Abstract
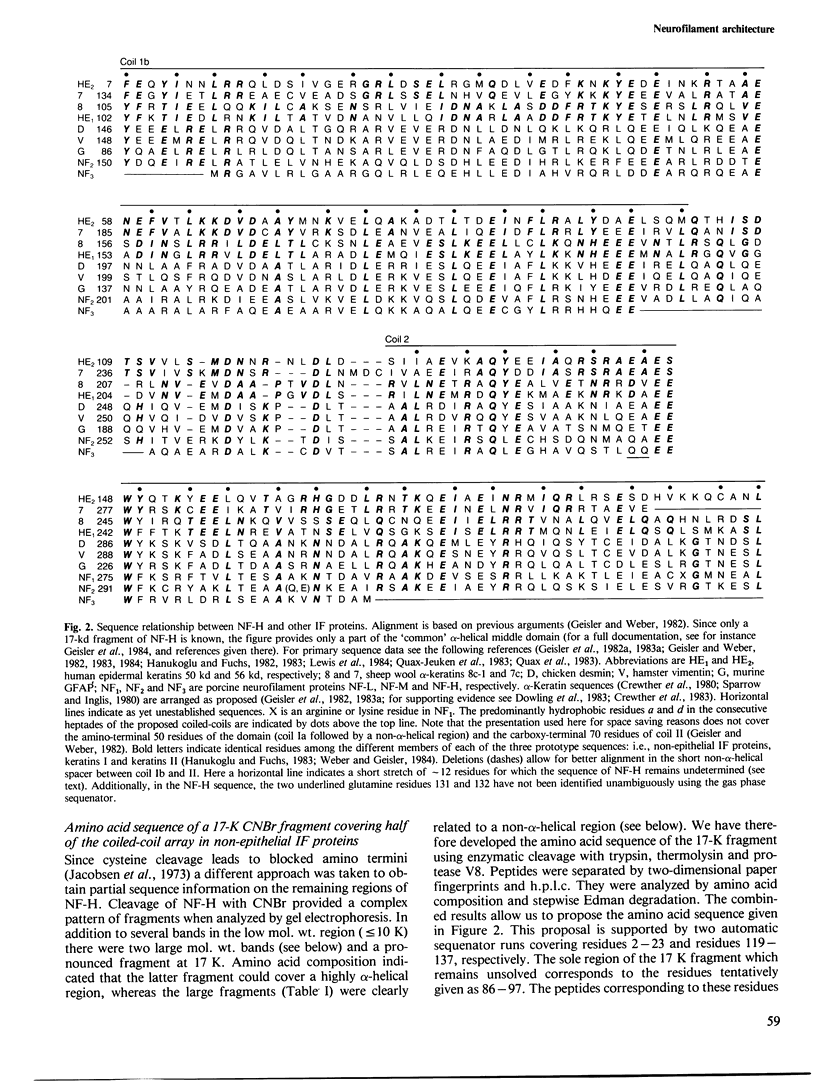
NF-H has the highest mol. wt. of the three mammalian neurofilament components (NF-L, NF-M, NF-H). In spite of its unusually large mol. wt., estimated to be 200 K by gel electrophoresis, NF-H contains sequences which identify it as an integral intermediate filament (IF) protein in its amino-terminal region. We have isolated and partially characterized a basic, non-α-helical segment located at the amino-terminal end with properties similar to headpieces of other non-epithelial IF proteins. The highly α-helical 40-K fragment excised by chymotrypsin is now identified by the amino acid sequence of a 17-K fragment. This sequence can be unambiguously aligned with the rod region of other IF proteins and covers about half of the presumptive coiled-coil arrays. NF-H and NF-M show 45% sequence identity in this region. The extra mass of NF-H in comparison with most other IF proteins arises from a carboxy-terminal extension thought to be responsible for inter-neurofilament cross-bridges in axons. This autonomous domain has a unique amino acid composition characterized by a high content of proline, alanine and particularly of lysine and glutamic acid. The NF-H tailpiece extension also carries a large number of serine phosphates, which are not evenly distributed, but are restricted to the amino-terminal part. Having now delineated the intermediate filament-type sequences for all three neurofilament proteins it seems very likely that the three components interact via coiled-coil interactions. They all carry unique carboxy-terminal extensions which increase in length from NF-L to NF-H and seem to extend from the filament wall.
Keywords: axons, coiled-coils, intermediate filaments, keratin, neurofilaments
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin T. K., Eagles P. A., Maggs A. The proteolytic digestion of ox neurofilaments with trypsin and alpha-chymotrypsin. Biochem J. 1983 Nov 1;215(2):239–252. doi: 10.1042/bj2150239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Flügge G., Weber K., Osborn M. A monoclonal antibody specific for the 200 K polypeptide of the neurofilament triplet. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):41–45. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling L. M., Parry D. A., Sparrow L. G. Structural homology between hard alpha-keratin and the intermediate filament proteins desmin and vimentin. Biosci Rep. 1983 Jan;3(1):73–78. doi: 10.1007/BF01121573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Winter S. Protein complexes of intermediate-sized filaments: melting of cytokeratin complexes in urea reveals different polypeptide separation characteristics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7113–7117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner E. E., Dahl D., Bignami A. Formation of 10-nanometer filaments from the 150K-dalton neurofilament protein in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1984;11(2):145–155. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490110204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Fischer S., Vandekerckhove J., Plessmann U., Weber K. Hybrid character of a large neurofilament protein (NF-M): intermediate filament type sequence followed by a long and acidic carboxy-terminal extension. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2701–2706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Fischer S., Plessmann U., Weber K. Neurofilament architecture combines structural principles of intermediate filaments with carboxy-terminal extensions increasing in size between triplet proteins. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1295–1302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01584.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. Amino acid sequence characterization of mammalian vimentin, the mesenchymal intermediate filament protein. FEBS Lett. 1983 Oct 31;163(1):22–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)81153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. Related amino acid sequences in neurofilaments and non-neural intermediate filaments. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):448–450. doi: 10.1038/296448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Amino acid sequence data on glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFA); implications for the subdivision of intermediate filaments into epithelial and non-epithelial members. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2059–2063. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01700.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Self-assembly in Vitro of the 68,000 molecular weight component of the mammalian neurofilament triplet proteins into intermediate-sized filaments. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):565–571. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a Type II cytoskeletal keratin reveals constant and variable structural domains among keratins. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Geisler N., Weber K. A periodic ultrastructure in intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1982 Feb 25;155(2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90444-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirokawa N., Glicksman M. A., Willard M. B. Organization of mammalian neurofilament polypeptides within the neuronal cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1523–1536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. Multiple phosphorylation sites in mammalian neurofilament polypeptides. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10467–10470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. The distribution of phosphorylation sites among identified proteolytic fragments of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4019–4025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Geisler N., Weber K. SDS-PAGE strongly overestimates the molecular masses of the neurofilament proteins. FEBS Lett. 1984 May 7;170(1):81–84. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81373-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis S. A., Balcarek J. M., Krek V., Shelanski M., Cowan N. J. Sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse glial fibrillary acidic protein: structural conservation of intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2743–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liem R. K., Hutchison S. B. Purification of individual components of the neurofilament triplet: filament assembly from the 70 000-dalton subunit. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3221–3226. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milam L., Erickson H. P. Visualization of a 21-nm axial periodicity in shadowed keratin filaments and neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):592–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax-Jeuken Y. E., Quax W. J., Bloemendal H. Primary and secondary structure of hamster vimentin predicted from the nucleotide sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3548–3552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan R. A., Cohlberg J. A., Schiller D. L., Hatzfeld M., Franke W. W. Heterotypic tetramer (A2D2) complexes of non-epidermal keratins isolated from cytoskeletons of rat hepatocytes and hepatoma cells. J Mol Biol. 1984 Sep 15;178(2):365–388. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp G. A., Shaw G., Weber K. Immunoelectronmicroscopical localization of the three neurofilament triplet proteins along neurofilaments of cultured dorsal root ganglion neurones. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Feb;137(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90042-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Osborn M., Weber K. An immunofluorescence microscopical study of the neurofilament triplet proteins, vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein within the adult rat brain. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):68–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Weber K. Differential expression of neurofilament triplet proteins in brain development. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):277–279. doi: 10.1038/298277a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and bovine epidermal keratinocytes have similar ultrastructures and subunit domain structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Hainfeld J. F., Trus B. L., Wall J. S., Steinert P. M. Epidermal keratin filaments assembled in vitro have masses-per-unit-length that scale according to average subunit mass: structural basis for homologous packing of subunits in intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;97(6):1939–1944. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.6.1939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Vorgias C. E. Involvement of the N-terminal polypeptide of vimentin in the formation of intermediate filaments. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:43–67. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Shaw G., Osborn M., Debus E., Geisler N. Neurofilaments, a subclass of intermediate filaments: structure and expression. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):717–729. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard M., Simon C. Antibody decoration of neurofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1981 May;89(2):198–205. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.2.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]