Abstract
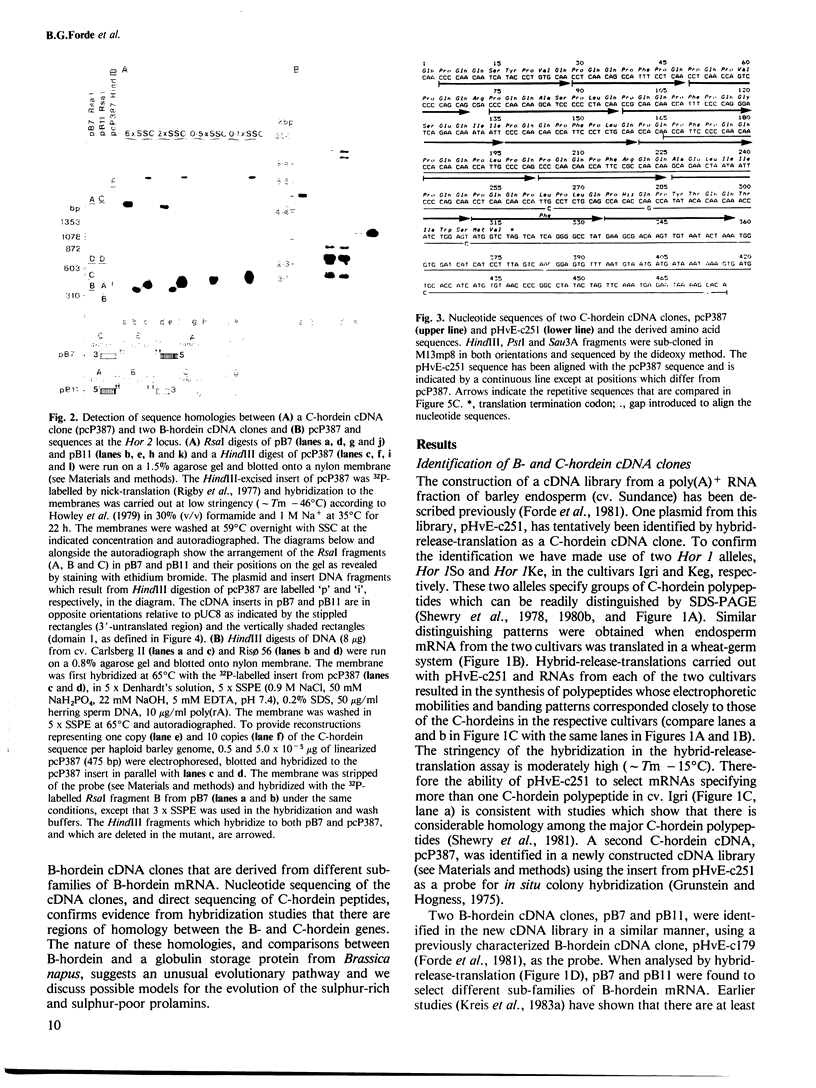
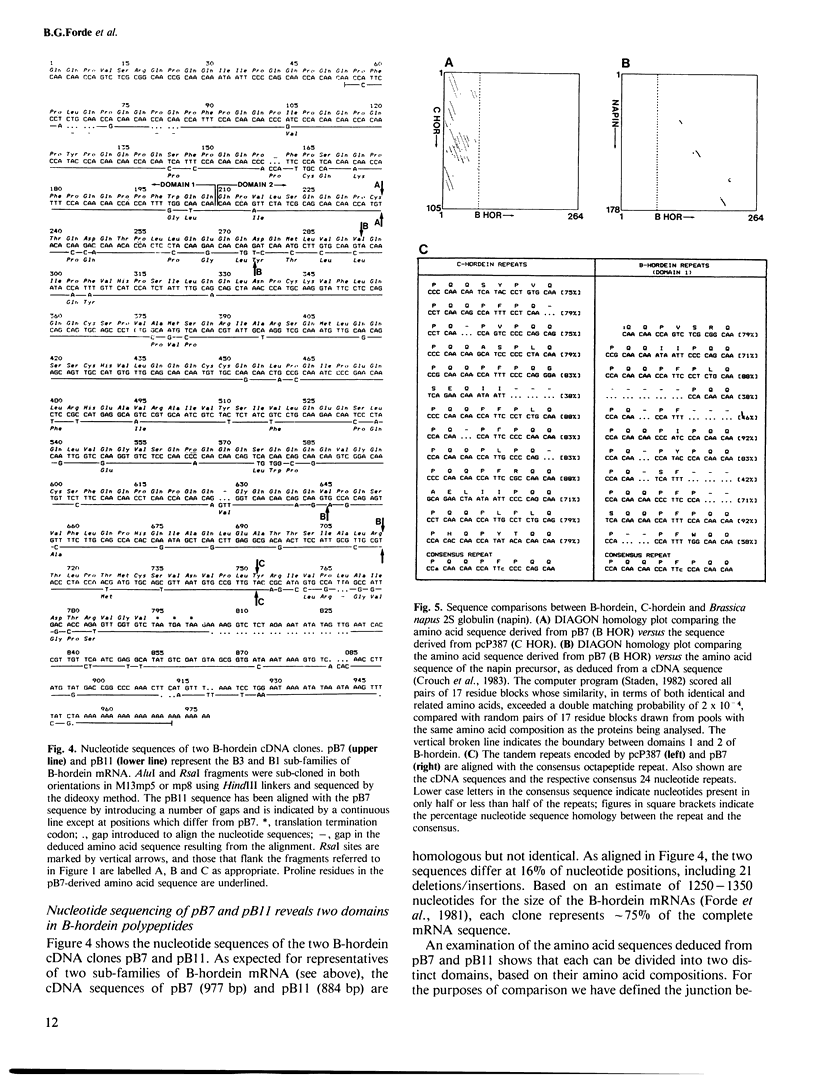
We have identified cDNA clones coding for the major sulphur-rich and sulphur-poor groups of barley storage proteins (the B- and C-hordeins, respectively). Hybridization studies have revealed unexpected homologies between B- and C-hordein mRNAs. Using a deletion mutant (Risø 56), we have mapped some C-hordein-related sequences within, or closely associated with, B-hordein genes at the Hor 2 locus. Nucleotide sequencing has shown that the primary structure of B-hordein polypeptides can be divided into at least two domains: domain 1 (repetitive, proline-rich, sulphur-poor), which is homologous to C-hordein sequences, and domain 2 (non-repetitive, proline-poor, sulphur-rich), which makes up two-thirds of the polypeptide and is partially homologous to a 2S globulin storage protein found in dicotyledons. The coding sequences that are homologous in B- and C-hordein mRNAs have an asymmetric base composition (>80% C-A) and are largely composed of a degenerate tandem repeat based on a 24 nucleotide consensus that encodes Pro-Gln-Gln-Pro-Phe-Pro-Gln-Gln. We discuss the evolutionary implications of the domain structure of the B-hordeins and the unusual relationship between the two groups of barley storage proteins.
Keywords: barley, cDNA sequences, mRNA sub-families, multigene families, structural domains
Full text
PDF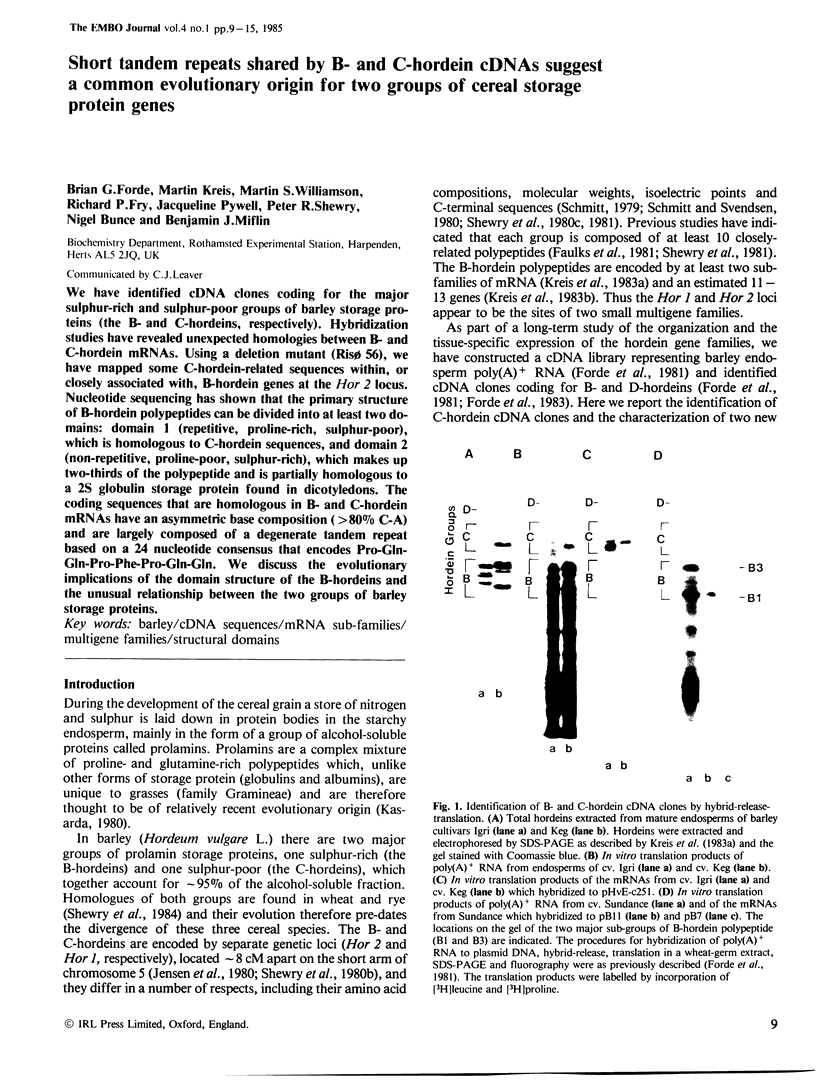




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartels D., Thompson R. D. The characterization of cDNA clones coding for wheat storage proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):2961–2977. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.2961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein P., Sage H. Structurally distinct collagen types. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:957–1003. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler P. M., Higgins T. J., Randall P. J., Spencer D. Regulation of Legumin Levels in Developing Pea Seeds under Conditions of Sulfur Deficiency: Rates of Legumin Synthesis and Levels of Legumin mRNA. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jan;71(1):47–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.1.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch M. L., Tenbarge K. M., Simon A. E., Ferl R. cDNA clones for Brassica napus seed storage proteins: evidence from nucleotide sequence analysis that both subunits of napin are cleaved from a precursor polypeptide. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):273–283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulks A. J., Shewry P. R., Miflin B. J. The polymorphism and structural homology of storage polypeptides (hordein) coded by the Hor-2 locus in barley (Hordeum vulgare L). Biochem Genet. 1981 Oct;19(9-10):841–858. doi: 10.1007/BF00504250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forde B. G., Kreis M., Bahramian M. B., Matthews J. A., Miflin B. J., Thompson R. D., Bartels D., Flavell R. B. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences derived from poly A+ RNA from barley endosperm: identification of B hordein related clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6689–6707. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., MacDonald R. J. Cloning of hormone genes from a mixture of cDNA molecules. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:75–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howley P. M., Israel M. A., Law M. F., Martin M. A. A rapid method for detecting and mapping homology between heterologous DNAs. Evaluation of polyomavirus genomes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4876–4883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasarda D. D., Okita T. W., Bernardin J. E., Baecker P. A., Nimmo C. C., Lew E. J., Dietler M. D., Greene F. C. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of alpha-type gliadins from wheat (Triticum aestivum). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4712–4716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis M., Shewry P. R., Forde B. G., Rahman S., Miflin B. J. Molecular analysis of a mutation conferring the high-lysine phenotype on the grain of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90146-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUCAS F., SHAW J. T., SMITH S. G. The silk fibroins. Adv Protein Chem. 1958;13:107–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60599-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohno S. Original domain for the serum albumin family arose from repeated sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7657–7661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peacock A. C., Dingman C. W. Resolution of multiple ribonucleic acid species by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1967 Jun;6(6):1818–1827. doi: 10.1021/bi00858a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafalski J. A., Scheets K., Metzler M., Peterson D. M., Hedgcoth C., Söll D. G. Developmentally regulated plant genes: the nucleotide sequence of a wheat gliadin genomic clone. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1409–1415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01985.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle, allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00270503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief F. S., Li S. S. Amino acid sequence of small and large subunits of seed storage protein from Ricinus communis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):14753–14759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker I. D., Bridgen J. The keratin chains of avian scale tissue. Sequence heterogeneity and the number of scale keratin genes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):283–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Martynoff G., Pays E., Vassart G. Synthesis of a full length DNA complementary to thyroglobulin 33 S messenger RNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Apr 14;93(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





