Abstract
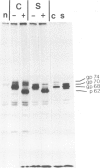
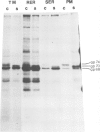
Three glycoprotein-processing inhibitors were used to resolve whether correct glycosylation was required for the oncogenic activity of erb B. The two glucosidase-I inhibitors, 1-deoxynojirimycin and 2,5-dihydroxymethyl 3,4-dihydroxypyrrolidine, arrested processing of v-erb B at the immature 68-kd form whereas, in the presence of the alpha-mannosidase-II inhibitor (swainsonine), cells synthesised an abnormally processed 70-kd form of v-erb B. Transport of incorrectly processed v-erb B to the cell surface was, however, unaffected, suggesting that correct processing is not a prerequisite for intracellular routing of v-erb B. Two systems were used to assess whether incorrectly processed erb B could maintain the transformed state. The first asked whether inhibitor treatment would release temperature-sensitive avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV) transformed erythroblasts kept at the viral permissive temperature from the erb B-induced block in differentiation, as seen when cells are normally shifted to the non-permissive temperature. The second tested the ability of AEV-transformed fibroblasts to grow in soft agar. In both systems, all three processing inhibitors did not alter the transformed phenotype suggesting that correct carbohydrate processing is not required for the transforming activity of erb B. In addition, none of the three processing inhibitors were found to have any effect on the normal maturation of bone marrow CFU-E or induced differentiation of temperature-sensitive AEV-transformed erythroblasts.
Full text
PDF


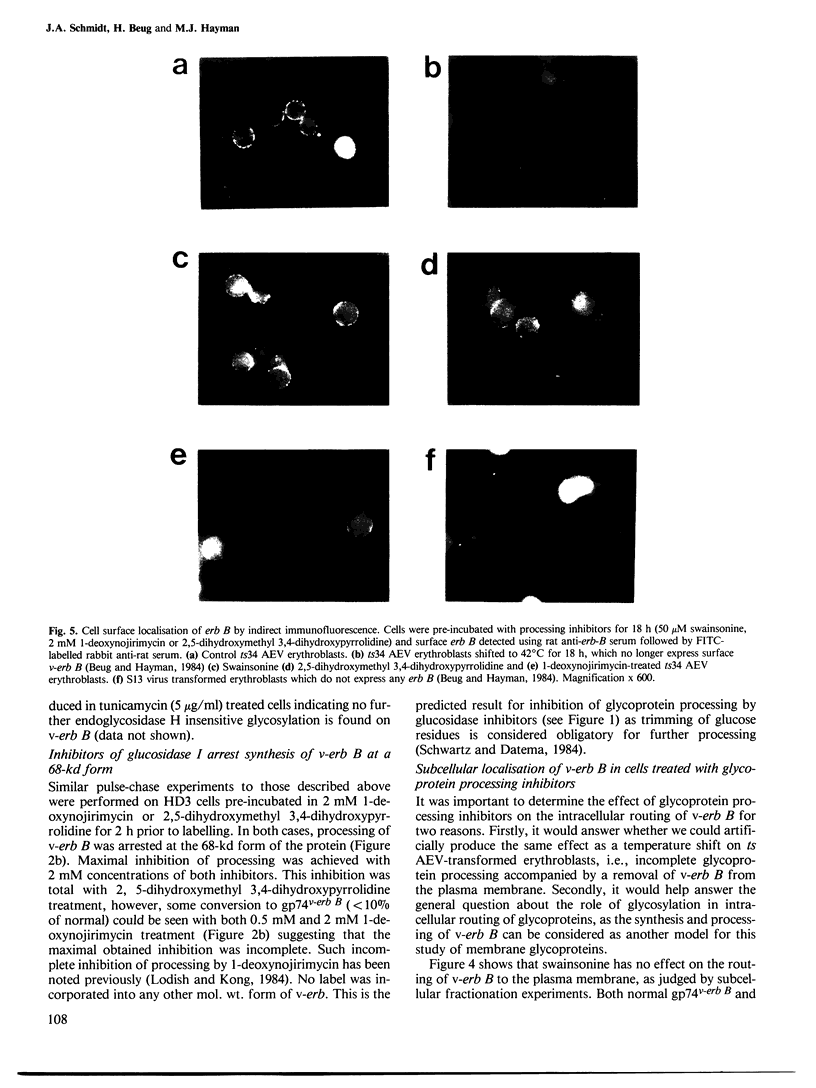



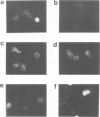
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arumugham R. G., Tanzer M. L. Abnormal glycosylation of human cellular fibronectin in the presence of swainsonine. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11883–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Hayman M. J. Temperature-sensitive mutants of avian erythroblastosis virus: surface expression of the erbB product correlates with transformation. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):963–972. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Palmieri S., Freudenstein C., Zentgraf H., Graf T. Hormone-dependent terminal differentiation in vitro of chicken erythroleukemia cells transformed by ts mutants of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):907–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Duesberg P. H. Structure and specific sequences of avian erythroblastosis virus RNA: evidence for multiple classes of transforming genes among avian tumor viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5023–5027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Matlin K., Bause E., Legler G., Peyrieras N., Ploegh H. Inhibition of N-linked oligosaccharide trimming does not interfere with surface expression of certain integral membrane proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):551–556. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01845.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Yarden Y., Mayes E., Scrace G., Totty N., Stockwell P., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Waterfield M. D. Close similarity of epidermal growth factor receptor and v-erb-B oncogene protein sequences. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):521–527. doi: 10.1038/307521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Mitchell M., Sanford B. A., Fellows L. E., Evans S. V. The pyrrolidine alkaloid, 2,5-dihydroxymethyl-3,4-dihydroxypyrrolidine, inhibits glycoprotein processing. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12409–12413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Pan Y. T., Solf R., Vosbeck K. Effect of swainsonine, an inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, on cultured mammalian cells. J Cell Physiol. 1983 Jun;115(3):265–275. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbein A. D., Solf R., Dorling P. R., Vosbeck K. Swainsonine: an inhibitor of glycoprotein processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7393–7397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frykberg L., Palmieri S., Beug H., Graf T., Hayman M. J., Vennström B. Transforming capacities of avian erythroblastosis virus mutants deleted in the erbA or erbB oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):227–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90513-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. Activation of the cellular oncogene c-erbB by LTR insertion: molecular basis for induction of erythroblastosis by avian leukosis virus. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90417-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfix B. M., Sanwal B. D. Relationship between cell surface asparagine-linked glycoproteins and myoblast differentiation. Analysis of wheat germ agglutinin-resistant mutants. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;62(1):60–71. doi: 10.1139/o84-010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Ade N., Beug H. Temperature-sensitive mutant of avian erythroblastosis virus suggests a block of differentiation as mechanism of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1978 Oct 12;275(5680):496–501. doi: 10.1038/275496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Royer-Pokora B., Schubert G. E., Beug H. Evidence for the multiple oncogenic potential of cloned leukemia virus: in vitro and in vitro studies with avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1976 Jun;71(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90370-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Beug H. Identification of a form of the avian erythroblastosis virus erb-B gene product at the cell surface. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):460–462. doi: 10.1038/309460a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Ramsay G. M., Savin K., Kitchener G., Graf T., Beug H. Identification and characterization of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB gene product as a membrane glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):579–588. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90477-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Royer-Pokora B., Graf T. Defectiveness of avian erythroblastosis virus: synthesis of a 75K gag-related protein. Virology. 1979 Jan 15;92(1):31–45. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90212-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. Synthesis and processing of avian sarcoma virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):475–486. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90454-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hihara H., Yamamoto H., Shimohira H., Arai K., Shimizu T. Avian erythroblastosis virus isolated from chick erythroblastosis induced by lymphatic leukemia virus subgroup A. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 May;70(5):891–897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang M. S., Elbein A. D. Alterations in the structure of the oligosaccharide of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein by swainsonine. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.60-69.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Hu S. S., Vogt P. K. Avian erythroblastosis virus: transformation-specific sequences form a contiguous segment of 3.25 kb located in the middle of the 6-kb genome. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):366–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Neil J. C., Vogt P. K. Cell-free translation of avian erythroblastosis virus RNA yields two specific and distinct proteins with molecular weights of 75,000 and 40,000. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90537-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin C. R., Chen W. S., Kruiger W., Stolarsky L. S., Weber W., Evans R. M., Verma I. M., Gill G. N., Rosenfeld M. G. Expression cloning of human EGF receptor complementary DNA: gene amplification and three related messenger RNA products in A431 cells. Science. 1984 May 25;224(4651):843–848. doi: 10.1126/science.6326261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N. Glucose removal from N-linked oligosaccharides is required for efficient maturation of certain secretory glycoproteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1720–1729. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Parent J. B., White S. L. Carbohydrate moieties of glycoproteins. A re-evaluation of their function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 12;650(4):209–232. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(82)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. J., Kissonerghis A. M., Lodish H. F. Biosynthesis of HLA-A and HLA-B antigens in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9678–9684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri S., Beug H., Graf T. Isolation and characterization of four new temperature-sensitive mutants of avian erythroblastosis virus (AEV). Virology. 1982 Dec;123(2):296–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90263-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Martin G. S. Cell-free translation of avian erythroblastosis virus RNA. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):280–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.280-284.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Bishop J. M. Proteins specified by avian erythroblastosis virus: coding region localization and identification of a previously undetected erb-B polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Sealy L., Bishop J. M., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the avian erythroblastosis virus erbB locus is a glycoprotein. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1257–1267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90307-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K., Saule S., Stéhelin D., Kitchener G., Hayman M. J. Revertants of rats cells transformed by avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):322–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero P. A., Datema R., Schwarz R. T. N-methyl-1-deoxynojirimycin, a novel inhibitor of glycoprotein processing, and its effect on fowl plague virus maturation. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):238–242. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Moscovici G., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Site-specific mutagenesis of avian erythroblastosis virus: v-erb-A is not required for transformation of fibroblasts. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):179–194. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90126-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealy L., Privalsky M. L., Moscovici G., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Site-specific mutagenesis of avian erythroblastosis virus: erb-B is required for oncogenicity. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):155–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck D. K., Lennarz W. J. Evidence for the participation of saccharide-lipids in the synthesis of the oligosaccharide chain of ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1007–1013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tartakoff A. M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1026–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tulsiani D. R., Harris T. M., Touster O. Swainsonine inhibits the biosynthesis of complex glycoproteins by inhibition of Golgi mannosidase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):7936–7939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Fanshier L., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian erythroblastosis virus genome and recovery of oncogenic virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):575–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.575-585.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Hihara H., Nishida T., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. A new avian erythroblastosis virus, AEV-H, carries erbB gene responsible for the induction of both erythroblastosis and sarcomas. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):225–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90153-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]