Abstract
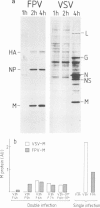
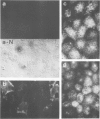
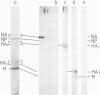
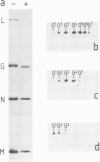
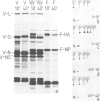
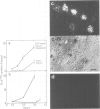
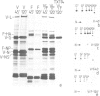
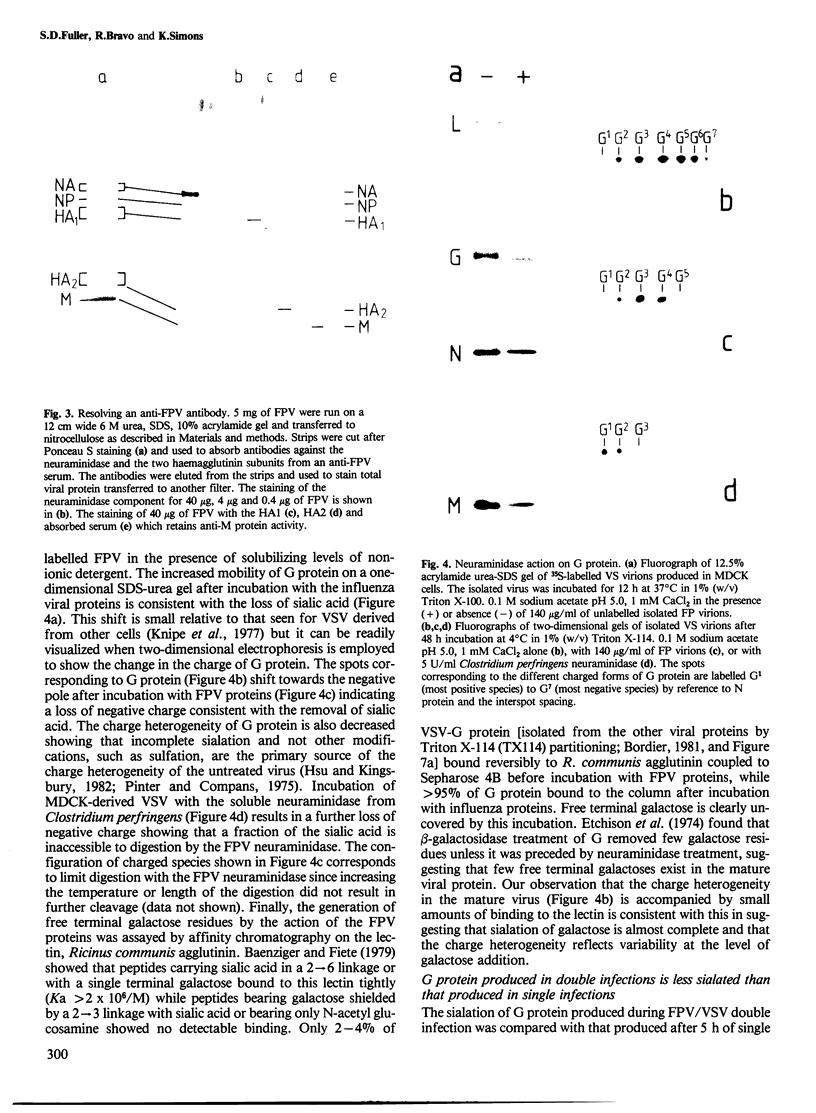
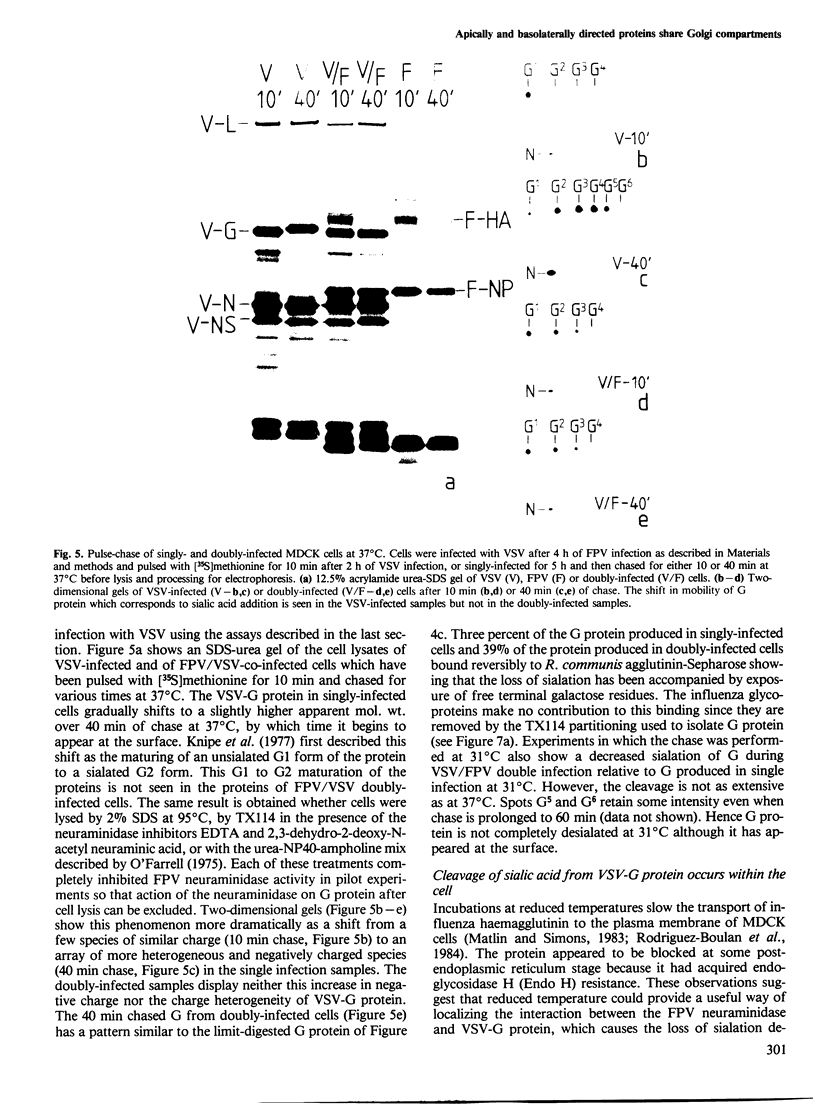
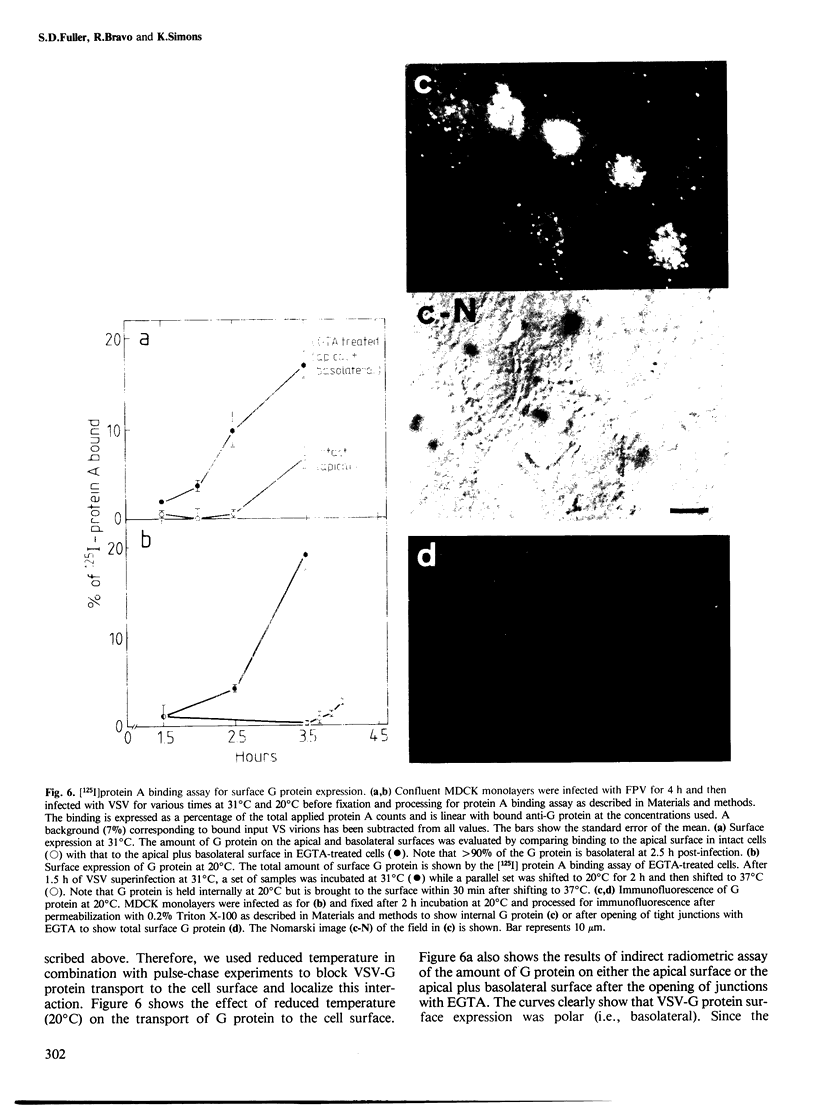
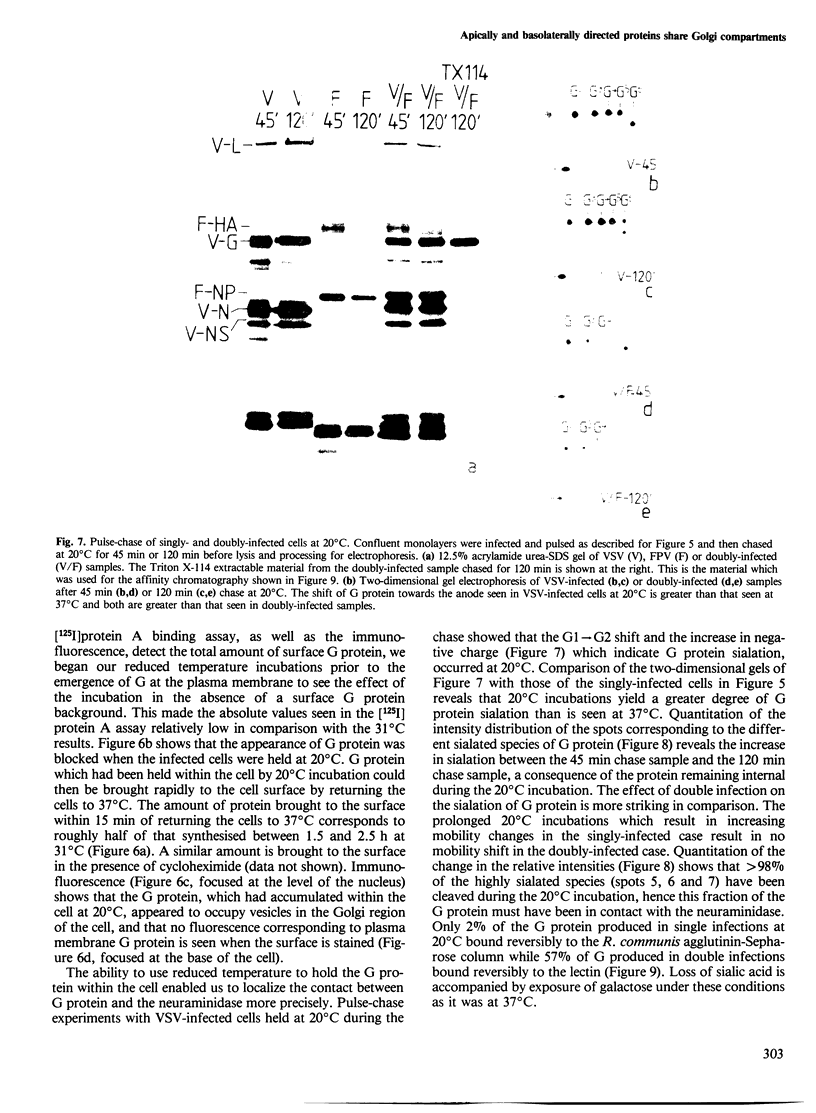
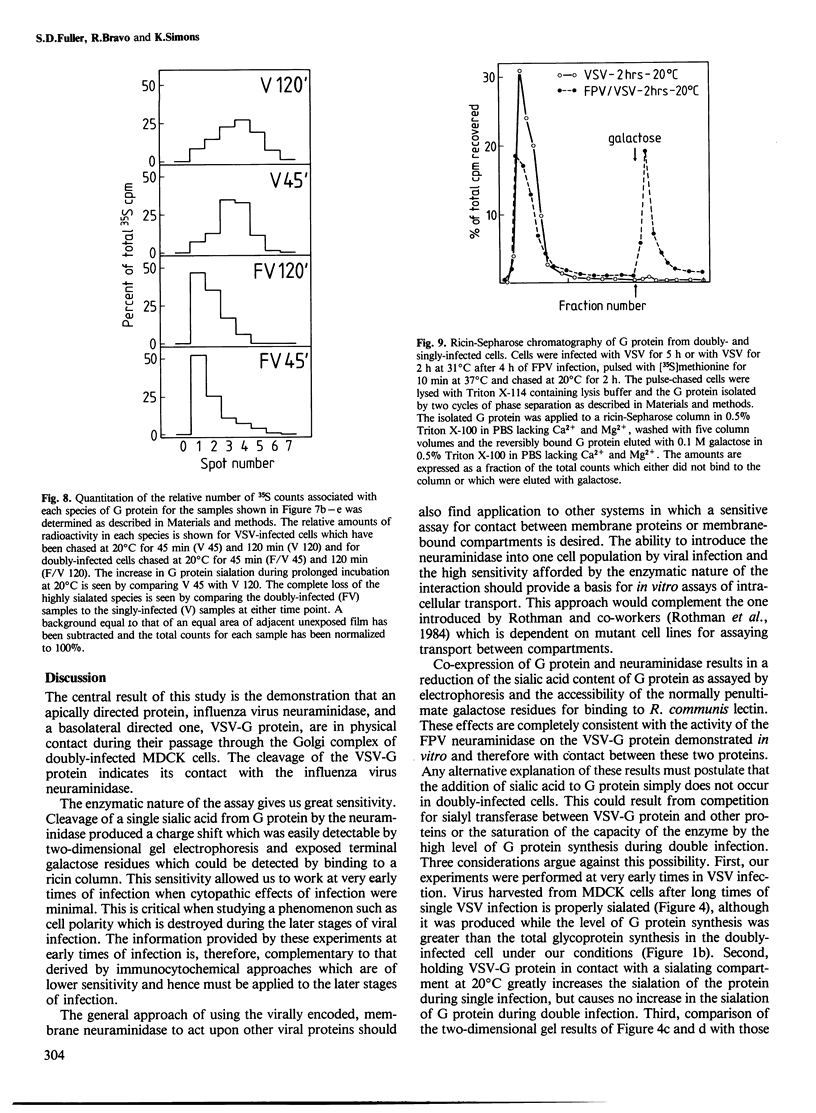
The expression of viral envelope proteins on the plasma membrane domains of the epithelial cell line, MDCK, is polar. Influenza virus infection of these cells leads to expression of the viral haemagglutinin and neuraminidase glycoproteins on the apical domain of the plasma membrane while vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) infection yields basolateral expression of the sialic acid-bearing G protein. We have exploited the ability of the influenza neuraminidase to desialate the G protein of VSV to test for contact between these proteins during their intracellular transport to separate plasma membrane domains. We were able to select for VSV-G protein expression in doubly-infected cells because VSV protein production was accelerated in cells pre-infected with influenza virus. During double infection the envelope proteins of both viruses displayed the same polar localization as during single infection but the VSG-G protein was undersialated due to the action of the influenza neuraminidase. Incubation of singly-infected cells at 20 degrees C blocked the transport of VSV-G protein to the cell surface and resulted in increased sialation of the protein over that seen at 37 degrees C. This suggests that G protein is held in contact with the sialyl transferase at this temperature. 20 degrees C incubations of doubly-infected cells also produced the undersialated G protein characteristic of interaction with the neuraminidase. We conclude that most of the newly synthesised basolaterally-directed G protein is in physical contact with the majority of the neuraminidase through the terminal steps of Golgi processing.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso F. V., Compans R. W. Differential effect of monensin on enveloped viruses that form at distinct plasma membrane domains. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jun;89(3):700–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.89.3.700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of Ricinus communis agglutinin and toxin specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9795–9799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balcarova-Ständer J., Pfeiffer S. E., Fuller S. D., Simons K. Development of cell surface polarity in the epithelial Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cell line. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2687–2694. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02194.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R. Epidermal growth factor inhibits the synthesis of the nuclear protein cyclin in A431 human carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4848–4850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretz R., Bretz H., Palade G. E. Distribution of terminal glycosyltransferases in hepatic Golgi fractions. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):87–101. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. J., Farquhar M. G. The mannose-6-phosphate receptor for lysosomal enzymes is concentrated in cis Golgi cisternae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):295–307. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke B., Griffiths G., Reggio H., Louvard D., Warren G. A monoclonal antibody against a 135-K Golgi membrane protein. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1621–1628. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Rothman J. E. Compartmentation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing in the Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;97(1):270–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.1.270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eagle H. Buffer combinations for mammalian cell culture. Science. 1971 Oct 29;174(4008):500–503. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4008.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison J. R., Holland J. J. Carbohydrate composition of the membrane glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus grown in four mammalian cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4011–4014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison J. R., Robertson J. S., Summers D. F. Partial structural analysis of the oligosaccharide moieties of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein by sequential chemical and enzymatic degradation. Virology. 1977 May 15;78(2):375–392. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller S., von Bonsdorff C. H., Simons K. Vesicular stomatitis virus infects and matures only through the basolateral surface of the polarized epithelial cell line, MDCK. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):65–77. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90527-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. E., Kornfeld S. Evidence for extensive subcellular organization of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing and lysosomal enzyme phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3159–3165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Brands R., Burke B., Louvard D., Warren G. Viral membrane proteins acquire galactose in trans Golgi cisternae during intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):781–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Quinn P., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. I. Monensin inhibits the transport of viral membrane proteins from medial to trans Golgi cisternae in baby hamster kidney cells infected with Semliki Forest virus. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):835–850. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. H., Kingsbury D. W. Contribution of oligosaccharide sulfation to the charge heterogeneity of a viral glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9035–9038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Localization of two cellular forms of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1121–1127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1121-1127.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-Vancell R., Beaty G., Stefani E., Rodríguez-Boulan E. E., Cereijido M. Changes in paracellular and cellular ionic permeabilities of monolayers of MDCK cells infected with influenza or vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Membr Biol. 1984;81(3):171–180. doi: 10.1007/BF01868711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meindl P., Bodo G., Palese P., Schulman J., Tuppy H. Inhibition of neuraminidase activity by derivatives of 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):457–463. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90080-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misfeldt D. S., Hamamoto S. T., Pitelka D. R. Transepithelial transport in cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1212–1216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Simons K. Transepithelial transport of a viral membrane glycoprotein implanted into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. II. Immunological quantitation. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):638–643. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinter A., Compans R. W. Sulfated components of enveloped viruses. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):859–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.859-866.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P., Griffiths G., Warren G. Dissection of the Golgi complex. II. Density separation of specific Golgi functions in virally infected cells treated with monensin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):851–856. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C. L., Penhoet E. E., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate structure of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5600–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. C., Simmons N. L. Demonstration of protein asymmetries in the plasma membrane of cultured renal (MDCK) epithelial cells by lactoperoxidase-mediated iodination. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Chuman L. M., Shaffer L., Saier M. H., Jr Retention of differentiated properties in an established dog kidney epithelial cell line (MDCK). J Cell Biol. 1979 Jun;81(3):635–648. doi: 10.1083/jcb.81.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Plesken H., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Viral glycoproteins destined for apical or basolateral plasma membrane domains traverse the same Golgi apparatus during their intracellular transport in doubly infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1304–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Rodriguez-Boulan E. J., Sabatini D. D. Biogenesis of epithelial cell plasma membranes. Ciba Found Symp. 1982;(92):184–208. doi: 10.1002/9780470720745.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Pendergast M. Polarized distribution of viral envelope proteins in the plasma membrane of infected epithelial cells. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Asymmetric budding of viruses in epithelial monlayers: a model system for study of epithelial polarity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5071–5075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Boulan E., Paskiet K. T., Salas P. J., Bard E. Intracellular transport of influenza virus hemagglutinin to the apical surface of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;98(1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.1.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Compans R. W. Delayed appearance of pseudotypes between vesicular stomatitis virus influenza virus during mixed infection of MDCK cells. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):848–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.848-860.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Compans R. W., Giusti L., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Influenza virus hemagglutinin expression is polarized in cells infected with recombinant SV40 viruses carrying cloned hemagglutinin DNA. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E., Miller R. L., Urbani L. J. Intercompartmental transport in the Golgi complex is a dissociative process: facile transfer of membrane protein between two Golgi populations. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):260–271. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons N. L. Ion transport in 'tight' epithelial monolayers of MDCK cells. J Membr Biol. 1981 Apr 15;59(2):105–114. doi: 10.1007/BF01875708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suissa M. Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grains eluted from autoradiograms. Anal Biochem. 1983 Sep;133(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suttajit M., Winzler R. J. Effect of modification of N-acetylneuraminic acid on the binding of glycoproteins to influenza virus and on susceptibility to cleavage by neuraminidase. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3398–3404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. Viruses budding from either the apical or the basolateral plasma membrane domain of MDCK cells have unique phospholipid compositions. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):847–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]