Abstract
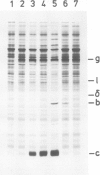
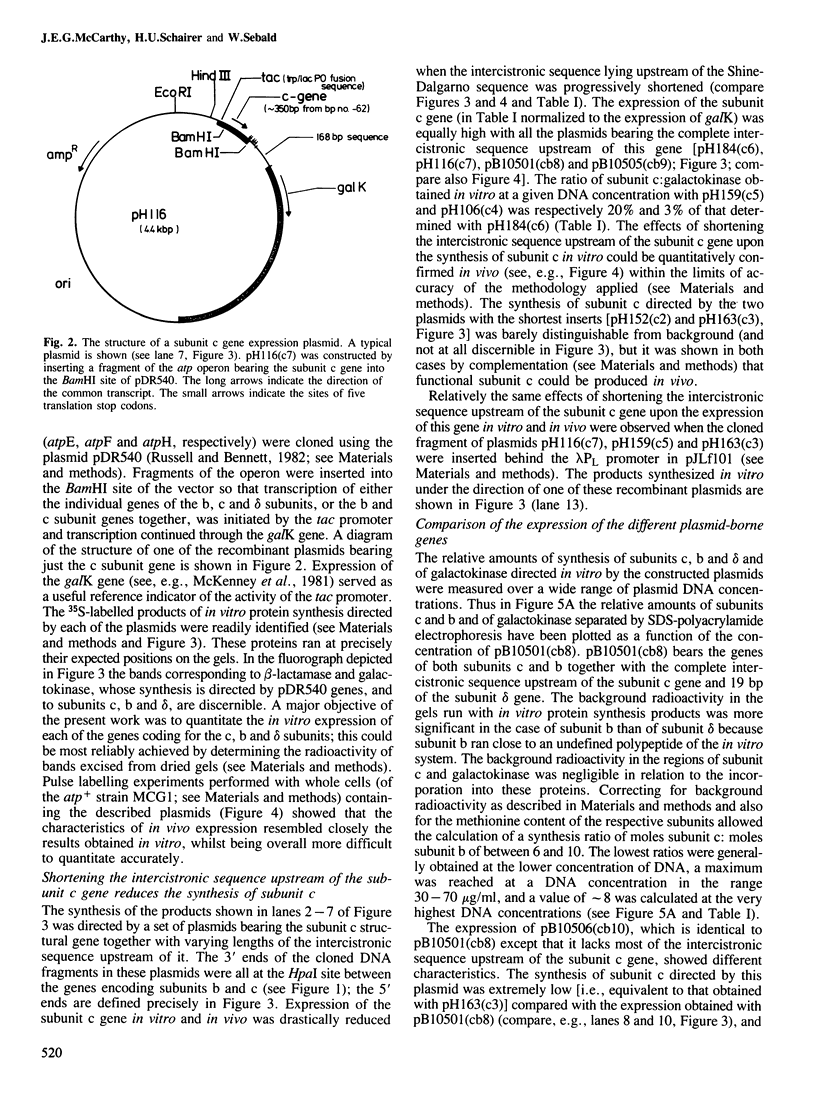
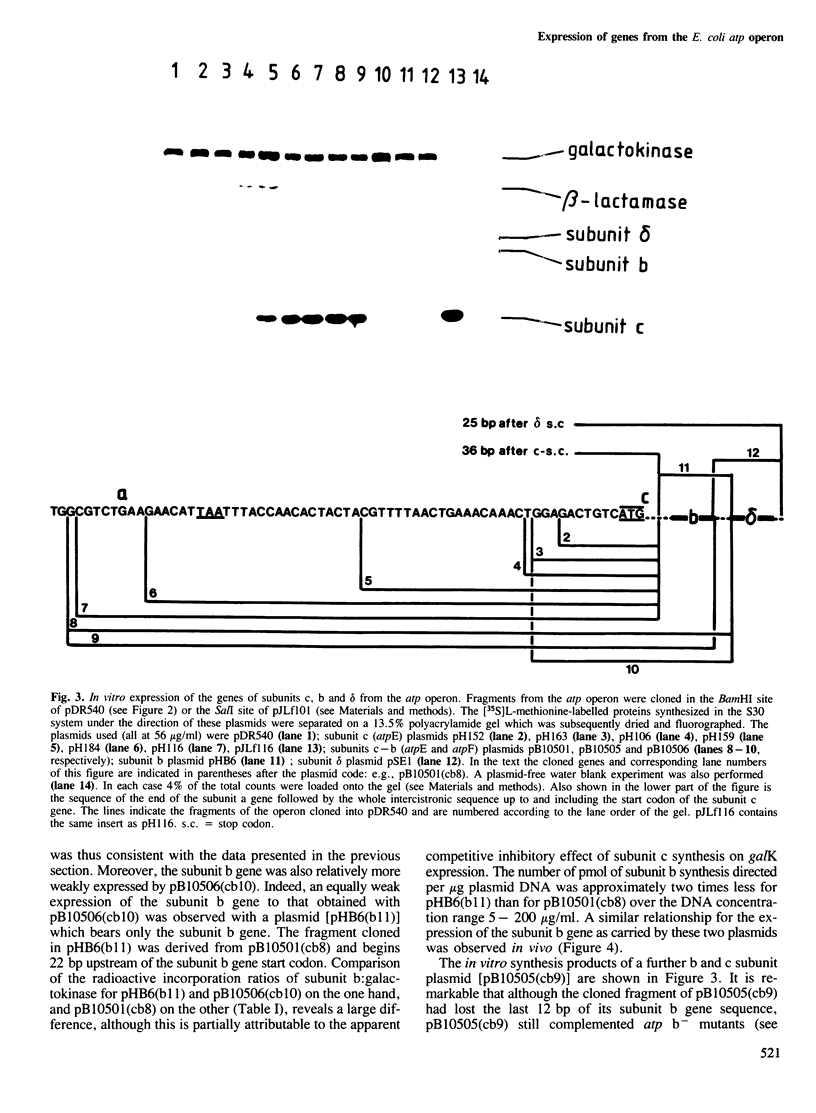
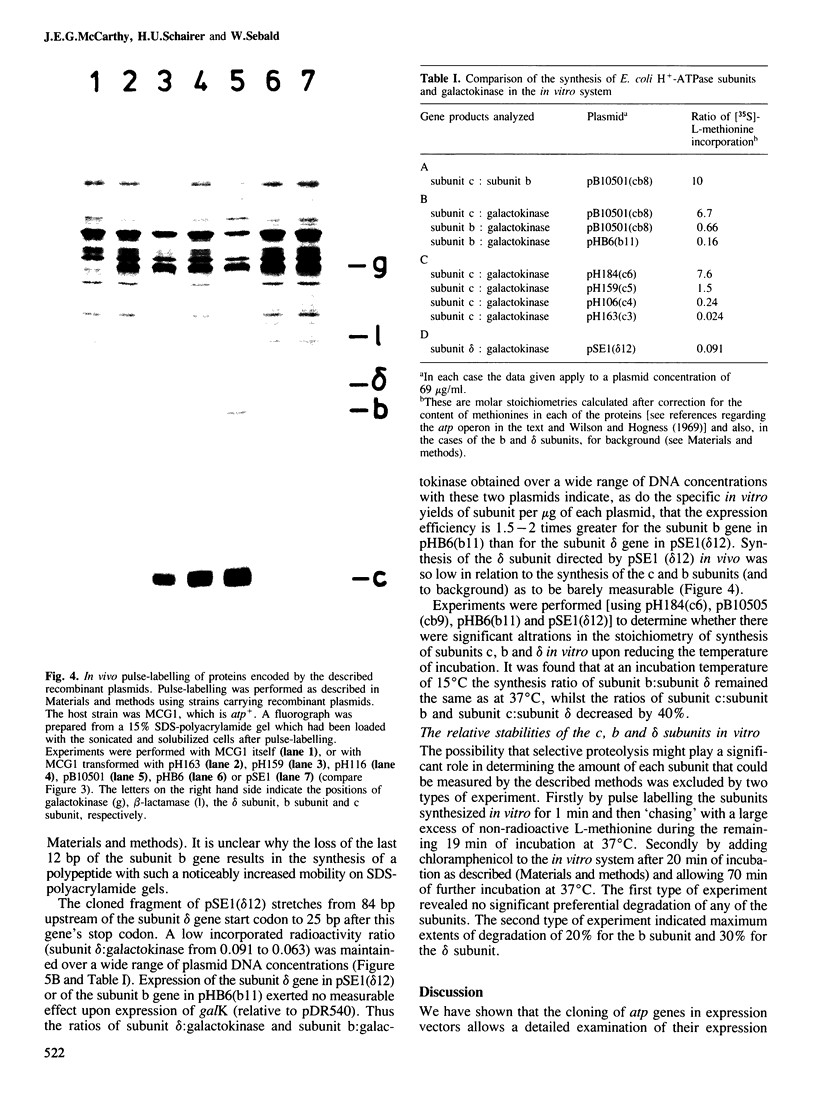
The c, b and delta subunit genes of the Escherichia coli atp operon were cloned individually in an expression vector between the tac fusion promoter and the galK gene. The relative rates of subunit synthesis directed by the cloned genes were similar in vitro and in vivo and compared favourably with the subunit stoichiometry of the assembled proton-translocating ATP synthase of E. coli in vivo. The rate of synthesis of subunit c was at least six times that of subunit b and 18 times that of subunit delta. Progressive shortening of the long intercistronic sequence lying upstream of the subunit c gene showed that maximal expression of this gene is dependent upon the presence of a sequence stretching greater than 20 bp upstream of the Shine-Dalgarno site. This sequence thus acts to enhance the rate of translational initiation. The possibility that similar sequences might perform the same function in other operons of E. coli and bacteriophage lambda is also discussed. Translation of the subunit b cistron is partially coupled to translation of the preceding subunit c cistron. In conclusion, the expression of all the atp operon genes could be adjusted to accommodate the subunit requirements of ATP synthase assembly primarily by means of mechanisms which control the efficiency of translational initiation and re-initiation at the respective cistron start codons.
Full text
PDF
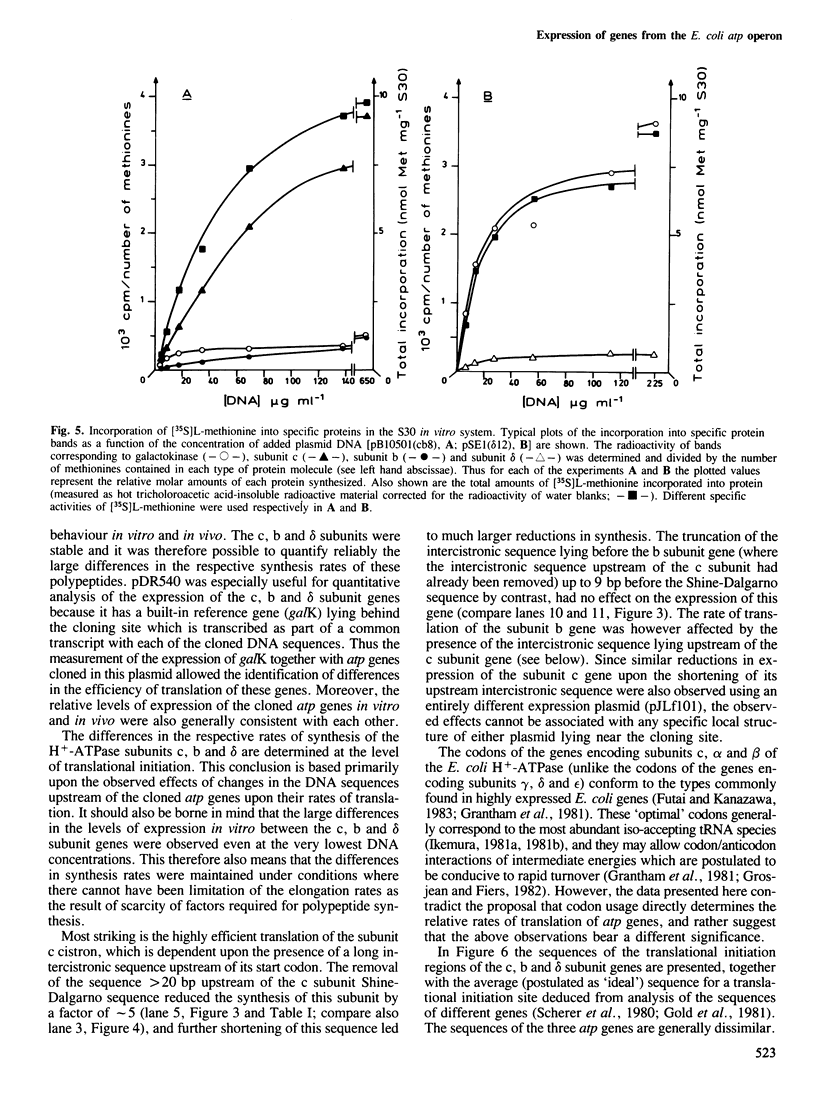



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beck E., Sommer R., Auerswald E. A., Kurz C., Zink B., Osterburg G., Schaller H., Sugimoto K., Sugisaki H., Okamoto T. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage fd DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Dec;5(12):4495–4503. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.12.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusilow W. S., Klionsky D. J., Simoni R. D. Differential polypeptide synthesis of the proton-translocating ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1363–1371. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1363-1371.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusilow W. S., Porter A. C., Simoni R. D. Cloning and expression of uncI, the first gene of the unc operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1265–1270. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1265-1270.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. Z., Zubay G. Prokaryotic coupled transcription-translation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:674–690. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dagert M., Ehrlich S. D. Prolonged incubation in calcium chloride improves the competence of Escherichia coli cells. Gene. 1979 May;6(1):23–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downie J. A., Gibson F., Cox G. B. Membrane adenosine triphosphatases of prokaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:103–131. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.000535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drahos D., Szybalski W. Antitermination and termination functions of the cloned nutL, N, and tL1 modules of coliphage lambda. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):261–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. L., Fillingame R. H. Stoichiometry of subunits in the H+-ATPase complex of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):2009–2015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedl P., Friedl C., Schairer H. U. The ATP synthetase of Escherichia coli K12: purification of the enzyme and reconstitution of energy-transducing activities. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct;100(1):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb02046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futai M., Kanazawa H. Structure and function of proton-translocating adenosine triphosphatase (F0F1): biochemical and molecular biological approaches. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):285–312. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.285-312.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the promoter and the genes for the membrane proteins, and the delta subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):3919–3926. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay N. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the region encoding the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli ATP-synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2187–2194. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Langner A., Chang A. C., Cohen S. N., Bujard H. Cloning and analysis of strong promoters is made possible by the downstream placement of a RNA termination signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4936–4940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M., Hogness D. S. Colony hybridization: a method for the isolation of cloned DNAs that contain a specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3961–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe J., Sebald W. The proton conducting F0-part of bacterial ATP synthases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Apr 9;768(1):1–27. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(84)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones H. M., Brajkovich C. M., Gunsalus R. P. In vivo 5' terminus and length of the mRNA for the proton-translocating ATPase (unc) operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1279–1287. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1279-1287.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa H., Mabuchi K., Kayano T., Noumi T., Sekiya T., Futai M. Nucleotide sequence of the genes for F0 components of the proton-translocating ATPase from Escherichia coli: prediction of the primary structure of F0 subunits. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):613–620. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90495-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastelein R. A., Berkhout B., Overbeek G. P., van Duin J. Effect of the sequences upstream from the ribosome-binding site on the yield of protein from the cloned gene for phage MS2 coat protein. Gene. 1983 Sep;23(3):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lünsdorf H., Ehrig K., Friedl P., Schairer H. U. Use of monoclonal antibodies in immuno-electron microscopy for the determination of subunit stoichiometry in oligomeric enzymes. There are three alpha-subunits in the F1-ATPase of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1984 Feb 15;173(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90408-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Hansen F. G., Hoppe J., Friedl P., von Meyenburg K. The nucleotide sequence of the atp genes coding for the F0 subunits a, b, c and the F1 subunit delta of the membrane bound ATP synthase of Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(1):33–39. doi: 10.1007/BF00271191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen J., Jørgensen B. B., van Meyenburg K. V., Hansen F. G. The promoters of the atp operon of Escherichia coli K12. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):64–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00327415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Brusilow W. S., Simoni R. D. Promoter for the unc operon of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1271–1278. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1271-1278.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Nomura M. DNA sequences from the str operon of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4660–4666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Strycharz G. D., Nomura M., Lewis H., Dennis P. P. Nucleotide sequence of the ribosomal protein gene cluster adjacent to the gene for RNA polymerase subunit beta in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt C. Kinetics and regulation of cell-free alkaline phosphatase synthesis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1265–1274. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1265-1274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P. N., Pearson M. L. Functional inactivation of bacteriophage lambda morphogenetic gene in RNA. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):647–650. doi: 10.1038/253647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. M., Kacich R., Ptashne M. A general method for maximizing the expression of a cloned gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):760–764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. R., Bennett G. N. Construction and analysis of in vivo activity of E. coli promoter hybrids and promoter mutants that alter the -35 to -10 spacing. Gene. 1982 Dec;20(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Hong G. F., Hill D. F., Petersen G. B. Nucleotide sequence of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):729–773. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90546-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Gay N. J., Eberle A., Runswick M. J., Walker J. E. The atp operon: nucleotide sequence of the genes for the gamma, beta, and epsilon subunits of Escherichia coli ATP synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5287–5296. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schairer H. U., Friedl P., Schmid B. I., Vogel G. The use of several energy-coupling reactions in characterizing mutants of Escherichia coli K12 defective in oxidative phosphorylation. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):257–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10515.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., Walkinshaw M. D., Arnott S., Morré D. J. The ribosome binding sites recognized by E. coli ribosomes have regions with signal character in both the leader and protein coding segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 11;8(17):3895–3907. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.17.3895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schottel J. L., Sninsky J. J., Cohen S. N. Effects of alterations in the translation control region on bacterial gene expression: use of cat gene constructs transcribed from the lac promoter as a model system. Gene. 1984 May;28(2):177–193. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90255-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. B., Hogness D. S. The enzymes of the galactose operon in Escherichia coli. 3. The size and composition of galactokinase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Apr 25;244(8):2137–2142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood C. R., Boss M. A., Patel T. P., Emtage J. S. The influence of messenger RNA secondary structure on expression of an immunoglobulin heavy chain in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 May 11;12(9):3937–3950. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.9.3937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zubay G. In vitro synthesis of protein in microbial systems. Annu Rev Genet. 1973;7:267–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.07.120173.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyenburg K., Hansen F. G., Nielsin L. D., Riise E. Origin of replication, oriC, or the Escherichia coli chromosome on specialized transducing phages lambda asn. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Apr 17;160(3):287–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00332972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyenburg K., Jørgensen B. B., Nielsen J., Hansen F. G., Michelsen O. The membrane bound ATP synthase of Escherichia coli: a review of structural and functional analyses of the atp operon. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 1982;7 (Suppl):23–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Meyenburg K., Jørgensen B. B., Nielsen J., Hansen F. G. Promoters of the atp operon coding for the membrane-bound ATP synthase of Escherichia coli mapped by Tn10 insertion mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):240–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00332682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]