Figure 4.
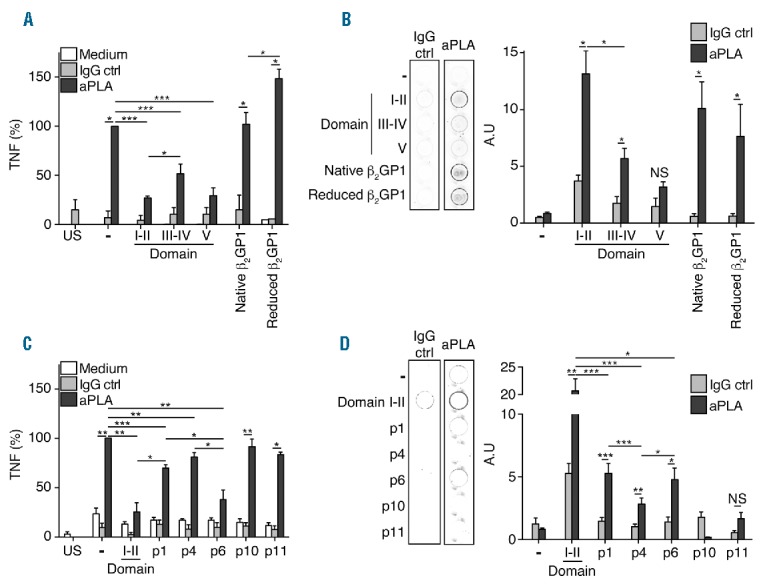
Motif containing domains and peptides inhibits aPLA activity. (A) Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) production induced by aPLA by domains I–II, III–IV, V, β2GP1 of reduced β2GP1. (B) Representative picture of IgG ctrl (control) or aPLA binding to domains I–II, III–IV, V and β2GP1-coated well. Quantification of aPLA binding to domains I–II, III–IV, V or β2GP1-coated well. aPLA to well coated with domains I–II, III–IV, V, β2GP1 of reduced β2GP1. (C) Inhibition by domain I–II, p1, p4, p6, p10 and p11 of TNF production induced by aPLA. (D) Representative picture of IgG ctrl or aPLA binding to domains I–II-, p1-, p4-, p6-, p10- and p11-coated well. Quantification of aPLA binding to domains I–II, p1, p4, p6, p10 and p11-coated well. aPLA to well coated with domains I–II, III–IV, V, β2GP1 of reduced β2GP1. Data are mean ± SEM of 9 different donors. Statistical significance was determined by Mann-Whitney U analysis. aPLA: antiphospholipid antibodies; IgG: immunoglobulin G; US: unstimulated; NS: non significant.
