Abstract
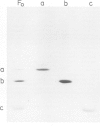
The membrane-integrated, proton-translocating F0 portion of the ATP synthase (F1F0) from Escherichia coli is built up from three kinds of subunits a, b and c with the proposed stoichiometry of 1:2:10 +/- 1. We have dissociated the F0 complex by treatment with trichloroacetate (3 M) at pH 8.0, in the presence of deoxycholate (1%) and N-tetradecyl-N, N-dimethyl-3-ammonio-1-propanesulfonate (Zwittergent 3-14, 5%). The subunits were separated by gel filtration with trichloroacetate (1 M) included in the elution buffer. The homogeneity of the fractions was checked by rechromatography and SDS-gel electrophoresis. After integration into phospholipid vesicles each subunit alone as well as all possible combinations were tested for H+ translocating activity and binding of F1. A functional H+ channel could only be reconstituted by the combination a1b2c10 which corresponds to that of native F0.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K. Purification of the DCCD-reactive protein of the energy-transducing adenosine triphosphatase complex from Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1977 Feb 1;73(2):271–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80997-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H., Mosher M. E., Negrin R. S., Peters L. K. H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli uncB402 mutation leads to loss of chi subunit of subunit of F0 sector. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):604–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillingame R. H. Purification of the carbodiimide-reactive protein component of the ATP energy-transducing system of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 10;251(21):6630–6637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Fillingame R. H. Stoichiometry of subunits in the H+-ATPase complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2009–2015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl P., Bienhaus G., Hoppe J., Schairer H. U. The dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding protein c of ATP synthase from Escherichia coli is not sufficient to express an efficient H+ conduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6643–6646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl P., Hoppe J., Gunsalus R. P., Michelsen O., von Meyenburg K., Schairer H. U. Membrane integration and function of the three F0 subunits of the ATP synthase of Escherichia coli K12. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):99–103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Kanazawa H. Structure and function of proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase (F0F1): biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):285–312. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.285-312.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the genes for the membrane proteins, and the delta subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3919–3926. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermolin J., Gallant J., Fillingame R. H. Topology, organization, and function of the psi subunit in the F0 sector of the H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14550–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Friedl P., Schairer H. U., Sebald W., von Meyenburg K., Jørgensen B. B. The topology of the proton translocating F0 component of the ATP synthase from E. coli K12: studies with proteases. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):105–110. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01389.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Schairer H. U., Friedl P., Sebald W. An Asp-Asn substitution in the proteolipid subunit of the ATP-synthase from Escherichia coli leads to a non-functional proton channel. FEBS Lett. 1982 Aug 16;145(1):21–29. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Sebald W. The proton conducting F0-part of bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 9;768(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa H., Mabuchi K., Kayano T., Noumi T., Sekiya T., Futai M. Nucleotide sequence of the genes for F0 components of the proton-translocating ATPase from Escherichia coli: prediction of the primary structure of F0 subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):613–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loo T. W., Bragg P. D. The DCCD-binding polypeptide alone is insufficient for proton translocation through F0 in membranes of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 16;103(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91659-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosher M. E., Peters L. K., Fillingame R. H. Use of lambda unc transducing bacteriophages in genetic and biochemical characterization of H+-ATPase mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1078–1092. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1078-1092.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Nelson H., Schatz G. Biosynthesis and assembly of the proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase complex from chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1361–1364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Hansen F. G., Hoppe J., Friedl P., von Meyenburg K. The nucleotide sequence of the atp genes coding for the F0 subunits a, b, c and the F1 subunit delta of the membrane bound ATP synthase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00271191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlin D. S., Cox D. N., Senior A. E. Integration of F1 and the membrane sector of the proton-ATPase of Escherichia coli. Role of subunit "b" (uncF protein). J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9793–9800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler H., Nelson N. Proteolipid of adenosinetriphosphatase from yeast mitochondria forms proton-selective channels in planar lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 9;21(23):5787–5794. doi: 10.1021/bi00266a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E., Altendorf K. ATP synthetase (F1F0) of Escherichia coli K-12. High-yield preparation of functional F0 by hydrophobic affinity chromatography. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Aug;126(1):149–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Wise J. G. The proton-ATPase of bacteria and mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(2):105–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01870434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigrist-Nelson K., Azzi A. The proteolipid subunit of the chloroplast adenosine triphosphatase complex. Reconstitution and demonstration of proton-conductive properties. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10638–10643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone N., Hamamoto T., Kagawa Y. pH dependence of H+ conduction through the membrane moiety of the H+-ATPase (F0 . F1) and effects of tyrosyl residue modification. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):2873–2877. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens K., Kiltz H. H., Schneider E., Schmid R., Altendorf K. ATP-synthetase complex (F1F0) from Escherichia coli. Purification and characterization of subunits A and B of the F0 part. FEBS Lett. 1982 Jun 1;142(1):151–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80240-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffens K., Schneider E., Herkenhoff B., Schmid R., Altendorf K. Chemical modification of the F0 part of the ATP synthase (F1F0) from Escherichia coli. Effects on proton conduction and F1 binding. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Feb 1;138(3):617–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07959.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Schmid R., Deckers G., Altendorf K. Amino acid replacement in dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-reactive proteins from mutant strains of Escherichia coli defective in the energy-transducing ATPase complex. FEBS Lett. 1980 May 5;113(2):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80606-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Gay N. J. E. coli F1-ATPase interacts with a membrane protein component of a proton channel. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):867–869. doi: 10.1038/298867a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]