Abstract
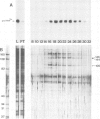
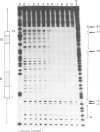
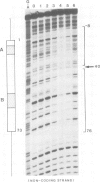
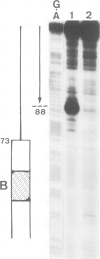
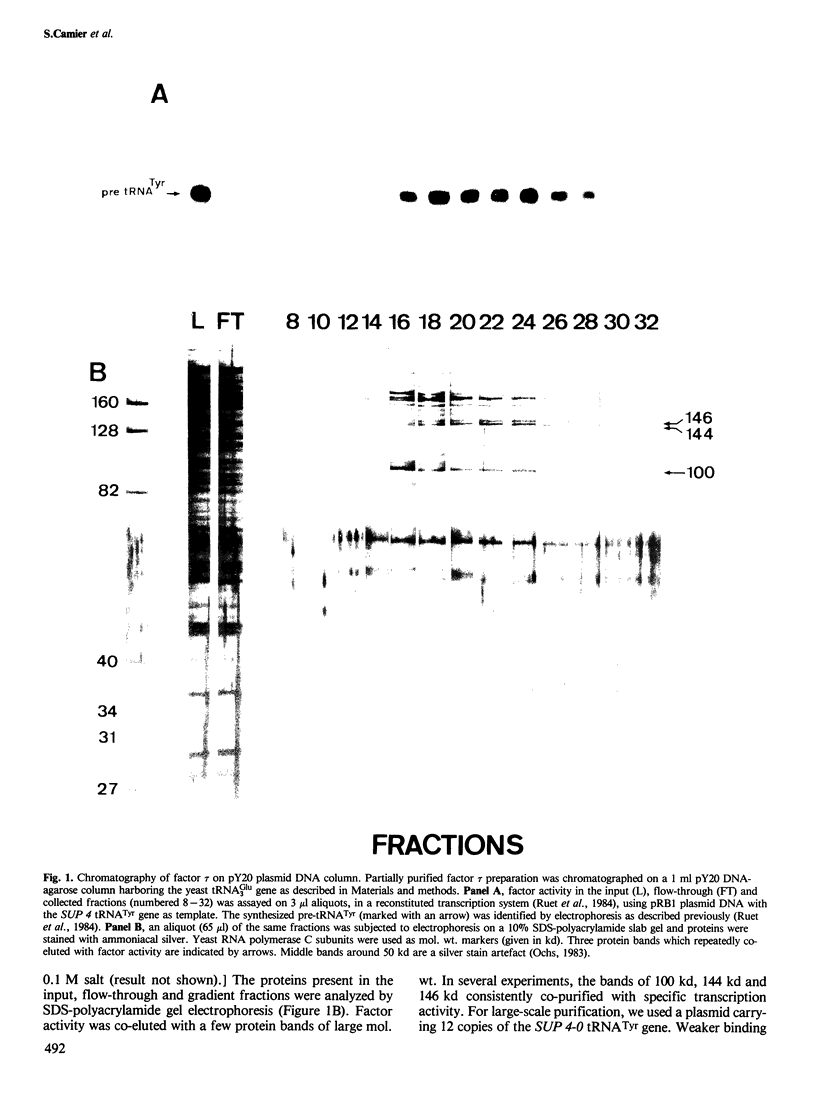
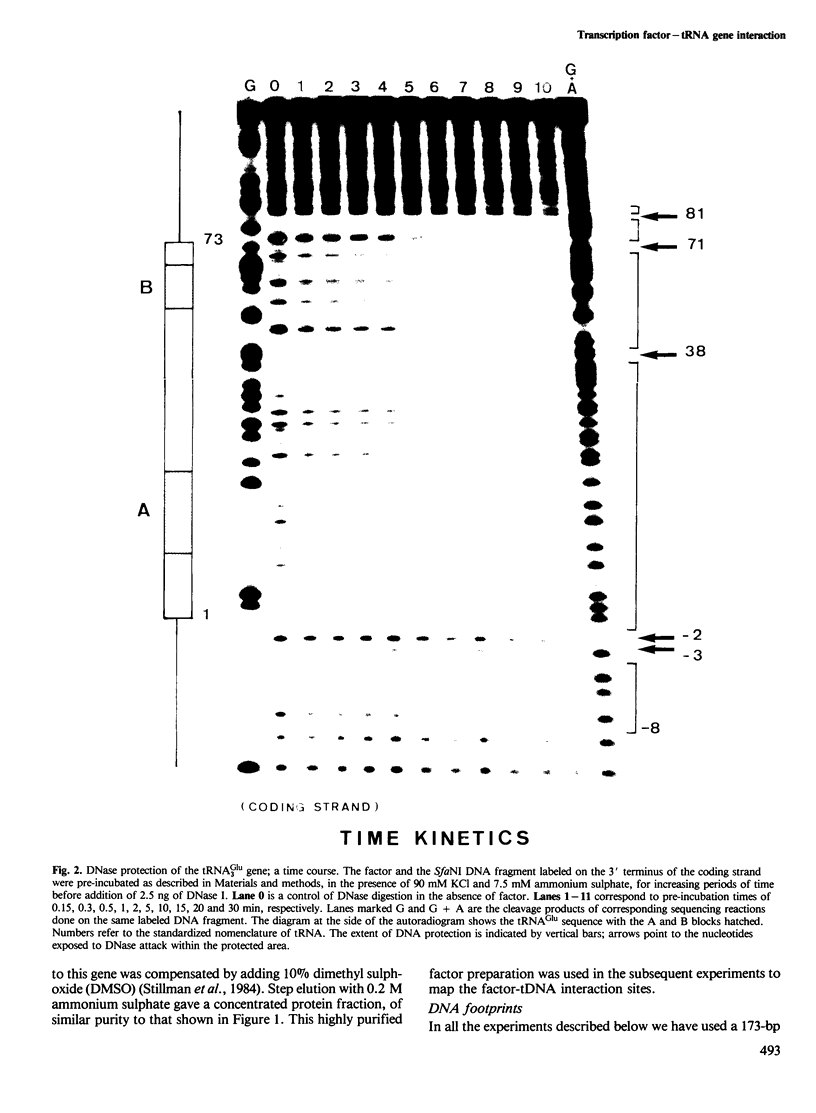
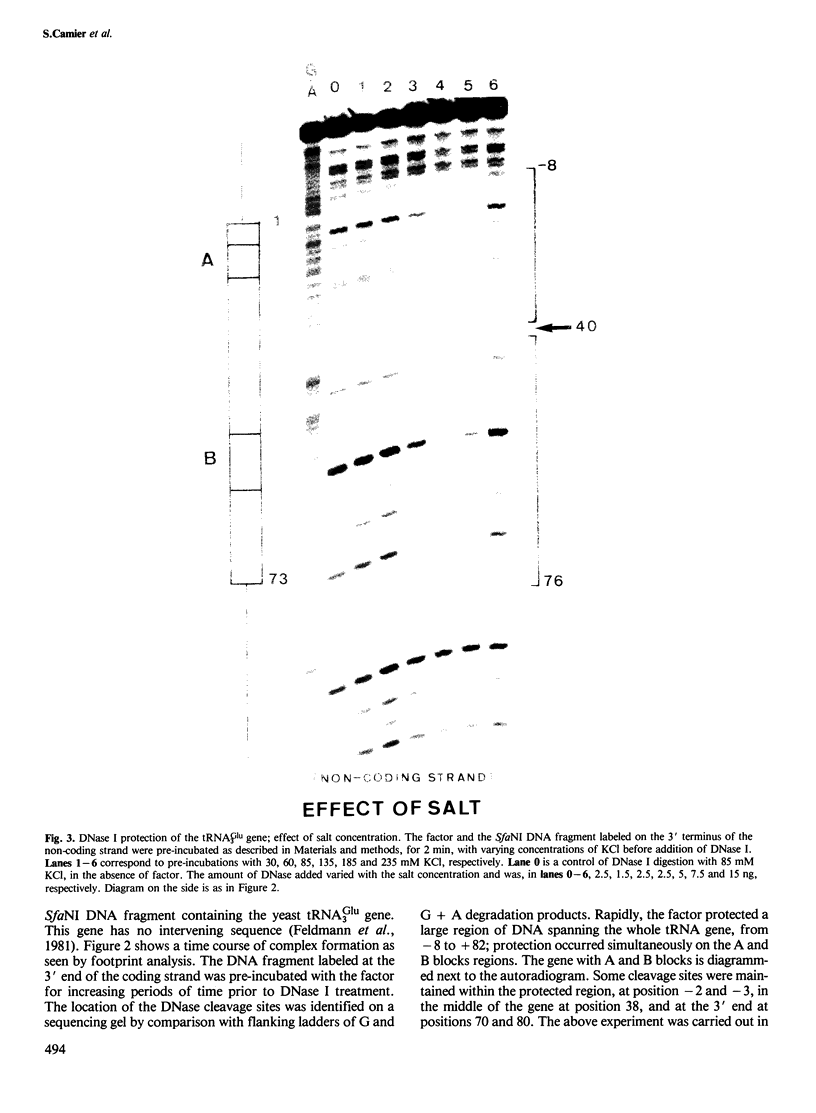
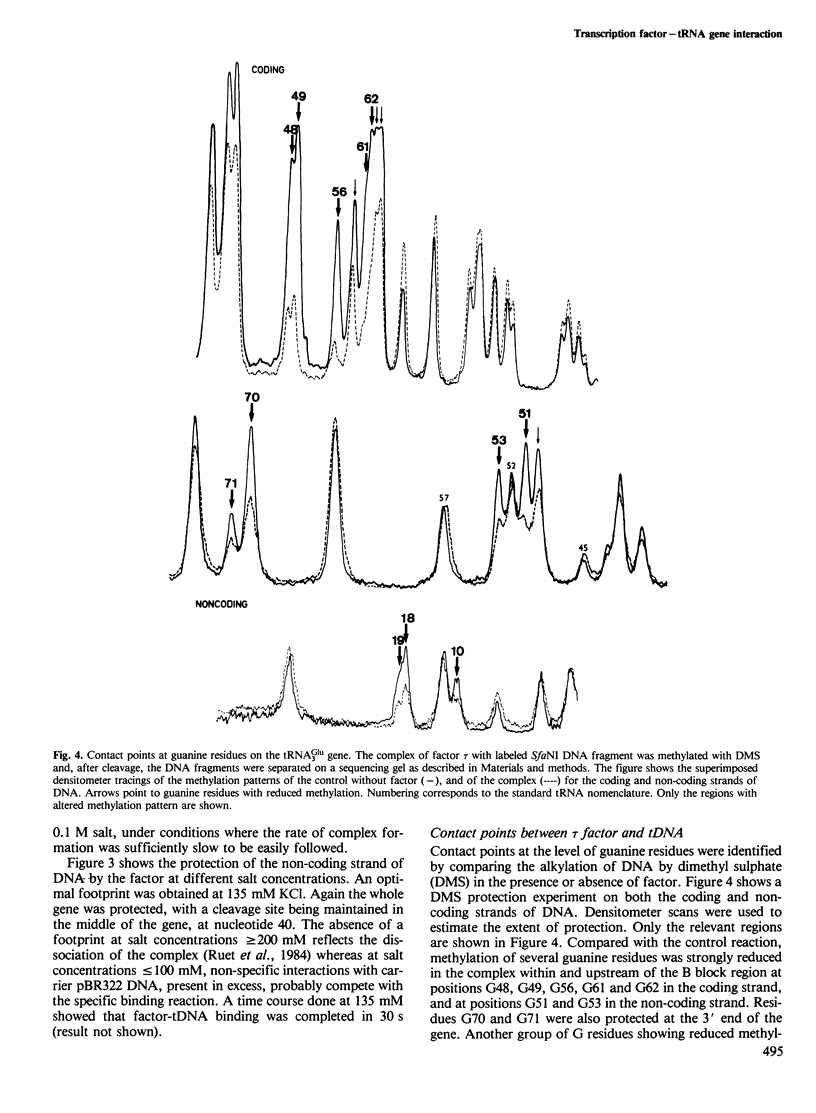
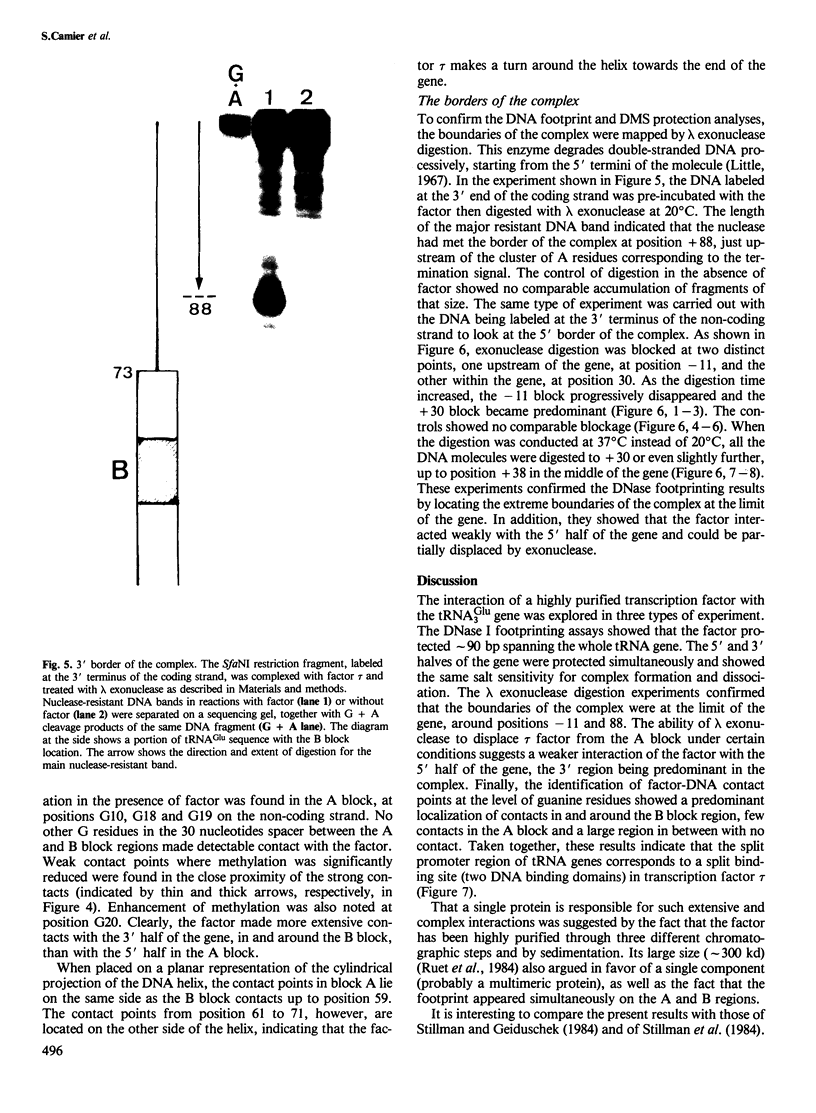
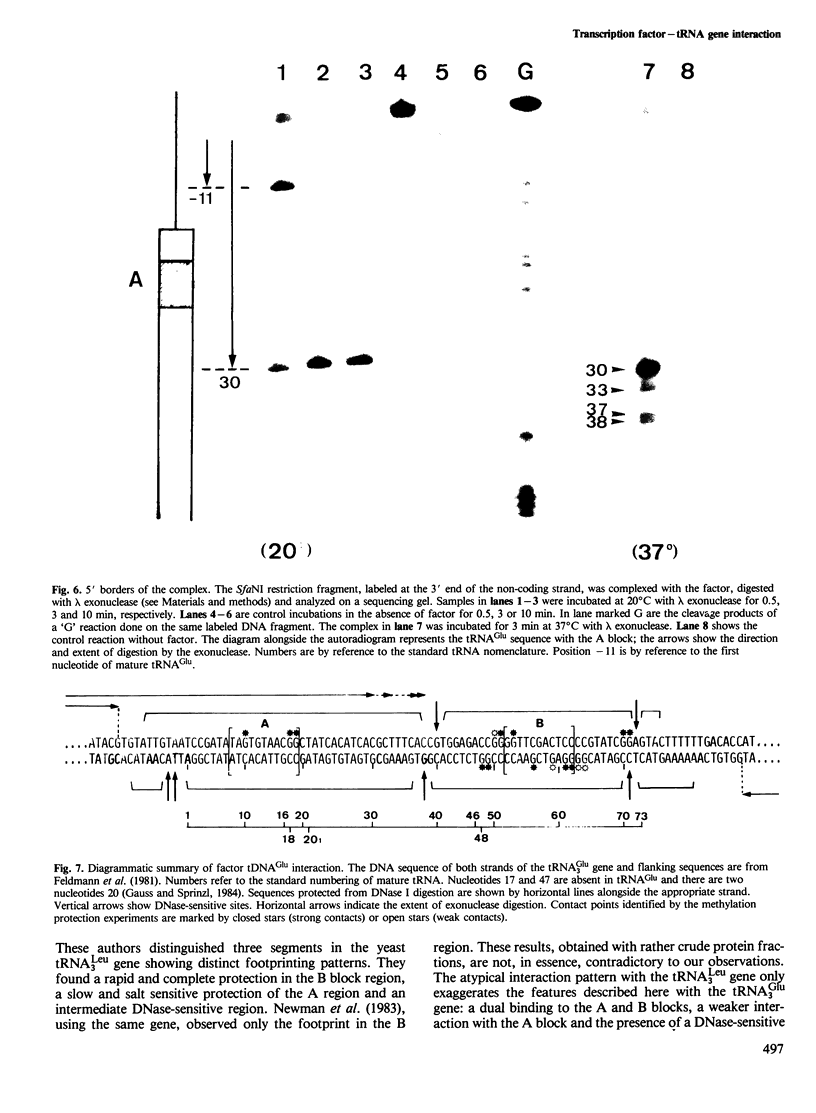
Yeast transcription factor tau forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. Using this property, the factor could be highly purified on a specific tDNA column. The purified factor was found by DNA footprinting to protect the whole yeast tRNA3Glu gene from position -8 to +81. A DNase-sensitive site was retained in the middle of the gene on both strands. The 3' border of the complex was mapped by exonuclease digestion at +88, just downstream of the termination signal. The 5' limit of the complex was found at position -11. However, upon prolonged incubation with exonuclease, the -11 blockage disappeared and the DNA molecules were digested to position +30 to 38 in the middle of the gene. Contact points at guanine residues were identified by dimethyl sulphate protection experiments. Reduced methylation of G residues in the presence of factor was found solely within the A block and in the B block region. All six invariant GC pairs (i.e., G10, G18, G19 and G53, C56 and C61) were found to have strong contacts with the factor. These results show that tau factor interacts with both the 5' and 3' half of the tRNA3Glu gene, with the B block region being the predominant binding site. The presence of this dual binding site suggests a model in which the factor would bind alternately at the A and B block regions to allow transcription of the internal promoter by RNA polymerase C.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Goh S. H., Hall B. D. The promoter sequence of a yeast tRNAtyr gene. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker R. E., Hall B. D. Structural features of yeast tRNA genes which affect transcription factor binding. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2793–2800. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. J., Schaack J., Sharp S., Söll D. Partial purification of Drosophila Kc cell RNA polymerase III transcription components. Evidence for shared 5 S RNA and tRNA gene factors. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15224–15231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrara G., Di Segni G., Otsuka A., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Deletion of the 3' half of the yeast tRNA-Leu3 gene does not abolish promotor function in vitro. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90420-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Cortese R. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1983;18:59–88. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60579-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Castagnoli L., Melton D. A., Cortese R. Promoter of a eukaryotic tRNAPro gene is composed of three noncontiguous regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1195–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Traboni C., Cortese R. Relationship between the two components of the split promoter of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Sharp S., Schaack J., Söll D. Stable transcription complex formation of eukaryotic tRNA genes is dependent on a limited separation of the two intragenic control regions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10395–10402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Olah J., Friedenreich H. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and a tRNA Glu 3 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2949–2959. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Hofstetter H. A detailed mutational analysis of the eucaryotic tRNAmet1 gene promoter. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90439-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerry P., LeBlanc D. J., Falkow S. General method for the isolation of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):1064–1066. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.1064-1066.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. D., Clarkson S. G., Tocchini-Valentini G. Transcription initiation of eucaryotic transfer RNA genes. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90083-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofstetter H., Kressman A., Birnstiel M. L. A split promoter for a eucaryotic tRNA gene. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):573–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Allison D. S., Worthington M., Hall B. D. An in vitro RNA polymerase III system from S. cerevisiae: effects of deletions and point mutations upon SUP4 gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8127–8143. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. II. Nature of the enzymatic reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):679–686. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. W., Lehman I. R., Kaiser A. D. An exonuclease induced by bacteriophage lambda. I. Preparation of the crystalline enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):672–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. Construction and functional analysis of a series of synthetic RNA polymerase III promoters. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10208–10211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. Directed semisynthetic point mutational analysis of an RNA polymerase III promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7695–7700. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. tRNA gene transcription in yeast: effects of specified base substitutions in the intragenic promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. Protein contaminants of sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):470–474. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90714-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Camier S., Smagowicz W., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Isolation of a class C transcription factor which forms a stable complex with tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):343–350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01809.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller H., Nüsslein C., Bonhoeffer F. J., Kurz C., Nietzschmann I. Affinity chromatography of DNA-binding enzymes on single-stranded DNA-agarose columns. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Apr 24;26(4):474–481. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprinzl M., Gauss D. H. Compilation of sequences of tRNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984;12 (Suppl):r59–131. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.suppl.r59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Differential binding of a S. cerevisiae RNA polymerase III transcription factor to two promoter segments of a tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):847–853. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman D. J., Sivertsen A. L., Zentner P. G., Geiduschek E. P. Correlations between transcription of a yeast tRNA gene and transcription factor-DNA interactions. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7955–7962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. A novel method for site-directed mutagenesis: its application to an eukaryotic tRNAPro gene promoter. EMBO J. 1982;1(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01184.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traboni C., Ciliberto G., Cortese R. Mutations in Box B of the promoter of a eucaryotic tRNAPro gene affect rate of transcription, processing, and stability of the transcripts. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]