Abstract
The Jonah genes constitute a family of approximately 20 genes expressed at two periods during the development of Drosophila melanogaster. They are expressed only in the midgut, where they yield very abundant transcripts of approximately 900 bases. The function of their products is not known. We have used in situ hybridization to show that transcripts homologous to two members of the Jonah family have quite different distributions within the midgut. Transcripts closely homologous to Jon65Aiv are expressed throughout most of the anterior midgut and in the posterior section of the middle midgut. Transcripts closely homologous to Jon99C beta are expressed only in the anterior region of the posterior midgut.
Full text
PDF

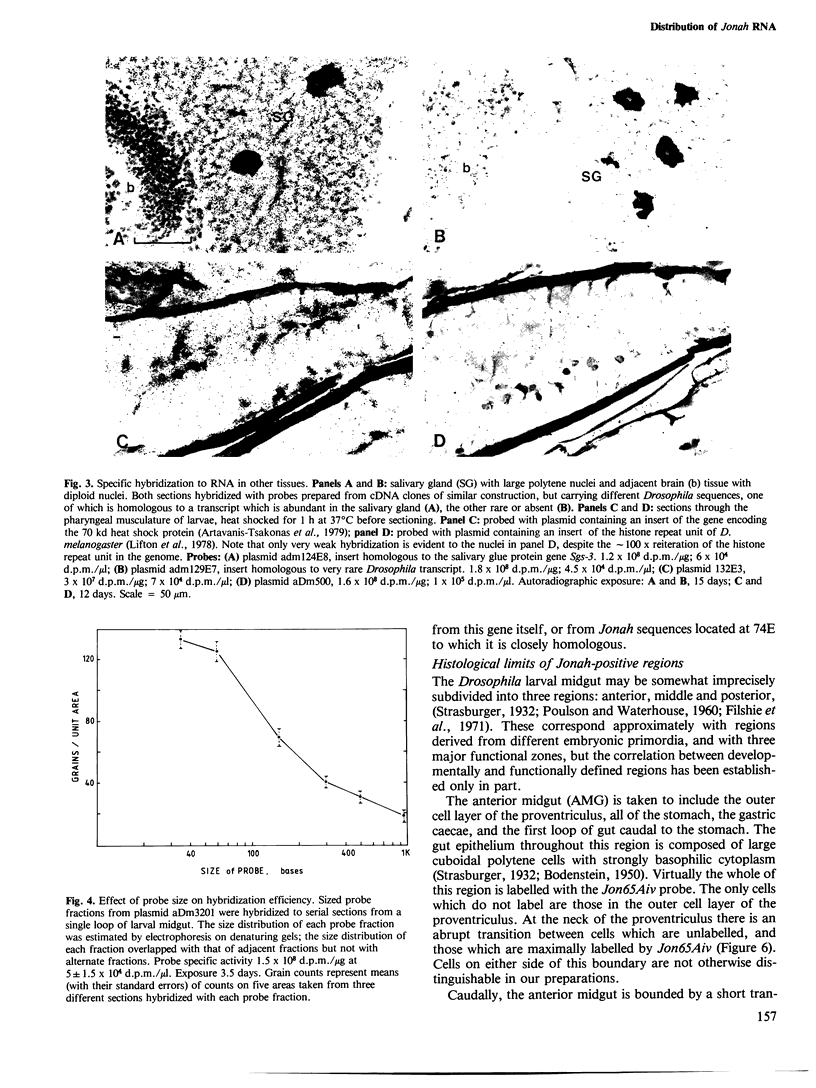
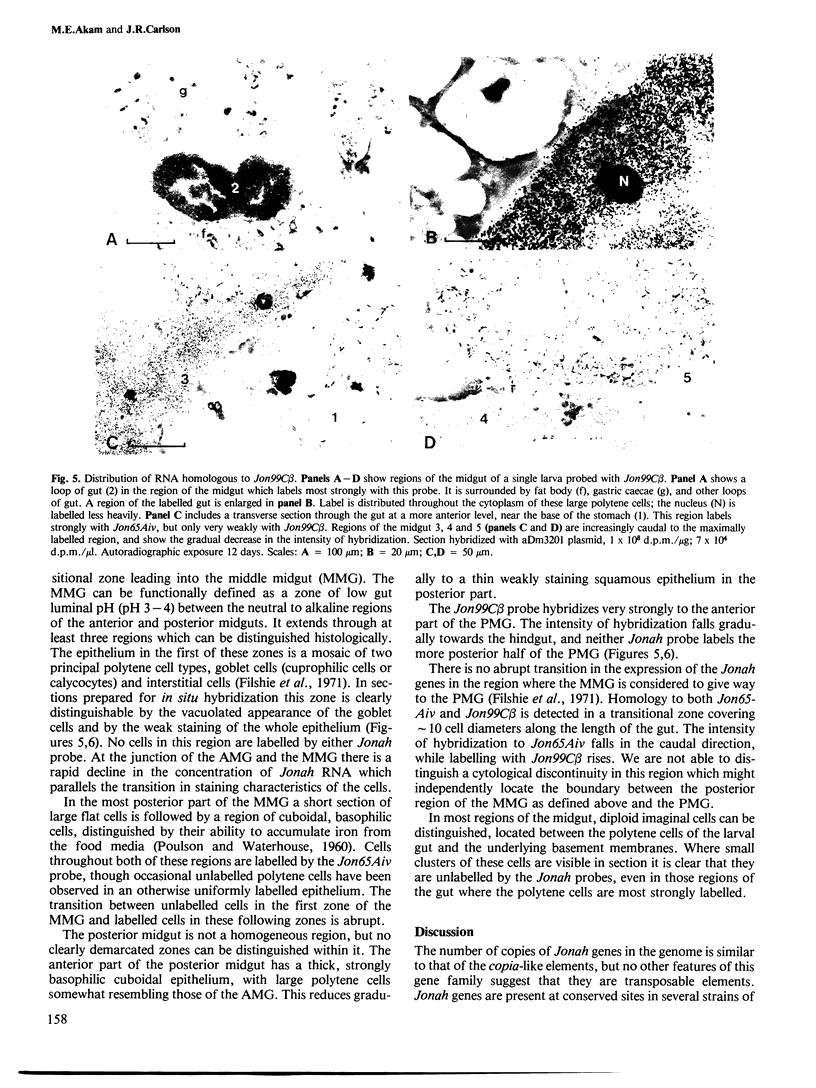
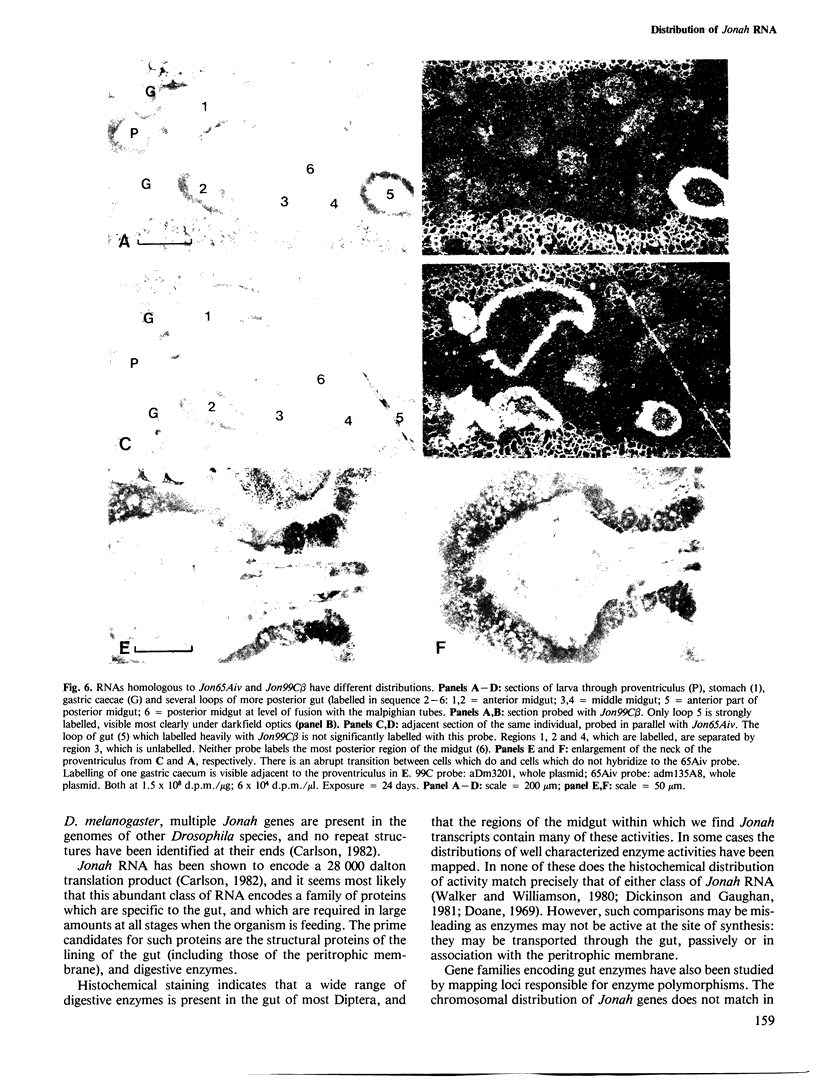


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham I., Doane W. W. Genetic regulation of tissue-specific expression of amylase structural genes in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akam M. E. The location of Ultrabithorax transcripts in Drosophila tissue sections. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2075–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Schedl P., Mirault M. E., Moran L., Lis J. Genes for the 70,000 dalton heat shock protein in two cloned D. melanogaster DNA segments. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90290-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtright J. B. Drosophila gene-enzyme systems. Adv Genet. 1976;18:249–314. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60440-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson W. J., Gaughan S. Aldehyde oxidases of Drosophila: contributions of several enzymes to observed activity patterns. Biochem Genet. 1981 Jun;19(5-6):567–583. doi: 10.1007/BF00484627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Levine M., Garber R. L., Gehring W. J. An improved in situ hybridization method for the detection of cellular RNAs in Drosophila tissue sections and its application for localizing transcripts of the homeotic Antennapedia gene complex. EMBO J. 1983;2(4):617–623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01472.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R., Black M. M., Williamson D. M., Scutt R. W. Herpes gestationis and bullous pemphigoid: a disease spectrum. Br J Dermatol. 1980 Nov;103(5):535–541. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1980.tb01668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie-Ahlberg C. C. Genetic, ontogenetic, and tissue-specific variation of dipeptidases in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem Genet. 1982 Jun;20(5-6):407–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00484692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifton R. P., Goldberg M. L., Karp R. W., Hogness D. S. The organization of the histone genes in Drosophila melanogaster: functional and evolutionary implications. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1047–1051. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerowitz E. M., Hogness D. S. Molecular organization of a Drosophila puff site that responds to ecdysone. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90386-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards A. G., Richards P. A. The peritrophic membranes of insects. Annu Rev Entomol. 1977;22:219–240. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.22.010177.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensink P. C., Finnegan D. J., Donelson J. E., Hogness D. S. A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):315–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]