Abstract
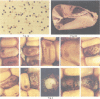
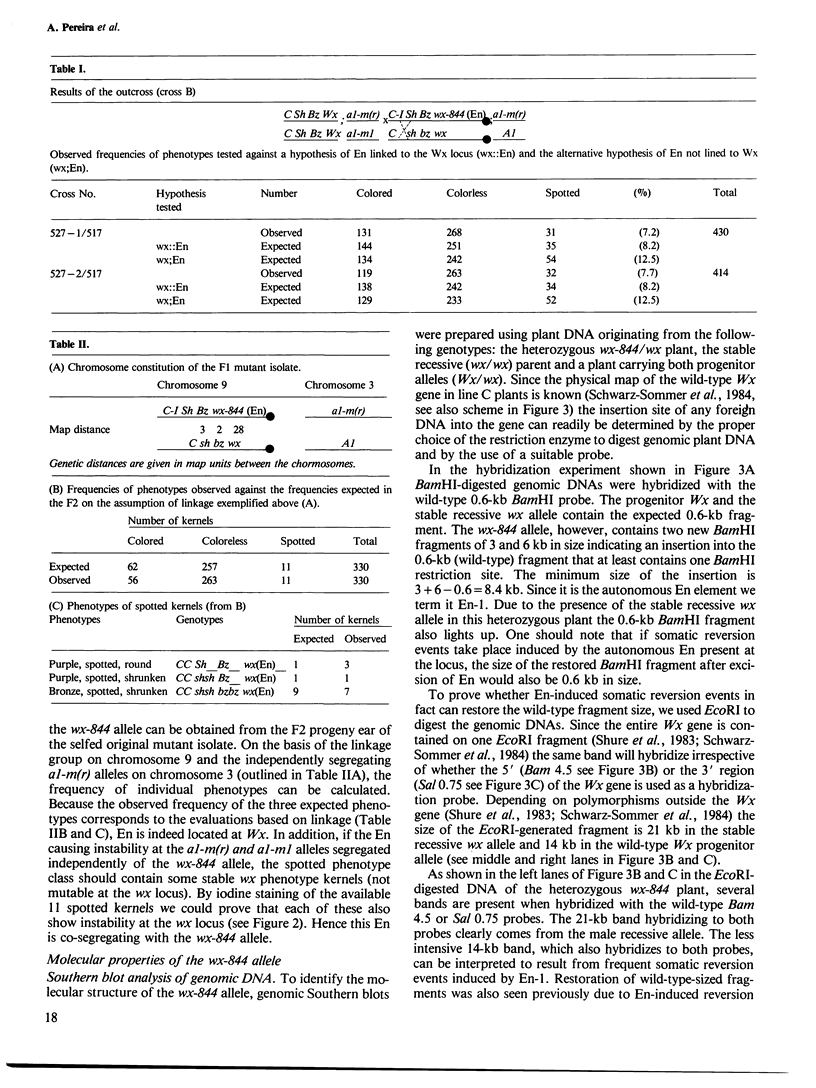
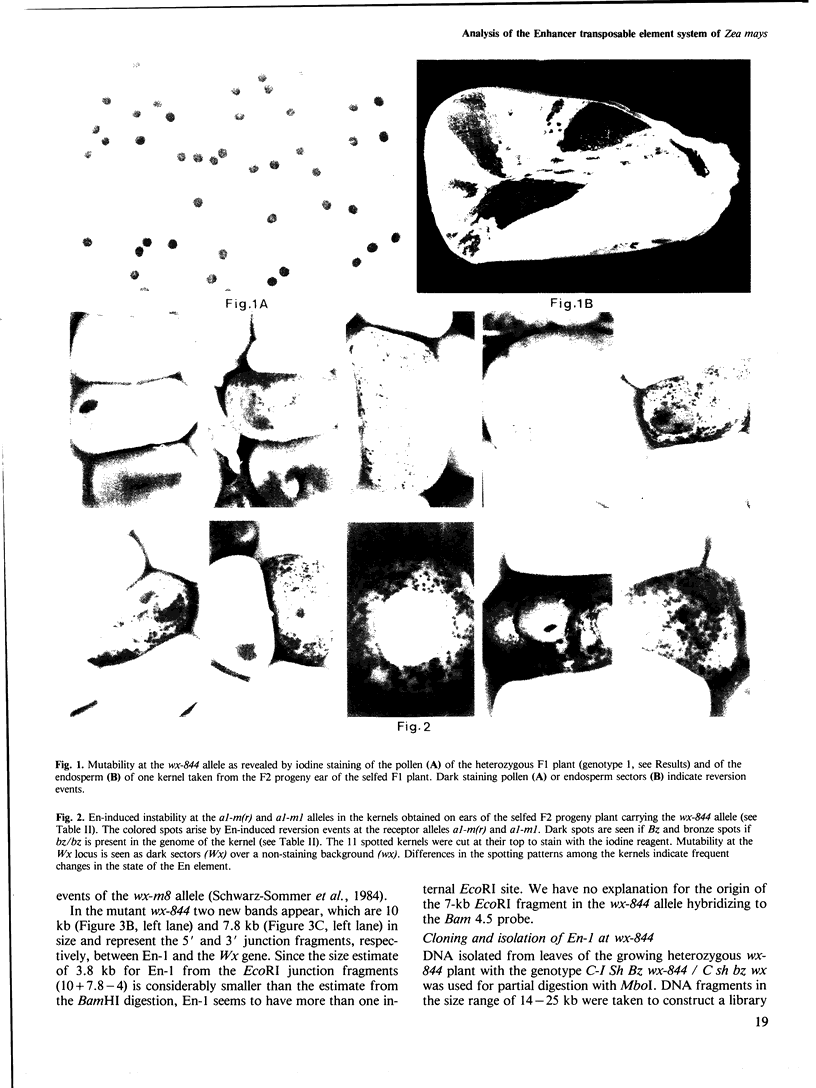
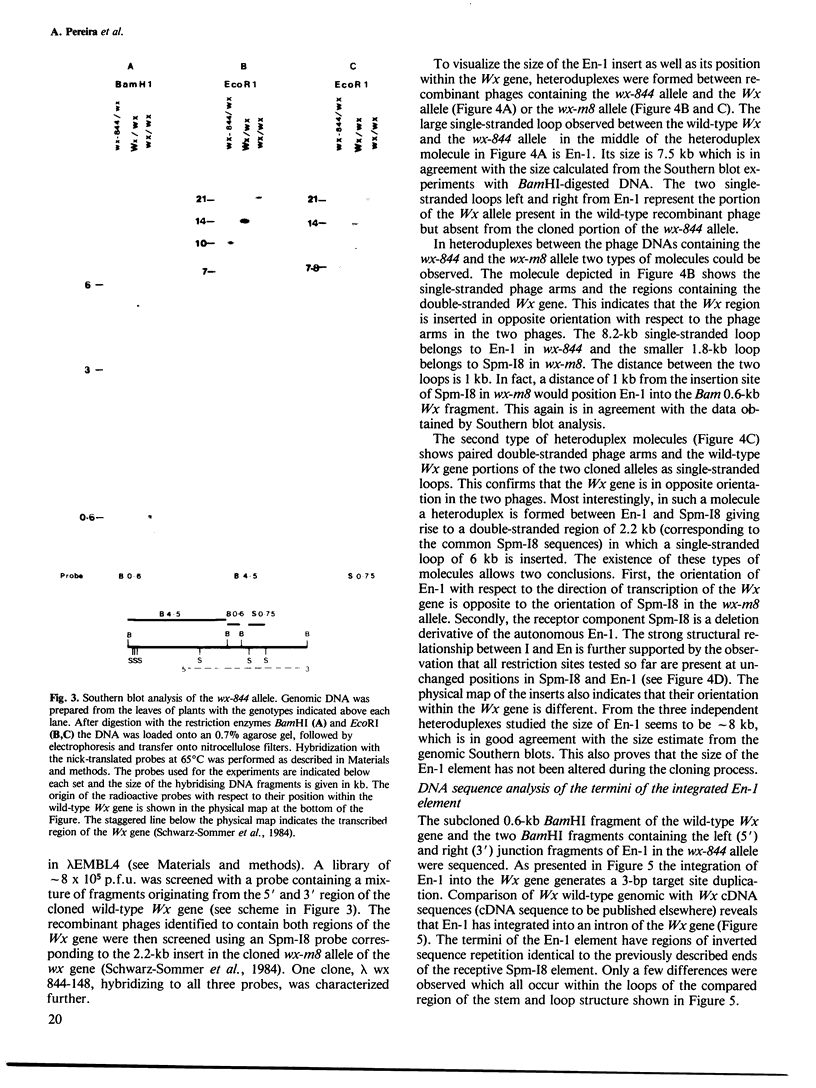
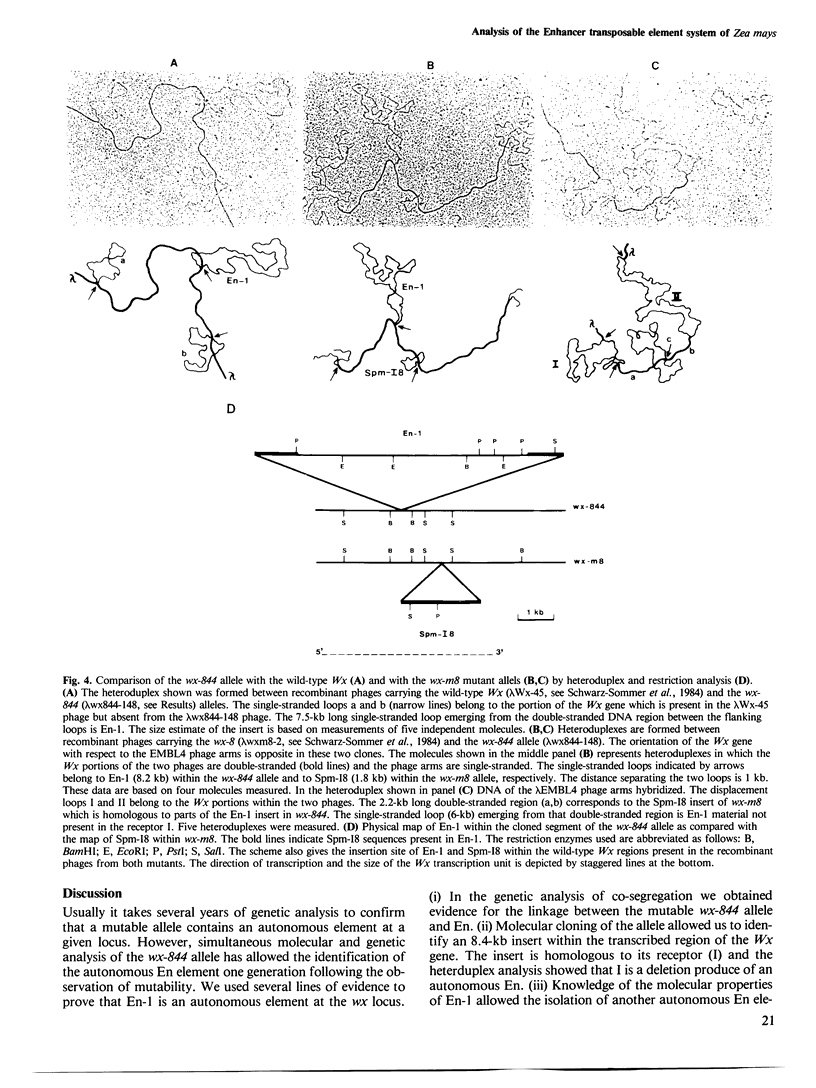
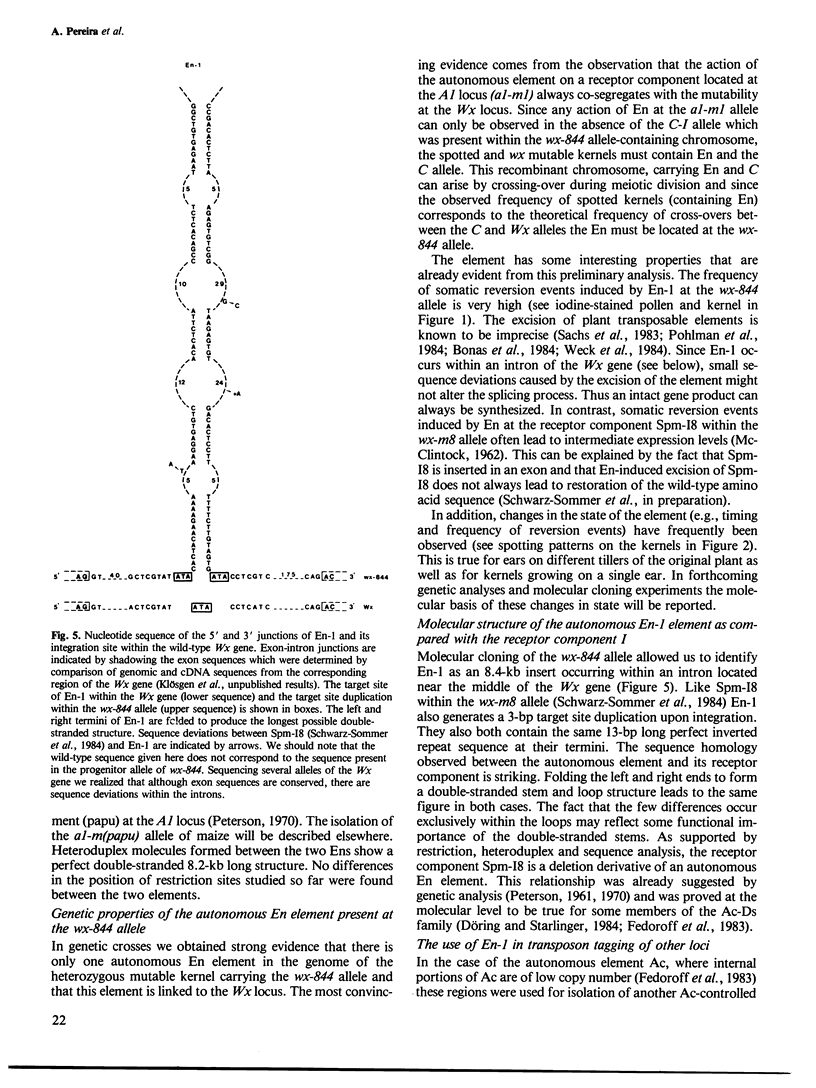
A newly isolated, unstable mutation wx-844::En-1 of Zea mays was proven to be caused by the insertion of the autonomous transposable element En into the Waxy (Wx) gene. Molecular analysis revealed that En-1 is 8.4 kb long, has a 13-bp long perfect inverted repeat at its termini and generates a 3-bp target site duplication. En-1 is integrated into an intron located approximately in the middle of the transcribed region of the Wx gene. Structural evidence is presented indicating that a receptor component (Inhibitor) can arise by internal deletion of an autonomous En element.
Keywords: autonomous element, receptor element, waxy locus, genetic analysis, sequence analysis
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonas U., Sommer H., Saedler H. The 17-kb Tam1 element of Antirrhinum majus induces a 3-bp duplication upon integration into the chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1015–1019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Hyman R. W. A study in evolution: the DNA base sequence homology between coliphages T7 and T3. J Mol Biol. 1971 Dec 14;62(2):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90428-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N. V., Furtek D. B., Nelson O. E. Cloning of the bronze locus in maize by a simple and generalizable procedure using the transposable controlling element Activator (Ac). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedoroff N., Wessler S., Shure M. Isolation of the transposable maize controlling elements Ac and Ds. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):235–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90226-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T., Schleif R. Size fractionation of double-stranded DNA by precipitation with polyethylene glycol. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Mar;2(3):383–389. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.3.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson O. E. The WAXY Locus in Maize. II. the Location of the Controlling Element Alleles. Genetics. 1968 Nov;60(3):507–524. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P A. Mutable a(1) of the En System in Maize. Genetics. 1961 Jul;46(7):759–771. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.7.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P A. The Pale Green Mutable System in Maize. Genetics. 1960 Jan;45(1):115–133. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman R. F., Fedoroff N. V., Messing J. The nucleotide sequence of the maize controlling element Activator. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):635–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90395-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RHOADES M. M. Meiosis in maize. J Hered. 1950 Mar;41(3):59–67. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jhered.a106089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weck E., Courage U., Döring H. P., Fedoroff N., Starlinger P. Analysis of sh-m6233, a mutation induced by the transposable element Ds in the sucrose synthase gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 Aug;3(8):1713–1716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Alberts B. M., Benzinger R., Lawhorne L., Treiber G. Rapid bacteriophage sedimentation in the presence of polyethylene glycol and its application to large-scale virus purification. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):734–744. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90218-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]