Abstract
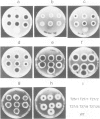
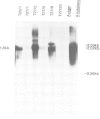
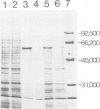
Aspergillus niger grows poorly on acetamide as a nitrogen or carbon source and lacks sequences detectably homologous to the amdS gene encoding the acetamidase of Aspergillus nidulans. We have taken advantage of these observations to develop a transformation system for A. niger using the amdS gene as a dominant heterologous marker for selecting transformants on the basis of acetamide utilization. Transformants varied in their ability to grow on amide media and the number of integrated copies of the amdS plasmid ranged from 1 or 2 to greater than 100. Southern analysis of transformants revealed that the multiple copies were integrated into the chromosome in tandem arrays. This result indicates that transformation of A. niger is more similar to mammalian cells than to yeast. Analysis of enzyme activity levels and RNA levels showed that most of the copies of amdS were expressed. Mitotic stabilities of transformants were found to be high. A transformant containing greater than 100 copies of the amdS gene was impaired in omega-amino acid utilization, a result that has also been found in A. nidulans. Since, in A. nidulans, omega-amino acids induce acetamidase via a characterizied regulatory gene (amdR/intA) this observation implies that titration of an analogous A. niger regulatory gene product by multiple amdS copies has occurred. Additional evidence suggested that the amdS gene is regulated in A. niger. It has also been shown that an unselected plasmid can be co-transformed with the amdS plasmid into A. niger.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arst H. N., Jr Integrator gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Nature. 1976 Jul 15;262(5565):231–234. doi: 10.1038/262231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballance D. J., Buxton F. P., Turner G. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by the orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase gene of Neurospora crassa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Apr 15;112(1):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91828-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beggs J. D. Transformation of yeast by a replicating hybrid plasmid. Nature. 1978 Sep 14;275(5676):104–109. doi: 10.1038/275104a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case M. E., Schweizer M., Kushner S. R., Giles N. H. Efficient transformation of Neurospora crassa by utilizing hybrid plasmid DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5259–5263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cove D. J. The induction and repression of nitrate reductase in the fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jan 11;113(1):51–56. doi: 10.1016/s0926-6593(66)80120-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Corrick C. M., King J. A. Isolation of genomic clones containing the amdS gene of Aspergillus nidulans and their use in the analysis of structural and regulatory mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1430–1439. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. Fine-structure mapping of the acetamidase structural gene and its controlling region in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics. 1979 Mar;91(3):381–392. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.3.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. Multiple independent control mechanisms affecting the acetamidase of Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 25;161(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00266615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J. Mutants with altered glucose repression of amidase enzymes in Aspergillus nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1972 Sep;111(3):717–722. doi: 10.1128/jb.111.3.717-722.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes M. J., Pateman J. A. The genetic analysis of regulation of amidase synthesis in Aspergillus nidulans. I. Mutants able to utilize acrylamide. Mol Gen Genet. 1970;108(2):97–106. doi: 10.1007/BF02430516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The new yeast genetics. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):391–397. doi: 10.1038/305391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilburn J., Scazzocchio C., Taylor G. G., Zabicky-Zissman J. H., Lockington R. A., Davies R. W. Transformation by integration in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):205–221. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90191-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton M. M., Hamer J. E., Timberlake W. E. Transformation of Aspergillus nidulans by using a trpC plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1470–1474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]