in ponds and food as well. Surprisingly, the presence of animal feces was associated with lower E. coli levels in tubewells and not associated with E. coli levels on flies. Because human feces were observed very infrequently (4% of households), we did not have sufficient statistical power to assess associations with this variable.
Sanitary Infrastructure vs Fecal Contamination
The presence of a latrine was associated with significantly lower E. coli in soil and ponds, while the presence of an improved latrine was associated with reduced contamination of ponds, and a higher number of latrines in the compound was associated with reduced contamination of soil, child hands and stored drinking water (Figure 2). In contrast, ponds had increased E. coli if there was a latrine within 10 m (Δlog10=0.21, 0.02–0.41) or if the latrine was observed to drain into the environment (Δlog10 = 0.22, 0.00–0.45) or directly into the pond (Δlog10 = 0.30, 0.13–0.47). The presence, number, improved vs unimproved status, proximity or drainage location of latrines in the compound was not associated with tubewell water quality or E. coli on flies.
Associations between Pathways
Contamination levels along different environmental pathways were associated with each other (Figure 3). Pond E. coli increased for each log10E. coli increase in soil (Δlog10 = 0.13, 0.03–0.23). E. coli on child hands increased for each log10E. coli in soil (Δlog10 = 0.07, 0.01–0.12) and ponds (Δlog10 = 0.15, 0.05–0.25). E. coli in stored water increased for each log10E. coli in soil (Δlog10 = 0.15, 0.06–0.24), ponds (Δlog10 = 0.27, 0.09–0.44), hands (Δlog10 = 0.21, 0.08–0.33), and source water (Δlog10 = 0.39, 0.23–0.55). Finally, E. coli in food increased with each log10E. coli in all other pathways, including soil (Δlog10 = 0.12, 0.02–0.22), ponds (Δlog10 = 0.28, 0.08–0.48), hands (Δlog10 = 0.18, 0.04–0.32), source water (Δlog10 = 0.21, 0.05–0.37), stored water (Δlog10 = 0.28, 0.17–0.39), and flies caught in the food preparation area (Δlog10 = 0.21, 0.08–0.34).
Figure 3.
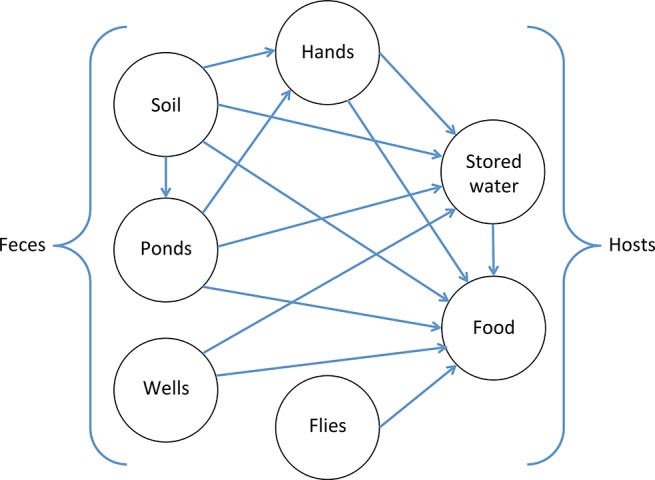
Associations between environmental transmission pathways, measured as increase in log10E. coli on a pathway associated with each log10 increase in E. coli along another pathway. Arrows indicate associations that are significant at the p < 0.05 level; the lack of an arrow between two sample types indicates that we did not observe a significant association.
Discussion
We found ubiquitous fecal contamination along multiple environmentally mediated pathways in rural Bangladeshi households with on-site sanitation access. We detected E. coli in 25% of tubewells, compared to 77% of stored drinking water, supporting prior evidence on tubewell water quality in Bangladesh29−31 and subsequent contamination at the point-of-use.32,33 We found E. coli on 43% of child hands. Hand contamination levels were similar to findings from Tanzania34 and urban Bangladesh23 but much higher than in high-income countries.35E. coli was detected in 58% of complementary food, consistent with previous studies in Bangladesh.6,36,37 Among flies captured at the food preparation area, 50% had E. coli, which could have been present on the outside or in the gut of the fly. Soil and ponds had high levels of E. coli, suggesting these are major reservoirs for fecal organisms. Soil E. coli levels in our study were substantially higher than previously documented in Tanzania and Zimbabwe.12,38 Our method may have had higher recovery efficiency since it did not require a settling step like the protocol used in the Tanzania study. Our results could also indicate heavier fecal input into the environment due to the high population density of Bangladesh and/or enhanced bacterial growth in soil due to the wet climate and high groundwater table in Bangladesh; saturated subsurface conditions favor the transport, survival and growth of microorganisms.39 This is consistent with our finding that soil with higher moisture content had higher E. coli counts. However, soil in our study was also more contaminated than measured in a similar rural Bangladeshi setting by enumerating soil homogenates on Petrifilm without a settling step;13 one reason for this could be our method’s high upper detection limit (2 419 000 MPN per wet gram of soil). We also found associations between E. coli levels measured in soil, ponds, groundwater, hands, flies, stored water, and food. Previous evidence supports these findings; however, few studies have explored associations between several different pathways. Ambient (pond) water quality has been shown to affect groundwater quality.40 Source water quality, in turn, is a known determinant of stored water quality.41 A link between contamination of stored water and hands has also been demonstrated.22,34,42
Our findings suggest that animal feces contribute more substantially to domestic fecal contamination in rural Bangladeshi households than human feces; 4% of compounds had observed human feces in the courtyard vs almost 90% having animal feces. This is not surprising considering that 97% of enrolled households had a latrine. Open defecation is commonly practiced by young children in this setting;43 nonetheless, our infrequent observation of human feces indicates that child feces are removed from the compound’s living area. Indeed, other work in our study area indicated that, among households where child feces are not disposed of in a latrine, 64% reported disposing of them in the bushes surrounding the compound, 18% in open waste heaps and 13% in drains while only 11% left the feces on the ground.44 However, human feces likely contribute to domestic fecal contamination through other routes, such as latrines draining into ponds/canals or pits leaking into the environment. Indeed, ponds with a latrine within 10 m and ponds receiving latrine effluent had higher E. coli levels in our study, consistent with previous evidence from rural Bangladesh.40,45
Chickens presented the most prevalent domestic animal exposure in our study. Roughly 90% of compounds had chickens, followed by cows (69%) and goats/sheep (39%). Similarly, 87% of courtyards had chicken feces, followed by cow feces (30%) and goat/sheep feces (19%). Chickens typically roam and deposit feces throughout the compound while scavenging for food,46 and because their feces are small and relatively odorless, they are likely to be left in place, even though some households collect chicken feces to use as fertilizer.47 Cow dung is often collected and used as cooking fuel and housing material in rural Bangladesh.48 This could explain the relatively low prevalence of cow feces; while 69% of compounds had cows, only 30% had observed cow feces.
Due to the infrequency of observed human feces, we had limited power to detect associations between this exposure and E. coli. Animal feces were associated with increased contamination of soil, ponds and complementary foods. The association with food contamination might indicate that, when preparing food, caregivers do not wash hands after handling animal feces. Previous work in Bangladesh found that, during food preparation, caregivers feed dung cakes to the fire with bare hands and resume food handling or feed children without washing hands.49 However, while dung cakes are moist when handled to form them for subsequent use, they are sun-dried before being used as fuel, and desiccation should substantially reduce pathogen concentrations.50 Surprisingly, the presence of animal (as well as human) feces was associated with lower tubewell contamination. Tubewells in rural Bangladesh are typically located on the periphery of the compound rather than in the central courtyard area. Animal and child feces are often disposed of in bushes or open waste heaps on the compound periphery as well. Observed feces in the courtyard area could indicate that feces have not been disposed of near the tubewell, where they could more easily infiltrate into the well. E. coli on flies was not associated with animal feces in the courtyard, potentially indicating that flies can acquire fecal contamination from distal sources beyond a given compound.
Evidence from microbial source tracking supports the contribution of animal feces to domestic fecal contamination in our study setting. A subset of 500 stored drinking water, child hand and soil samples from our study were analyzed by quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) for human, ruminant and avian molecular fecal markers.20 Over 50% of soil and hands and 22% of stored water contained ruminant markers while the avian marker was detected in 33% of soil, 16% of hand rinses and 9% of water samples.20 Ruminant and avian markers were more commonly detected in compounds that had ruminants and birds, respectively,20 consistent with our finding of higher E. coli levels in compounds with animals. In contrast, human fecal markers were detected in 9% of soil, 2% of hand rinse and none of the water samples.20 Others have reported similar findings. A recent study in India detected animal fecal markers in 75% of ponds, 15% of tubewells, 52% of stored water, and 96% of hands in contrast to human markers detected in 8% of ponds, 2% of tubewells, 20% of stored water and 37% of hands.22 A similar study found evidence of animal contamination in 70% of households in rural India compared to human contamination in 35%, based on testing stored drinking water and hands.21 Ruminant fecal markers have also been detected on child hands and household floors in urban Bangladesh.23
The high prevalence of animals and animal feces in our study and their associations with fecal contamination in the domestic environment suggest that animals can be a source of fecal pathogen exposure. A previous study in Bangladesh found 8.5 log10 MPN E. coli and 7.8 log10 MPN Enterococcus per gram of chicken feces23 and 6.8 log10 MPN E. coli and 3.8 log10 MPN Enterococcus per gram of cow feces.23 Animal feces also carry pathogens that infect humans, such as pathogenic E. coli, Salmonella and Campylobacter.50 A study in Ecuador found that 76% of chickens were positive for Campylobacter;51Campylobacter can persist in chicken feces for days after deposition.38,52 Animal feces pose variable levels of human health risk, depending on the prevalence of human-infective pathogen strains in the host species.53−55 A study in rural India found similar odds of diarrhea associated with animal and human fecal markers in the domestic environment.21 Identical strains of Campylobacter were isolated from the feces of children and chickens in Ecuador, suggesting zoonotic transmission.51 Pathogens can be transmitted from animal feces to human hosts through direct and indirect routes. Previous studies have observed children ingesting chicken feces.38,52 Structured observations of 148 children in our study demonstrated that roughly 20% of young children touched animal feces but direct ingestion was rare (<3%).56 However, up to 35% of children placed soil in their mouth or put their hands in their mouth without handwashing after touching soil.56 Compounds with animals had higher levels of soil contamination in our study, as well as higher contamination of stored water and food. Taken together, these findings suggest that animal feces are a source of fecal exposure for children in this setting. Environmental pathways, including highly contaminated soil, potentially mediate transmission by direct and indirect ingestion.
Our findings are consistent with an emerging body of literature that exposure to domestic animals, especially chickens, is associated with increased risk of enteric infection and adverse child growth. A meta-analysis found associations between diarrheal infections and domestic animal exposure, with an almost 3-fold increase in Campylobacter infections associated with poultry exposure.19 The presence of animal fecal markers in the household environment was associated with an over 4-fold increase in the odds of child diarrhea in rural India; the magnitude of the effect was similar to that observed for the presence of human markers.21 The presence of animal feces was associated with lower height-for-age in children in Ethiopia and Bangladesh.24 In rural Ethiopia, while poultry ownership was associated with improved child growth (presumably by providing nutrition-rich foods such as eggs), corralling poultry inside the home overnight was associated with growth faltering; indoor corralling of other domestic animals was not associated with adverse growth outcomes.46 Similarly, keeping animals in the room where children sleep was associated with environmental enteric dysfunction scores and stunting among rural Bangladeshi children; chickens were the most common animal corralled in the sleeping area (61%) followed by cows (39%).57 In Peruvian shantytowns, children living in households with chickens were at increased risk of Campylobacter infections;58 an intervention to corral chickens in an attempt to reduce children’s exposure to feces deposited by free-ranging chickens substantially increased rather than decreased the risk of Campylobacter-related diarrhea compared to letting the chickens free-range.59 This could have been due to exposure to concentrated rather than dispersed fecal matter from chickens. In contrast, cow exposure was not associated with child diarrhea or growth in rural India.60
Limitations
One limitation of our study is that E. coli is an imperfect proxy for fecal contamination. It has been suggested that tropical soils and waters can harbor naturally present E. coli;61,62 these are phenotypically identical to E. coli from fecal sources and can only be distinguished by genotypic comparison.63,64 While soil collected from compounds with animals and observed animal feces consistently had higher levels of E. coli in our study, the level of contamination in compounds without animal feces was still high (4.7 log10 MPN). This could indicate that soil accumulates fecal indicator contamination beyond the immediate contribution of feces observed at the time of sampling; however, it could also point to the presence of naturally present E. coli. Soilborne E. coli can persist and multiply outside animal hosts, especially in warm and moist tropical conditions; when incubated at 30–37 °C in the laboratory, naturally present E. coli can grow in soil to concentrations of ∼5 log10 per gram (similar to the soil E. coli levels in our study).65 However, testing of a subset of our soil samples with biochemical assays, phylogrouping and PCR detection of genes associated with enteric vs environmental origin showed no differences between E. coli isolates in soil vs those from fecal samples collected from cattle, chickens, and humans in the study area.66 Additionally, qPCR testing of our soil samples for microbial source tracking markers revealed high prevalence of ruminant and avian fecal molecular markers, providing evidence for contamination of fecal origin from animal sources, while human fecal markers were rare.20 This evidence suggests that, while E. coli can signal fecal contamination, its presence should not be interpreted as evidence of strictly human fecal contamination when animals are present.
E. coli is also imperfectly correlated with the presence of fecal pathogens.50 The associations we observed between animal feces and E. coli therefore do not provide standalone evidence for pathogen transmission from animal feces to the domestic environment.67 Multiplex PCR testing of a subset of E. coli-positive food and fly samples from our study found pathogenic E. coli genes in 14% of E. coli-positive food and 2% of E. coli-positive flies.68 A previous study in rural Bangladesh found that among tubewells with 1–10 MPN/100 mL E. coli (similar to our tubewell E. coli levels), pathogenic E. coli was detected by qPCR in 21%, rotavirus in 57%, Shigella in 7% and Vibrio cholerae in 7% of wells.69 Another study in a similar Bangladeshi setting found that, while 97% of soil samples were positive for E. coli, only 14% contained pathogenic E. coli detected by multiplex PCR.13 However, despite its limitations as an indicator organism, E. coli is used globally to monitor microbiological contamination.70−72 A systematic review has demonstrated that E. coli in drinking water is associated with diarrhea, supporting its use as an indicator for diarrhea-causing pathogens.73
Another limitation is that we collected all environmental samples simultaneously; we therefore cannot ascertain the causal direction of observed associations. For example, we can only hypothesize that soil contamination preceded the associated contamination of hands, stored water and food, and not vice versa. However, while we cannot directly compare levels of contamination along the different pathways due to different reporting units and detection limits, the environmental media we would expect to be more proximal to fecal sources (e.g., soil, ponds, flies) were more heavily contaminated than those further down the transmission pathway (e.g., hands, stored water, food). Similarly, all molecular fecal markers had higher prevalence in soil than on hands or in stored water,20 although it is difficult to compare PCR results across sample types because of differential recovery efficiency. This pattern is consistent with the assumption that contamination would progressively decrease as we move further from fecal sources due to limited transfer efficiencies of transmitting vectors/fomites. One could therefore assume that heavily contaminated soils and ponds led to the lower levels of contamination observed on hands, stored water, and food, and not vice versa.
A related limitation is that we sampled each household once. Domestic contamination levels vary temporally, even within 1 day;74 this variation is not captured by our one-time sampling. E. coli counts in duplicate samples collected simultaneously from the same household in 10% of households were correlated 69–79% depending on sample type; repeat samples collected at different times would likely exhibit greater variability.
Finally, our analysis was observational and therefore susceptible to confounding. A recent study in India found that animal ownership was associated with higher socioeconomic status.60 Almost all compounds in our study owned domestic animals. Socioeconomic proxies were not associated with animal ownership but significantly associated with the presence of animal feces. We controlled for housing materials, reported income, land ownership, presence of electricity, and caregivers’ education in all models; however, it is possible that residual confounding remained in our analysis.
Conclusions
We provide a novel assessment of fecal contamination along several different pathogen transmission pathways in the household environment in a setting with high on-site sanitation coverage. Our findings demonstrate widespread fecal contamination. The presence of animals and animal feces, especially chickens, was associated with domestic fecal contamination. It is likely that animal feces are a dominant source of fecal contamination in low-income country settings with high sanitation coverage and low rates of open defecation; under these circumstances, fecal indicator bacteria will be poor proxies for human fecal contamination. Intervention studies on hygienic removal of animal feces from children’s environment can assess whether reducing exposure to fecal contamination from animal sources can reduce child enteric illness.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported [in part] by Grant OPPGD759 from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation to the University of California, Berkeley, and by a grant from the World Bank to the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Research, Bangladesh.
Author Contributions
○ Co-primary author with equal contribution.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Eisenberg J. N. S.; Scott J. C.; Porco T. Integrating disease control strategies: balancing water sanitation and hygiene interventions to reduce diarrheal disease burden. Am. J. Public Health 2007, 97 (5), 846. 10.2105/AJPH.2006.086207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawata K. Water and other environmental interventions--the minimum investment concept. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1978, 31 (11), 2114–2123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B. F.; Colford J. M. Treating water with chlorine at point-of-use to improve water quality and reduce child diarrhea in developing countries: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg 2007, 76 (2), 354–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clasen T. F.; Alexander K. T.; Sinclair D.; Boisson S.; Peletz R.; Chang H. H.; Majorin F.; Cairncross S.. Interventions to improve water quality for preventing diarrhoea. In Cochrane Database Syst. Rev.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd: New York, 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanata C. Studies of food hygiene and diarrhoeal disease. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2003, 13 (sup1), S175–S183. 10.1080/0960312031000102921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Islam M. A.; Ahmed T.; Faruque A. S. G.; Rahman S.; Das S. K.; Ahmed D.; Fattori V.; Clarke R.; Endtz H. P.; Cravioto A. Microbiological quality of complementary foods and its association with diarrhoeal morbidity and nutritional status of Bangladeshi children. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66 (11), 1242–1246. 10.1038/ejcn.2012.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram P. K.; Jahid I.; Halder A. K.; Nygren B.; Islam M. S.; Granger S. P.; Molyneaux J. W.; Luby S. P. Variability in Hand Contamination Based on Serial Measurements: Implications for Assessment of Hand-Cleansing Behavior and Disease Risk. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2011, 84 (4), 510–516. 10.4269/ajtmh.2011.10-0299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. C.; Stocks M. E.; Cumming O.; Jeandron A.; Higgins J. P. T.; Wolf J.; Prüss-Ustün A.; Bonjour S.; Hunter P. R.; Fewtrell L.; et al. Systematic review: Hygiene and health: systematic review of handwashing practices worldwide and update of health effects. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2014, 19 (8), 906–916. 10.1111/tmi.12339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Förster M.; Sievert K.; Messler S.; Klimpel S.; Pfeffer K. Comprehensive Study on the Occurrence and Distribution of Pathogenic Microorganisms Carried by Synanthropic Flies Caught at Different Rural Locations in Germany. J. Med. Entomol. 2009, 46 (5), 1164–1166. 10.1603/033.046.0526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szalanski A. L.; Owens C. B.; McKay T.; Steelman C. D. Detection of Campylobacter and Escherichia coli O157: H7 from filth flies by polymerase chain reaction. Med. Vet Entomol 2004, 18 (3), 241–246. 10.1111/j.0269-283X.2004.00502.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavasse D. C.; Shier R. P.; Murphy O. A.; Huttly S. R. A.; Cousens S. N.; Akhtar T. Impact of fly control on childhood diarrhoea in Pakistan: community-randomised trial. Lancet 1999, 353 (9146), 22–25. 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)03366-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering A. J.; Julian T. R.; Marks S. J.; Mattioli M. C.; Boehm A. B.; Schwab K. J.; Davis J. Fecal Contamination and Diarrheal Pathogens on Surfaces and in Soils among Tanzanian Households with and without Improved Sanitation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46 (11), 5736–5743. 10.1021/es300022c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. M.; Oldja L.; Biswas S.; Perin J.; Lee G. O.; Kosek M.; Sack R. B.; Ahmed S.; Haque R.; Parvin T.; Faruque A. G.; et al. Geophagy is Associated with Environmental Enteropathy and Stunting in Children in Rural Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 92 (6), 1117–1124. 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivoga W. A.; Moturi W. N. Geophagia as a risk factor for diarrhoea. J. Infect. Dev. Countries 2009, 3 (02), 094–098. 10.3855/jidc.55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clasen T.; Boisson S.; Routray P.; Torondel B.; Bell M.; Cumming O.; Ensink J.; Freeman M.; Jenkins M.; Odagiri M.; et al. Effectiveness of a rural sanitation programme on diarrhoea, soil-transmitted helminth infection, and child malnutrition in Odisha, India: a cluster-randomised trial. Lancet Glob Health 2014, 2 (11), e645–e653. 10.1016/S2214-109X(14)70307-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patil S. R.; Arnold B. F.; Salvatore A. L.; Briceno B.; Ganguly S.; Colford J. M. Jr; Gertler P. J. The Effect of India’s Total Sanitation Campaign on Defecation Behaviors and Child Health in Rural Madhya Pradesh: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial. PLOS Med. 2014, 11 (8), e1001709. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering A. J.; Djebbari H.; Lopez C.; Coulibaly M.; Alzua M. L. Effect of a community-led sanitation intervention on child diarrhoea and child growth in rural Mali: a cluster-randomised controlled trial. Lancet Glob Health 2015, 3 (11), e701–e711. 10.1016/S2214-109X(15)00144-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sclar G. D.; Penakalapati G.; Amato H. K.; Garn J. V.; Alexander K.; Freeman M. C.; Boisson S.; Medlicott K. O.; Clasen T. Assessing the impact of sanitation on indicators of fecal exposure along principal transmission pathways: A systematic review. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2016, 219 (8), 709–723. 10.1016/j.ijheh.2016.09.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambrano L. D.; Levy K.; Menezes N. P.; Freeman M. C. Human diarrhea infections associated with domestic animal husbandry: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 108 (6), 313–325. 10.1093/trstmh/tru056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boehm A. B.; Wang D.; Ercumen A.; Shea M.; Harris A. R.; Shanks O. C.; Kelty C.; Ahmed A.; Mahmud Z. H.; Arnold B. F.; et al. Occurrence of Host-Associated Fecal Markers on Child Hands, Household Soil, and Drinking Water in Rural Bangladeshi Households. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2016, 3 (11), 393–398. 10.1021/acs.estlett.6b00382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odagiri M.; Schriewer A.; Daniels M. E.; Wuertz S.; Smith W. A.; Clasen T.; Schmidt W.-P.; Jin Y.; Torondel B.; Misra P. R.; et al. Human fecal and pathogen exposure pathways in rural Indian villages and the effect of increased latrine coverage. Water Res. 2016, 100, 232–244. 10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schriewer A.; Odagiri M.; Wuertz S.; Misra P. R.; Panigrahi P.; Clasen T.; Jenkins M. W. Human and Animal Fecal Contamination of Community Water Sources, Stored Drinking Water and Hands in Rural India Measured with Validated Microbial Source Tracking Assays. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93 (3), 509–516. 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris A. R.; Pickering A. J.; Harris M.; Doza S.; Islam M. S.; Unicomb L.; Luby S.; Davis J.; Boehm A. B. Ruminants Contribute Fecal Contamination to the Urban Household Environment in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50 (9), 4642–4649. 10.1021/acs.est.5b06282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headey D.; Nguyen P.; Kim S.; Rawat R.; Ruel M.; Menon P. Is Exposure to Animal Feces Harmful to Child Nutrition and Health Outcomes? A Multicountry Observational Analysis. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 961–969. 10.4269/ajtmh.16-0270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold B. F.; Null C.; Luby S. P.; Unicomb L.; Stewart C. P.; Dewey K. G.; Ahmed T.; Ashraf S.; Christensen G.; Clasen T.; et al. Cluster-randomised controlled trials of individual and combined water, sanitation, hygiene and nutritional interventions in rural Bangladesh and Kenya: the WASH Benefits study design and rationale. BMJ. Open 2013, 3 (8), e003476. 10.1136/bmjopen-2013-003476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO/UNICEF Progress on Sanitation and Drinking Water; Joint Water Supply and Sanitation Monitoring Programme; World Health Organization; UNICEF, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Pickering A. J.; Boehm A. B.; Mwanjali M.; Davis J. Efficacy of waterless hand hygiene compared with handwashing with soap: a field study in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82 (2), 270–278. 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed K. M.; Bhattacharya P.; Hasan M. A.; Akhter S. H.; Alam S. M. M.; Bhuyian M. A. H.; Imam M. B.; Khan A. A.; Sracek O. Arsenic enrichment in groundwater of the alluvial aquifers in Bangladesh: an overview. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19 (2), 181–200. 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2003.09.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- van Geen A.; Ahmed K. M.; Akita Y.; Alam M. J.; Culligan P. J.; Emch M.; Escamilla V.; Feighery J.; Ferguson A. S.; Knappett P.; et al. Fecal contamination of shallow tubewells in Bangladesh inversely related to arsenic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1199–1205. 10.1021/es103192b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luby S. P.; Gupta S. K.; Sheikh M. A.; Johnston R. B.; Ram P. K.; Islam M. S. Tubewell water quality and predictors of contamination in three flood-prone areas in Bangladesh. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 105 (4), 1002–1008. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03826.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leber J.; Rahman M. M.; Ahmed K. M.; Mailloux B.; van Geen A. Contrasting influence of geology on E. coli and arsenic in aquifers of Bangladesh. Groundwater 2011, 49 (1), 111–123. 10.1111/j.1745-6584.2010.00689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercumen A.; Naser A. M.; Unicomb L.; Arnold B. F.; Colford J. M. Jr; Luby S. P. Effects of Source- versus Household Contamination of Tubewell Water on Child Diarrhea in Rural Bangladesh: A Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS One 2015, 10 (3), e0121907. 10.1371/journal.pone.0121907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J.; Gundry S.; Conroy R. Household drinking water in developing countries: a systematic review of microbiological contamination between source and point-of-use. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9 (1), 106–117. 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2003.01160.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering A. J.; Davis J.; Walters S. P.; Horak H. M.; Keymer D. P.; Mushi D.; Strickfaden R.; Chynoweth J. S.; Liu J.; Blum A.; et al. Hands, water, and health: fecal contamination in Tanzanian communities with improved, non-networked water supplies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44 (9), 3267–3272. 10.1021/es903524m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian T. R.; Pickering A. J.; Leckie J. O.; Boehm A. B. Enterococcus spp on fomites and hands indicate increased risk of respiratory illness in child care centers. Am. J. Infect. Control 2013, 41 (8), 728–733. 10.1016/j.ajic.2012.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E.; Brown K. H.; Becker S.; Alim A. R. M.; Merson M. H. Contamination of weaning foods and transmission of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhoea in children in rural Bangladesh. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1982, 76 (2), 259–264. 10.1016/0035-9203(82)90292-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry F. J.; Patwary Y.; Huttly S. R. A.; Aziz K. M. A.; et al. Bacterial contamination of weaning foods and drinking water in rural Bangladesh. Epidemiol. Infect. 1990, 104 (1), 79–85. 10.1017/S0950268800054558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ngure F. M.; Humphrey J. H.; Mbuya M. N. N.; Majo F.; Mutasa K.; Govha M.; Mazarura E.; Chasekwa B.; Prendergast A. J.; Curtis V.; et al. Formative Research on Hygiene Behaviors and Geophagy among Infants and Young Children and Implications of Exposure to Fecal Bacteria. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89 (4), 709–716. 10.4269/ajtmh.12-0568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santamaría J.; Toranzos G. A. Enteric pathogens and soil: a short review. Int. Microbiol 2003, 6 (1), 5–9. 10.1007/s10123-003-0096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knappett P. S. K.; McKay L. D.; Layton A.; Williams D. E.; Alam M. J.; Huq M. R.; Mey J.; Feighery J. E.; Culligan P. J.; Mailloux B. J.; et al. Implications of fecal bacteria input from latrine-polluted ponds for wells in sandy aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46 (3), 1361–1370. 10.1021/es202773w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. K.; Ensink J. H. J.; Jayasinghe G.; Van Der Hoek W.; Cairncross S.; Dalsgaard A. Domestic transmission routes of pathogens: the problem of in-house contamination of drinking water during storage in developing countries. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2002, 7 (7), 604–609. 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2002.00901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattioli M. C.; Boehm A. B.; Davis J.; Harris A. R.; Mrisho M.; Pickering A. J. Enteric Pathogens in Stored Drinking Water and on Caregiver’s Hands in Tanzanian Households with and without Reported Cases of Child Diarrhea. PLoS One 2014, 9 (1), e84939. 10.1371/journal.pone.0084939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BBS-UNICEF. Multiple Indicator Cluster Survey 2012–2013. Key Findings; Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2014.
- Islam M.; Ercumen A.; Ashraf S.; Rahman M.; Shoab A.; Luby S.; Unicomb L.. Unsafe disposal of feces of children < 3 years among households with latrine access in rural Bangladesh: association with household characteristics, fly presence and child diarrhea. PLoS One 2017, In review [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Knappett P. S. K.; Escamilla V.; Layton A.; McKay L. D.; Emch M.; Williams D. E.; Huq R.; Alam J.; Farhana L.; Mailloux B. J.; et al. Impact of population and latrines on fecal contamination of ponds in rural Bangladesh. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409 (17), 3174–3182. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.04.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Headey D.; Hirvonen K. Is Exposure to Poultry Harmful to Child Nutrition? An Observational Analysis for Rural Ethiopia. PLoS One 2016, 11 (8), e0160590. 10.1371/journal.pone.0160590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aini I. Indigenous chicken production in South-east Asia. World's Poult. Sci. J. 1990, 46 (01), 51–57. 10.1079/WPS19900010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pant K. P. Cheaper Fuel and Higher Health Costs Among the Poor in Rural Nepal. Ambio 2012, 41 (3), 271–283. 10.1007/s13280-011-0189-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizame F. A.; Leontsini E.; Luby S. P.; Nuruzzaman M.; Parveen S.; Winch P. J.; Ram P. K.; Unicomb L. Hygiene Practices During Food Preparation in Rural Bangladesh: Opportunities to Improve the Impact of Handwashing Interventions. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 95 (2), 288–297. 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D.; Khatib L. A.; Hill V. R.; Alocilja E.; Pillai S.. Pathogens in animal wastes and the impacts of waste management practices on their survival, transport and fate. White Papers on Animal Agriculture and the Environment. MidWest Plan Service (MWPS); Iowa State University, Ames, IA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Vasco K.; Graham J. P.; Trueba G. Detection of zoonotic enteropathogens in children and domestic animals in a semi-rural community in Ecuador. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4218. 10.1128/AEM.00795-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquis G. S.; Ventura G.; Gilman R. H.; Porras E.; Miranda E.; Carbajal L.; Pentafiel M. Fecal contamination of shanty town toddlers in households with non-corralled poultry, Lima, Peru. Am. J. Public Health 1990, 80 (2), 146–149. 10.2105/AJPH.80.2.146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soller J.; Bartrand T.; Ravenscroft J.; Molina M.; Whelan G.; Schoen M.; Ashbolt N. Estimated human health risks from recreational exposures to stormwater runoff containing animal faecal material. Environ. Model Softw 2015, 72, 21–32. 10.1016/j.envsoft.2015.05.018. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Soller J. A.; Schoen M. E.; Bartrand T.; Ravenscroft J. E.; Ashbolt N. J. Estimated human health risks from exposure to recreational waters impacted by human and non-human sources of faecal contamination. Water Res. 2010, 44 (16), 4674–4691. 10.1016/j.watres.2010.06.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoen M. E.; Soller J. A.; Ashbolt N. J. Evaluating the importance of faecal sources in human-impacted waters. Water Res. 2011, 45 (8), 2670–2680. 10.1016/j.watres.2011.02.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwong L. H.; Ercumen A.; Pickering A. J.; Unicomb L.; Davis J.; Luby S. P. Hand- and Object-Mouthing of Rural Bangladeshi Children 3–18 Months Old. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13 (6), 563. 10.3390/ijerph13060563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. M.; Oldja L.; Biswas S. K.; Perin J.; Lee G. O.; Ahmed S.; Haque R.; Sack R. B.; Parvin T.; Azmi I. J.; et al. Fecal Markers of Environmental Enteropathy are Associated with Animal Exposure and Caregiver Hygiene in Bangladesh. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2015, 93 (2), 269–275. 10.4269/ajtmh.14-0694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grados O.; Bravo N.; Black R. E.; Butzler J. P. Paediatric campylobacter diarrhoea from household exposure to live chickens in Lima, Peru. Bull. World Health Organ 1988, 66 (3), 369–374. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhelman R. A.; Gilman R. H.; Sheen P.; Cordova J.; Zimic M.; Cabrera L.; Meza R.; Perez J. An intervention-control study of corralling of free-ranging chickens to control Campylobacter infections among children in a Peruvian periurban shantytown. Am. J. Trop Med. Hyg 2006, 74 (6), 1054–1059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt W.-P.; Boisson S.; Routray P.; Bell M.; Cameron M.; Torondel B.; Clasen T. Exposure to cows is not associated with diarrhoea or impaired child growth in rural Odisha, India: a cohort study. Epidemiol. Infect. 2016, 144 (01), 53–63. 10.1017/S0950268815001090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka R.; Sian-Denton C.; Borja M.; Castro J.; Morphew K. Soil: the environmental source of Escherichia coli and Enterococci in Guam’s streams. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1998, 85 (S1), 83S–89S. 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1998.tb05286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardina C. M.; Fujioka R. S. Soil: The environmental source of Escherichia coli and enterococci in Hawaii’s streams. Environ. Toxicol. Water Qual. 1991, 6 (2), 185–195. 10.1002/tox.2530060208. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S.; Buddenborg S.; Yoder-Himes D. R.; Tiedje J. M.; Konstantinidis K. T. Genomic Diversity of Escherichia Isolates from Diverse Habitats. PLoS One 2012, 7 (10), e47005. 10.1371/journal.pone.0047005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto D. K.; Yan T. Genotypic Diversity of Escherichia coli in the Water and Soil of Tropical Watersheds in Hawaii. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77 (12), 3988–3997. 10.1128/AEM.02140-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii S.; Ksoll W. B.; Hicks R. E.; Sadowsky M. J. Presence and Growth of Naturalized Escherichia coli in Temperate Soils from Lake Superior Watersheds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72 (1), 612–621. 10.1128/AEM.72.1.612-621.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julian T. R.; Islam M. A.; Pickering A. J.; Roy S.; Fuhrmeister E. R.; Ercumen A.; Harris A.; Bishai J.; Schwab K. J. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates from Feces, Hands, and Soils in Rural Bangladesh via the Colilert Quanti-Tray System. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81 (5), 1735–1743. 10.1128/AEM.03214-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J.; Long S. C.; Das D.; Dorner S. M. Are microbial indicators and pathogens correlated? A statistical analysis of 40 years of research. J. Water Health 2011, 9 (2), 265–278. 10.2166/wh.2011.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doza S.; Rahman M.; Islam M.; Unicomb L.; Kwong L.; Ercumen A.; Pickering A.; Parvez S.; Naser A.; Ashraf S.; et al. Prevalence and association of E. coli and diarrheagenic E. coli in stored complementary foods and flies caught in the same households in rural Bangladesh. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2017, 22 (5), 547. 10.1111/tmi.12849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson A. S.; Layton A. C.; Mailloux B. J.; Culligan P. J.; Williams D. E.; Smartt A. E.; Sayler G. S.; Feighery J.; McKay L. D.; Knappett P. S. K.; et al. Comparison of fecal indicators with pathogenic bacteria and rotavirus in groundwater. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 431, 314–322. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.05.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHO. Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th ed..; World Health Organization: Geneva, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Recreational Water Quality Criteria; 2012.
- Gilbert R.; de Louvois J.; Donovan T.; Little C.; Nye K.; Ribeiro C.; Richards J.; Roberts D.; Bolton F. Guidelines for the microbiological quality of some ready-to-eat foods sampled at the point of sale. PHLS Advisory Committee for Food and Dairy Products. Commun. Dis Public Health 2000, 3 (3), 163–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber J. S.; Ercumen A.; Colford J. M. Jr Coliform bacteria as indicators of diarrheal risk in household drinking water: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2014, 9 (9), e107429. 10.1371/journal.pone.0107429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy K.; Hubbard A. E.; Nelson K. L.; Eisenberg J. N. S. Drivers of water quality variability in northern coastal Ecuador. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43 (6), 1788–1797. 10.1021/es8022545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




