Abstract
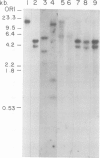
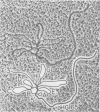
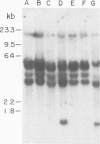
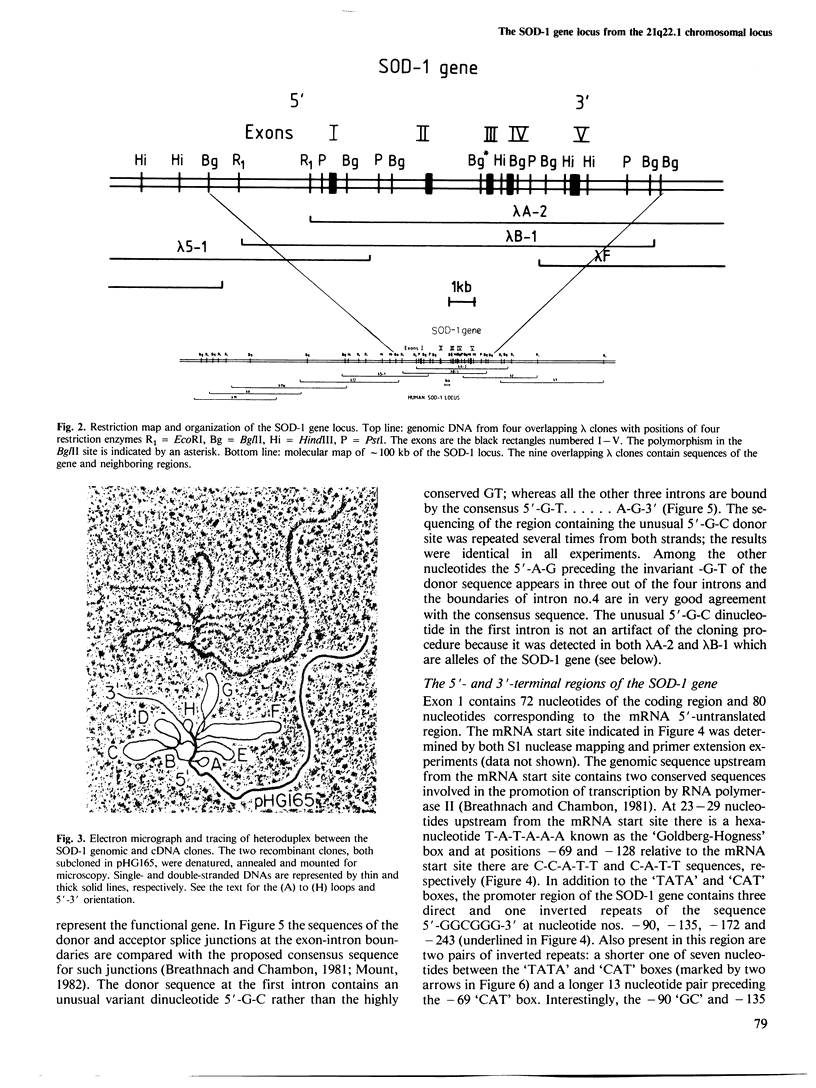
The SOD-1 gene on chromosome 21 and approximately 100 kb of chromosomal DNA from the 21q22 region have been isolated and characterized. The gene which is present as a single copy per haploid genome spans 11 kb of chromosomal DNA. Heteroduplex analysis and DNA sequencing reveals five rather small exons and four introns that interrupt the coding region. The donor sequence at the first intron contains an unusual variant dinucleotide 5'-G-C, rather than the highly conserved 5'-GT. The unusual splice junction is functional in vivo since it was detected in both alleles of the SOD-1 gene, which were defined by differences in the length of restriction endonuclease fragments (RFLPs) that hybridize to the cDNA probe. Genomic blots of human DNA isolated from cells trisomic for chromosome 21 (Down's syndrome patients) show the normal pattern of bands. At the 5' end of gene there are the 'TATA' and 'CAT' promoter sequences as well as four copies of the -GGCGGG- hexanucleotide. Two of these -GC- elements are contained within a 13 nucleotide inverted repeat that could form a stem-loop structure with stability of -33 kcal. The 3'-non coding region of the gene contains five short open reading-frames starting with ATG and terminating with stop codons.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avvedimento V. E., Vogeli G., Yamada Y., Maizel J. V., Jr, Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Correlation between splicing sites within an intron and their sequence complementarity with U1 RNA. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barra D., Martini F., Bannister J. V., Schininà M. E., Rotilio G., Bannister W. H., Bossa F. The complete amino acid sequence of human Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 20;120(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)81044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., White R. L., Skolnick M., Davis R. W. Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet. 1980 May;32(3):314–331. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs R. G., Fee J. A. Further characterization of human erythrocyte superoxide dismutase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 20;537(1):86–99. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90605-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunke K. J., Anthony J. G., Sternberg E. J., Weeks D. P. Repeated consensus sequence and pseudopromoters in the four coordinately regulated tubulin genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1115–1124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger P. C., Vogel F. S. The development of the pathologic changes of Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia in patients with Down's syndrome. Am J Pathol. 1973 Nov;73(2):457–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrne B. J., Davis M. S., Yamaguchi J., Bergsma D. J., Subramanian K. N. Definition of the simian virus 40 early promoter region and demonstration of a host range bias in the enhancement effect of the simian virus 40 72-base-pair repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):721–725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerino G., Grzeschik K. H., Jaye M., De La Salle H., Tolstoshev P., Lecocq J. P., Heilig R., Mandel J. L. Regional localization on the human X chromosome and polymorphism of the coagulation factor IX gene (hemophilia B locus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cervenka J., Gorlin R. J., Djavadi G. R. Down syndrome due to partial trisomy 21q. Clin Genet. 1977 Feb;11(2):119–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosti N., Serra A., Rigo A., Viglino P. Dosage effect of SOD-A gene in 21-trisomic cells. Hum Genet. 1976 Feb 29;31(2):197–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00296146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Pearson P. L., Harper P. S., Murray J. M., O'Brien T., Sarfarazi M., Williamson R. Linkage analysis of two cloned DNA sequences flanking the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the short arm of the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2303–2312. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. The nucleotide sequence of the adult chicken alpha-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4623–4629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayna D., Davies K., Hartley D., Mandel J. L., Camerino G., Williamson R., White R. Genetic mapping of the human X chromosome by using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. The promoter-specific transcription factor Sp1 binds to upstream sequences in the SV40 early promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90210-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis W. G., McCulloch J. R., Corley C. L. Presenile dementia in Down's syndrome. Ultrastructural identity with Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1974 Feb;24(2):101–106. doi: 10.1212/wnl.24.2.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erbil C., Niessing J. The primary structure of the duck alpha D-globin gene: an unusual 5' splice junction sequence. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1339–1343. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01589.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everett R. D., Baty D., Chambon P. The repeated GC-rich motifs upstream from the TATA box are important elements of the SV40 early promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2447–2464. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaster W. W., Kwok L. W., Epstein C. J. Dosage effects for superoxide dismutase-1 in nucleated cells aneuploid for chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1977 Nov;29(6):563–570. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer H. D., Dodgson J. B., Hughes S., Engel J. D. An unusual 5' splice sequence is efficiently utilized in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2733–2737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fridovich I. The biology of oxygen radicals. Science. 1978 Sep 8;201(4359):875–880. doi: 10.1126/science.210504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Transcription in vivo from SV40 early promoter deletion mutants without repression by large T antigen. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):127–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Sherratt D. J. Sequence analysis at IS1 insertion sites: models for transposition. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 2):1257–1261. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagemeijer A., Smit E. M. Partial trisomy 21. Further evidence that trisomy of band 21q22 is essential for Down's phenotype. Hum Genet. 1977 Aug 31;38(1):15–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00295803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen U., Sharp P. A. Sequences controlling in vitro transcription of SV40 promoters. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2293–2303. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Yamaguchi J., Subramanian K. N. SV40 deletion mutants lacking the 21-bp repeated sequences are viable, but have noncomplementable deficiencies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1601–1616. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L. L. Alzheimer's disease, trisomy 21, and myeloproliferative disorders: associations suggesting a genetic diathesis. Science. 1977 Apr 15;196(4287):322–323. doi: 10.1126/science.196.4287.322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabusch J. R., Farb D. L., Kerschensteiner D. A., Deutsch H. F. Some sulfhydryl properties and primary structure of human erythrocyte superoxide dismutase. Biochemistry. 1980 May 27;19(11):2310–2316. doi: 10.1021/bi00552a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J. DNA sequence variants in the G gamma-, A gamma-, delta- and beta-globin genes of man. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90348-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Lawrence J. B., Ruddle F. H. A sequential staining technique for the chromosomal analysis of the interspecific mouse/hamster and mouse/human somatic cell hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Jeanpierre M., Young B. D. Construction and characterization of genomic libraries from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEJEUNE J., GAUTIER M., TURPIN R. Etude des chromosomes somatiques de neuf enfants mongoliens. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Mar 16;248(11):1721–1722. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebowitz P., Ghosh P. K. Initiation and regulation of simian virus 40 early transcription in vitro. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):449–461. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.449-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Lewis S. A., Wilde C. D., Cowan N. J. Evolutionary history of a multigene family: an expressed human beta-tubulin gene and three processed pseudogenes. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90429-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieman-Hurwitz J., Dafni N., Lavie V., Groner Y. Human cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase cDNA clone: a probe for studying the molecular biology of Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2808–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. M. Genetic syndromes in man with potential relevance to the pathobiology of aging. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1978;14(1):5–39. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. C., Spence A., Smith M. The distal transcription signals of the herpesvirus tk gene share a common hexanucleotide control sequence. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. W., Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Caskey C. T. Structure, expression, and mutation of the hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2147–2151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mory Y., Chernajovsky Y., Feinstein S. I., Chen L., Nir U., Weissenbach J., Malpiece Y., Tiollais P., Marks D., Ladner M. Synthesis of human interferon beta 1 in Escherichia coli infected by a lambda phage recombinant containing a human genomic fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Nov;120(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. C., Mills K. A., Demopulos C. M., Hornung S., Motulsky A. G. Linkage disequilibrium and evolutionary relationships of DNA variants (restriction enzyme fragment length polymorphisms) at the serum albumin locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3486–3490. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Rio D. C., Robbins A. K., Tjian R. SV40 gene expression is modulated by the cooperative binding of T antigen to DNA. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):373–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niebuhr E. Down's syndrome. The possibility of a pathogenetic segment on chromosome no. 21. Humangenetik. 1974 Jan 22;21(1):99–101. doi: 10.1007/BF00278575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens D., Dawson J. C., Losin S. Alzheimer's disease in Down's syndrome. Am J Ment Defic. 1971 Mar;75(5):606–612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer R. A., Kessel E. K., Soer K. H. Partial trisomies of chromosome 21 in man. Two new observations due to translocations 19;21 and 4;21. Clin Genet. 1977 Mar;11(3):207–213. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1977.tb01301.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philip T., Fraisse J., Sinet P. M., Lauras B., Robert J. M., Freycon F. Confirmation of the assignment of the human SODS gene to chromosome 21q22. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1978;22(1-6):521–523. doi: 10.1159/000131014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poissonnier M., Saint-Paul B., Dutrillaux B., Chassaigne M., Gruyer P., de Blignières-Strouk G. Trisomie 21 partielle (21q21 leads to 21q22.2) Ann Genet. 1976 Mar;19(1):69–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saffer J. D., Singer M. F. Transcription from SV 40-like monkey DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4769–4788. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Dafni N., Lieman-Hurwitz J., Groner Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of human chromosome 21-encoded superoxide dismutase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5465–5469. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Allard D., Lejeune J., Jérôme H. Augmentation d'activité de la superoxyde dismutase érythrocytaire dans la trisomie pour le chromosome 21. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1974 Jun 17;278(25):3267–3270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M., Couturier J., Dutrillaux B., Poissonnier M., Raoul O., Rethore M. O., Allard D., Lejeune J., Jerome H. Trisomie 21 et superoxyde dismutase-1 (IPO-A). Tentative de localisation sur la sous bande 21Q22.1. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Jan;97:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90653-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinet P. M. Metabolism of oxygen derivatives in down's syndrome. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;396:83–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb26845.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solitare G. B., Lamarche J. B. Alzheimer's disease and senile dementia as seen in mongoloids: neuropathological observations. Am J Ment Defic. 1966 May;70(6):840–848. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Y. H., Tischfield J., Ruddle F. H. The linkage of genes for the human interferon-induced antiviral protein and indophenol oxidase-B traits to chromosome G-21. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):317–330. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. D., Summitt R. L., Martens P. R., Kimbrell R. A. Familial Down syndrome due to t(10;21) translocation: evidence that the Down phenotype is related to trisomy of a specific segment of chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1975 Jul;27(4):478–485. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehner Z. E., Paterson B. M. Characterization of the chicken vimentin gene: single copy gene producing multiple mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):911–915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]