Fig. 5.
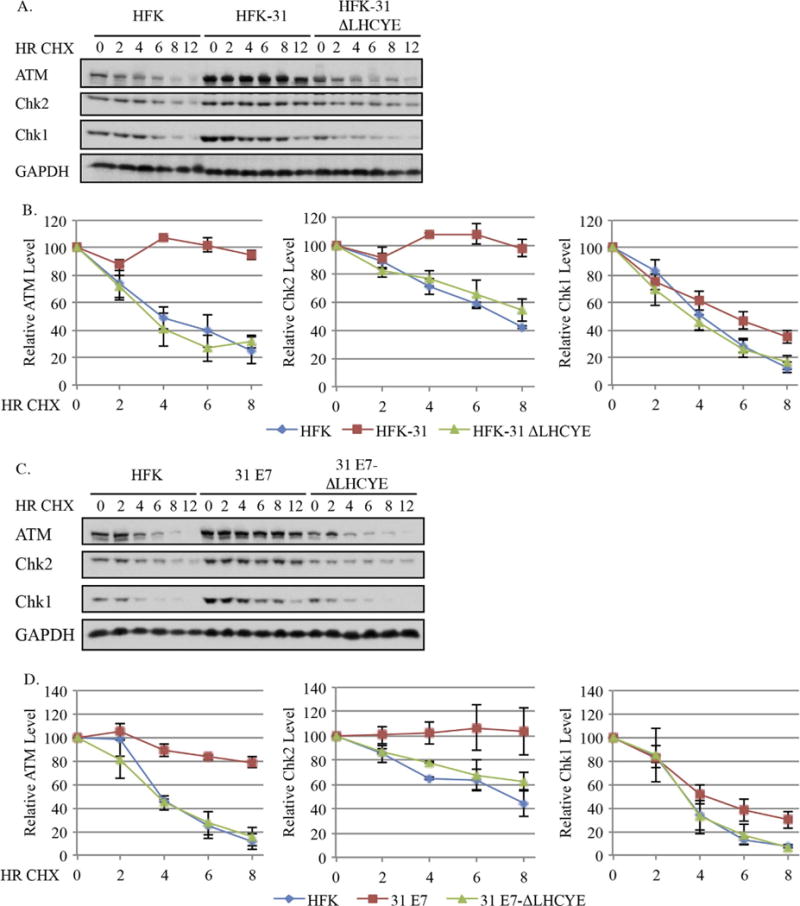
The half-lives of ATM, Chk2 and Chk1 are increased in HPV31 positives cells in an E7-dependent manner. (A, B) Uninfected HFKs, HFKs maintaining wild type HPV31 genomes (HFK-31), HPV31 genomes containing a mutation in the E7 Rb binding site (HFK-31 ΔLHYCE), as well as (C, D) HFKs stably transduced with a retroviral vector expressing wild type E7 (pLXSN-31 E7), or E7 with a mutation in the Rb binding domain (pLXSN-31 E7 ΔLHCYE) were treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide over 12 h time course, with whole cell lysates being harvested at the indicated time points. Western blot analysis was performed using antibodies targeting ATM, Chk2, and Chk1, as well as GAPDH, which served as a loading control. (A, B) Shown is representative Western blots from three independent experiments from two different HFK donors. (C, D) Data shown are representative Western blots from three independent experiments from one HFK donor. (B) Graphed are the average protein levels of ATM, Chk2, and Chk1 in HFK, HFK-31, and HFK-31 ΔLHCYE cells over three independent experiments +/− the standard error of the mean. Westerns were digitally imaged using the Bio-Rad Chemidoc MP system, and densitometry was performed with the Biorad ImageLab 5.0 software. Values are shown relative to each T0, which was set to100. (D) Graphed are the average protein levels of ATM, Chk2 and Chk1 in HFKs, pLXSN-E7 and pLXSN E7 ΔLHCYE cells over three independent experiments. Densitometry was performed as described above. Error bars represent +/− the standard error of the mean.
