Abstract
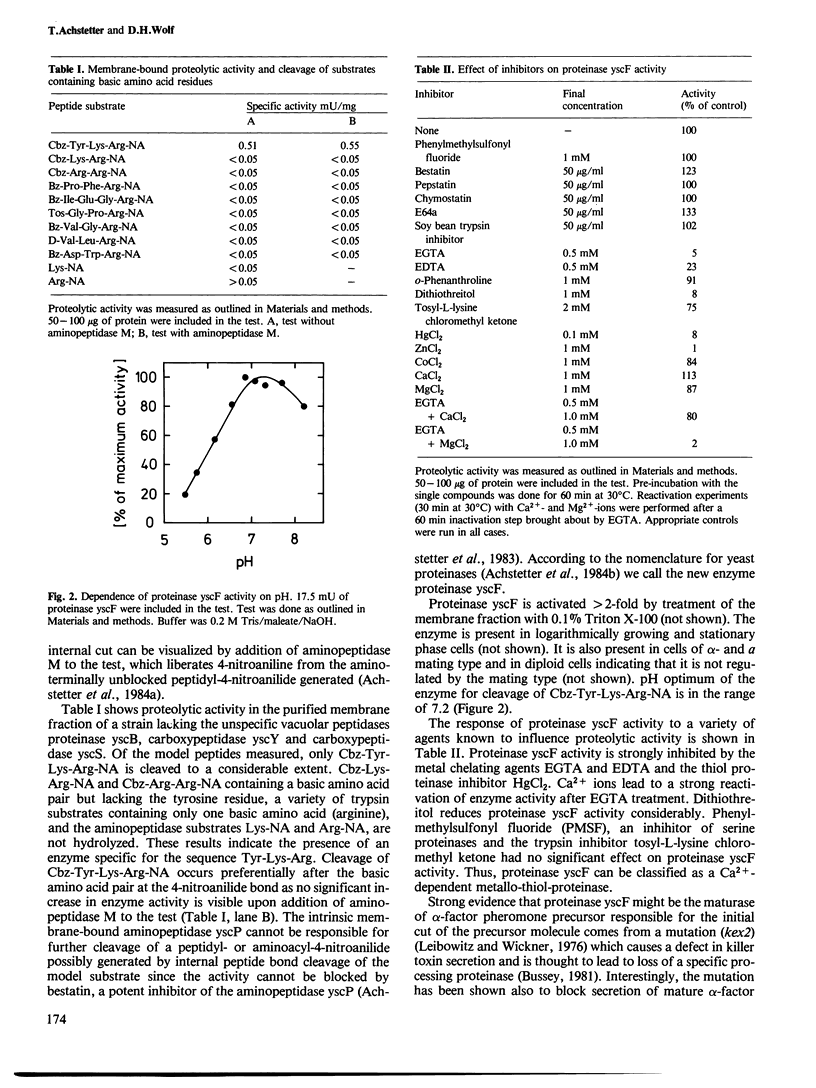
A search for maturating peptidases of the precursor protein of the mating hormone (pheromone) alpha-factor of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was performed using short model peptides representing those sequences of the precursor protein, where cleavage is thought to occur in vivo. This search was done in a mutant lacking several of the unspecific vacuolar peptidases. The chromogenic peptide Cbz-Tyr-Lys-Arg-4-nitroanilide led to the detection of a membrane-bound enzyme called proteinase yscF. Cleavage of the synthetic peptide derivative occurs after the basic amino acid pair, a proposed signal for hormone processing. Optimum pH for the reaction is 7.2. The enzyme does not cleave after single basic amino acid residues indicating that it is distinct from trypsin-like proteinases. Proteolytic activity is enhanced by Triton X-100. The enzyme is strongly inhibited by EGTA, EDTA and mercurials but insensitive to phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. The enzyme activity is strongly dependent on Ca2+ ions. In a mutant (kex2), which accumulates an over-glycosylated alpha-factor precursor, no proteinase yscF activity can be found. Membrane-bound peptidase activity possibly involved in removal of the arginyl and lysyl residues remaining at the carboxy terminus of the alpha-factor pheromone peptide after the initial cut of the precursor molecule could be identified by using the model peptides Cbz-Tyr-Lys-Arg and Cbz-Tyr-Lys.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achstetter T., Ehmann C., Osaki A., Wolf D. H. Proteolysis in eukaryotic cells. Proteinase yscE, a new yeast peptidase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13344–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achstetter T., Ehmann C., Wolf D. H. New proteolytic enzymes in yeast. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Apr 1;207(2):445–454. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90052-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achstetter T., Ehmann C., Wolf D. H. Proteolysis in eucaryotic cells: aminopeptidases and dipeptidyl aminopeptidases of yeast revisited. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Oct 1;226(1):292–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90296-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Achstetter T., Emter O., Ehmann C., Wolf D. H. Proteolysis in eukaryotic cells. Identification of multiple proteolytic enzymes in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13334–13343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. R., Hare P. E. O-phthalaldehyde: fluorogenic detection of primary amines in the picomole range. Comparison with fluorescamine and ninhydrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):619–622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. Physiology of killer factor in yeast. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:93–122. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Physiological characterization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):21–29. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emter O., Mechler B., Achstetter T., Müller H., Wolf D. H. Yeast pheromone alpha-factor is synthesized as a high molecular weight precursor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Nov 15;116(3):822–829. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Blair L., Brake A., Sprague G., Thorner J. Yeast alpha factor is processed from a larger precursor polypeptide: the essential role of a membrane-bound dipeptidyl aminopeptidase. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):839–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90070-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Brake A., Blair L., Kunisawa R., Thorner J. Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-alpha-factor. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1075–1089. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90442-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Schekman R., Thorner J. Glycosylation and processing of prepro-alpha-factor through the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):309–318. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato N., Sahm H., Schütte H., Wagner F. Purification and properties of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase and 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase from a methanol-utilizing yeast, Candida boidinii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jan 12;566(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz M. J., Wickner R. B. A chromosomal gene required for killer plasmid expression, mating, and spore maturation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):2061–2065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R., Jackson P., Meade J. Two temperature-sensitive mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with altered expression of mating-type functions. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;96(6):1592–1600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.6.1592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno K., Matsuo H. A novel protease from yeast with specificity towards paired basic residues. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):558–560. doi: 10.1038/309558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., Quinn P. S., Chan S. J., Marsh J., Tager H. S. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. H., Ehmann C. Carboxypeptidase S- and carboxypeptidase Y-deficient mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Aug;147(2):418–426. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.2.418-426.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





